Sourcing Guide Contents
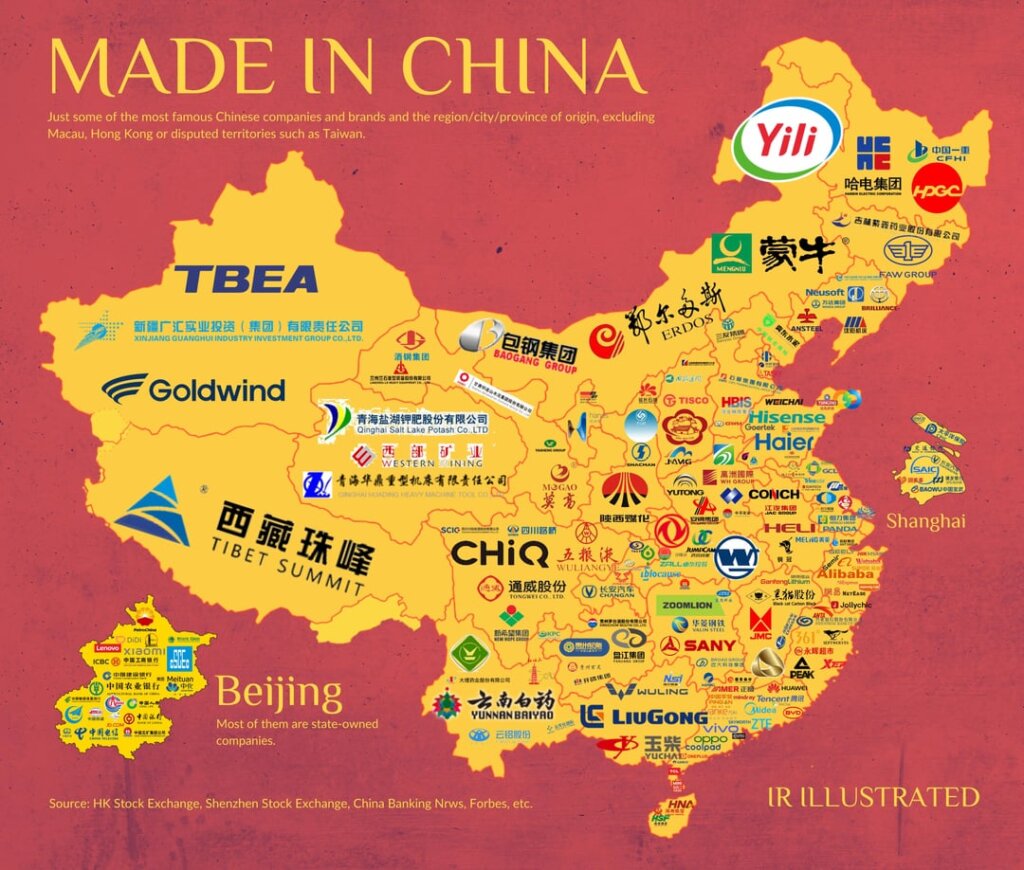
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Companies Owned By China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Executives
Confidential – Not for Distribution Without Authorization
Critical Clarification: Understanding “Companies Owned by China”
This report addresses a fundamental market misconception. China’s manufacturing ecosystem operates under a mixed-ownership model:
– State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): 5–7% of manufacturers (e.g., CATL, Sinopec), concentrated in strategic sectors (energy, defense, heavy machinery).
– Private Enterprises: 93–95% of manufacturers (e.g., Huawei, BYD), driving export-oriented production.
– Foreign-Invested Enterprises (FIEs): Factories owned by non-Chinese entities (e.g., Apple’s Foxconn suppliers).
There is no monolithic “list of companies owned by China” for sourcing. Global buyers source from private Chinese manufacturers (the true engine of export supply chains). This report analyzes clusters for procuring goods from China’s private manufacturing sector.
