The global demand for reliable battery performance testing has surged in tandem with the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy storage markets. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global battery market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 11.5% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing EV adoption and government initiatives promoting clean energy. This growth places unprecedented pressure on battery manufacturers to ensure quality, safety, and longevity—making load testing a critical component in production and quality control processes. As batteries become more complex and power-dense, advanced load testers capable of simulating real-world discharge scenarios, monitoring thermal performance, and validating cycle life are no longer optional, but essential. In this evolving landscape, selecting the right load testing equipment can significantly impact production efficiency, product reliability, and time-to-market. The following analysis identifies the top 9 load testers shaping the industry, evaluated based on accuracy, scalability, software integration, and compliance with international testing standards.
Top 9 Load Tester For Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ZTS, Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ztsinc.com
Key Highlights: ZTS home | products | accessories | military | contact | where to buy | about ZTS | pdf files | tips & info | warranty ……
#2 Battery Testing and Energy Storage Solutions
Domain Est. 2001
Website: intertek.com
Key Highlights: Intertek offers industry-leading battery testing, energy storage, and lifecycle evaluation services that help manufacturers, developers, and innovators ……
#3 Car Battery Testers & System Analyzers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: midtronics.com
Key Highlights: Midtronics offers a wide range of quality battery testers for all types of battery and electrical system service needs….
#4 Battery Testers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bkprecision.com
Key Highlights: B&K Precision designs and manufactures reliable and cost-effective test and measurement equipment, used for a wide range of applications by engineers and ……
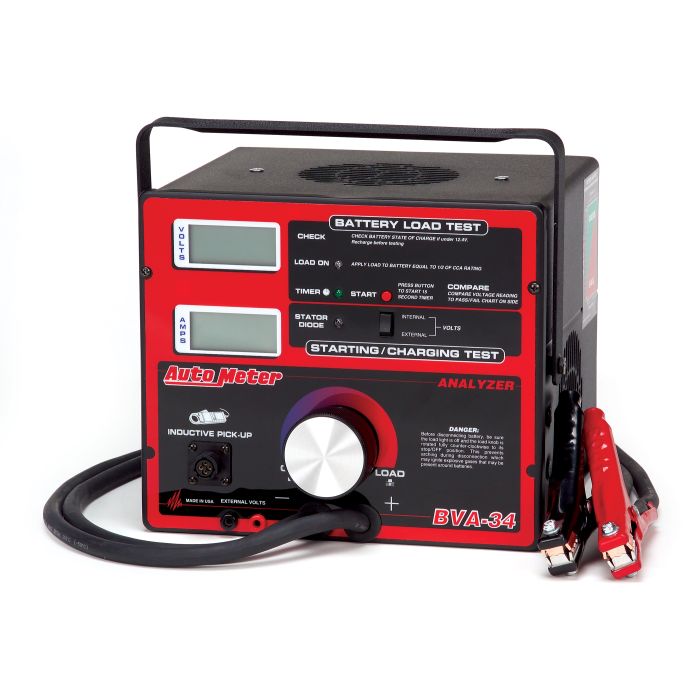
#5 Automotive Car Battery Load Testers
Domain Est. 1996
#6 Battery Load Tester
Domain Est. 1999
Website: schumacherelectric.com
Key Highlights: Easy to operate. Test load, battery condition, starter motor draw and complete charging system diagnosis. Works on 6 and 12 volt batteries….
#7 Battery Load Tester Industry Leader For Fast, Accurate And Portable …
Domain Est. 2005
Website: soctester.com
Key Highlights: The SOC Is The Trusted Choice For Mission Critical Battery Testing Apps – By Safety & Security Industry Leaders….
#8 Heavy Duty Battery Tester
Domain Est. 2006
Website: boschdiagnostics.com
Key Highlights: The BAT 155 is an advanced heavy duty battery & electrical system tester designed for the commercial vehicle industry. Featuring patented single load, dynamic ……
#9 DK-Tester
Domain Est. 2021
Website: dk-tester.com
Key Highlights: Discover DK-Tester’s wide range of professional battery testers and testing equipment, including automotive battery testers and load testers, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Load Tester For Battery

2026 Market Trends for Load Tester for Battery
The global market for battery load testers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in energy storage technologies, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and increasing demand for reliable battery performance diagnostics across multiple industries. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the battery load tester landscape in 2026.
