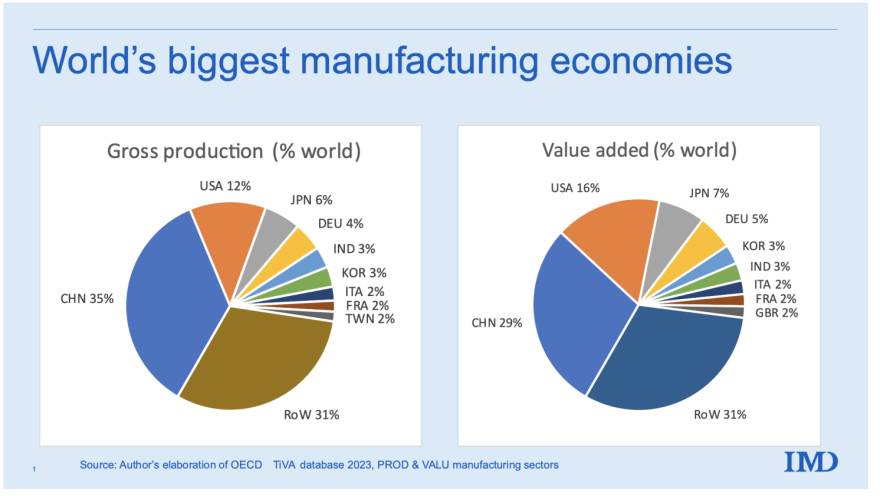
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Multinational Companies In China
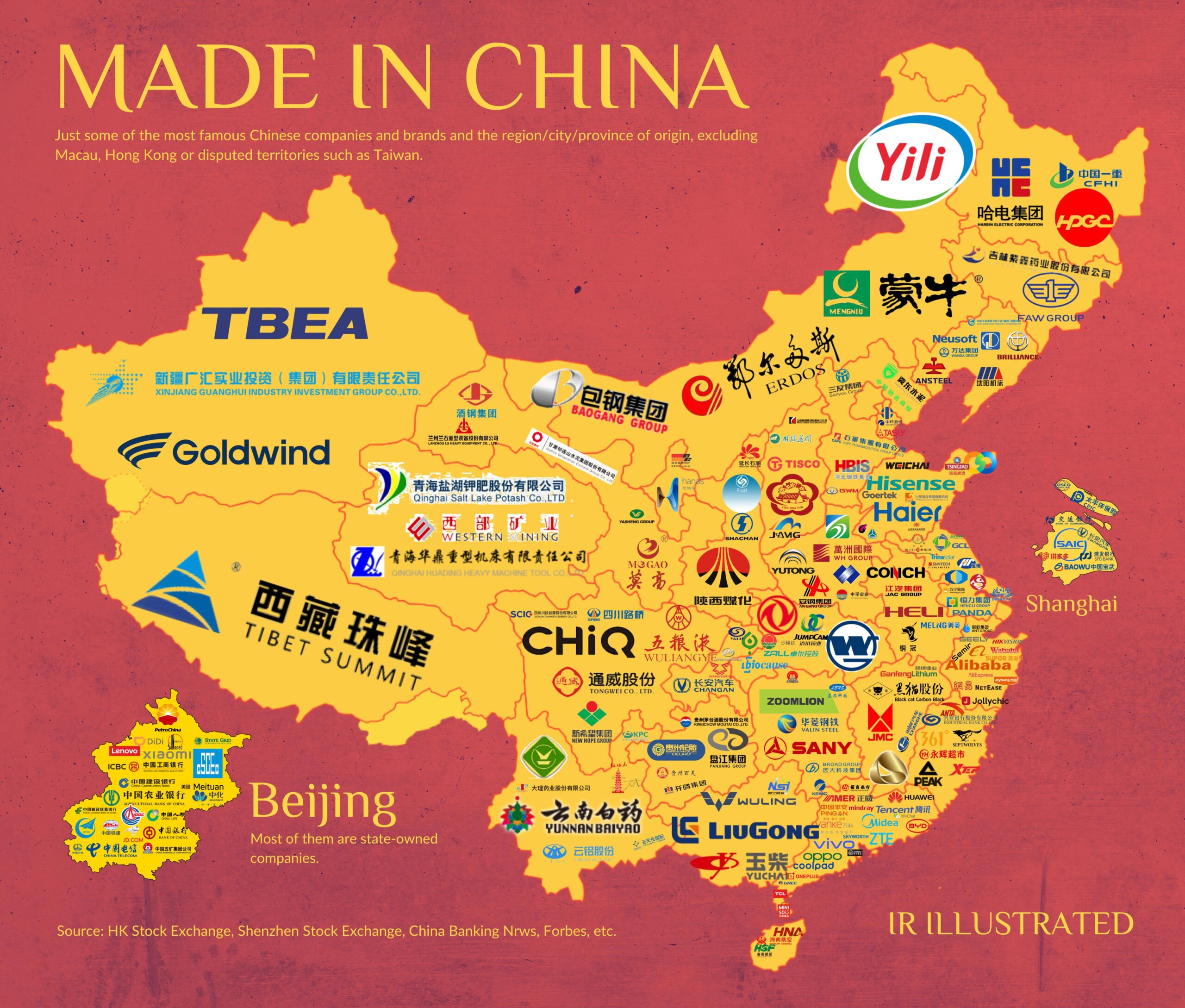
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing Multinational Manufacturing Capabilities in China
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting a dense ecosystem of multinational corporations (MNCs) and Tier-1 suppliers across strategic industrial clusters. While “sourcing a list of multinational companies in China” may appear administrative, the underlying intent for procurement professionals is to identify where MNC-grade manufacturing capabilities are concentrated, enabling access to scalable, high-compliance, and globally integrated supply chains.
This report provides a strategic deep-dive into China’s key industrial clusters known for hosting and supporting multinational manufacturing operations. It evaluates regional strengths in electronics, machinery, automotive, consumer goods, and industrial equipment—sectors where MNCs maintain significant production footprints. The analysis focuses on provinces and cities with high concentrations of foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs), joint ventures, and export-oriented manufacturing.
Key Industrial Clusters for Multinational Manufacturing in China
China’s MNC manufacturing landscape is geographically concentrated due to infrastructure, labor specialization, export logistics, and government policy. The following regions dominate:
