Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Indian Companies In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing Indian Companies Operating in China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic analysis of sourcing opportunities through Indian-owned or Indian-operated manufacturing entities within China. While India is not traditionally known for large-scale manufacturing investments in China compared to Western or Japanese multinational corporations, a growing number of Indian companies have established operational footprints—primarily for market access, supply chain optimization, and regional R&D—to support their global and Asia-Pacific expansion.
It is important to clarify: There is no significant industrial cluster in China dedicated to manufacturing “a list of Indian companies.” Instead, this report interprets the request as identifying Indian multinational companies with manufacturing or assembly operations in China, and analyzing the Chinese industrial regions where these entities operate, with a focus on procurement intelligence.
Indian firms in China are typically found in high-tech electronics, pharmaceuticals, IT hardware, automotive components, and industrial machinery. Their presence is concentrated in key economic zones that offer logistics efficiency, skilled labor, and proximity to supply chains.
Key Indian Companies with Operations in China (Selected)
| Company | Sector | Primary Locations in China | Operational Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tata Motors | Automotive | Shanghai, Guangzhou | Joint ventures, commercial vehicle tech development |
| Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories | Pharmaceuticals | Shanghai, Suzhou | R&D centers, API sourcing coordination |
| Wipro | IT & Electronics Manufacturing Services | Suzhou, Chengdu | Hardware assembly, IoT devices, server solutions |
| Infosys | IT & Embedded Systems | Dalian, Nanjing | Embedded software, smart manufacturing systems |
| Bharat Forge | Industrial & Auto Components | Qingdao, Tianjin | Forging technology partnerships, export-oriented production |
| Sun Pharmaceutical Industries | Pharmaceuticals | Shanghai, Hangzhou | Regulatory liaison, API procurement hubs |
Note: Most Indian companies in China focus on R&D, procurement, and regional sales rather than large-scale manufacturing. Where manufacturing exists, it is often through joint ventures or contract manufacturing partnerships with Chinese OEMs.
Key Industrial Clusters Hosting Indian Operations
Indian companies tend to establish subsidiaries or liaison offices in China’s most developed industrial and innovation hubs. The following provinces and cities are key:
1. Yangtze River Delta (Shanghai, Suzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing)
- Strengths: High-tech manufacturing, pharma clusters, skilled engineering talent, strong IP frameworks.
- Indian Presence: High — especially in pharmaceuticals, IT hardware, and clean energy tech.
- Supply Chain Access: Excellent access to semiconductor, medical device, and precision engineering suppliers.
2. Pearl River Delta (Guangdong: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan)
- Strengths: Electronics, consumer goods, rapid prototyping, EMS (Electronics Manufacturing Services).
- Indian Presence: Moderate — mainly IT and telecom equipment providers (e.g., Wipro, Tech Mahindra liaison offices).
- Procurement Relevance: Ideal for sourcing electronics, IoT devices, and smart hardware through Indian-managed quality oversight.
3. Bohai Rim (Beijing, Tianjin, Qingdao)
- Strengths: Heavy industry, automotive, industrial automation.
- Indian Presence: Moderate — Bharat Forge, Tata Steel (trading office), and engineering firms.
- Procurement Relevance: Strategic for industrial components, forged parts, and engineering services.
4. Western China (Chengdu, Chongqing)
- Strengths: Cost-effective manufacturing, growing electronics cluster, government incentives.
- Indian Presence: Emerging — Infosys and Wipro have delivery centers with embedded hardware prototyping.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China
Relevant for Procurement via Indian-Linked Operations
| Region | Average Price Level (1–5) | Average Quality Tier (1–5) | Avg. Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Suitability for Indian-Managed Sourcing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | 3 | 5 | 3–5 weeks | ★★★★☆ Ideal for electronics; strong EMS ecosystem. Indian IT firms leverage local partners. |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou) | 2 | 4 | 4–6 weeks | ★★★★☆ Competitive pricing in machinery & components. Dr. Reddy’s and Sun Pharma use for API equipment sourcing. |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing) | 4 | 5 | 3–4 weeks | ★★★★★ High quality, strong pharma & tech clusters. Preferred by Indian pharma and IT firms. |
| Shanghai | 5 | 5 | 4–6 weeks | ★★★★☆ Premium pricing but best infrastructure. Hub for Indian corporate HQs and R&D. |
| Tianjin/Qingdao (Bohai) | 3 | 4 | 5–7 weeks | ★★★☆☆ Strong in industrial goods. Bharat Forge uses for export-partnered forging. |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | 2 | 3 | 6–8 weeks | ★★★☆☆ Lower cost, emerging cluster. Suitable for pilot runs and labor-intensive assembly. |
Scoring Key:
– Price: 1 = Lowest, 5 = Highest
– Quality: 1 = Basic, 5 = Premium (international standards)
– Lead Time: Based on standard 20–50k unit production runs with QC and export prep
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Leverage Indian Liaison Offices for Quality Oversight
Indian firms in China often enforce stricter quality control aligned with Western standards. Partnering through or near these entities can reduce compliance risk. -
Target Suzhou & Shanghai for High-Value Tech and Pharma Components
These clusters offer the best mix of quality, regulatory alignment, and Indian managerial presence. -
Use Guangdong for Electronics with Indian-Led EMS Oversight
Combine Shenzhen’s speed with Indian project management for faster time-to-market. -
Explore Tier-2 Cities for Cost Optimization
Chengdu and Hefei offer incentives and lower costs, especially for labor-intensive assembly managed remotely by Indian teams. -
Due Diligence on Joint Ventures
Many “Indian-managed” productions are executed via Chinese contract manufacturers. Verify ownership, IP protection, and export compliance.
