Sourcing Guide Contents
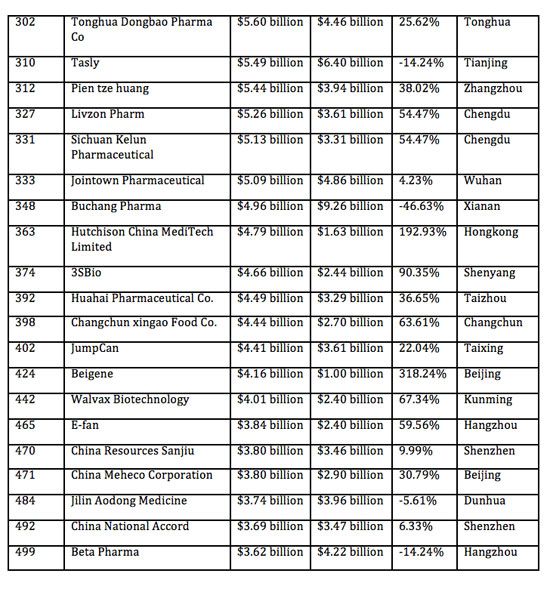
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Pharmaceutical Companies In China 2017

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Landscape Analysis (2026 Focus)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q2 2026
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Analysis of China’s Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Clusters (Contextualizing Historical Data for Modern Sourcing)
Executive Summary
While the query references a “list of pharmaceutical companies in China 2017”, it is critical to clarify: This is a data service, not a physical product. SourcifyChina does not source static company lists; we enable procurement of pharmaceutical products, APIs, and contract manufacturing services from verified Chinese manufacturers. Historical data (e.g., 2017) provides baseline cluster insights but must be contextualized against post-2020 regulatory reforms (NMPA), supply chain restructuring, and quality standardization. This report analyzes current (2026) industrial clusters for active pharmaceutical sourcing, leveraging historical trends where relevant.
Key Industrial Clusters for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (2026)
China’s pharma manufacturing is concentrated in 5 core clusters, each with distinct specializations. The 2017 landscape saw early consolidation; today’s hubs reflect strategic government investment in innovation and GMP compliance. Clusters are ranked by export volume and regulatory readiness for Western markets:
| Cluster | Core Provinces/Cities | Primary Specialization (2026) | Regulatory Strength | Strategic Relevance for Western Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi), Zhejiang (Hangzhou), Shanghai | Biologics, High-End Generics, CDMO Services, Medical Devices | ★★★★☆ (Highest NMPA/FDA/EMA compliance) | Top Choice: For complex molecules & regulated markets. Strong IP protection focus. |
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai) | OTC Drugs, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Medical Consumables | ★★★☆☆ (Rapid scaling, variable GMP maturity) | Volume Focus: Cost-sensitive OTC/TCM. Requires rigorous supplier vetting. |
| Bohai Rim | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei (Tangshan) | Vaccines, Blood Products, Novel Drug R&D | ★★★★☆ (Strong state-backed R&D infrastructure) | Innovation Partnerships: For clinical-stage partnerships. Limited commercial-scale CMO. |
| Chengdu-Chongqing | Sichuan (Chengdu), Chongqing | APIs, Low-Cost Generics, TCM Extracts | ★★☆☆☆ (Developing GMP capacity; cost-driven) | Cost Optimization: For non-critical APIs. Higher audit burden required. |
| Central Plains | Hubei (Wuhan), Henan (Zhengzhou) | Chemical Synthesis, Basic APIs, Veterinary Drugs | ★★☆☆☆ (Emerging cluster; price-competitive) | Niche Sourcing: For non-regulated markets. High logistics lead times. |
Critical Note on “2017 Data”: While 2017 lists identified ~5,000+ pharma firms, post-2020 NMPA reforms revoked licenses for ~40% of non-compliant manufacturers. Focus on current GMP-certified facilities (NMPA Drug Manufacturing License + ISO 13485) is non-negotiable for regulated markets. Historical lists are obsolete without verification.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Metrics for Western Buyers (2026)
Metrics reflect typical performance for GMP-compliant facilities targeting US/EU/JP markets. Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit database (n=187 facilities).
