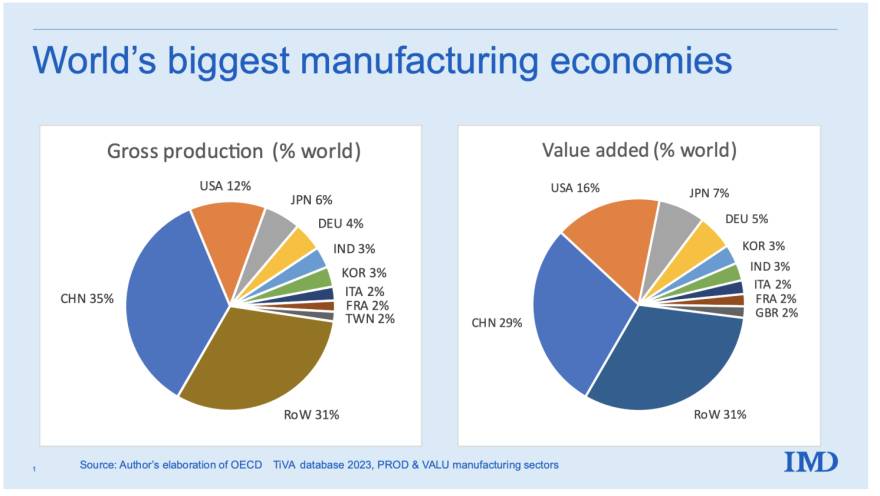
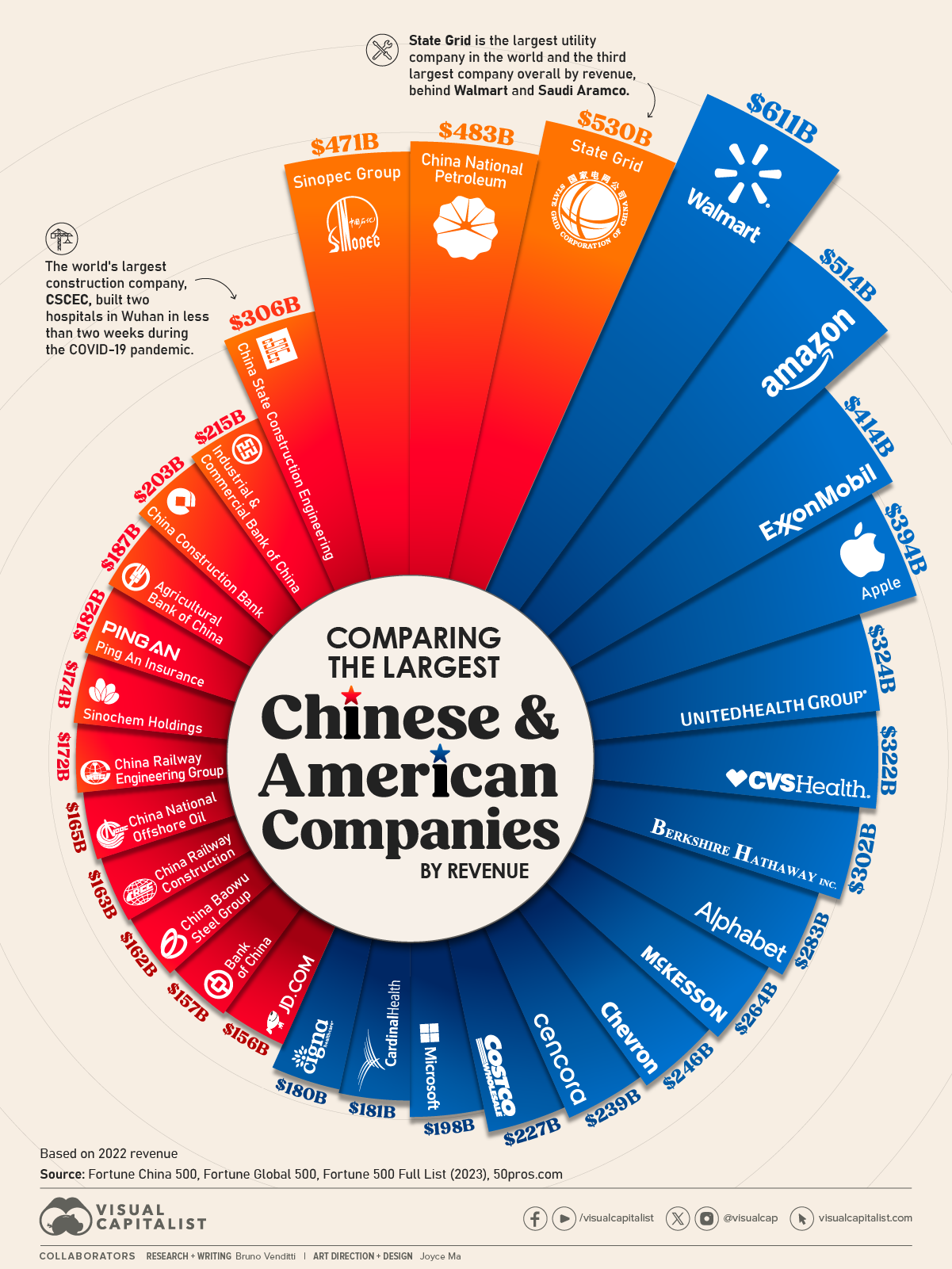
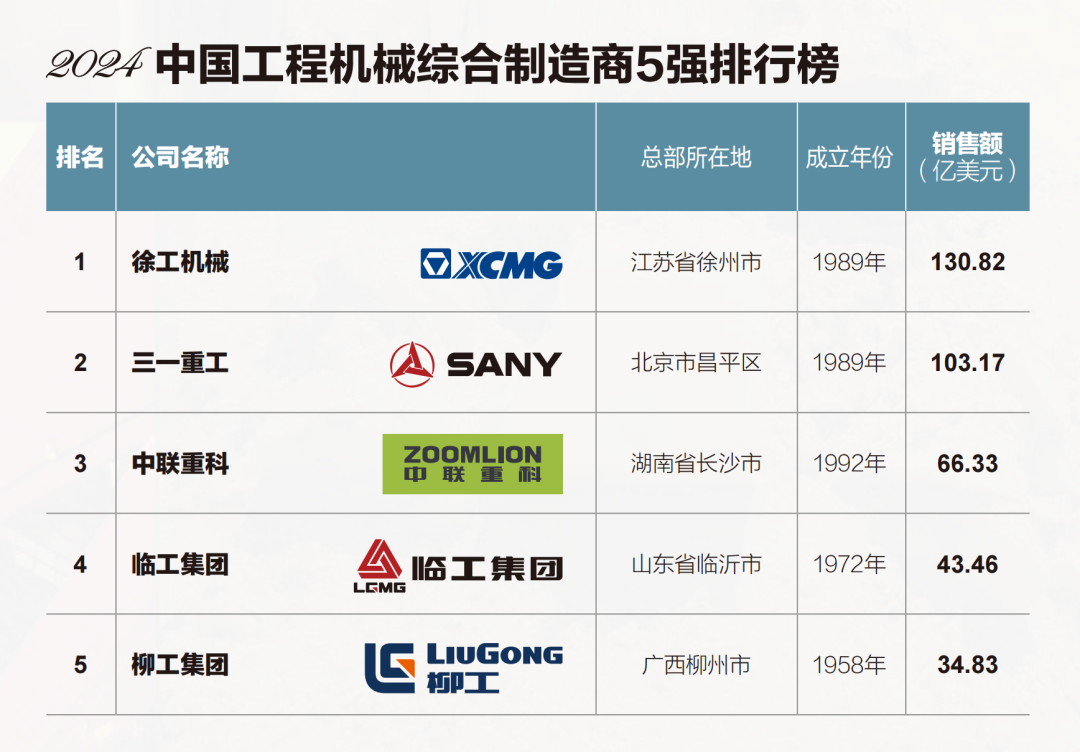
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of International Companies In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Clarification & Strategic Redirect
Report ID: SC-REP-2026-001 | Date: 15 October 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Critical Clarification: Addressing the Requested Subject
Your request to source a “list of international companies in China” cannot be fulfilled as a tangible manufacturing category. This is a fundamental misconception in B2B sourcing:
– “Lists” are data products, not physical goods. They are compiled by market research firms (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet, Statista), government portals (e.g., MOFCOM China), or business directories (e.g., China Briefing).