Rising Demand from the Electric Vehicle Sector
The electric vehicle industry remains the primary growth driver for battery load testers. As EV adoption accelerates worldwide due to government mandates and environmental concerns, the need for precise and efficient battery testing solutions intensifies. By 2026, automakers and service centers will increasingly rely on advanced load testers capable of evaluating high-capacity lithium-ion and emerging solid-state batteries. Integration with EV diagnostic software platforms will become standard, enabling real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance.
Advancements in Smart and Portable Testing Devices
In 2026, a major trend is the proliferation of smart, handheld load testers equipped with IoT connectivity and cloud-based data analytics. These devices allow technicians to remotely monitor battery health, store historical test data, and generate automated reports via mobile applications. Enhanced user interfaces, wireless communication (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi), and compatibility with multiple battery chemistries (lead-acid, Li-ion, NiMH) will define the next generation of portable load testers, improving accuracy and usability in field and industrial environments.
Expansion in Renewable Energy Storage Applications
With the global push toward renewable energy, battery energy storage systems (BESS) are being deployed at residential, commercial, and utility scales. Load testers play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and longevity of these storage systems. By 2026, demand will grow for industrial-grade load testers capable of handling large-scale battery banks used in solar and wind installations. These testers will emphasize safety features, scalability, and integration with energy management systems (EMS).
Emphasis on Automation and AI-Driven Diagnostics
Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming battery testing protocols. In 2026, AI-powered load testers will analyze historical performance data to predict battery failure, optimize charge cycles, and recommend maintenance actions. Machine learning algorithms will enable adaptive testing procedures, customizing load profiles based on battery type, usage history, and environmental conditions. This shift toward intelligent diagnostics will enhance testing efficiency and reduce operational downtime.
Regional Market Growth and Regulatory Influence
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will lead in market growth due to strong manufacturing bases for EVs and consumer electronics. North America and Europe will see steady growth, fueled by stringent regulatory standards for battery safety and performance. By 2026, regulatory bodies may introduce mandatory battery testing requirements for EVs and stationary storage, further boosting demand for certified load testing equipment.
Consolidation and Innovation Among Key Players
The competitive landscape will witness consolidation as major test equipment manufacturers acquire niche battery diagnostics firms to expand product portfolios. Simultaneously, startups will drive innovation in miniaturization, energy efficiency, and cloud integration. Strategic partnerships between load tester manufacturers and battery producers will become common, enabling co-development of tailored testing solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the battery load tester market will be characterized by technological sophistication, increased connectivity, and broader application across transportation, energy, and industrial sectors. As batteries become central to modern infrastructure, load testers will evolve from simple diagnostic tools into intelligent, integrated systems essential for ensuring performance, safety, and sustainability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Load Tester for Battery (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a battery load tester—especially for industrial or high-precision applications—requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes. Overlooking key factors can compromise product quality, reliability, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are common pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Inaccurate Measurements
Many low-cost load testers on the market use substandard components, leading to inconsistent or inaccurate discharge readings. Inaccurate current, voltage, or capacity measurements can result in faulty battery assessments, risking safety and performance in end applications. Always verify specifications with third-party test reports and request samples for validation before bulk orders.
Lack of IP Protection and Risk of Design Copying
When working with certain manufacturers—especially in regions with lax IP enforcement—there’s a significant risk that your customized load tester design or firmware could be replicated and sold to competitors. Ensure that non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and IP ownership clauses are clearly defined in contracts, and consider working with legally vetted partners.
Inadequate Environmental Protection (IP Rating Misrepresentation)
Suppliers may claim high Ingress Protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP65 or IP67), but actual product testing often reveals poor sealing, inadequate dust/water resistance, or use of low-quality enclosures. This is critical for field-deployable testers exposed to harsh environments. Always request certified IP test reports or conduct your own environmental testing.
Hidden Costs and Unreliable After-Sales Support
Initial quotes may appear competitive, but hidden costs for firmware customization, calibration, or replacement parts can inflate the total cost of ownership. Additionally, poor technical support or long lead times for spare parts can disrupt operations. Evaluate supplier responsiveness and support structure before finalizing procurement.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Some load testers fail to meet essential safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS), especially when produced by less-regulated suppliers. Using non-compliant equipment can expose your company to legal liability and hinder market access. Confirm that the product adheres to relevant international standards and request compliance documentation.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, thorough testing of prototypes, and robust contractual safeguards—especially concerning quality assurance and IP rights.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Load Tester For Battery
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the shipment, handling, storage, and regulatory adherence of load testers used for batteries. Proper procedures ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Classification & Product Description
Load testers for batteries are electronic diagnostic tools designed to assess the health and performance of various battery types (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion) by applying a controlled electrical load. These devices typically include resistive elements, voltage/current sensors, display units, and safety features. Most models operate on battery or AC power and are classified as electronic test equipment.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Use electrostatic discharge (ESD)-safe packaging materials to protect internal circuitry.