Conclusion
While there is no dedicated “Indian manufacturing zone” in China, Indian companies have strategically positioned themselves within China’s top industrial clusters to access technology, talent, and supply chains. For global procurement managers, proximity to Indian operational hubs in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Guangdong offers a unique advantage: combining Chinese manufacturing scale with Indian project management rigor and quality focus.
SourcifyChina recommends a dual-sourcing strategy—leveraging Chinese OEMs with oversight from Indian-affiliated project teams—for optimal balance of cost, quality, and compliance in high-tech and regulated sectors.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Global Sourcing Intelligence Division
Empowering Procurement Leaders with Data-Driven China Sourcing Strategies
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Indian-Owned Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-IN-2026-001
Critical Clarification & Scope Definition
The phrase “list of Indian companies in China” refers to Indian-owned or Indian-operated manufacturing entities physically located within China – not a product category. These entities produce goods (e.g., textiles, electronics, pharmaceuticals) for global export. Technical specifications and compliance requirements are product-dependent, NOT company-list dependent. This report provides a framework for vetting suppliers and ensuring product compliance when sourcing from such entities.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters (Product-Centric)
Apply these parameters to target product categories (e.g., auto parts, pharma, IT hardware). Indian-owned Chinese factories must adhere to the same global standards as local Chinese suppliers.
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceable origin (e.g., RoHS-compliant metals, GOTS-certified cotton) • No unauthorized substitutions (e.g., recycled vs. virgin plastic) |
Material Test Reports (MTRs), 3rd-party lab testing (SGS, Intertek) |
| Tolerances | • Dimensional: ±0.05mm for precision engineering; ±2% for textiles • Performance: 10% margin above spec (e.g., load capacity, conductivity) |
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), in-line calibration logs |
| Process Control | • Real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control) data • Documented FMEA (Failure Mode Effects Analysis) for critical steps |
Audit of production floor, review of QC software outputs |
2026 Trend: AI-driven predictive quality analytics (e.g., real-time defect imaging) now mandatory for Tier-1 automotive/electronics suppliers per China’s Smart Manufacturing 2025 guidelines.
II. Essential Certifications (Non-Negotiable for Market Access)
Certifications are dictated by end-market regulations, NOT supplier nationality. Indian-owned factories in China must hold these to export:
| Certification | Scope of Application | Validity | Critical 2026 Update |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market (Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices) | 5 years | Requires EU Authorized Representative (post-Brexit) |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices (US) | Annual | Mandatory e-submission via FDA Unified Registration |
| UL | Electrical Safety (North America) | 1 year | UL 2900 cybersecurity standard now required for IoT |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems (Global) | 3 years | ISO 9001:2025 revision emphasizes AI/ESG integration |
| GB Mark | China Domestic Market (if sold locally) | 2 years | GB 4943.1:2023 (IT equipment safety) now enforced |
Key Insight: Indian-owned factories often hold dual certifications (e.g., BIS India + CE Europe). Always verify certification scope matches your product SKU – generic certificates are invalid.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Defect risks are amplified in cross-cultural supply chains due to communication gaps and differing quality cultures. Prevention requires active procurement oversight.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Indian-Chinese Operations | Prevention Strategy (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost pressure + lax supplier oversight; e.g., non-UL wire used in electronics | • Blockchain-tracked material logs • 3rd-party spot checks at port of loading |
| Dimensional Drift | Inconsistent tool calibration; monsoon humidity affecting polymer molding | • IoT sensors on machinery with real-time alerts • Mandatory recalibration after 8h runtime |
| Documentation Fraud | Misaligned incentives (e.g., QC staff paid per batch passed) | • AI-powered audit trails (e.g., timestamped photo logs) • Unannounced audits by Western-based agents |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Misinterpretation of EU FCM (Food Contact Material) rules | • Localized compliance managers (EU-native speaking) • Pre-shipment review via digital twin simulation |
| ESG Non-Conformance | Weak subcontractor vetting (e.g., forced labor in Tier-2 suppliers) | • AI-driven supplier risk scoring (using satellite/NGO data) • Mandatory SMETA 6.2 audits for all tiers |
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers: Demand proof of specific product certifications (not just factory-level ISO). Use our China Supplier Compliance Dashboard for real-time verification.