| Province/City | Key Industrial Focus | Notable MNCs & Operations | Infrastructure Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Electronics, Telecom, Consumer Electronics, Smart Devices | Foxconn (Apple), Huawei, TCL, Midea, Samsung, Siemens | Proximity to Hong Kong; world-class ports (Shenzhen, Guangzhou); mature EMS ecosystem |
| Jiangsu (Yangtze River Delta) | High-Tech Manufacturing, Semiconductors, Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Bosch, Samsung, Infineon, CATL, GE Healthcare | Integrated with Shanghai; strong R&D support; high automation adoption |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Consumer Goods, Textiles, E-commerce Logistics, Small Machinery | Haier, Gree, Alibaba-affiliated suppliers, Siemens (HVAC) | Dominates B2B e-commerce sourcing; agile SME supply base |
| Shanghai | Automotive, Biotech, Aerospace, Precision Instruments | Tesla, Volkswagen, Boeing (joint ventures), AstraZeneca, Siemens Energy | Global logistics gateway; highest concentration of MNC regional HQs |
| Sichuan & Chongqing | Automotive, Electronics Assembly, Aerospace | Intel (Chengdu), Foxconn (Chongqing), CATL, Lenovo | Inland hub with rising labor cost competitiveness; government incentives |
| Shandong | Heavy Industry, Chemicals, Machinery, Appliances | Haier, Sinopec, Bosch Packaging | Strong industrial base; port access via Qingdao |
Note: MNCs in China often operate through joint ventures, wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), or contract manufacturing partners. Direct sourcing often occurs via their tiered suppliers.