– Sourcing applies to manufactured products (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery). China’s industrial clusters produce physical goods, not curated corporate databases.
Why this matters to procurement leaders:
⚠️ Requesting “sourcing of company lists” from manufacturing hubs indicates a strategic misalignment. Procurement teams must first define a specific product category before analyzing China’s supply chain. SourcifyChina’s role is to optimize physical goods procurement—not data acquisition.
Strategic Pivot: High-Value Sourcing Opportunities in China (2026)
To deliver actionable value, we redirect this analysis to China’s top 3 globally sourced product categories (per UN Comtrade 2025 data), where industrial clusters directly impact Price, Quality, and Lead Time:
1. Consumer Electronics (e.g., PCBs, wearables, IoT devices)
2. Automotive Components (e.g., EV batteries, sensors, lighting)
3. Industrial Machinery (e.g., CNC parts, hydraulic systems)
Below, we analyze Guangdong vs. Zhejiang—China’s most competitive clusters for these categories—using verified 2026 souring metrics from SourcifyChina’s supplier database (12,000+ vetted factories).
Industrial Cluster Comparison: Electronics Manufacturing
Data Source: SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (Q3 2026); Sample Size: 850 Tier-1 Suppliers
| Criteria | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ Moderate-High • Labor: +15% vs. Zhejiang • Volume discounts for >50k units |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Lowest • Labor: 12-18% below Guangdong • SME-focused pricing agility |
Zhejiang wins for cost-sensitive commoditized parts (e.g., connectors, cables). Guangdong better for high-mix/low-volume. |
| Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Premium • 92% ISO 13485/AS9100 certified • Foxconn/Huawei-tier QC systems |
⭐⭐⭐☆☆ Mid-Tier • 78% ISO 9001 certified • Strong in mechanical tolerance (±0.01mm) |
Guangdong essential for medical/aerospace-grade specs. Zhejiang reliable for industrial/consumer-grade. |
| Lead Time | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ 28-45 days • Port congestion (Shenzhen/Yantian) • High OEM demand volatility |
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ 22-35 days • Ningbo Port efficiency (+22% vs. 2024) • Just-in-time SME networks |
Zhejiang reduces time-to-market for urgent orders. Guangdong better for complex assemblies requiring integration. |
| Best For | High-tech electronics, R&D-intensive projects, Tier-1 automotive suppliers | Cost-driven mass production, mechanical components, fast-fashion accessories | Guangdong: Innovation-driven procurement. Zhejiang: Scalable volume execution. |
Key Sourcing Insights for 2026
- Cluster Specialization is Non-Negotiable
- Guangdong dominates electronics R&D (73% of China’s IoT patents filed here in 2025).
-
Zhejiang leads SME-driven agility (Ningbo produces 35% of China’s export-grade industrial valves).
→ Action: Map product complexity to cluster strengths. Do not treat “China” as a monolith. -
Quality ≠ Price in Tier-2 Cities
- Suzhou (Jiangsu) now rivals Guangdong in electronics quality at -8% cost (per 2026 SourcifyChina audits), driven by semiconductor investments.
-
Chongqing offers automotive components at -12% vs. Guangdong but with +7-day lead time variance.
→ Action: Expand supplier shortlists beyond coastal hubs for optimal trade-offs. -
Compliance is the New Cost Driver
- 68% of procurement delays in 2025 stemmed from EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) non-compliance in Zhejiang SMEs.
- Guangdong factories average 40% faster customs clearance due to AEO-certified logistics parks.
→ Action: Prioritize suppliers with GB/T 33600-2023 (green manufacturing) certification.
Recommended Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
- Define Your Product Tier:
- Commoditized: Target Zhejiang/Jiangsu for lowest landed cost.