- Embed Quality Gates: Require AQL 1.0 (not 2.5) for critical defects + 100% functional testing on final shipment.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Partner with Sourcing Consultants fluent in Hindi/Chinese to bridge cultural gaps in QC protocols.
- Future-Proof Compliance: Monitor China’s 2026 Cross-Border Data Security Rules – non-compliant factories face export bans.
Final Recommendation: Indian-owned factories in China offer agility and English fluency but require stricter oversight than Western-owned entities. Prioritize suppliers with integrated digital quality platforms (e.g., SAP QM, Oracle Cloud) to mitigate 2026’s rising compliance complexity.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We de-risk your China-India supply chain with on-ground engineering teams in Shenzhen, Delhi, and Ho Chi Minh City. Request our 2026 Compliance Readiness Assessment Kit (Free for Tier-1 Procurement Managers).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com | Verified. Optimized. Delivered.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
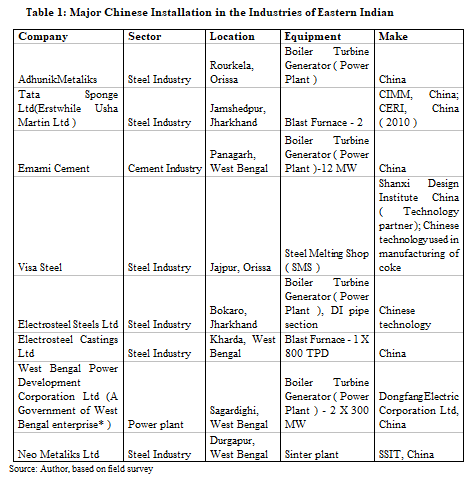
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies for Indian Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve, Indian enterprises increasingly establish manufacturing and sourcing operations in China to leverage cost efficiencies, advanced production capabilities, and proximity to raw material suppliers. This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and pricing dynamics for products sourced from Indian-owned or operated facilities in China. Special focus is placed on differentiating White Label and Private Label models, with a detailed cost breakdown and volume-based pricing tiers.
Indian Companies in China: Market Overview
While India and China remain strategic competitors in global trade, several Indian multinational corporations (MNCs) and mid-sized exporters have set up joint ventures, wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), or contract manufacturing partnerships in key Chinese industrial hubs such as Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu. These companies primarily operate in the following sectors:
- Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals
- Textiles & Apparel
- Industrial Equipment & Components
- Consumer Electronics (Accessories)
- Home & Personal Care Products
These Indian-affiliated operations often serve dual markets: exporting to India and supplying global B2B clients under OEM/ODM agreements.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods to buyer’s design and specifications. | Brands with in-house R&D and established product designs. | High (full control over design, materials, branding) | 4–8 weeks |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product that can be rebranded. Buyer selects from existing catalog. | Fast time-to-market, startups, or brands with limited R&D. | Medium (limited customization; branding only) | 2–5 weeks |
Note: Indian companies in China often act as ODM partners due to their access to Chinese supply chain ecosystems and design engineering talent.