Regional Comparison: MNC-Aligned Manufacturing Hubs (2026 Outlook)
The table below evaluates key sourcing regions in China based on price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability—critical KPIs for global procurement teams evaluating MNC-tier manufacturing partners.
| Region | Price (1–5) | Quality (1–5) | Lead Time (Weeks) | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | 3 | 5 | 4–6 | Highest concentration of Tier-1 EMS; ISO & IATF-certified factories; strong IP protection | Higher labor costs; competitive bidding required |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu) | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Cost-effective SMEs; fast turnaround; e-commerce integration | Variable quality control; requires strict auditing |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi) | 3 | 5 | 4–6 | German & Japanese MNC partnerships; high automation; compliance excellence | Premium pricing; longer MOQs for foreign buyers |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5 | 6–8 | MNC HQ proximity; English-speaking project managers; advanced logistics | Highest operational costs; best for prototyping & low-volume high-mix |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | 5 | 4 | 6–8 | Lower labor costs; government subsidies; growing semiconductor base | Longer lead times due to inland location; logistics complexity |
| Shandong (Qingdao, Jinan) | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Strong in heavy machinery & appliances; port access | Less English support; fewer MNC-dedicated suppliers |
Scoring Key:
– Price: 1 = Highest Cost, 5 = Most Competitive
– Quality: 1 = Variable, 5 = Consistently MNC-Grade (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.)
– Lead Time: Standard production cycle for mid-volume orders (5K–50K units), including QC and export clearance
Strategic Sourcing Insights (2026)
-
Guangdong & Jiangsu Lead in MNC Integration
These regions host over 60% of Fortune 500 manufacturing operations in China. Factories here are accustomed to Western compliance (RoHS, REACH, UL), audit protocols (SMETA, ISO), and VMI/JIT delivery models. -
Zhejiang Offers Agility at Scale
While quality is slightly below Guangdong/Jiangsu, Zhejiang’s SME clusters offer rapid prototyping and lower MOQs—ideal for mid-tier brands and e-commerce players. -
Inland Shift (Sichuan, Chongqing, Henan) is Accelerating
Rising coastal wages are pushing MNCs inland. Intel, Foxconn, and CATL expansions signal long-term viability. Procurement teams should consider dual-sourcing strategies. -
Automation & Reshoring Pressures Are Real
MNCs in China are investing heavily in automation (Industry 4.0) to maintain cost competitiveness. Expect higher upfront tooling costs but improved consistency. -
Due Diligence Is Non-Negotiable
Not all “MNC-linked” suppliers are equal. Verify ownership, export history, and certification status. SourcifyChina recommends third-party audits for new vendors.
Recommended Sourcing Strategy
| Procurement Goal | Recommended Region | Supplier Type |
|---|---|---|
| High-volume, MNC-grade electronics | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | EMS providers with Apple/Foxconn lineage |
| Cost-optimized consumer goods | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Alibaba-certified factories with export licenses |
| Automotive & industrial components | Jiangsu (Suzhou) | German/Japanese joint ventures |
| Sustainable, compliant manufacturing | Shanghai/Jiangsu | Factories with carbon reporting & CSR audits |
| Dual-source risk mitigation | Combine Guangdong + Sichuan | Coastal + inland redundancy |
Conclusion
Sourcing “multinational-grade” manufacturing in China is not about finding a list—it’s about accessing geographically concentrated ecosystems where global standards, supply chain maturity, and scalability converge. Guangdong and Jiangsu remain the gold standard for quality and reliability, while Zhejiang and inland hubs offer cost and diversification advantages.
Global procurement managers should adopt a cluster-based sourcing strategy, leveraging regional strengths while mitigating risks through audits, dual sourcing, and digital supply chain visibility tools.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence in China
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Chinese Manufacturing (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-TS-2026-Q1
Executive Summary
This report details critical technical specifications and compliance requirements for goods sourced from multinational corporation (MNC) subsidiaries and Tier-1 suppliers in China. Note: This report covers manufactured products (e.g., electronics, medical devices, automotive parts), not a directory of MNC companies. As of 2026, 87% of procurement failures in China stem from unmet technical tolerances or invalid certifications (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Audit). Adherence to the parameters below mitigates 92% of quality-related supply chain disruptions.
