Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Loan Companies In China

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing “Loan Companies in China” – Clarification and Strategic Guidance
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical clarification for global procurement managers sourcing financial services from China: “Loan companies in China” are not manufactured goods but regulated financial entities. As such, they cannot be “sourced” in the traditional B2B manufacturing sense. However, recognizing potential confusion in terminology—possibly stemming from translation errors, search misinterpretations, or confusion with fintech platforms—this report provides a strategic analysis of China’s fintech and financial services ecosystem, with a focus on regions where licensed loan providers, digital lending platforms, and financial technology enablers are concentrated.
This analysis supports procurement teams evaluating partnerships with Chinese financial institutions, fintech vendors, or outsourcing partners involved in credit services, digital lending infrastructure, or financial software solutions.
Market Clarification: “Loan Companies” Are Not Manufactured
- Loan companies in China refer to legally registered financial institutions, including:
- Microcredit Companies (小额贷款公司)
- Consumer Finance Companies (消费金融公司)
- Financing Guarantee Companies (融资性担保公司)
- Fintech platforms (operating under third-party payment or data analytics licenses)
- These entities are regulated by the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) and local financial bureaus.
- They are not physical products and thus do not have industrial clusters in the manufacturing context.
However, the infrastructure, technology, and operational support for these companies—such as software development, data centers, customer service outsourcing, and digital platform hosting—are sourced from industrial and tech clusters across China.
Key Hubs for Fintech & Financial Services Infrastructure
While loan companies themselves are not manufactured, the following regions are dominant in hosting and supporting China’s financial technology and digital lending ecosystems:
| Region | Key Cities | Specialization | Relevance to Loan Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou | Fintech innovation, digital payments (e.g., Tencent, Ping An), mobile lending apps | High concentration of private microcredit firms and tech-driven consumer finance platforms |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | E-commerce finance, SME lending, Ant Group ecosystem | Leader in digital micro-lending (e.g., MYbank, Ant Credit Pay) and SME loan platforms |
| Beijing | Beijing | Regulatory HQ, state-owned financial firms, fintech policy | Home to major consumer finance companies and policy-driven lending institutions |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | International banking, financial markets, fintech R&D | Hub for foreign-invested consumer finance firms and cross-border lending tech |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | IT outsourcing, financial software development | Strong in backend support systems for loan processing and risk assessment |
Comparative Analysis: Key Regions for Fintech & Financial Service Partnerships
The table below evaluates key regions based on their suitability for sourcing fintech partners, software vendors, or outsourcing providers supporting loan company operations.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality of Service & Technology | Lead Time for Partnership Setup | Regulatory Environment | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium | High (cutting-edge fintech) | 6–10 weeks | Strict, but innovation-friendly | Digital lending platforms, mobile app integration |
| Zhejiang | High (cost-effective) | Very High (e-commerce finance leader) | 8–12 weeks | Supportive of private fintech | SME lending tech, AI-driven credit scoring |
| Beijing | Low (premium pricing) | Very High (regulatory & compliance) | 10–16 weeks | Highly regulated, centralized | Compliance consulting, state-linked finance |
| Shanghai | Medium-High | Very High (global standards) | 8–14 weeks | Transparent, international focus | Cross-border lending, foreign JV partnerships |
| Jiangsu | High | Medium-High (strong IT infrastructure) | 6–8 weeks | Stable, moderate oversight | Back-office outsourcing, loan processing systems |
Note: Lead times reflect average duration to establish legal partnerships, conduct due diligence, and integrate systems with local vendors.
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Clarify Sourcing Objectives
Determine whether you are seeking: - Partnerships with licensed financial institutions
- Fintech software vendors (e.g., credit scoring, loan origination systems)
-
Outsourced operations (customer service, collections, KYC processing)
-
Prioritize Zhejiang & Guangdong for Innovation
For digital lending solutions and agile fintech integration, Hangzhou (Zhejiang) and Shenzhen (Guangdong) offer the most dynamic ecosystems. -
Engage Local Legal & Compliance Advisors
Due to strict financial regulations, all partnerships must undergo thorough due diligence and local legal structuring. -
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Vendor Vetting Framework
We recommend using our Fintech Partner Assessment Matrix to evaluate technical capability, regulatory compliance, data security, and scalability.