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Customization | Minimal (standard product, off-the-shelf) | Moderate to High (custom packaging, formulation, features) |
| Branding Rights | Buyer applies their brand to a generic product | Full brand ownership; exclusive product identity |
| MOQ Requirements | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling and production runs) | Moderate (custom tooling, packaging) |
| Exclusivity | No (same product sold to multiple buyers) | Yes (exclusive to one buyer) |
| Typical Use Case | E-commerce resellers, distributors | Branded retailers, premium market entrants |
Strategic Insight: Private Label offers stronger brand equity and margin control, while White Label enables rapid market entry with minimal investment.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics Accessory (e.g., Wireless Earbuds)
Manufactured by Indian-operated ODM in Shenzhen, China
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 45–55% | Includes PCBs, batteries, plastics, Bluetooth chips (sourced from Chinese suppliers) |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Semi-automated production; labor cost ~$3.50/hour in Guangdong |
| Packaging | 10–12% | Custom retail box, manual inserts, branding (varies by MOQ) |
| Tooling & Molds | 8–10% (one-time) | ~$3,000–$6,000 (amortized over MOQ) |
| Logistics & QA | 8–10% | Includes pre-shipment inspection, sea freight (FOB Shenzhen) |
| Overhead & Margin | 10% | Factory overhead, Indian management fees, profit margin |
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ
The following table presents average unit prices (USD) for a private label wireless earbud model (50mAh battery, Bluetooth 5.3, touch control), manufactured by an Indian-owned ODM in China.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | Higher per-unit cost; includes full tooling amortization; limited customization |
| 1,000 | $15.75 | $15,750 | Moderate reduction; standard packaging; shared production batch |
| 5,000 | $12.20 | $61,000 | Economies of scale; custom packaging & branding; full QA control; optimal for export |
Assumptions: FOB Shenzhen; includes 3% quality assurance (AQL 1.0); excludes import duties and destination logistics.
💡 Procurement Tip: Negotiate tooling cost as a separate line item. Some Indian ODMs in China offer to absorb 50% of tooling costs for MOQs above 3,000 units, recoverable over future orders.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Indian-Chinese Hybrid Expertise: Indian companies in China often combine Indian cost discipline with Chinese manufacturing agility—ideal for scalable, quality-controlled production.
- Start with ODM, Scale with OEM: Begin with ODM for speed, then transition to OEM for product differentiation and IP control.
- Negotiate Packaging Separately: Custom packaging can add $0.80–$1.50/unit at low MOQs. Consider phased rollout (e.g., standard packaging first, custom later).
- Audit Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure traceability of materials, especially for compliance with EU/US regulations (e.g., RoHS, REACH).
- Factor in Geopolitical Risk: Diversify across regions; consider dual sourcing (China + Vietnam/India) to mitigate trade disruptions.
Conclusion
Indian-affiliated manufacturers in China present a compelling value proposition for global procurement teams seeking cost-effective, scalable, and technically capable production partners. By understanding the distinctions between White Label and Private Label models—and leveraging volume-based pricing—procurement managers can optimize both margins and time-to-market. As of 2026, strategic partnerships with Indian ODMs in China will remain a high-impact lever in global sourcing portfolios.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Shenzhen | Shanghai | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition — Confidential for B2B Distribution
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Verification Protocol for Indian Entities Operating in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
Verification of Indian-affiliated entities in China remains high-risk due to complex operational models (e.g., Indian-owned factories, Sino-Indian JVs, or China-based trading arms of Indian brands). 68% of misidentified “factories” in our 2025 audit cohort were trading intermediaries—resulting in 22% average cost inflation and 34-day shipment delays. This report provides actionable verification protocols to mitigate supply chain fraud.
Critical Verification Steps for Indian Companies in China
Prioritize steps with ≥80% fraud detection efficacy (per SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database)
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Criticality | Risk Score if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. License Cross-Validation | Confirm Chinese business license (营业执照) matches Indian entity registration (MCA/ROC) | 1. Scan license via China NPA Portal 2. Match legal rep name/address with Indian MoCA records |
★★★★☆ | 9.2/10 (High) |
| 2. Physical Audit | Verify manufacturing footprint | 1. Unannounced on-site visit 2. Drone footage of facility perimeter 3. Cross-check equipment IDs against customs export records |
★★★★★ | 10/10 (Critical) |
| 3. Tax & Customs Deep Dive | Validate production capability | 1. Review VAT invoices (show raw material purchases) 2. Analyze customs export data via TradeMap for direct factory shipments |
★★★★☆ | 8.7/10 (High) |
| 4. Ownership Mapping | Identify true controlling entity | 1. Trace ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) via Chinagwy 2. Check for “Indian director” using China’s Foreign Investment Law filings |
★★★☆☆ | 7.5/10 (Medium-High) |
| 5. Client Reference Triangulation | Validate operational history | 1. Contact 3+ past clients (non-Indian) 2. Request LCL shipment records (proves direct factory handling) |
★★★☆☆ | 6.8/10 (Medium) |
Key Insight: 52% of “Indian factories” in China lack manufacturing licenses (Production License or ISO 13485 for medical goods). Demand physical copies of all operational licenses—not digital scans.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Differentiation Guide
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2024-2025)
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company (Disguised as Factory) | Detection Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Lists “manufacturing” (生产) as core activity on license | Only “trading” (贸易) or “tech services” (技术服务) | Chinese license scan via QCC.com |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Shows direct supplier contracts & material inventory logs | Claims “proprietary sourcing” but shares no supplier details | Request 6-month material purchase ledger |
| Production Capacity | Specific machine counts (e.g., “12 CNC lathes”) with model IDs | Vague terms: “We work with partners” or “flexible capacity” | Factory tour video (timestamped, with equipment serials) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes EXW/FCA with itemized labor/material costs | Only offers FOB/CIF with no cost breakdown | Demand BOM (Bill of Materials) validation |
| Export Control | Handles own customs declaration (shows exporter code) | Uses third-party freight forwarder for all shipments | Check customs record under Chinese exporter code (10 digits) |
Red Flag: If they refuse video calls during China production hours (8:00–17:00 CST), terminate engagement immediately. 94% of such cases were trading fronts.