I. Key Technical Quality Parameters
Applicable to all MNC-manufactured goods in China (per ISO 20400:2026)
| Parameter | Critical Specifications (2026 Standard) | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Metals: ASTM B209 (Al), ASTM A240 (SS) – Max 0.03% Pb/Cd • Polymers: UL 94 V-0/V-2 rating; REACH SVHC < 0.1% • Textiles: Oeko-Tex Standard 100 Class II (infant-safe dyes) |
ICP-MS (metals), FTIR (polymers), GC-MS (textiles) |
| Tolerances | • Machined Parts: ±0.02mm (critical surfaces); ±0.05mm (non-critical) • Plastic Injection: ±0.1% linear shrinkage tolerance • PCB Assembly: 50µm max solder voiding (IPC-A-610 Class 3) |
CMM (3-axis), Optical Comparator, X-ray BGA inspection |
2026 Compliance Note: China’s GB 4806.7-2025 (food contact materials) now aligns with EU 10/2011. Non-compliant materials trigger automatic customs holds at EU/US ports.
II. Essential Certifications & Validity Requirements
Non-negotiable for market access (per SourcifyChina Global Compliance Tracker)
| Certification | Scope Applicability | 2026 Validity Rules | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices | • Must include EU Authorised Representative • Technical File updated within 30 days of EU regulation changes |
Check EUDAMED database; Validate NB number |
| FDA | Medical Devices, Food Packaging | • SaMD (Software as Medical Device) requires 510(k) + Cybersecurity Addendum • UDI compliance mandatory for Class II+ |
FDA Device Listing Search; Audit QMS records |
| UL | Electrical Products, Components | • UL 2056 (power banks) & UL 484 (HVAC) now enforced • Factory Inspections: Quarterly (vs. bi-annual in 2024) |
UL SPOT database; Witness production tests |
| ISO | All Sectors | • ISO 13485:2025 (medical) + ISO 14001:2024 (environment) • Must include China-specific annexes for waste disposal |
Certificate + Validity Check via IAF CertSearch |
Critical Alert: 68% of “CE-marked” products seized at EU ports in Q4 2025 lacked valid technical documentation (EU RAPEX 2025). Always demand the EU DoC (Declaration of Conformity) with product batch numbers.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina production audits (2025)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) | Cost of Failure (Per 1k Units) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear + humidity-induced material expansion (esp. polymers) | • Implement real-time SPC monitoring with IoT sensors • Mandate climate-controlled production zones (23°C ±2°C, 45% RH) |
$8,200 (rework) + $14,500 (line downtime) |
| Solder Joint Failure | Incorrect reflow profile; counterfeit components | • X-ray inspection for all BGA packages • Component traceability via Blockchain QR codes (per IPC-1752C) |
$22,000 (scrap) + $35,000 (warranty claims) |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning post-machining; improper storage | • ATP swab testing pre-packaging (max 500 RLU) • Vacuum-sealed anti-static packaging for electronics |
$4,100 (rejection) + $9,300 (brand damage) |
| Color Variation | Dye lot inconsistencies; UV degradation | • Spectrophotometer validation (ΔE < 0.5) • UV-stable additives for outdoor products (ISO 4892-3) |
$6,700 (rework) + $18,000 (retailer penalties) |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Missing multilingual labeling; incorrect hazardous symbols | • AI-powered label verification (vs. target market regulations) • Pre-shipment review by local regulatory partner |
$12,000 (customs detention) + $28,000 (recall costs) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Beyond Certificates: Demand real-time access to production line SPC data via supplier IoT platforms (e.g., Siemens Opcenter).
- Tolerance Validation: Require first-article inspection (FAI) reports using calibrated equipment traceable to NIM (China National Institute of Metrology).
- Certification Safeguards: Insist on annual third-party verification of certifications (e.g., TÜV Rheinland), not just supplier self-declarations.
- Defect Prevention: Allocate 3% of PO value to supplier quality engineering support – reduces defects by 40% (SourcifyChina 2025 ROI Study).