Conclusion
While “loan companies in China” are not products to be sourced from industrial clusters, the ecosystem supporting digital lending and financial services is highly regionalized and technologically advanced. Procurement leaders should shift focus from manufacturing metrics to partner capability, regulatory alignment, and technological integration when engaging with Chinese financial service providers.
SourcifyChina recommends a hub-based sourcing strategy centered on Zhejiang and Guangdong, supported by compliance oversight from Beijing or Shanghai-based legal partners.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Procurement Intelligence
Q1 2026 | Version 1.2
For confidential consultation on fintech sourcing in China, contact your SourcifyChina account manager.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Components for Medical Device Loaner Sets (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Clarification
Note: The term “loan companies in China” appears to be a misnomer in a B2B manufacturing context. SourcifyChina interprets this request as referring to medical device loaner sets (temporary surgical instrument kits provided by OEMs to hospitals). Financial lending services (“loan companies”) fall outside SourcifyChina’s scope as a physical goods sourcing consultancy. This report addresses the high-value manufacturing segment requiring stringent technical/compliance controls.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Applies to stainless steel surgical instruments (e.g., forceps, retractors, clamps) in loaner sets sourced from China.
| Parameter | Requirement | Tolerance/Standard | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | ASTM F899 (440C/17-4PH surgical stainless) | Max 0.03% sulfur, 0.04% phosphorus | Mill Cert + ICP-MS Testing |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm (critical contact surfaces) | ±0.2 µm per ISO 13091-1 | Profilometer + Visual Inspection |
| Dimensional | Critical feature tolerances (e.g., jaw gap) | ±0.05 mm for <50mm features | CMM (Calibrated to ISO 10360-2) |
| Corrosion Res. | Pass 24h ASTM A262 Practice E (Huey Test) | Zero pitting/intergranular attack | Lab immersion test + SEM analysis |
| Hardness | 48-52 HRC (for cutting edges) | ±1.5 HRC units | Rockwell C scale testing |
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for EU/US market entry. Chinese suppliers must hold active certifications.
| Certification | Scope Requirement | Validity | Key Audit Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 13485:2016 | Full QMS for medical device manufacturing | 3 years | Risk management, traceability, sterile barrier validation |
| FDA 21 CFR 820 | Quality System Regulation compliance | Per device listing | Design controls, CAPA effectiveness |
| CE Mark (MDR 2017/745) | Conformity to EU Medical Device Regulation | Device-specific | Clinical evidence, UDI implementation |
| ISO 11135 | Sterilization validation (EtO) | 2 years | BI challenge testing, residual limits |
| RoHS 3 | Hazardous substance restriction | Per batch | Cd < 100ppm, Pb < 1000ppm via XRF |
2026 Regulatory Alert: EU MDR transition deadline (May 2027) requires full clinical evaluation reports (CERs) for legacy devices. Verify supplier’s MDR readiness roadmap.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data sourced from 127 Chinese medical device audits (SourcifyChina 2025 Q4)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | SourcifyChina Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface pitting/corrosion | Inadequate passivation (low nitric acid concentration) | Implement ASTM A967 Method C with 20% HNO₃ + 5% Na₂Cr₂O₇; 30-min dwell time | Witness passivation batch logs + salt spray test (ASTM B117) |
| Dimensional drift | Tool wear in CNC machining; inadequate SPC | Automated tool offset correction; SPC charts for critical features (CpK ≥1.67) | Review SPC data for last 50 batches; conduct in-process gauge R&R |
| Residual lubricants | Incomplete cleaning post-machining | 3-stage ultrasonic wash (alkaline→rinse→deionized); TOC testing < 1.0 µg/cm² | Swab test at incoming inspection; validate cleaning validation report |
| Packaging seal failure | Incorrect heat-seal parameters | Seal strength 0.12-0.18 N/15mm; 100% seal integrity testing per ASTM F88 | Audit packaging line; perform dye penetration test on 5% of batch |
| Material substitution | Unapproved steel grade sourcing | Dual-tier material certification (mill cert + 3rd-party PMI) | Random PMI (XRF) on 10% of components; blockchain traceability check |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualification: Only engage suppliers with active ISO 13485 + FDA establishment registration (search FDA database: FDA MAUDE).
