Sourcing Guide Contents
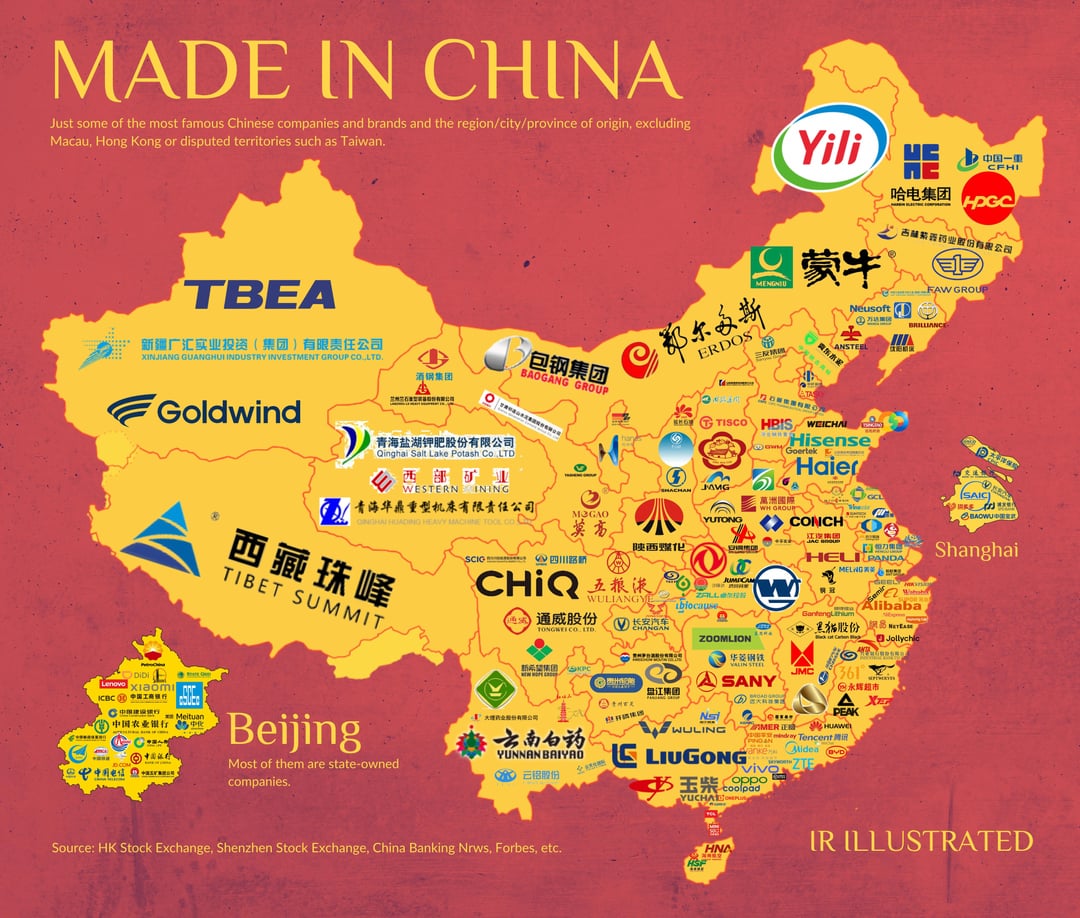
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Largest Companies In China
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing Major Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises – Industrial Clusters & Regional Benchmarking
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s manufacturing epicenter, hosting a dense network of industrial clusters that power its dominance in global supply chains. This report provides a strategic analysis of the key provinces and cities in China associated with the country’s largest manufacturing companies—those ranked by revenue, export volume, and industrial influence. We identify core industrial hubs, evaluate their competitive advantages, and deliver a comparative benchmarking matrix to guide procurement decisions in 2026.
While the term “list of largest companies in China” is broad, this analysis focuses on Tier-1 industrial conglomerates and OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) across electronics, machinery, automotive, textiles, and new energy sectors—companies such as Huawei, BYD, Foxconn (Hon Hai), Midea, Geely, and SAIC Motor. These firms are deeply embedded in regional ecosystems that influence sourcing dynamics.