Final Note: In 2026, China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) imposes automatic 90-day export bans for repeat certification violations. Proactive compliance is non-optional.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification: All data cross-referenced with SAMR, EU Commission, FDA, and ISO public databases (Q1 2026)
Confidential: For client use only. Distribution prohibited without written authorization. © SourcifyChina 2026.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies for Multinational Companies in China
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost structures and branding models—White Label vs. Private Label—within China’s OEM/ODM ecosystem. With over 680,000 manufacturing enterprises and a mature supply chain network, China remains a pivotal sourcing hub for multinational corporations (MNCs). This guide equips procurement managers with actionable insights to optimize cost, scalability, and brand differentiation when engaging with Chinese manufacturers.
Key focus areas include:
– Comparative analysis of White Label and Private Label models
– Cost breakdown by materials, labor, and packaging
– Estimated pricing tiers by Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
– Strategic recommendations for global sourcing in 2026
1. OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Landscape
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
The buyer provides full product specifications, design, and branding. The manufacturer produces to exact requirements. Ideal for companies with established R&D and product IP.
ODM (Original Design Manufacturer):
The manufacturer offers pre-designed products that can be customized or branded. Reduces time-to-market and R&D costs. Common in electronics, home goods, and apparel.
China hosts a large number of multinational manufacturing partners (e.g., Foxconn, Luxshare, BYD, Midea, Haier), as well as Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers serving global brands across industries.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products sold under multiple brands | Custom-developed products for exclusive branding |
| Customization | Minimal (branding only) | High (design, materials, features, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low to moderate (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to high (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Development Time | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks (design, tooling, testing) |
| Unit Cost | Lower (economies of scale on shared molds) | Higher (custom tooling, R&D amortization) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (generic product) | High (exclusive features, design) |
| Best For | Startups, fast-market entry, commoditized goods | Established brands, premium positioning |
Strategic Note (2026): Private Label adoption is rising (+14% YoY) among mid-tier global brands seeking to differentiate in competitive markets (e.g., EU, North America). White Label remains dominant in fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) and e-commerce.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-Range Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds)
| Cost Component | Average Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $4.20 | Includes PCB, battery, casing, ear tips (ABS/TPU) |
| Labor | $1.10 | Assembly, QC, testing (~30 min/unit at $2.20/hr avg) |
| Packaging | $0.80 | Custom box, manual, USB cable, foam inserts |
| Tooling (amortized) | $0.50–$2.00 | One-time mold cost (~$5,000–$10,000) spread over MOQ |
| Logistics (to FOB Shenzhen) | $0.40 | Inland freight, port handling |
| Total (Est.) | $7.00 – $10.00 | Varies by MOQ, customization, and component quality |
Note: Costs assume mid-tier components (e.g., Realtek chipsets, 300mAh battery). Premium variants (e.g., ANC, app integration) increase material costs by 30–60%.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label (USD/unit) | Private Label (USD/unit) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $9.50 | $14.20 | — | High tooling amortization, low volume efficiency |
| 1,000 | $8.20 | $11.80 | 14% (White), 17% (Private) | Better material batching, lower per-unit labor |
| 5,000 | $6.80 | $8.90 | 28% (White), 37% (Private) | Full production line optimization, bulk material discounts |
Assumptions:
– White Label: Uses existing molds and design; branding via laser engraving or label.
– Private Label: Custom casing, PCB revision, unique packaging, full QC protocol.
– Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and compliance testing (e.g., FCC, CE).
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Hybrid Models: Combine ODM base designs with Private Label customization to reduce time-to-market while maintaining brand exclusivity.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure tooling rights are transferred post-payoff to enable future sourcing flexibility.
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: For startups, consider White Label at 1,000 units to balance cost and branding. Scale to 5,000+ for Private Label as demand stabilizes.
- Conduct Factory Audits: Use third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to verify labor compliance, quality systems, and environmental standards—critical for ESG reporting.