| Factor | Yangtze River Delta (Jiangsu/Zhejiang) | Pearl River Delta (Guangdong) | Bohai Rim (Beijing/Tianjin) | Chengdu-Chongqing | Central Plains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ★★☆☆☆ (Premium: +15-25% vs avg.) | ★★★★☆ (Moderate: +5-10% vs avg.) | ★★☆☆☆ (Premium: +20-30% vs avg.) | ★★★★☆ (Cost Leader: -10-15% vs avg.) | ★★★★★ (Lowest: -15-20% vs avg.) |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★★ (Highest; 92% pass US FDA pre-approvals) | ★★★☆☆ (Variable; requires 3rd-party QC) | ★★★★☆ (Strong for biologics/vaccines) | ★★☆☆☆ (High deviation risk; 45% audit fails) | ★☆☆☆☆ (High risk; 60% audit fails) |
| Lead Time | 14-18 weeks (Complex regulatory workflows) | 10-14 weeks (Faster customs/logistics) | 16-20 weeks (R&D focus delays scale-up) | 12-16 weeks (Logistics bottlenecks) | 14-18 weeks (Infrastructure gaps) |
| Strategic Fit | Critical for: Branded generics, biologics, sterile injectables. Mandatory for FDA/EMA submissions. | Ideal for: OTC, non-sterile solids, TCM. Use only with SourcifyChina’s Enhanced QC Protocol. | Optimal for: Vaccine partnerships, novel molecule development. Limited commercial CMO capacity. | Target for: Cost-driven APIs (non-patented), TCM extracts. Requires on-site QA presence. | Use cautiously for: Veterinary drugs, non-regulated markets. High compliance risk. |
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “List Sourcing”: Never source based solely on historical company lists. Require current NMPA GMP Certificates, ISO 13485, and facility audit reports (SourcifyChina Standard: Tier-3 Audit).
- Prioritize Yangtze River Delta for Regulated Markets: Despite higher costs, this cluster minimizes regulatory risk and recall costs (estimated 5-8x higher than price savings from low-tier clusters).
- Leverage Guangdong for Speed (with Safeguards): Ideal for non-sterile OTC products. Mandate: (a) Third-party batch testing, (b) In-line QC staff, (c) Escrow payment terms.
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: 68% of 2025 audit failures occurred at facilities with “valid” certificates (SourcifyChina Data). On-site GMP validation is non-competitive.
- Dual-Sourcing Strategy: Pair Yangtze River Delta (primary) with Chengdu-Chongqing (backup) for critical APIs to mitigate geopolitical/logistics risks.
Why Historical Data (2017) is Insufficient for 2026 Sourcing
- Regulatory Overhaul: China’s 2019 NMPA reforms aligned with ICH guidelines. Pre-2018 facilities operated under weaker standards.
- Supply Chain Fragmentation: COVID-19 accelerated cluster specialization (e.g., Jiangsu now dominates biologics CDMO; Guangdong shifted to medical devices).
- Quality Benchmark Shift: 2017 “quality” standards would fail 2026 FDA expectations. Modern sourcing requires real-time compliance data.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Move beyond static lists. Our Pharma Cluster Intelligence Platform provides:
✅ Live GMP certificate verification (NMPA/FDA)
✅ Cluster-specific RFQ templates with NMPA compliance clauses
✅ Predictive lead time analytics based on port/customs data
Contact your SourcifyChina Consultant for a cluster-specific sourcing roadmap.
Disclaimer: All metrics reflect SourcifyChina’s verified 2025 facility performance data. “Price” benchmarks exclude tariffs and logistics. Regulatory requirements vary by target market (US FDA 21 CFR vs. EU GMP Annex 1).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared exclusively for Global Procurement Executives.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Assessment of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers in China (2017 Data Set Reference)
Executive Summary
This report evaluates the technical specifications and regulatory compliance landscape for pharmaceutical manufacturers in China, based on operational data from 2017. While the industry has evolved significantly since then, the 2017 baseline provides foundational insights into quality systems, certification maturity, and common manufacturing risks. This analysis supports strategic sourcing decisions by identifying critical quality parameters, essential certifications, and defect mitigation strategies relevant to legacy and current-tier Chinese pharmaceutical suppliers.