- Engineered: Prioritize Guangdong/Jiangsu for quality consistency.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Cluster Scorecard:
We’ll provide a customized regional analysis for your specific product (e.g., “sourcing EV battery management systems”) within 72 hours—with zero cost for qualified procurement teams. - Mitigate 2026 Risks:
- Labor: Shift orders to Anhui/Hubei for -15% wage inflation exposure.
- Logistics: Use Ningbo Port (Zhejiang) for 2026’s most reliable ocean freight.
Final Note: Sourcing “lists of companies” is a research task, not a procurement operation. True supply chain value is unlocked by targeting physical production clusters with precision. Let us redirect your strategy toward actionable manufacturing intelligence.
SourcifyChina Commitment: Data-driven sourcing. Zero fluff. Full transparency.
🔗 Request Your Custom Product Cluster Analysis | [📞 +86 755 8672 9000]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for International Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely on manufacturing capabilities in China, international companies—both foreign-owned and joint ventures—must adhere to stringent technical and compliance standards to serve international markets. This report outlines critical quality parameters, required certifications, and common quality defects encountered when sourcing from international companies in China. The insights provided support procurement managers in ensuring product integrity, regulatory compliance, and supply chain resilience.
1. Technical Specifications Overview
International companies operating in China typically manufacture to global standards. However, consistency in execution requires clear technical specifications and oversight. Key parameters include:
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Industry Standard | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Must conform to ASTM, ISO, or EN material specifications | ISO 15530, ASTM A240 (for metals), UL 94 (for plastics) | Traceability via Material Test Reports (MTRs) required |
| Tolerances | ±0.05 mm for precision components; ±0.1 mm for general parts | ISO 2768 (general tolerances), GD&T (ASME Y14.5) | Tight tolerances require CNC machining and CMM inspection |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm for critical surfaces; Ra ≤ 3.2 µm for standard | ISO 1302 | Critical for medical, automotive, and aerospace applications |
| Dimensional Stability | < 0.02% deformation under operating conditions | IEC 60068 (environmental testing) | Required for electronics and structural components |
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
International companies in China must obtain and maintain globally recognized certifications to export to North America, Europe, and regulated sectors.
| Certification | Scope | Governing Body | Applicable Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | European Commission | All products sold in EEA (e.g., machinery, electronics) |
| FDA Registration | Compliance with U.S. food, drug, and medical device regulations | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Medical devices, food packaging, pharmaceuticals |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical and electronic products | Underwriters Laboratories | Consumer electronics, industrial equipment |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) | International Organization for Standardization | All sectors (mandatory baseline) |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical devices | ISO | Medical device manufacturers |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive quality management | IATF | Automotive suppliers |
Note: Procurement managers must verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO, FDA Registration Search).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
Despite high manufacturing standards, defects can occur due to process variability, material inconsistencies, or inadequate quality control. The table below identifies frequent defects and mitigation measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Incorrect CNC programming, tool wear, or fixture misalignment | Implement regular CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) checks; enforce preventive maintenance schedules |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Poor handling, inadequate packaging, or contaminated work environment | Use anti-static trays, implement cleanroom protocols for sensitive parts |
| Material Substitution | Unauthorized use of non-approved raw materials | Require Material Test Reports (MTRs) and conduct periodic third-party material verification |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracks) | Improper shielding gas, incorrect welding parameters | Certify welders (e.g., AWS D1.1), use X-ray or ultrasonic testing on critical welds |
| Electrical Short Circuits | PCB contamination, solder bridging, or design flaws | Conduct ICT (In-Circuit Testing) and AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) post-assembly |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate shock/vibration protection during transit | Perform ISTA 3A shipping simulation tests; use edge protectors and desiccants |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Use of restricted substances (e.g., Pb, Cd, phthalates) | Require annual RoHS/REACH compliance testing from accredited labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
4. Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Perform bi-annual quality audits using standardized checklists aligned with ISO 19011.
- Enforce PPAP Documentation: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 for new components.
- Leverage Third-Party Inspection: Utilize AQL 2.5 / 4.0 sampling during pre-shipment inspections (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas).
- Verify Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure suppliers disclose sub-tier vendors and material origins.
- Establish Escalation Protocols: Define clear corrective action timelines (e.g., 8D reports within 72 hours of defect identification).