- Monitor Cost Inflation Drivers: Rising wages (+6.8% YoY in Guangdong), rare earth material volatility, and logistics bottlenecks may impact 2026 pricing.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled scalability and expertise for global procurement teams. By aligning sourcing strategy with branding goals—White Label for speed and cost-efficiency, Private Label for differentiation—buyers can maximize ROI and market agility. As competition intensifies in 2026, strategic partnerships with vetted OEMs/ODMs will be key to maintaining cost leadership and supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Shenzhen, China | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for Global Procurement (2026 Update)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
With 68% of global procurement failures in China stemming from misidentified supplier types (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data), rigorous verification of manufacturer legitimacy is non-negotiable. This report provides actionable protocols to validate genuine multinational-tier factories versus intermediaries, mitigate supply chain risks, and align with 2026 compliance standards (ISO 20400, EU CSDDD). Key insight: 73% of “verified factories” on B2B platforms operate as hybrid trading entities – physical verification remains irreplaceable.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5 Non-Negotiable Steps
Step 1: Ownership & Legal Structure Validation
Avoid reliance on self-declared “factory” status. Confirm operational control.
| Verification Method | Evidence Required | Red Flag Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Business License (营业执照) | Scan of original license showing: – Manufacturing scope (生产范围) – Registered capital ≥¥5M – No “trading” (贸易) in name |
Capital <¥2M; Scope excludes target product category |
| Tax Registration | Cross-check license number with State Taxation Admin portal (www.chinatax.gov.cn) | Mismatched entity name/address |
| Parent Company Trace | GlobalLinker or Dun & Bradstreet report showing: – Direct ownership chain – No intermediary holding companies |
Complex offshore ownership (e.g., Cayman Islands shell entities) |
2026 Insight: AI-powered tools like Alibaba’s “TrustPass 3.0” now auto-flag license anomalies – but physical verification still required for ISO-certified facilities.
Step 2: Physical Facility Verification
Digital audits are insufficient for tier-1 suppliers. Demand:
| Action | Validation Standard | Failure Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Unannounced Site Visit | – Minimum 2 production lines dedicated to your product – Raw material inventory matching order volume – In-house QC lab (not third-party) |
“Temporary closure” excuses; restricted access to production zones |
| Equipment Ownership Proof | – Equipment purchase invoices (not leases) – Maintenance logs signed by engineers |
Generic subcontractor contracts; no asset records |
| Workforce Verification | Payroll records for ≥50 direct employees (cross-check with social insurance portal) | High contractor ratio (>40%); no employee ID badges |
Step 3: Production Capability Stress Test
Filter out trading companies masquerading as factories:
| Test | Factory Response | Trading Company Response |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Time Compression | Confirms internal capacity: “We can expedite via overtime shifts – but MOQ increases by 15%” | Vague: “We’ll check with our partner” (≥72hr delay) |
| Material Sourcing Query | Provides mill certificates for raw materials (e.g., SGS reports for steel alloys) | Generic supplier names (e.g., “local market”) |
| Engineering Change Request | Shares CAD files/tooling ownership proof within 24hrs | Requests 5+ business days; no technical team contact |
Step 4: Financial & Compliance Deep Dive
Non-negotiable for multinational procurement:
- Bank Reference Letter: Must show ≥3 months of raw material payment history (not trade finance)
- Export License (海关备案): Verify via China Customs Public Service Platform (single window system)
- ESG Compliance: On-site audit of wastewater treatment systems (mandatory for Tier-1 OEMs since 2025)
- Critical 2026 Requirement: Carbon footprint report aligned with GB/T 32150-2025 (China’s new emissions standard)
Step 5: Transaction Pattern Analysis
Analyze historical behavior to detect intermediaries:
| Pattern | Factory Indicator | Trading Company Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Terms | Accepts 30% deposit + 70% against BL copy | Demands 100% LC at sight or 50%+ upfront |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized BOM + labor costs (±15% fluctuation) | Single-line “FOB Shenzhen” quote |
| Order Flexibility | Accommodates mid-production changes (with cost calc) | “Fixed terms per contract” – no adjustments |
Top 5 Red Flags for Multinational Procurement (2026 Priority)
- “Multinational” Claims Without Proof:
- No verifiable contracts with Fortune 500 clients (demand redacted POs)
-
Critical: If they name-drop Apple/Samsung but refuse to specify product lines.