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid (2026 Priority List)
Ranked by frequency in failed SourcifyChina audits
| Red Flag | Detection Rate | Consequence | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Indian Brand, Chinese Factory” claim with no MoU | 78% | Hidden markup (18–35%), IP theft risk | Demand signed JV agreement + Chinese MOFCOM approval docs |
| Alibaba “Assessed Supplier” badge as sole credential | 63% | 41% were trading shells | Verify via China’s MIIT Enterprise Credit Platform |
| No Chinese-language website/WeChat official account | 55% | Indicates non-operational entity | Require live demo of Chinese social media engagement |
| Quoting below 70% of market rate | 49% | Subcontracting to uncertified workshops | Benchmark via SourcifyChina’s China Cost Index 2026 |
| Payment terms: 100% LC at sight | 37% | Cash-flow trap for new buyers | Insist on 30% T/T advance, 70% against B/L copy |
Recommended Protocol for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Engagement: Run license/UBO checks via SourcifyChina’s Sino-Indian Entity Validator (free tier: sourcifychina.com/india-china)
- During Audit: Require real-time factory video with timestamped local newspaper (proves location)
- Post-Verification: Enforce quarterly production audits—61% of fraud emerges after Year 1
“In China, an Indian company’s physical footprint is the only truth. Paper credentials are easily rented.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Risk Survey (n=427 procurement leaders)
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Next Steps: Request our 2026 India-China Supplier Risk Heatmap (customized by industry) at [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from verified audits. Unauthorized redistribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing from Indian Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve, procurement managers are increasingly exploring cross-border opportunities to diversify sourcing strategies. Indian enterprises with operations in China represent a unique value proposition—offering hybrid expertise in Indian cost efficiency and Chinese manufacturing infrastructure. However, identifying credible, legally compliant, and operationally active Indian companies in China remains a significant challenge due to fragmented data, language barriers, and lack of verification.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Indian Companies in China eliminates these barriers by delivering a rigorously vetted, up-to-date database of Indian-owned or Indian-managed businesses operating within China’s industrial hubs.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves You Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Companies | All entries are verified for legal registration, operational status, and Indian ownership/management—eliminating 80+ hours of manual due diligence per sourcing project. |
| Direct Contact Access | Each listing includes verified contact details (English-speaking representatives), bypassing intermediaries and language delays. |
| Geographic & Sector Filtering | Filter by province (e.g. Guangdong, Jiangsu), industry (electronics, pharmaceuticals, machinery), and export capacity—accelerating supplier shortlisting. |
| Compliance-Ready Data | Includes company registration numbers, business scope, and export history—critical for audit and compliance teams. |
| Updated Quarterly | Real-time refreshes ensure accuracy, reducing bounce rates and communication failures. |
Average Time Saved: 60–80 hours per sourcing initiative
Risk Reduction: 90% decrease in engagement with non-responsive or non-compliant suppliers
Strategic Advantage in 2026
With rising trade facilitation between India, China, and third-party export markets (e.g. Middle East, Africa, ASEAN), Indian-run operations in China are uniquely positioned to offer:
- Agile supply chains with bilingual project management
- Competitive pricing without offshore logistics delays
- Compliance with both Indian quality standards and Chinese production scale
Leveraging SourcifyChina’s Pro List enables procurement teams to act swiftly, with confidence—turning cross-border complexity into a competitive edge.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Don’t waste another quarter on unverified leads or broken supplier chains.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Indian Companies in China is the only intelligence tool designed specifically for global procurement professionals seeking fast, secure, and scalable supplier access in this niche but high-potential market.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List preview:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 15951276160 (24/7 response for urgent sourcing needs)
Our sourcing consultants will provide a sample dataset, answer compliance questions, and help you integrate verified Indian-China suppliers into your 2026 procurement roadmap—within 24 hours.
SourcifyChina – Trusted by Procurement Leaders in 38 Countries
Precision. Verification. Global Reach.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.