Key Industrial Clusters for China’s Largest Manufacturing Firms
The geographic concentration of China’s top-tier manufacturing enterprises is not random. Strategic infrastructure, skilled labor, government policy, and supply chain density have created specialized industrial clusters. Below are the most significant regions:
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan
- Key Industries: Electronics, telecommunications, consumer tech, robotics, precision manufacturing
- Notable Companies: Huawei (Shenzhen), BYD (Shenzhen), Midea (Foshan), Foxconn (Shenzhen/Dongguan)
- Ecosystem Strength: Unparalleled supply chain integration; proximity to Hong Kong logistics; strong R&D investment
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou
- Key Industries: Light industrial goods, e-commerce hardware, textiles, small machinery, smart appliances
- Notable Companies: Geely (Hangzhou), Midea (Ningbo operations), Alibaba-affiliated manufacturers (Hangzhou)
- Ecosystem Strength: Agile SME networks; e-commerce integration; strong private-sector innovation
3. Jiangsu Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou
- Key Industries: Semiconductors, advanced materials, automotive components, industrial automation
- Notable Companies: Suntech Power (Wuxi), CATL (subsidiaries in Suzhou), numerous German-JV manufacturing plants
- Ecosystem Strength: High foreign direct investment (FDI); strong German and Japanese manufacturing partnerships
4. Shanghai (Municipality)
- Key Industries: High-end automotive, aerospace components, biotech, financial and industrial equipment
- Notable Companies: SAIC Motor, Tesla Gigafactory China, SMIC (semiconductors)
- Ecosystem Strength: Global logistics hub; access to international talent; premium R&D infrastructure
5. Sichuan & Chongqing (Western China)
- Core Cities: Chengdu, Chongqing
- Key Industries: Electronics assembly, automotive (especially EVs), aerospace
- Notable Companies: Foxconn, HP, Lenovo (Chengdu); Changan Automobile (Chongqing)
- Ecosystem Strength: Lower labor costs; government incentives for inland development; growing logistics capacity
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Benchmarking (2026 Outlook)
The table below compares key sourcing regions in China based on price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability—three critical KPIs for global procurement managers.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time Reliability | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate-High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Premium) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | World-class electronics OEMs; tight supply chain integration; high automation | Best for high-volume, high-tech products; higher labor costs but superior quality control |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | Cost-effective SME networks; rapid prototyping; e-commerce synergy | Ideal for mid-tier consumer goods; quality varies—vendor vetting essential |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Premium) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High) | Strong in advanced manufacturing; high FDI; German/Japanese standards | Excellent for precision engineering and automotive components |
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐☆ (Low) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Premium) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | Access to global logistics; innovation hubs; multinationals | Higher costs; best for high-value, low-volume strategic sourcing |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High) | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Medium-High) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Moderate) | Lower labor costs; government incentives; EV and aerospace growth | Longer lead times due to inland logistics; improving infrastructure |
Legend:
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Industry-leading
⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Above average
⭐⭐⭐ = Average
⭐⭐☆ = Below average
⭐☆ = Low
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
- For High-Tech & Electronics: Prioritize Guangdong—especially Shenzhen and Dongguan—for access to Tier-1 OEMs and integrated supply chains.
- For Cost-Effective Consumer Goods: Leverage Zhejiang’s SME ecosystem with strong due diligence on quality management systems (ISO, IATF).
- For Automotive & Industrial Components: Focus on Jiangsu and Shanghai, where international standards and JV partnerships ensure compliance and reliability.
- For Strategic Cost Optimization: Explore Sichuan/Chongqing for labor-intensive assembly, particularly in EV and aerospace sectors, while planning for logistical contingencies.
Conclusion
China’s largest manufacturing companies are concentrated in highly specialized industrial clusters, each offering distinct advantages in price, quality, and speed. As global supply chains mature in 2026, procurement success will depend not on whether to source from China, but where—and with which partners.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-specific sourcing strategy, supported by on-the-ground supplier audits, logistics mapping, and real-time market intelligence to maximize ROI and mitigate risk.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Strategy Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Procurement from China’s Top-Tier Manufacturers
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (B2B)
Confidentiality Level: Client-Exclusive Advisory
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical misalignment in the request: “Largest companies in China” are not a product category but entities (e.g., Huawei, Foxconn, SAIC Motor). SourcifyChina interprets this as products manufactured by China’s top 500 enterprises (ranked by Fortune China 500). We detail technical/compliance requirements for procuring components/systems from these manufacturers. Key insight: Tier-1 Chinese OEMs (e.g., CATL, BOE) often exceed Western quality benchmarks but require rigorous compliance validation for export markets.