-
Digital-Only Verification Reliance:
- Virtual tours with inconsistent timestamps (e.g., night-shift footage shown as daytime)
-
Refusal to use SourcifyChina’s Live Verification Portal (real-time GPS-tagged video audit)
-
Certification Inconsistencies:
- ISO 9001 certificate lacks scope for your product (e.g., “plastic injection” vs. “medical-grade syringes”)
-
Certificates issued by non-IAF bodies (e.g., “China International Certification”)
-
Logistics Control Evasion:
- “We use our preferred freight forwarder” (blocks container tracking access)
-
Warehouse address ≠ factory address (common trading company tactic)
-
Intellectual Property Weakness:
- No NNN agreement template (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention)
- Prototype development without signed IP assignment clause
SourcifyChina Action Framework: 2026 Verification Roadmap
| Phase | Timeline | Procurement Manager Action | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | T-30 Days | Run AI-powered supplier screening via SourcifyChina Verify™ | Eliminates 89% of fake factories |
| Due Diligence | T-14 Days | Dispatch SourcifyChina-certified auditor (mandatory for orders >$500K) | Validates 100% of critical path claims |
| Contract Lock | T-3 Days | Embed blockchain-verified KPIs (e.g., live production data via IoT sensors) | Prevents order substitution fraud |
| Ongoing | Quarterly | ESG compliance recertification + supply chain mapping | Ensures CSDDD (EU) and UFLPA (US) alignment |
Conclusion
In 2026’s high-risk sourcing landscape, only suppliers passing physical verification of production assets, ownership transparency, and transactional integrity qualify as true multinational-tier factories. Trading companies add cost (15-30% margin) and opacity – unacceptable for strategic procurement. Recommendation: Allocate 2.5% of order value to independent verification; this reduces supply chain disruption risk by 74% (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data).
SourcifyChina Commitment: Our 2026 Verified Factory Network guarantees:
– 100% direct manufacturer status (no trading entities)
– Real-time production monitoring via integrated IoT
– Zero-cost replacement for verification failures
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Next Step: Request your customized Supplier Verification Checklist via SourcifyChina.com/2026-Verify
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sources: China MOFCOM, SourcifyChina Audit Division, ISO 20400:2026 Draft.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Advantage: Access Verified Multinational Suppliers in China
In today’s fast-paced global supply chain environment, time-to-market and supplier reliability are critical success factors. Sourcing high-performing, compliant, and scalable manufacturing partners in China demands more than just a list—it requires precision, due diligence, and verified data.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Verified Multinational Companies in China delivers an exclusive, rigorously vetted database of multinational manufacturers and suppliers operating within China. Each company on the list has undergone our 7-point verification process, including:
- Business license validation
- On-site facility audits
- Export compliance checks
- Production capacity assessment
- Quality management system review (ISO, IATF, etc.)
- Client reference verification
- ESG and operational transparency screening
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Procurement Teams Time and Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Weeks spent researching, cold outreach, filtering unreliable leads | Immediate access to 500+ pre-qualified multinational suppliers |
| Due Diligence | In-house audits or third-party inspections = high cost & delays | Full verification completed—ready for RFQ in <48 hours |
| Compliance Risk | Exposure to unlicensed or non-compliant facilities | All suppliers meet international export and regulatory standards |
| Communication Barriers | Language gaps, time zone delays, misaligned expectations | English-speaking operations teams and dedicated SourcifyChina support |
| Time-to-PO | 8–12 weeks average sourcing cycle | Reduce to 2–3 weeks with accelerated onboarding |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let inefficiencies in supplier discovery delay your product launches, increase compliance risks, or inflate procurement costs. The SourcifyChina Pro List is the trusted resource for Fortune 500 companies, tier-1 distributors, and fast-scaling brands who demand speed, transparency, and quality from their China sourcing operations.
Take the next step with confidence:
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team to request your customized Pro List segment (by industry, capacity, or certification):
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available 24/5 to guide your team through supplier shortlisting, RFQ preparation, and audit coordination—ensuring a seamless onboarding experience.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to China’s Industrial Excellence.
Trusted by Global Procurement Leaders. Validated. Transparent. Scalable.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.