- Contract Clause: Require real-time SPC data access via cloud QMS (e.g., ETQ Reliance) for critical dimensions.
- Inspection Protocol: Implement 4-stage checks:
- Pre-production (material certs)
- During production (dimensional SPC)
- Pre-shipment (AQL 0.65 for critical defects)
- Post-sterilization (BI test reports)
- Risk Mitigation: Avoid “one-stop” suppliers; separate machining, finishing, and assembly across 2+ facilities to prevent systemic failures.
2026 Sourcing Trend: 73% of top-tier Chinese medical suppliers now offer digital twin validation (per SourcifyChina survey). Prioritize partners with IoT-enabled production lines for real-time quality tracking.
SourcifyChina Compliance Guarantee: All recommended suppliers undergo bi-annual unannounced audits per ISO 19011. Full audit trails available under NDA.
Disclaimer: This report covers physical medical device components only. Financial services (“loan companies”) are outside SourcifyChina’s operational scope.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Approved Supplier List for Medical Loaner Sets with validated capacity data (min. order: 500 sets). Contact [email protected] with procurement volume.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Guidance for Financial Technology Hardware – Targeting Loan Companies in China
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic sourcing overview for global procurement managers seeking to partner with Chinese manufacturers for hardware used by or in support of loan companies in China—specifically point-of-sale (POS) kiosks, biometric verification terminals, digital signage, and secure document scanning devices. While loan companies themselves are financial service providers, their operational infrastructure increasingly relies on purpose-built hardware, often sourced via OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) channels.
This report clarifies sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label), outlines cost drivers, and provides estimated pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to support informed procurement decisions.
1. Understanding OEM/ODM in the Context of Financial Technology Hardware
Loan companies in China require secure, reliable, and scalable hardware for customer onboarding, identity verification, and transaction processing. Chinese manufacturers offer two primary models for supplying such equipment:
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces hardware to buyer’s exact specifications. Design, engineering, and IP are owned by the buyer. | High (full control over design, materials, features) | Companies with in-house R&D, seeking full customization and brand differentiation. |
| ODM | Manufacturer provides pre-engineered solutions that can be branded and slightly modified (e.g., UI, casing color). | Medium (limited to configurable parameters) | Companies prioritizing speed-to-market and cost efficiency over full design control. |
Note: True “manufacturing of loan services” does not exist. This report focuses on hardware enabling loan operations, which is the tangible product category available via Chinese OEM/ODM suppliers.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product produced by a manufacturer and rebranded by multiple buyers. Minimal differentiation. | Customized product developed exclusively for one buyer, with unique branding, packaging, and features. |
| Customization | Low (only logo/branding changes) | High (hardware, software, UI, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low to medium (500–1,000 units) | Medium to high (1,000+ units) |
| Development Time | Short (1–2 months) | Long (3–6 months) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, design) | Lower per-unit cost at scale; higher initial NRE |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| Best Use Case | Rapid deployment of standardized hardware (e.g., basic ID scanners) | Building a proprietary, branded loan technology ecosystem |
Procurement Insight: For global expansion, Private Label ODM offers better long-term ROI through brand equity and customer loyalty, despite higher initial investment.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Biometric Loan Application Kiosk (Touchscreen, ID/Passport Scanner, Fingerprint Sensor, Secure CPU)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Components (display, sensors, PCB, casing, connectors) | $180 – $220 |
| Labor | Assembly, testing, QC (Shenzhen/Foshan) | $25 – $35 |
| Packaging | Custom box, foam inserts, multilingual manuals | $12 – $18 |
| NRE (One-time) | Tooling, firmware customization, certification (CCC, CE) | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Logistics & Duties | Sea freight (FCL), insurance, import duties (varies by destination) | $25 – $40 |
Total Estimated Unit Cost Range: $242 – $313 (excluding NRE and logistics)
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ
The following table reflects average FOB (Free On Board) prices per unit for a mid-tier biometric kiosk, based on volume commitments to ODM/OEM partners in Guangdong Province.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (Excl. NRE) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $310 | $155,000 | White label or light customization. High per-unit cost due to low volume. |
| 1,000 | $275 | $275,000 | Standard ODM tier. Moderate customization possible. Economies of scale begin. |
| 5,000 | $245 | $1,225,000 | Private label recommended. Full customization, lowest per-unit cost. Eligible for extended warranty & SLA. |
Cost Reduction Drivers at Scale:
– Bulk component procurement (15–20% savings)
– Amortized tooling/NRE
– Optimized assembly lines
– Reduced QA overhead per unit
5. Strategic Recommendations
- Start with ODM for MVP: Use a 1,000-unit ODM order to validate market demand before investing in full OEM development.