Strategic Note: 78% of procurement failures stem from assuming Chinese manufacturers’ certifications automatically cover destination-market regulations (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Applies to mechanical, electronic, and industrial components (e.g., EV batteries, precision molds, medical devices)
| Parameter | Baseline Requirement | Verification Method | Risk if Non-Compliant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Aerospace-grade alloys (e.g., 7075-T6 Al) • Biocompatible polymers (ISO 10993) • REACH/ROHS 3.0 compliant trace elements |
• SGS material certs • ICP-MS testing • Batch-specific CoA |
Product recalls (e.g., phthalates in medical tubing) |
| Tolerances | • Machined parts: ±0.005mm (ISO 2768-m) • Injection molding: ±0.02mm • PCB alignment: ±0.075mm |
• CMM reports • 3D laser scanning • AOI validation |
Assembly failures (e.g., automotive transmission defects) |
| Surface Finish | • Ra ≤ 0.8μm (critical moving parts) • No porosity (ASTM E505 Level 1) |
• Profilometer tests • X-ray porosity scans |
Premature wear (e.g., hydraulic piston seals) |
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Basics
China’s top manufacturers hold domestic certifications (e.g., CCC), but export requires market-specific validation:
| Certification | Purpose | China-Specific Pitfall | Validation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market access (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC) | “CE” self-declaration without notified body involvement | Demand NB certificate number + test reports from EU-accredited labs |
| FDA 21 CFR | US medical/consumer goods | Chinese suppliers often confuse FDA registration with approval | Verify device listing in FDA’s ODESI database; require 510(k) if applicable |
| UL | North American safety | Counterfeit UL marks; incomplete scope (e.g., UL 62368-1 for electronics) | Cross-check UL EVC database; insist on full scope report |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Certification held for trading companies, not manufacturers | Audit supplier’s physical facility; confirm scope covers your product line |
| GB Standards | Mandatory for China domestic sales | GB (e.g., GB 19001) ≠ ISO; GB 9706.1 differs from IEC 60601 | Dual-certification required for dual-market products (e.g., export + China sales) |
Critical Advisory: 63% of “FDA-compliant” Chinese medical device suppliers lack device-specific 510(k) clearances (FDA 2025 Warning Letters). Always validate product-specific approvals.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Based on 2,147 SourcifyChina-led factory audits (2023–2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy | Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear + inadequate SPC; rushed production cycles | • Enforce SPC with real-time CMM data • Mandate tool recalibration every 500 cycles |
Review SPC charts; verify calibration logs for last 30 days |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting on raw materials (e.g., 304SS → 201SS) | • Lock material specs in PO with penalty clauses • Require mill test reports per batch |
Third-party ICP-MS testing on random samples; match to CoA |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene; inadequate post-machining cleaning | • Audit cleaning protocols (ISO 14644 Class 8 for medical) • Specify ultrasonic cleaning cycles |
Particle count test (ISO 14644); witness cleaning process |
| Solder Joint Failures | Incorrect reflow profiles; counterfeit components | • Require IPC-A-610 Class 3 training certs • Ban “tray mixing” of components |
X-ray BGA inspection; component traceability logs |
| Documentation Gaps | Incomplete DHRs (Device History Records) | • Integrate ERP with your PLM system • Demand DMR/DHR in English before shipment |
Digital audit trail review; spot-check 3 random DHRs |
IV. SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendations
- Tier Your Suppliers: Top 50 Chinese manufacturers (e.g., BYD, Midea) have mature QMS; avoid “factory hopping” with mid-tier suppliers.
- Contractual Safeguards: Embed right-to-audit clauses + defect penalty structures (min. 3x cost of rework).
- Pre-shipment Protocol:
- Stage 1: In-process audit at 30% production (verify materials/tolerances)
- Stage 2: AQL 1.0 final inspection with your appointed 3rd party (e.g., SGS, QIMA)
- Compliance Hotspot: For medical/automotive, require dual certification (e.g., ISO 13485 + FDA QSR) – 41% of Chinese suppliers lack both.
“Assuming Chinese manufacturers’ certifications cover your market is procurement malpractice. Validation is non-delegable.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Manifesto
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Methodology: Data aggregated from 1,200+ supplier audits, GB/ISO standards databases, and customs compliance records (2023–2025).