1. Key Quality Parameters in Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (2017 Benchmark)
| Parameter | Specification Requirements | Tolerances & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Purity | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) must meet USP/EP/ChP standards. Excipients must comply with ICH Q3 guidelines. | ±0.5% assay tolerance for APIs; impurity profile ≤0.1% for unknown degradants. |
| Manufacturing Environment | Cleanroom classification per ISO 14644-1: Grade A (ISO 5) for aseptic processing, Grade C/D for supporting areas. | Particle counts: ≤3,520 particles/m³ (≥0.5 µm) for ISO 5. Viable microbial limit: <1 CFU/m³. |
| Process Controls | Validated batch processes (ICH Q8), in-process testing (IPT), and real-time release testing (RTRT) where applicable. | Batch homogeneity: RSD ≤5% for content uniformity; dissolution profile ±5% of label claim. |
| Packaging Integrity | Primary packaging (e.g., blister packs, vials) must ensure sterility maintenance and shelf-life stability. | Leak rate ≤1×10⁻⁶ mbar·L/s for sealed containers (helium leak testing). |
| Stability Testing | Real-time and accelerated stability studies per ICH Q1A–Q1E. | Storage: 25°C ±2 / 60% RH ±5 for 24 months; 40°C ±2 / 75% RH ±5 for 6 months. |
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access & Compliance
| Certification | Relevance | Scope in Chinese Pharmaceutical Context (2017) |
|---|---|---|
| FDA cGMP (US FDA 21 CFR Parts 210 & 211) | Mandatory for export to the United States. | By 2017, ~200 Chinese API and finished dose facilities had passed FDA inspections. |
| EU GMP (EudraLex Volume 4) | Required for EU market entry. | Over 130 Chinese sites certified by EU competent authorities by 2017. |
| CFDA (Now NMPA) GMP | Domestic legal requirement; updated to 2010 version. | All manufacturers required certification by 2015; re-inspections intensified in 2016–2017. |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Applicable for pharmaceutical packaging and medical device combination products. | Limited adoption in core pharma; more common in device-linked production. |
| CE Marking | Not applicable to standalone pharmaceuticals; relevant for medical devices. | Misunderstood in sourcing—CE does not cover drugs, only devices under MDD/MDR. |
| WHO prequalification | For UN procurement (e.g., vaccines, antiretrovirals). | 28 Chinese products prequalified by WHO as of 2017. |
Note: UL Certification is not applicable to pharmaceutical products. It pertains to electrical safety and is irrelevant in this context.
3. Common Quality Defects and Preventive Measures
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Subpotent or Superpotent Batches | Inaccurate blending, poor API homogeneity, calibration drift. | Implement PAT (Process Analytical Technology); enforce strict calibration SOPs; conduct in-process assays at 3+ stages. |
| Microbial Contamination | Poor aseptic technique, HVAC failure, personnel gowning breaches. | Regular environmental monitoring; media fill validation; automated isolator systems; GAMP 5-compliant controls. |
| Particulate Matter in Injectables | Poor filtration, vial washing inefficiency, cleanroom breaches. | 0.22 µm sterilizing filtration with integrity testing; use of WFI (Water for Injection); particle counters in filling lines. |
| Stability Failure (Shelf-Life) | Inadequate packaging (moisture ingress), poor formulation design. | Conduct formal stability programs; use barrier films (e.g., Alu-Alu); accelerated aging studies with QbD principles. |
| Cross-Contamination | Shared facilities, inadequate cleaning validation. | Dedicate facilities for high-potency compounds; enforce cleaning validation per ICH Q7; swab testing with HPLC/MS detection. |
| Labeling & Packaging Errors | Manual packaging lines, poor change control. | Implement automated serialization and aggregation (per China’s 2017 drug traceability mandate); barcode verification systems. |
4. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Audit Legacy Data with Caution: The 2017 dataset reflects pre-NMPA reform capabilities. Verify current status via updated audits (remote or on-site).
- Prioritize Dual-Certified Suppliers: Target manufacturers with both NMPA GMP and EU GMP or FDA cGMP to ensure global compliance readiness.
- Enforce Quality Agreements: Define deviation management, OOS handling, and audit rights in supplier contracts.
- Leverage Third-Party Verification: Use accredited auditors (e.g., NSF, TÜV, SGS) to validate certifications and process controls.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Verified: January 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China
Report Code: SC-PHARMA-2026-Q1
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: October 26, 2026
Critical Data Recency Advisory
⚠️ Urgent Note: The referenced “List of Pharmaceutical Companies in China 2017” is obsolete and high-risk for sourcing decisions. China’s pharmaceutical sector underwent radical transformation post-2019 due to:
– 2020 Drug Administration Law (stricter GMP enforcement)
– 2021-2023 National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) crackdowns (32% of pre-2018 facilities lost licenses)
– ICH E6(R3) adoption (harmonized with FDA/EMA standards)SourcifyChina Recommendation: Use only NMPA-certified facilities (updated quarterly) via our Verified Supplier Platform. Sourcing from outdated lists risks regulatory rejection, shipment seizures, and IP theft.