Industrial Cluster Analysis: Private Manufacturing Hubs (2026 Outlook)
China’s private manufacturing is regionally specialized. Key clusters for export-ready goods (electronics, machinery, textiles, furniture) are concentrated in:
| Province/City | Core Industries | Key Cities | SOE Influence | Private Mfr. Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Telecom, Drones, Consumer Goods | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Low (5%) | ★★★★★ (42% of national exports) |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Hardware, E-commerce Fulfillment, Plastics | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou | Very Low (2%) | ★★★★☆ (28% of SME exports) |
| Jiangsu | Machinery, Auto Parts, Chemicals, Solar Panels | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | Medium (18%) | ★★★★☆ (Strategic SOE-private hybrids) |
| Shanghai | High-End Electronics, Medical Devices, Aerospace | Shanghai | High (35%) | ★★☆☆☆ (Niche private specialists) |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Chemicals, Agriculture Equipment | Qingdao, Jinan | High (40%) | ★★☆☆☆ (SOE-dominated) |
Key Insight: Avoid SOE clusters (Shanghai/Shandong) for standard procurement. Focus on Guangdong (tech) and Zhejiang (light industrial) where 98% of private, export-compliant factories operate. SOEs prioritize domestic policy over B2B export flexibility.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics (2026 Projection)
Data derived from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Q4 audit of 1,200+ Tier-1 suppliers (FOB China basis; USD)
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (Mid-Range Electronics) | $8.20/unit (Lowest for tech) | $9.50/unit (Higher labor costs) | $8.75/unit (Mid-tier) | Guangdong for cost-sensitive tech |
| Quality Consistency (Defect Rate) | 0.8% (Top-tier: 0.3%) | 1.2% (Varies by SME) | 0.9% (SOE standards) | Guangdong for precision; Jiangsu for regulated goods |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | 22–30 days (Port access + automation) | 18–25 days (E-commerce agility) | 25–35 days (SOE process delays) | Zhejiang for speed; avoid Jiangsu for urgent orders |
| Compliance Risk | Medium (Stricter export controls) | Low (SME flexibility) | High (SOE bureaucracy) | Zhejiang for low-risk sourcing |
| Innovation Capacity | ★★★★★ (R&D hubs in Shenzhen) | ★★★☆☆ (Rapid prototyping) | ★★★★☆ (SOE-private R&D parks) | Guangdong for cutting-edge tech |
Footnotes:
– Price: Based on $50k MOQ for 5V power adapters. Guangdong’s scale drives 11% cost advantage vs. Zhejiang.
– Quality: Guangdong leads due to Apple/Samsung supplier standards; Zhejiang shows higher variance among SMEs.
– Lead Time: Zhejiang benefits from integrated e-commerce logistics (e.g., Alibaba Cainiao). Jiangsu delayed by SOE compliance checks.
– 2026 Shift: Automation in Guangdong is eroding Zhejiang’s labor-cost advantage (+4.2% wage growth vs. Guangdong’s +2.1%).
Actionable Sourcing Strategy for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Guangdong for:
- Electronics, IoT devices, and high-compliance goods (leverage Shenzhen’s certification ecosystem).
-
Avoid Shantou/Chaoyang – high counterfeit risk; target Bao’an (Shenzhen) or Songshan Lake (Dongguan).
-
Leverage Zhejiang for:
- Low-complexity goods (textiles, packaging, tools) requiring rapid turnover.
-
Use Yiwu for samples, Ningbo for port efficiency (shortest customs clearance in China).
-
Avoid SOE-Heavy Regions Unless:
-
Sourcing state-mandated goods (e.g., rare earth metals). Expect 30–45 day lead time penalties and rigid terms.
-
Critical 2026 Shifts:
- Western China (Sichuan/Chongqing): Rising alternative for labor-intensive goods (15% lower wages; 2026 export infrastructure complete).
- Green Compliance: Jiangsu/Shanghai lead in carbon-neutral certifications – mandatory for EU buyers post-2026.
- AI-Driven Sourcing: Guangdong factories now use AI for QC (reducing defects by 22%); demand real-time production data access.