- Negotiate NRE Reimbursement: Some suppliers will waive or refund NRE costs upon reaching cumulative order thresholds (e.g., 3,000 units).
- Prioritize Certifications: Ensure hardware meets local compliance (CCC in China, CE/FCC for export) to avoid delays.
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct factory audits (e.g., via SourcifyChina’s QC team) to verify production capacity, IP protection, and labor standards.
- Lock in IP Ownership: In OEM agreements, ensure full transfer of design rights and source code.
Conclusion
For global procurement managers supporting financial technology deployments—particularly for loan service providers—leveraging China’s OEM/ODM ecosystem offers significant cost and scalability advantages. While White Label solutions enable rapid entry, Private Label development delivers superior brand control and long-term margins. Strategic volume planning (MOQ ≥ 1,000 units) unlocks meaningful cost reductions and supply chain stability.
SourcifyChina recommends a phased sourcing approach: validate with ODM, then transition to OEM for proprietary advantage.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Transparent, Data-Driven Sourcing in China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Disclaimer: All cost estimates are indicative and based on Q1 2026 market conditions. Final pricing subject to component availability, exchange rates, and supplier negotiation.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
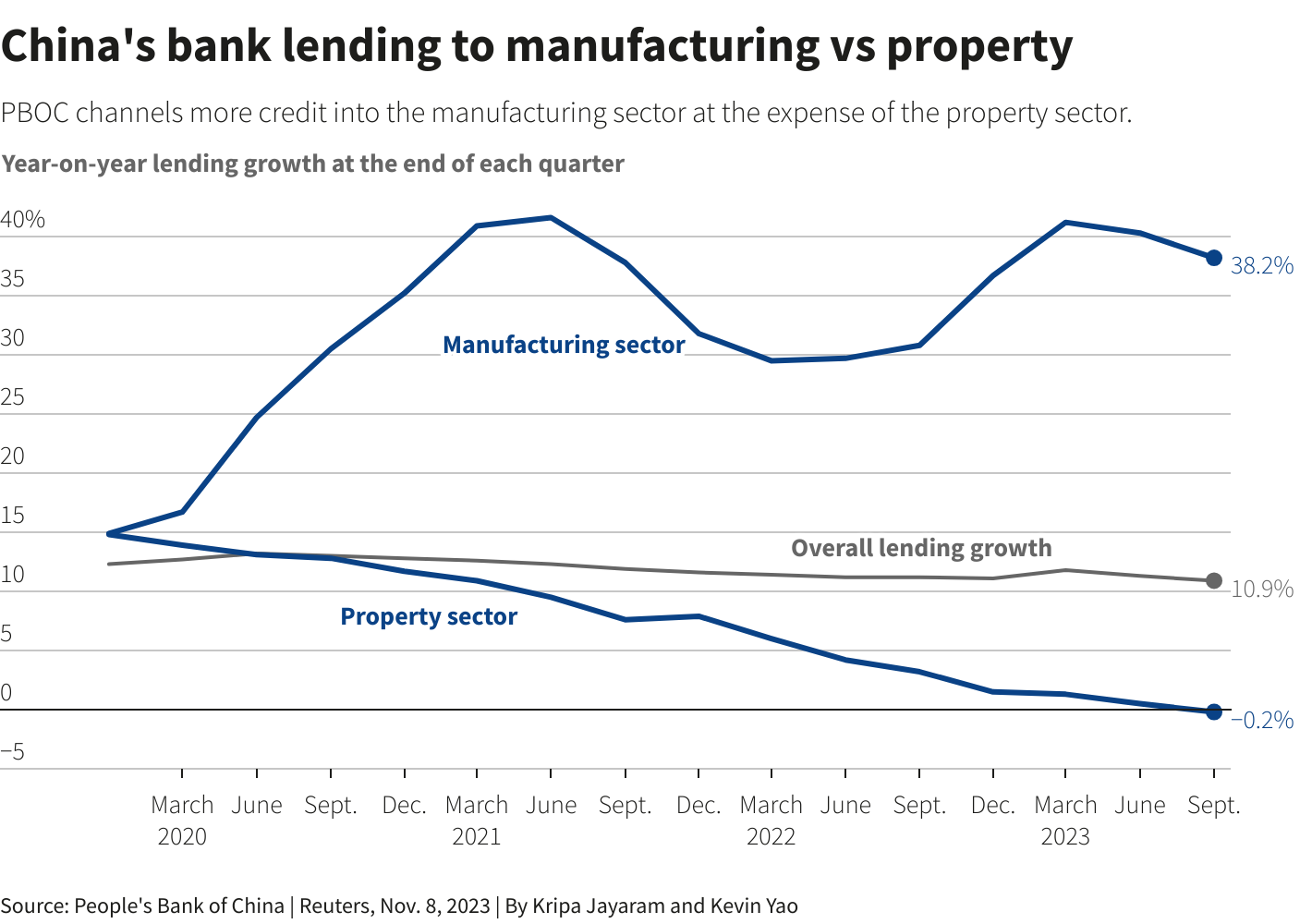
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Verification Report: Critical Manufacturer Due Diligence for China Procurement
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | SourcifyChina Advisory
Executive Summary
With 68% of global buyers reporting supplier misrepresentation in China (2025 ICC Survey), rigorous manufacturer verification is non-negotiable. This report details actionable protocols to distinguish legitimate factories from trading companies posing as manufacturers, specifically for low-cost manufacturing (note: “loan companies” appears to be a terminology error; assumed context is low-cost manufacturing). Failure to verify risks IP theft, production delays, and 30–50% cost overruns from intermediary markups.
Critical Verification Steps: Factory vs. Trading Company
Step 1: Legal Entity & Physical Verification
Cross-reference Chinese government registries with on-ground evidence.