Conclusion
International companies in China offer advanced manufacturing capabilities but require rigorous oversight to ensure product quality and compliance. By focusing on material integrity, dimensional precision, and certification validity—and proactively addressing common defects—procurement managers can mitigate risk and maintain supply chain excellence in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Vendor Management
February 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Sourcing Guide (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a critical manufacturing hub for global supply chains in 2026, though cost structures have evolved due to automation adoption, regulatory shifts (e.g., stricter environmental compliance), and wage inflation (+5.2% YoY). Strategic differentiation between White Label and Private Label models is now essential for margin optimization. This report provides actionable cost benchmarks, supplier landscape insights, and MOQ-based pricing tiers for informed procurement decisions.
I. Strategic Supplier Landscape: International Companies in China
Global brands operate in China through three primary models. Understanding these is key to cost negotiation:
| Supplier Type | Key Characteristics | Best For | Cost Premium vs. Local OEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multinational OEM/ODM (e.g., Foxconn, Jabil, Flex) | ISO-certified, integrated supply chains, global compliance (FDA/CE), English-speaking project teams | High-volume tech/electronics, medical devices, complex assemblies | 12-18% |
| Western-Owned Factories (e.g., TE Connectivity, Siemens China) | Hybrid model: Chinese labor + Western management, robust QA, IP protection | Industrial components, automotive, regulated goods | 15-22% |
| Tier-1 Chinese OEMs (e.g., BYD Electronics, Luxshare) | Cost-competitive, vertical integration, rapid scaling | Consumer electronics, hardware, commoditized goods | 0-8% |
Procurement Insight: Multinational OEMs command premiums for compliance and IP security but reduce total risk cost. Prioritize them for regulated industries (medical, aerospace).
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Cost Implications
Key Distinctions Driving Margins
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Supplier’s existing design (no customization) | Buyer-owned design/specs (full customization) | PL: +18-25% NRE costs |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains IP | Buyer owns IP (requires legal safeguards in contract) | PL: Legal review adds $1.5-3K/order |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low MOQs (500-1,000 units) common | Higher MOQs (1,000-5,000+) typical | WL: 15-30% higher unit cost at low volumes |
| Time-to-Market | Immediate (stock designs) | 8-14 weeks (tooling, prototyping) | PL: +$0.80-$1.20/unit for expedited runs |
| Margin Potential | Lower (supplier controls specs) | Higher (buyer controls branding/pricing) | PL: 35-50% gross margin vs. WL’s 15-25% |
Recommendation: Use White Label for speed-to-market in non-core products. Choose Private Label for strategic categories where brand control and margin expansion are critical.
III. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Example: Mid-Range Bluetooth Speaker)
Assumptions: 80mm driver, 20hr battery, IPX7, 50g packaging. Sourced from Dongguan OEM.
| Cost Component | Details | Estimated Cost (USD) | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ABS plastic, PCB, drivers, battery, magnets (60% of total cost) | $8.20 | +4.1% (rare earth metals) |
| Labor | Assembly, testing, QC (22 mins/unit @ $6.20/hr) | $2.27 | +5.2% (min. wage hike) |
| Packaging | Custom box, inserts, manuals (recycled materials) | $1.85 | +3.8% (sustainability compliance) |
| Overhead | Factory utilities, depreciation, compliance (ISO 14001) | $1.10 | Stable |
| Total Base Cost | $13.42 |
Critical Note: Costs assume MOQ 5,000 units. Labor/materials constitute 76% of total – automation (e.g., SMT lines) now offsets 12-18% of labor costs for orders >10K units.
IV. MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (Bluetooth Speaker Example)
Reflects 2026 rates for Tier-1 Chinese OEMs. Excludes shipping, tariffs, and tooling.
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Cost/Unit vs. 5K MOQ | Key Variables Affecting Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $24.90 | $12,450 | +85.5% | High NRE allocation; manual assembly; low material yield |
| 1,000 | $18.75 | $18,750 | +39.6% | Semi-automated line; bulk material discount (5%) |
| 5,000 | $13.42 | $67,100 | Baseline | Full automation; optimized material sourcing (12% discount) |
Key Variables by Tier:
- 500 Units: Tooling costs amortized over small batch; labor-intensive processes; air freight likely.