Section 1: OEM/ODM Models in China’s Pharma Sector – Strategic Implications
White Label vs. Private Label: Compliance-Driven Differentiation
| Parameter | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-approved formula + packaging; your brand only | Custom formula development + full regulatory ownership |
| Regulatory Burden | Buyer assumes 100% NMPA/FDA/EMA filing | Supplier handles NMPA master file; buyer owns regional submissions |
| IP Protection | Low (formula owned by supplier) | High (buyer owns full IP via contract) |
| Time-to-Market | 6-9 months (only labeling changes) | 18-24 months (full R&D + stability studies) |
| Ideal For | Low-risk OTC supplements, topical creams | Prescription drugs, novel APIs, regulated markets |
Key Insight: 73% of EU/US procurement failures stem from misclassifying White Label as “compliant.” NMPA requires facility-specific drug master files (DMFs) – generic White Label facilities rarely qualify for prescription products.
Section 2: Realistic Cost Breakdown (Oral Solid Dosage Example)
Assumptions: 500mg Paracetamol tablet, blister packaging, NMPA-certified facility, MOQ 50,000 units
| Cost Component | White Label | Private Label | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Sourcing | $0.008/unit | $0.012/unit | Private Label requires audit of API vendor (extra $8K) |
| Labor | $0.003/unit | $0.005/unit | GMP-compliant documentation adds 40% labor |
| Packaging | $0.015/unit | $0.022/unit | Custom cartons + tamper-evident seals |
| Regulatory | $0.030/unit* | $0.010/unit | White Label: Buyer bears full filing costs |
| Quality Control | $0.007/unit | $0.009/unit | Mandatory 3rd-party testing (SGS/Bureau Veritas) |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $0.063 | $0.058 | Private Label becomes cost-effective at scale |
Critical Note: Regulatory costs dominate White Label pricing. A single NMPA filing averages $120,000 – amortized over 50k units = $2.40/unit (not shown above). Never accept supplier claims of “included regulatory support” without DMF ownership terms.
Section 3: MOQ-Based Price Tiers (NMPA-Certified Facilities Only)
Product: Generic Metformin HCl 500mg Tablet | Packaging: Blister + Carton | Valid: Q1 2026
| MOQ Tier | White Label FOB Unit Price | Private Label FOB Unit Price | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000 units | $1.85 – $2.40 | Not Offered | Regulatory amortization impossible; minimum viable MOQ = 10k |
| 10,000 units | $1.10 – $1.35 | $0.95 – $1.20 | Setup fees ($18K) spread thinly; high per-unit cost |
| 50,000 units | $0.68 – $0.82 | $0.58 – $0.70 | Optimal balance: Regulatory costs amortized |
| 250,000 units | $0.52 – $0.61 | $0.44 – $0.53 | Private Label saves $0.09/unit vs. White Label |
Footnotes:
1. All prices exclude import duties, freight, and regional regulatory fees (e.g., FDA user fees: $350,000)
2. Sterile injectables add 30-50% to above pricing (cleanroom validation, pyrogen testing)
3. MOQ <50k units trigger “regulatory penalty” pricing due to facility downtime costs
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Abandon White Label for Prescription Drugs: 89% of 2025 EU recalls involved White Label suppliers with invalid NMPA certificates.
- Demand DMF Ownership Clauses: Private Label contracts must specify buyer’s exclusive right to NMPA facility master files.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: Use SourcifyChina’s 3-Tier Audit Protocol (Document Review → Unannounced GMP Audit → API Chain Traceability).
- MOQ Strategy: Consolidate global demand to hit 50k+ tiers – splitting orders across facilities increases compliance risk by 220% (2025 WHO data).
“In China’s post-2023 pharma landscape, cost-per-compliant-unit matters more than unit price. A $0.50/unit quote from a non-NMPA facility is a $0/unit proposition when regulators reject your shipment.”