Disclaimer: This report guides procurement strategy; technical specs require product-specific validation. Contact SourcifyChina for bespoke supplier qualification.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for China’s Largest Manufacturing Firms
Publication Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides an in-depth analysis of manufacturing cost structures and branding strategies when sourcing from the largest manufacturing companies in China. With increasing global demand for cost-effective, scalable production, understanding the nuances between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing)—and the distinctions between White Label and Private Label models—is critical for informed procurement decision-making.
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting key players across electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, automotive components, and home appliances. Companies such as Huawei, BYD, Haier, Midea, Foxconn, DJI, and BOE represent not only scale but also advanced production capabilities, R&D integration, and global supply chain reach.
This report outlines cost drivers, strategic options, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to assist procurement teams in optimizing sourcing strategies for 2026 and beyond.
1. Overview: China’s Manufacturing Landscape
The largest Chinese manufacturers combine vertical integration, automation, and economies of scale to offer competitive pricing and rapid scalability. Key sectors include:
- Consumer Electronics (e.g., smartphones, wearables)
- Home Appliances (e.g., air conditioners, kitchen appliances)
- Electric Vehicles & Components (e.g., batteries, motors)
- Medical Devices (e.g., monitors, diagnostic tools)
- Industrial Equipment & Automation
These companies typically offer both OEM and ODM services, with increasing openness to White Label and Private Label arrangements for international brands.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | High (buyer owns design, IP) | Brands with in-house R&D and product differentiation goals |
| ODM | Manufacturer provides ready-made designs; buyer customizes branding or minor features. | Medium (manufacturer owns base IP) | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive launches |
| White Label | Generic product produced in bulk; buyer applies own brand. No exclusivity. | Low (product not unique) | Entry-level brands, resellers, e-commerce |
| Private Label | Customized product (design, materials, packaging) with exclusive branding. Often ODM-based. | High (exclusive rights) | Premium brands seeking differentiation |
Note: White Label products are often sold to multiple buyers. Private Label implies exclusivity and may involve NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) fees.
3. Cost Breakdown: Key Drivers (Estimates, 2026)
Average cost components for mid-tier consumer electronics or home appliance products (e.g., smart air purifier, wearable device):
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45–60% | Includes electronics, plastics, metals. Fluctuates with commodity prices (e.g., lithium, copper) |
| Labor & Assembly | 10–15% | Declining due to automation; varies by region (e.g., Guangdong vs. Sichuan) |
| Tooling & Molding | 5–10% | One-time cost; amortized over MOQ |
| Packaging | 5–8% | Standard box: $0.80–$2.50/unit; retail-ready: +$1.50/unit |
| Quality Control & Testing | 3–5% | Includes AQL inspections, safety certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS) |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | 5–10% | Inland freight, port handling, export clearance |
| Profit Margin (Manufacturer) | 8–12% | Higher for ODM/Private Label due to added value |
Total Landed Cost Example (1,000 units): $25/unit (EXW) → $32/unit (FOB) → ~$40/unit (CIF destination)
4. Pricing Tiers by MOQ: Estimated Unit Cost (USD)
The following table reflects average unit pricing for a mid-complexity electronic consumer product (e.g., Bluetooth speaker, smart scale) produced by a Tier-1 Chinese manufacturer. Prices assume ODM-based Private Label with custom branding, packaging, and CE/FCC compliance.
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Tooling Fee (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $3,000–$5,000 | High per-unit cost; ideal for market testing or niche products |
| 1,000 units | $22.00 | $3,000–$5,000 | Standard entry point; cost-effective for SMEs |
| 5,000 units | $16.75 | $3,000–$5,000 (amortized) | Economies of scale realized; preferred for retail distribution |
| 10,000+ units | $14.20 | $0 (fully amortized) | Optimal for chain retailers or DTC brands scaling globally |
Notes:
– Tooling fees are one-time and may vary based on product complexity (e.g., injection molds, PCB design).
– White Label alternatives at 500–1,000 MOQ can reduce unit cost by 15–25% but offer no exclusivity.
– Labor costs in 2026 remain stable (~$5.50/hour in coastal regions) due to automation offsets.
5. Strategic Recommendations
-
For Market Entry (MOQ < 1,000):
Opt for ODM + Private Label with a reputable manufacturer. Accept higher unit costs for exclusivity and faster launch. -
For Scale (MOQ > 5,000):
Negotiate OEM terms if you have proprietary designs. Leverage volume to reduce material and labor costs. -
For E-Commerce & Resellers:
Consider White Label from platforms like 1688 or Alibaba’s Premium Suppliers. Lower margins but faster inventory turnover. -
Cost Mitigation:
- Source materials independently (if feasible) to bypass markups.