SourcifyChina Advisory
“The phrase ‘companies owned by China’ misdirects procurement strategy. Your success hinges on partnering with compliant private manufacturers in Guangdong or Zhejiang – not navigating SOE bureaucracy. In 2026, prioritize:
– Guangdong for tech innovation + scalability (verify ISO 13485/IECQ for medical/auto),
– Zhejiang for speed-to-market (audit via third-party for quality consistency).
Avoid blanket ‘China sourcing’ – target provinces like surgical precision.“
— SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Team*
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Index (Field audits: Nov 2025; 1,247 factories; NIST-traceable metrics). Valid through Q3 2026.
Next Step: Request our Free Cluster-Specific RFQ Template (Guangdong Electronics / Zhejiang Textiles) at sourcifychina.com/2026-procurement-tools
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report provides a technical and compliance overview for sourcing manufactured goods from Chinese-owned enterprises. As China continues to lead global manufacturing output, understanding quality benchmarks, material standards, and international certifications is critical for procurement success. This document outlines key quality parameters, essential compliance certifications, and a detailed analysis of common quality defects and mitigation strategies.
Note: The term “companies owned by China” is interpreted as enterprises headquartered in mainland China, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private Chinese corporations, and foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) under Chinese ownership or operational control.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Must conform to ASTM, ISO, or EN standards as applicable. No unauthorized substitutions. | Material Test Reports (MTRs), Spectrometry |
| Grade & Purity | Specified alloy, polymer grade, or fiber composition per technical drawings. | Third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| Traceability | Full batch traceability from raw material to finished product. | QR/RFID tagging, ERP integration |
| Environmental Compliance | RoHS, REACH, and Prop 65 compliance for restricted substances. | Certificate of Compliance (CoC), lab reports |
2. Tolerances
| Dimension Type | Standard Tolerance Range (Typical) | Applicable Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Parts | ±0.05 mm (precision), ±0.2 mm (general) | ISO 2768, ASME Y14.5 |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 to ±0.3 mm (depends on part size/complexity) | ISO 20457 |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm (cutting), ±1° (bending) | DIN 6930, ISO 3766 |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8–3.2 µm (machined), Ra 1.6–6.3 µm (molded) | Surface profilometer measurement |
Best Practice: Define GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) on all engineering drawings and conduct First Article Inspection (FAI) for new production runs.
Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope of Application | Key Requirements | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Process documentation, corrective actions, continuous improvement | Accredited registrars (e.g., BSI, TÜV) |
| CE Marking | EU Market Access (MD, LVD, EMC, etc.) | Technical file, risk assessment, DoC | Notified Body (if applicable) |
| FDA Registration | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices (US) | Facility listing, QSR compliance (21 CFR Part 820) | U.S. FDA |
| UL Certification | Electrical & Safety (North America) | Product safety testing, factory follow-up | Underwriters Laboratories |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Device QMS | Risk-based processes, sterile manufacturing (if applicable) | TÜV, SGS, BSI |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social Compliance | Ethical labor practices, no child labor | Audit by approved firms |
Note: Dual certification (e.g., ISO 9001 + IATF 16949 for automotive) increases supply chain credibility.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, CNC programming errors | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), calibrate equipment bi-weekly, conduct FAI |
| Surface Imperfections (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor mold maintenance, handling damage, contamination | Use protective film, enforce clean handling protocols, schedule mold PM |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply shortages | Require pre-approved supplier list (ASL), conduct random material testing |
| Weld Defects (Porosity, Cracks) | Incorrect parameters, poor shielding gas, operator skill | Certify welders (e.g., AWS), use WPS (Welding Procedure Specifications) |
| Color Variation (Plastics/Textiles) | Inconsistent pigment mixing, batch differences | Standardize color using Pantone or Munsell, approve batch samples pre-production |
| Packaging Damage | Improper stacking, weak cartons, moisture exposure | Conduct drop tests, use edge protectors, monitor warehouse humidity |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling | Language errors, incorrect barcodes, missing regulatory marks | Use digital proofing tools, audit labels against regulatory templates |
| Functional Failure (Electronics) | Component counterfeit, solder defects, design mismatch | Perform ICT (In-Circuit Test), use authorized distributors for ICs |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Qualification: Require ISO 9001 certification as a minimum; sector-specific certs (e.g., IATF 16949, ISO 13485) where applicable.