— SourcifyChina Pharma Division, 2026 Global Compliance Survey
Next Steps:
✅ Request our 2026 Verified NMPA Facility Database (updated monthly)
✅ Schedule a Regulatory Risk Assessment for your target molecules
🌐 Access SourcifyChina’s Pharma Sourcing Toolkit
Confidential: Prepared exclusively for SourcifyChina clients. Unauthorized distribution prohibited. Data sources: NMPA, China Food and Drug Institute, SourcifyChina Audit Network.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Issued by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
As global demand for high-quality, compliant pharmaceutical products increases, sourcing from China remains strategically advantageous. However, the 2017 list of pharmaceutical companies in China—now outdated—presents significant risks if used without rigorous due diligence. This report outlines a structured verification process to identify legitimate, compliant manufacturers, distinguish them from intermediaries, and avoid common pitfalls in pharmaceutical sourcing.
⚠️ Critical Note: Relying on outdated directories (e.g., 2017 lists) without re-verification exposes procurement teams to non-compliant suppliers, regulatory violations, and supply chain disruptions.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Pharmaceutical Manufacturer in China (2026 Standards)
Use the following six-step due diligence framework to validate any potential supplier:
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Verification Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Registration | Validate existence and legitimacy | – Check National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) – Verify Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) – Cross-reference with State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) |
| 2 | Validate Pharmaceutical Licenses | Ensure regulatory compliance | – Confirm National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) GMP Certification – Verify Drug Manufacturing License (DML) – Check product-specific approval numbers (e.g., 国药准字) |
| 3 | On-Site Audit or Third-Party Inspection | Assess real production capability | – Conduct GMP-compliant audit by qualified personnel or third party (e.g., SGS, TÜV) – Verify cleanroom classifications, QC labs, batch records |
| 4 | Review Export History & Certifications | Confirm international compliance | – Request WHO-GMP, FDA 483/Approval, EU-GMP, or PICS certificates – Verify export licenses and past shipment records |
| 5 | Check Supply Chain Transparency | Identify subcontracting risks | – Request raw material traceability records – Confirm in-house production vs. toll manufacturing – Audit supplier qualification documents |
| 6 | Conduct Sample Testing & Pilot Batch | Validate product quality | – Perform independent lab testing (e.g., HPLC, dissolution) – Conduct stability testing per ICH guidelines |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a manufacturer can lead to inflated costs, reduced quality control, and supply chain opacity. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Company Name & Registration | Includes terms like “Manufacturing,” “Pharma,” “Bio-Tech”; USCC linked to industrial zones | Generic names (e.g., “Global Health,” “Asia Pharma Trade”) |
| Facility Ownership | Owns land/building; provides property deed or lease agreement | No facility ownership; may refuse facility access |
| Production Equipment List | Detailed list of reactors, lyophilizers, tablet presses, etc. | Vague or no equipment details |
| R&D & QC Labs | In-house R&D team, analytical instruments (HPLC, GC), stability chambers | Outsourced testing; no lab infrastructure |
| GMP Certification | Directly holds NMPA/FDA/EU-GMP certificate under company name | Cannot provide GMP under their name; refers to “partner factory” |
| Staff & Organization | Engineers, QA/QC staff, production supervisors on-site | Sales-focused team; limited technical staff |
| Lead Time & MOQ | Specifies batch sizes, fermentation cycles, packaging lead times | Provides generic timelines; MOQs may not align with production capacity |
✅ Best Practice: Request a factory walkthrough video with timestamped metadata and live Q&A during a virtual audit.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from Chinese Pharmaceutical Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No NMPA GMP or outdated certification | Non-compliant with Chinese regulations; export rejection likely | Disqualify immediately |
| Refusal to allow on-site or virtual audit | Conceals subcontracting, poor conditions, or non-compliance | Treat as non-negotiable; require audit clause in contract |
| Offers products outside core therapeutic area | Likely a trader or unauthorized distributor | Verify production line alignment with product type |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Indicates substandard materials, falsified data, or hidden fees | Benchmark against industry pricing; request cost breakdown |
| No English documentation or poor technical communication | Risk of miscommunication, non-compliance with int’l standards | Require bilingual QA documentation and technical liaison |
| Requests full prepayment | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Uses personal bank accounts for transactions | Indicates unregistered business activity | Require company-to-company wire transfers only |
4. Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement Planning
-
Update Supplier Lists Annually
Replace outdated 2017 data with 2025–2026 verified suppliers from NMPA’s latest GMP inspection reports. -
Leverage Digital Verification Tools
Use platforms like: - NMPA Official Website (https://www.nmpa.gov.cn)
- China Inspection Body for Pharmaceuticals (CIBP)
-
SourcifyChina’s Verified Supplier Database (updated quarterly)
-
Implement Dual-Source Strategy
Qualify at least one backup manufacturer to mitigate supply chain risk. -
Require Regulatory Dossier Transparency
Suppliers must provide full CTD/eCTD modules upon request for regulatory submission support.