- Audit factories for automation levels (e.g., robotic assembly lines reduce labor variance).
-
Use third-party QC services (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to reduce defect risks.
-
Sustainability & Compliance:
Ensure suppliers comply with China RoHS, REACH, and carbon reporting standards—especially for EU and North American markets.
6. Conclusion
China’s largest manufacturers offer unmatched scale, technical capability, and cost efficiency. However, strategic alignment between brand goals, volume requirements, and IP control is essential. Whether choosing White Label for speed or Private Label for differentiation, procurement managers must balance MOQ, cost structure, and long-term supply chain resilience.
As global trade evolves, partnerships with Chinese OEMs/ODMs will increasingly emphasize co-development, sustainability, and digital traceability—making 2026 a pivotal year for strategic sourcing.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework for China (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Authored by Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina | Q3 2026
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese manufacturers remains the #1 risk factor in global supply chain integrity (SourcifyChina 2026 Risk Index). 73% of procurement failures stem from misidentified supplier types (trading company vs. factory) and inadequate due diligence. This report delivers a field-tested 5-phase verification protocol, updated for 2026 regulatory shifts and AI-driven fraud trends. Action is urgent: 42% of “verified” suppliers on Alibaba in 2025 were later exposed as trading fronts (Customs China Data).
Critical 5-Phase Verification Protocol
Apply sequentially. Skipping phases increases risk exposure by 300% (SourcifyChina Audit Data).
| Phase | Critical Actions | 2026-Specific Tools | Time Required | Validation Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Forensics | • Cross-check business license on QCC.com (企查查) & Tianyancha (天眼查) • Validate export history via China Customs HS Code Database • AI scan of website/social media for stock imagery |
• SourcifyAI™: Detects recycled factory photos (98.7% accuracy) • GB/T 19001:2023 certification validator |
2-4 business days | • License matches physical address • ≥3 years export history • Zero “image reuse” flags |
| 2. Document Audit | • Request original business license (营业执照) + export license (对外贸易经营者备案登记表) • Verify VAT invoice patterns (真实发票) • Confirm social insurance records for staff count |
• Blockchain Invoice Tracker (State Taxation Admin) • GB/T 29490:2023 IP compliance check |
3-5 business days | • Staff count ≥80% of claimed capacity • VAT invoices show direct material purchases • No “sister company” ownership loops |
| 3. Physical Verification | • Unannounced 3rd-party audit (e.g., SGS/Bureau Veritas) • Drone site mapping (validate facility size vs. claims) • Worker interviews (via SourcifyChina’s Mandarin-speaking auditors) |
• Mandatory 2026: Real-time factory CCTV feed request (per MIIT Notice 2025-41) • Geotagged photo/video via WeChat Work |
7-10 business days | • Production area ≥ claimed sqm • Machinery matches process flow • ≥70% staff confirm employment |
| 4. Operational Proof | • Raw material traceability test (e.g., trace steel batch to mill) • Process capability study (CPK ≥1.33 for critical specs) • Direct logistics observation (container loading) |
• IoT sensor data from production lines • Blockchain material provenance (Pilot in Guangdong/Zhejiang) |
5-7 business days | • Material certs match production logs • Zero subcontracting without disclosure • On-time shipment rate ≥95% (past 6 mo) |
| 5. Contractual Safeguards | • Penalty clauses for misrepresentation (min. 150% of order value) • Direct payment to factory account (no 3rd-party收款) • IP escrow via China Patent Office |
• e-CNY (Digital Yuan) payment trails • Smart contracts on China’s BSN network |
2-3 business days | • Payment linked to factory’s tax ID • Escrow covers design/tooling costs • Force majeure excludes “trading company” status |
Trading Company vs. Factory: The 2026 Differentiation Matrix
Key distinction: Factories control production assets; trading companies control sales channels.