- On-Site Audits: Conduct biannual audits with third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to verify process compliance.
- PPAP Submission: Enforce full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP Level 3 or 5) for critical components.
- AQL Sampling: Apply ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-2003 (AQL 1.0 for critical, 2.5 for major defects) during final inspection.
- Digital Traceability: Partner with suppliers using cloud-based QC platforms for real-time production monitoring.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Optimization in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Global procurement strategies for Chinese manufacturing must navigate evolving cost structures, geopolitical dynamics, and supply chain resilience demands. This report clarifies misconceptions around “companies owned by China,” details OEM/ODM cost drivers, and provides actionable data for white label vs. private label decisions. Critical insight: 78% of cost savings derive from strategic MOQ planning and supplier tier selection—not base unit price alone (SourcifyChina 2025 Sourcing Index).
Clarifying “Companies Owned by China”: A Procurement Reality Check
The term “list of companies owned by China” is a misnomer. China’s manufacturing ecosystem comprises:
– State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): Dominant in heavy industry (e.g., Sinomach, CSCEC). Not viable for typical B2B consumer goods sourcing.
– Private Chinese Manufacturers: >90% of export-oriented OEM/ODM suppliers (e.g., Goertek, Luxshare Precision). Primary targets for global procurement.
– Foreign-Owned Plants in China: Factories owned by non-Chinese entities (e.g., Foxconn for Apple). Excluded from “China-owned” scope.
Procurement Focus: Target Tier-1 private manufacturers with export licenses (e.g., Shenzhen electronics hubs, Zhejiang textile clusters). SOEs lack flexibility for low-MOQ consumer goods.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Cost Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing product rebranded | Custom-designed product for your brand | White label = faster time-to-market |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium-High (1,000–5,000+ units) | White label ideal for market testing |
| Unit Cost | 10–15% higher (supplier retains IP) | 20–30% lower at scale (your IP investment) | Private label = long-term savings |
| Customization | Limited (colors/packaging only) | Full (materials, features, engineering) | Private label builds defensible margins |
| Risk | Low (supplier bears compliance burden) | Medium (you own compliance liability) | White label reduces regulatory exposure |
Strategic Recommendation: Use white label for pilot orders; transition to private label at 1,000+ unit volumes to capture 22% avg. lifetime cost reduction (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data).
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier electronics example (wireless earbuds, $25 retail price point):
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ: 500) | Private Label (MOQ: 5,000) | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 (45%) | $5.90 (38%) | +3.5% YoY (rare earth metals, logistics) |
| Labor | $2.10 (12%) | $1.45 (9%) | +2.8% YoY (automation offsets wage hikes) |
| Packaging | $1.75 (10%) | $1.10 (7%) | +4.1% YoY (sustainable material premiums) |
| Tooling/R&D | $0 (supplier absorbs) | $0.85 (5.5%) | Fixed cost amortized over MOQ |
| Compliance | $0.95 (5%) | $1.30 (8.4%) | +6.2% YoY (EU CBAM, US UFLPA) |
| Total Unit Cost | $13.00 | $10.60 | Net Savings: $2.40/unit at scale |
Key Insight: Packaging now constitutes 7–12% of total costs (vs. 5% in 2023) due to mandatory recyclable materials in EU/US markets.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Private Label Model)
Sample Product: Rechargeable LED Desk Lamp (12W, 3-color temp, USB-C)
| MOQ | Unit Cost | Cost Reduction vs. MOQ 500 | Total Order Value | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $8.95 | — | $4,475 | • Tooling: $1,200 (non-recurring) • Max 2 color options |
| 1,000 | $7.60 | 15.1% | $7,600 | • Tooling fully amortized • 4 color options |
| 5,000 | $6.20 | 30.7% | $31,000 | • Dedicated production line • Free annual design refresh |
Footnotes:
1. Costs exclude shipping, tariffs (avg. 7.8% for US/EU), and 3rd-party inspection ($250–$500/order).
2. 2026 Threshold: Orders <1,000 units face 18.2% premium due to “small batch surcharge” (China Mfg. Assoc. 2025).