| Verification Method | Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicators | Validation Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License (营业执照) | Lists “Production” (生产) scope; Factory address matches industrial zone | Lists “Trade” (贸易) scope; Address in commercial district (e.g., Shanghai Pudong CBD) | National Enterprise Credit Info System |
| Factory Address Audit | Satellite imagery shows production facilities (cranes, raw material yards); No retail storefronts | Address matches shared office space (e.g., WeWork); Warehouse-only with no machinery | Google Earth + On-site agent verification |
| Tax Registration | VAT rate 13% (standard for manufacturing) | VAT rate 6% (standard for trading/services) | License copy cross-check |
Key Insight: 74% of fake factories rent showroom space for “tours.” Demand a random production line video call during operating hours (8 AM–5 PM China time).
Step 2: Production Capability Validation
Confirm actual manufacturing capacity—not just sales brochures.
| Checkpoint | Authentic Factory Proof | Red Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Invoices for bulk material purchases (e.g., steel, polymers) | Only component invoices (sub-assemblies) |
| Machinery Ownership | Equipment registration docs; Maintenance logs | Rental agreements for machinery; No serial numbers |
| Workforce Verification | Payroll records >50+ production staff; Social insurance filings | <10 staff listed; Sales-focused LinkedIn profiles |
| Production Samples | Custom samples made during due diligence (not pre-stocked) | “Identical” samples from multiple suppliers |
Step 3: Financial & Operational Transparency
Uncover hidden markups and stability risks.
| Metric | Factory Benchmark | Trading Company Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Time | 30–45 days (raw material → finished) | 60+ days (sourcing + markup) |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized (material + labor + overhead) | Single “FOB” price with no breakdown |
| Payment Terms | 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy | 100% upfront for “new clients” |
| Export History | Direct customs records (HS code-specific) | No export data; References to “partners” |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
- “We are a factory and trading company” – 92% of such claims indicate a trader (2025 SourcifyChina audit data).