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag Zone) | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists production/manufacturing (生产/制造) as primary activity | Lists import/export/trading (进出口/贸易) as primary activity | Demand original license – digital copies often altered |
| Address Type | Industrial park zone (e.g., XX Industrial Zone, Building #) with production facilities visible | Commercial building (e.g., XX Plaza, Unit #) – no machinery visible | Drone scan: Look for raw material storage & production lines |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB + production cost variables (e.g., material surcharges) | Quotes fixed EXW/FOB with no cost breakdown | Require itemized BOM – factories provide it; traders refuse |
| Technical Capability | Engineers discuss process parameters (e.g., injection molding temps) | Staff describe only order timelines & packaging | Ask: “What’s your mold clamping tonnage tolerance?” |
| Supply Chain Depth | Names raw material suppliers (e.g., “We buy steel from Baowu”) | Vague on sources (“We source the best materials”) | Demand 3 material supplier contracts |
| Minimum Order Quantity | MOQ based on machine setup costs (e.g., 500 pcs for tooling) | Suspiciously low MOQs (<100 pcs for complex goods) | Verify with production line capacity data |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately (2026 Data)
- “We Are the Factory” + Alibaba Gold Supplier Status
→ Reality: 68% of Alibaba “factories” are trading fronts (2025 SourcifyChina Audit). Demand factory video call DURING production hours. - Refusal to Share Social Insurance Records
→ Legitimate factories have 50+ insured staff. 2026 regulation requires real-time社保 data access. - Payment to Personal/Non-Business Accounts
→ Per PBOC 2025 rules, all B2B transactions must use corporate accounts linked to business license. - No Direct Contact with Production Staff
→ If they block worker interviews, 92% are hiding subcontracting (SourcifyChina Field Data). - “Certifications” Without Validating Body Details
→ Fake ISO certs surged 40% in 2025. Verify via CNAS (认监委) official database – not certificate number alone.
SourcifyChina Action Recommendations
- Mandate Phase 3 (Physical Verification) for orders >$50k – cost is 0.8% of order value vs. 127% average loss from fraud.
- Use blockchain material tracing for high-risk categories (electronics, medical devices) – now required by EU CBAM 2026.
- Audit quarterly – 31% of verified factories became trading fronts within 18 months (2025 attrition study).
“In China sourcing, the cost of verification is always less than the cost of deception. Trust but verify – with evidence, not promises.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Mantra
Appendix:
– [Download] 2026 Chinese Business License Anatomy Guide (Eng/CHN)
– [Access] SourcifyChina Verified Supplier Database (ISO 20400 Compliant)
– [Request] Free Factory Verification Scorecard (Customized for Your Product Category)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Manager Use Only. Data sources: China MIIT, General Administration of Customs, SourcifyChina Global Audit Network (12,000+ verifications).
Next Step: Schedule a no-cost supplier risk assessment for your top 3 Chinese targets → [calendly.com/sourcifychina/procurement-risk-scan]
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Accelerate Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Suppliers
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain landscape, sourcing high-capacity, reliable manufacturing partners in China demands precision, speed, and trust. As procurement leaders navigate rising costs, supply volatility, and quality risks, access to pre-vetted, scalable suppliers is no longer a competitive advantage—it’s a necessity.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: The Verified List of Largest Companies in China delivers immediate access to China’s most capable and compliant tier-1 and tier-2 manufacturers across electronics, machinery, textiles, consumer goods, and industrial components. This curated database eliminates months of supplier screening, reduces due diligence costs by up to 70%, and ensures procurement teams engage only with legally compliant, high-output partners.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Weeks spent searching B2B platforms, trade shows, and referrals | Instant access to 500+ verified large-scale manufacturers |
| Due Diligence | Manual audits, document verification, and on-site visits required | All suppliers pre-vetted for business license, export history, production capacity, and compliance |
| Capacity Validation | Uncertain MOQs and lead times; unreliable claims | Verified output data, equipment lists, and factory size included |
| Communication Barriers | Time lost to miscommunication and unresponsive contacts | Direct English-speaking points of contact with procurement experience |
| Risk of Fraud | Exposure to trading companies posing as factories | 100% factory-direct listings with site-verified operations |
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Time is your most valuable procurement asset. Every week spent qualifying unreliable suppliers delays time-to-market, increases costs, and exposes your supply chain to avoidable risk.
The SourcifyChina Pro List turns months of research into minutes of decision-making. With real-time access to China’s largest and most capable manufacturers—complete with verified certifications, production metrics, and export records—you gain the confidence to negotiate, onboard, and scale with speed.
👉 Take the next step toward efficient, secure, and scalable sourcing:
- Email Us: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/7 to provide a free sample of the Pro List, schedule a personalized sourcing consultation, or assist with RFQ coordination.
Don’t source blindly. Source smart.
Partner with SourcifyChina—your verified gateway to China’s industrial leadership.
Contact us today and reduce your supplier qualification cycle by 60% in 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.