- Secure devices in rigid inner packaging with cushioning (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent impact damage.
- Outer packaging must meet ISTA 3A or equivalent standards for transit robustness.
- Include desiccants in packaging if shipping to high-humidity regions.
- Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators.
Shipping & Transportation
- Domestic (US): Ship via ground or air using carriers compliant with DOT 49 CFR regulations. No hazardous material designation is typically required unless the load tester contains lithium batteries.
- International: Use IATA-compliant packaging and documentation when air shipping. Ensure compliance with regional carrier standards (e.g., DHL, FedEx, UPS).
- Temperature Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures (below -10°C or above 50°C) during transit.
- Storage: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–30°C) with relative humidity below 80%.
Regulatory Compliance
International Regulations
- CE Marking (EU): Comply with the EU’s Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), and RoHS 2 (2011/65/EU) for restricted substances.
- UKCA Marking (UK): Required for sale in Great Britain; aligns with CE standards post-Brexit.
- FCC Certification (USA): Must meet FCC Part 15 Class B for electromagnetic interference.
- PSE Mark (Japan): Required for electrical safety under the DENAN Act.
- KC Certification (South Korea): Mandatory for electronic devices under KCC regulations.
Environmental & Chemical Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensure lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances are below allowable limits.
- REACH (EU): Declare Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if present above 0.1% weight.
- WEEE Directive (EU): Provide take-back and recycling information for end-of-life equipment.
Battery-Specific Considerations
If the load tester includes an internal rechargeable battery (e.g., for portable models):
– Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) Section II for lithium batteries when shipping by air.
– Package batteries to prevent short circuits (e.g., terminals protected, individual wrapping).
– Include UN38.3 test summary for lithium batteries if required by carrier.
Import & Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Must include detailed product description, HS code, value, country of origin, and harmonized system classification.
- Packing List: Itemize contents, weights, and dimensions per package.
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC): Required for many markets (e.g., CE, KC, PSE).
- Export Declarations: File through AES (US) or equivalent national systems (e.g., EU’s AES, Canada’s CBSA).
- HS Code Guidance: Typical classification: 9030.89 (measuring or checking instruments for electrical quantities, not elsewhere specified).
Labeling Requirements
- Include product name, model number, serial number, manufacturer details, and compliance marks.
- Safety labels: caution for electrical hazards, hot surfaces during use, and proper ventilation.
- Language: Use local language(s) per destination country (e.g., French in Canada, German in Austria).
Quality & Traceability
- Implement batch/lot tracking for each unit to support recalls or field service actions.
- Maintain technical documentation (including test reports and conformity assessments) for minimum 10 years (per EU requirements).
- Conduct periodic audits of manufacturing and logistics partners to ensure ongoing compliance.
End-of-Life & Sustainability
- Design for disassembly and recyclability.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers.
- Provide user instructions for proper disposal and recycling.
Summary
Adhering to logistics and compliance standards ensures safe, legal, and efficient distribution of battery load testers globally. Regular updates to regulatory requirements and proactive risk management are essential for market access and customer safety.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Load Tester for Battery Applications
After evaluating various options, technical requirements, and supplier capabilities, sourcing a suitable load tester for battery testing is a critical step in ensuring battery performance, reliability, and safety across applications. The decision should be guided by specific testing needs such as battery type (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion), voltage and capacity ranges, portability requirements, data logging capabilities, and compliance with industry standards.
A high-quality load tester enables accurate assessment of battery health by simulating real-world load conditions, identifying weak or failing cells, and verifying charge/discharge performance. Whether choosing a handheld device for field use or a programmable benchtop system for laboratory environments, it is essential to balance precision, durability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness.
Ultimately, selecting a reputable supplier with proven technical support, calibration services, and product warranty adds long-term value. Investing in the right load tester not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also contributes to improved maintenance efficiency, reduced downtime, and extended battery lifecycle. Therefore, a well-informed sourcing decision today supports safer, more reliable power systems tomorrow.