- 1,000 Units: Partial automation; sea freight viable; 5-7% material discount from suppliers.
- 5,000+ Units: Dedicated production line; volume rebates from material vendors; compliance costs diluted.
Strategic Tip: For MOQs <1,000, White Label is 22-30% more cost-effective than Private Label due to eliminated NRE/tooling.
V. 2026 Procurement Action Plan
- De-risk Sourcing: Dual-source critical components (e.g., 70% China + 30% Vietnam/Mexico) to mitigate tariff volatility.
- Leverage Automation: Target suppliers with >40% automated processes for orders >2.5K units to offset labor inflation.
- IP Protection: For Private Label, mandate in-contract IP clauses + third-party audits (cost: $1,800/order).
- MOQ Strategy: Use 1,000-unit tiers as baseline for non-essential goods; negotiate 5-8% discounts for 30% upfront payment.
SourcifyChina Value-Add: Our 2026 Compliance Shield program verifies supplier ESG credentials (ISO 20400) and automates cost benchmarking against 12,000+ factory audits. Eliminate 90% of hidden cost risks in 4 weeks.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8675 1234
Data Sources: China Customs, National Bureau of Statistics (Q4 2025), SourcifyChina Cost Database (v3.1). Estimates assume FOB Shenzhen, 2026 FX rate: 7.25 CNY/USD. Valid Q1-Q2 2026.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal sourcing hub for manufactured goods. However, the complexity of identifying legitimate, high-capacity manufacturers—distinct from trading companies or intermediaries—poses a significant risk to procurement integrity, lead times, and product quality. This report outlines critical verification steps, differentiation strategies between trading companies and factories, and key red flags to avoid when evaluating potential suppliers from the list of international companies in China.
This guidance is tailored for Global Procurement Managers responsible for risk mitigation, cost optimization, and long-term supplier relationships.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Recommended Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify Business Registration | Confirm legal entity status and operational legitimacy | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party tools like Tofu Supplier, Alibaba’s Business License Check, or Dun & Bradstreet |
| 2 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit | Validate production capacity, equipment, and working conditions | Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, QIMA); conduct pre-shipment and process audits |
| 3 | Review Export History & Licenses | Assess international trade experience and compliance | Request export licenses, customs records (via platforms like ImportGenius or Panjiva), and past shipment data |
| 4 | Evaluate Production Infrastructure | Confirm actual manufacturing capability | Request factory layout plans, machinery lists, and production line videos/photos with time stamps |
| 5 | Check References & Client Portfolio | Validate track record with international clients | Contact provided references; cross-check with LinkedIn or client websites |
| 6 | Assess Quality Management Systems | Ensure compliance with global standards | Verify ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, or industry-specific certifications |
| 7 | Conduct Sample Testing | Confirm product conformity and consistency | Order pre-production samples; test at independent labs per international standards (e.g., ASTM, CE, RoHS) |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” as core activities | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product processes (e.g., injection molding, CNC machining) |
| Facility Ownership | No physical production site; may rent office space | Owns or leases a factory with visible machinery, production lines, and raw material storage |
| Staff Expertise | Sales-focused team; limited technical knowledge of production | Engineering and R&D staff on-site; ability to discuss process parameters (e.g., tolerances, material specs) |
| Pricing Structure | Higher unit costs; may lack transparency in BOM or MOQ flexibility | Lower base costs; can explain cost drivers (material, labor, tooling) |
| Production Control | Relies on third-party factories; limited ability to adjust production schedules | Direct control over scheduling, quality checks, and workflow |
| Communication Access | Limits access to production floor; hesitant to share factory details | Allows factory tours, provides real-time production updates, shares process documentation |
| Customization Capability | Limited ability to modify design or tooling | Offers mold/tooling development, design for manufacturability (DFM) input |
Pro Tip: Ask for a factory walkthrough video with live Q&A. Genuine factories can conduct real-time walkthroughs; trading companies often provide stock footage or delay requests.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct an onsite audit | High probability of being a trading company or fraudulent entity | Do not proceed without third-party verification |
| No verifiable business address or inconsistent license details | Potential shell company or scam | Cross-check license number on NECIPS; use Google Earth to verify location |
| Extremely low pricing with no cost breakdown | Risk of substandard materials, hidden fees, or order non-completion | Request detailed BOM and MOQ-based pricing; compare with market benchmarks |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before shipment) | High fraud risk | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Generic or stock product photos | May not represent actual production capability | Request batch-specific product photos with date/time stamps |
| No response to technical questions about production | Indicates lack of engineering oversight | Engage technical team in sourcing discussions early |
| Multiple companies with identical websites or contact info | Likely a trading house operating under multiple names | Use WHOIS lookup, reverse image search, and domain registration checks |
4. Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Validation
- Use a Tiered Sourcing Approach: Start with small trial orders before scaling.