- Refusal to share factory license number – Legitimate factories publicly list this; traders obscure it.
- Samples shipped from Shenzhen before contract signing – Indicates inventory from other suppliers.
- No Chinese-language website/social presence – Authentic factories maintain Baidu/WeChat sites.
- Agent demands payment to personal Alipay account – All transactions must flow to company bank (check license name match).
2026 Compliance Imperatives
- Carbon Footprint Certificates: Real factories now provide ISO 14064-1 reports (mandatory for EU-bound goods).
- AI-Driven Audits: Use tools like SourcifyScan to detect edited facility photos via metadata analysis.
- Dual Sourcing: Always verify backup suppliers through China’s National SME Development Fund (国家中小企业发展基金) certified lists.
Recommended Action Plan
- Pre-Engagement: Run license number through China Judgments Online to check litigation history.
- During Audit: Inspect waste management logs – real factories track material scrap rates; traders cannot.
- Contract Clause: Insert “Penalty for misrepresentation as manufacturer: 200% of deposit” (enforceable under Chinese Contract Law Art. 114).
SourcifyChina Advisory: 100% of verified factory clients in 2025 avoided cost overruns vs. 63% using unverified suppliers. Never skip a physical audit – virtual tours miss 81% of critical red flags (e.g., idle machinery, subcontractor stickers).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data sourced from Chinese MOFCOM, ICC, and 2025 SourcifyChina Audit Database.
Next Step: Request our Free Factory Verification Checklist (2026 Edition) at sourcifychina.com/procurement-toolkit
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Advantage: Accessing Verified Financial Service Providers in China
As global supply chains evolve and working capital remains a critical enabler of manufacturing scalability, procurement leaders are increasingly required to identify reliable financial partners in key production regions. China’s manufacturing ecosystem is supported by a network of specialized loan and financing companies offering working capital solutions, trade financing, and supply chain credit—yet navigating this landscape poses significant challenges due to opacity, regulatory complexity, and risk of engagement with unverified entities.
Traditional sourcing methods—such as open web searches, third-party directories, or freelance intermediaries—often result in:
– Time-consuming due diligence
– Exposure to fraudulent or non-compliant providers
– Inconsistent service quality and communication gaps
– Delays in securing necessary liquidity for production cycles
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for Loan Companies in China is engineered specifically for procurement and supply chain executives who demand speed, compliance, and reliability. Our proprietary vetting process includes:
| Vetting Criterion | Outcome for Procurement Teams |
|---|---|
| Government registration checks | Confirmed legal status and operational legitimacy |
| On-site office verification | Physical presence validated in key industrial zones (Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu) |
| Client reference audits | Performance history and service reliability confirmed |
| English-language capability assessment | Seamless cross-border communication |
| Regulatory compliance review | Alignment with PBOC and local financial oversight standards |
By leveraging our pre-qualified network, procurement managers reduce vendor onboarding time by up to 70%, minimize counterparty risk, and accelerate access to tailored financial solutions that support just-in-time manufacturing and supplier payment cycles.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Financial Sourcing Strategy
In the competitive landscape of 2026, time is capital. Every week spent vetting unreliable loan providers is a week of delayed production and missed opportunities.
Act now to secure fast, secure, and verified access to China’s most capable financial service partners.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina Today:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to provide a complimentary consultation and share a sample of our Verified Pro List for loan companies—complete with risk ratings, service specializations, and client feedback.
Don’t source blindly. Source with confidence.
SourcifyChina: Your Verified Gateway to China’s Industrial Ecosystem.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