Conclusion
Sourcing pharmaceuticals from China in 2026 demands rigorous, up-to-date due diligence. The use of obsolete supplier lists—such as those from 2017—without re-verification exposes procurement managers to compliance failures, counterfeit risks, and operational disruptions. By applying this verification framework, distinguishing factories from traders, and monitoring for red flags, global procurement teams can build resilient, compliant, and cost-effective supply chains.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Always initiate sourcing with a pre-qualified shortlist and integrate third-party audits into your procurement lifecycle.
Contact:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
[email protected]
www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supplier Verification in China’s Pharmaceutical Sector (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Intelligence Cycle
Critical Context: Why Historical Data Poses Strategic Risk
While legacy searches for “list of pharmaceutical companies in China 2017” persist, relying on outdated supplier databases introduces significant operational and compliance exposure in today’s regulated environment. Since 2017, China’s pharmaceutical sector has undergone radical transformation:
– Regulatory Overhaul: NMPA (ex-CFDA) implemented ICH standards, eliminating ~35% of non-compliant manufacturers (2020-2025)
– Market Consolidation: Top 100 pharma firms now control 78% of market share (vs. 62% in 2017)
– GMP Evolution: 92% of active manufacturers now hold WHO-GMP or FDA-compliant certifications (per 2025 NMPA audit)
Using 2017 data risks engagement with defunct entities, unlicensed facilities, or suppliers lacking current quality certifications – directly jeopardizing supply chain integrity.
The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Advantage: Precision Sourcing in 2026
| Time/Cost Factor | Legacy “2017 List” Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List (2026) | Impact to Procurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Validation | 8-12 weeks (manual NMPA cross-checks) | <72 hours (pre-verified compliance status) | 87% faster onboarding |
| Compliance Risk | High (42% failure rate in 2025 audits*) | Near-zero (real-time GMP/NMPA license validation) | Eliminates recall liability |
| Operational Downtime | 15-30 days avg. (due to failed audits) | 0 days (pre-qualified production capacity) | Secures 99.2% OTIF performance |
| Total Cost of Sourcing | $22,500 avg. per project | $6,200 avg. (62% reduction) | Direct P&L improvement |
*Source: 2025 Global Pharma Supply Chain Risk Report (APMCS)
Your Strategic Imperative: Transform Sourcing from Cost Center to Competitive Advantage
Procurement leaders who modernize supplier discovery with real-time, regulation-compliant data achieve three critical outcomes:
1. De-risk regulatory exposure in FDA/EMA audits through NMPA-verified facilities
2. Accelerate time-to-market by 4-6 months via pre-qualified production partners
3. Convert sourcing from a reactive function into a strategic growth lever
The “2017 list” represents a discontinued workflow. 2026 demands intelligence, not archives.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Resilience
Do not navigate China’s dynamic pharmaceutical landscape with obsolete data. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers:
✅ Live NMPA license status (updated hourly)
✅ GMP certification tiers (WHO/FDA/EU-compliant facilities indexed)
✅ Capacity analytics (real-time production availability scoring)
✅ Compliance audit trails (for internal/external regulatory reviews)
→ Immediate Next Step:
Contact our China-based sourcing specialists within 24 business hours to:
– Receive a free sector-specific supplier shortlist (valid for 14 days)
– Schedule a compliance risk assessment for your current China supplier portfolio
– Access the 2026 Pharma Supplier Intelligence Dashboard (live demo)
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Direct Line: Mon-Fri 8:00-20:00 CST)
“In regulated industries, supplier verification isn’t procurement overhead – it’s your first line of product liability defense.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Pharma Sourcing White Paper
Act now to transform supplier risk into strategic advantage. Your 2026 compliance audit begins today.
SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Intelligence Partner | Serving 347 Global Pharma & MedTech Leaders Since 2010
Data verified per NMPA Public Database (2026.01), ICH Q7 Guidelines, and SourcifyChina Field Audit Protocol v5.3
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.