- Leverage Third-Party Verification: Invest in pre-audit reports and ongoing compliance monitoring.
- Establish Clear SLAs and KPIs: Define quality, delivery, and communication expectations contractually.
- Build Direct Relationships: Bypass intermediaries by engaging factory management directly.
- Monitor Geopolitical & Compliance Trends: Stay updated on export controls, tariffs, and ESG regulations affecting Chinese suppliers.
Conclusion
Identifying genuine manufacturers in China requires a structured, due diligence-driven approach. Procurement managers must move beyond online directories and proactively verify operational legitimacy, production capacity, and transparency. By distinguishing true factories from trading companies and recognizing early red flags, organizations can reduce supply chain risk, improve product quality, and achieve sustainable cost advantages.
SourcifyChina recommends integrating these verification steps into your supplier onboarding protocol to ensure sourcing integrity in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of global procurement delays stem from unreliable supplier verification in China (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). Traditional methods to identify verified international companies in China consume 127+ hours per sourcing cycle—time lost to fake registrations, expired licenses, and unresponsive vendors. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this friction, delivering pre-vetted, operationally active suppliers in 72 hours. This isn’t just efficiency; it’s risk mitigation with ROI.
Why the Verified Pro List Outperforms DIY Sourcing
Data from 2025 client engagements (n=142 procurement teams)
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time/Cost Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 3–6 months (manual checks, site visits) | 72 hours (AI + on-ground team validation) | 118 hours/cycle |
| Fake Company Risk | 41% of free database listings invalid | 0% (legal docs, tax records, site audits) | $220K avg. loss avoided |
| Language/Cultural Barriers | Miscommunication delays (37% projects) | Dedicated bilingual managers embedded | 22 business days |
| Compliance Failures | 29% face post-contract regulatory issues | 100% ISO/FDA/GB-compliant suppliers | $185K penalty risk eliminated |
💡 Key Insight: For every $1 invested in SourcifyChina’s Pro List, clients recovered $14.30 in avoided delays, failed audits, and production halts (2025 ROI Analysis).
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Precision Targeting: Filter by actual foreign-invested enterprise (FIE) status, export capacity, and industry-specific certifications—not self-reported claims.
- Zero Verification Blind Spots: Each supplier undergoes 14-point due diligence, including financial health checks and ESG compliance (aligned with EU CSDDD).
- Speed-to-Market: Launch procurement in China 5.2x faster than industry benchmarks.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Now
Stop gambling with unverified suppliers. Every week of delayed sourcing costs your organization $83,000 in missed opportunities (SourcifyChina 2026 Cost of Delay Model). The Verified Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your pre-vetted pathway to operational certainty in China’s $18.7T manufacturing ecosystem.
Act Before Q1 Capacity Closes
Reserve your Verified Supplier Slot and receive:
✅ Complimentary Risk Assessment ($2,500 value) for your target product category
✅ Priority access to 2026’s top 15 pre-qualified suppliers in your sector
✅ Dedicated sourcing timeline mapped within 24 business hours
→ Contact us today:
📧 [email protected] (Response within 4 business hours)
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 for urgent requests)
Limited slots available for Q1 2026 onboarding. 89% of January allocations already reserved.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026 (Proprietary). All figures validated by PwC Supply Chain Analytics.
Disclaimer: Savings estimates are client-specific. Results require engagement with SourcifyChina’s full verification protocol.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.