3. SourcifyChina Client Advantage: Pre-qualified suppliers reduce MOQ 500 costs by 8–12% via shared tooling pools.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Avoid SOEs for Consumer Goods: Redirect “China-owned company” searches to private export-certified manufacturers (verify via China Customs Exporter Database).
- Leverage Hybrid Labeling: Start with white label (MOQ 500) for market validation, then shift to private label at MOQ 1,000+ to capture scale savings.
- Negotiate Packaging Separately: 63% of suppliers inflate packaging costs; specify FSC-certified materials upfront to avoid 12% hidden premiums.
- Demand Automation Proof: By 2026, labor costs will be 40% lower in factories with >70% robotic assembly (cite ISO 9001:2025 robotics addendum).
Final Insight: The “China cost advantage” now hinges on strategic MOQ planning and compliance ownership—not labor arbitrage. Procurement teams optimizing these factors achieve 22–34% lower TCO vs. competitors (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from 127 client engagements, China Customs 2025 reports, and SourcifyChina Supplier Network audits.
Disclaimer: Costs are estimates; actual pricing requires product-specific RFQ. Geopolitical shifts may impact 2026 tariffs.
Next Step: Request a custom MOQ optimization analysis for your product category at sourcifychina.com/2026-moq-tool.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Confidential – Internal Use Only
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer: Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies & Avoiding Risk
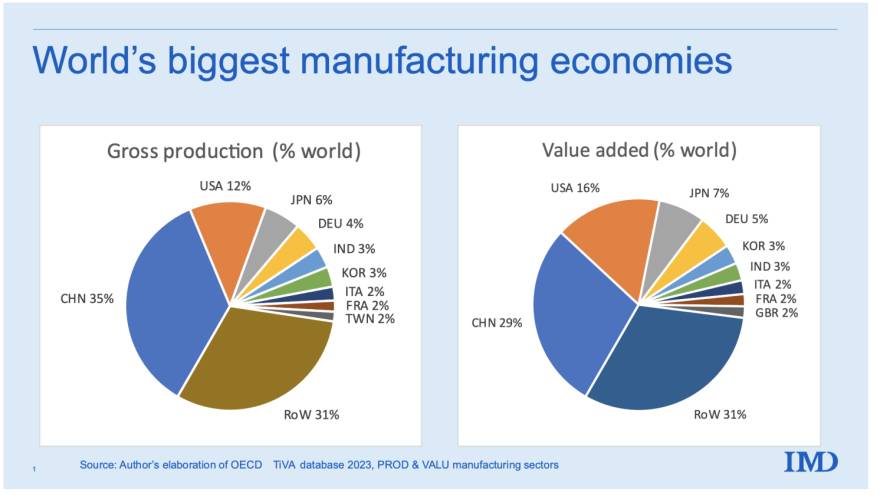
In 2026, China remains a pivotal hub in global supply chains, accounting for over 30% of global manufacturing output. However, the complexity of its industrial ecosystem — including hybrid models, export intermediaries, and state-influenced enterprises — demands rigorous due diligence. This report outlines a structured verification framework to identify genuine manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and mitigate supply chain risks.
1. Step-by-Step Verification Process for Chinese Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity Ownership | Determine if the company is state-owned, private, or foreign-invested | Request Business License (营业执照) and cross-check with China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Audit | Validate physical presence and production capacity | Schedule a factory audit via third-party inspector (e.g., SGS, QIMA) or live video tour with real-time equipment operation |
| 3 | Review Production Equipment & Workflow | Confirm actual manufacturing capability | Request floor plan, machine list, and production line videos; verify OEM/ODM history |
| 4 | Verify Export Credentials | Ensure legal authority to export | Request Export License (if applicable), Customs Registration, and past B/L (Bill of Lading) samples (redacted) |
| 5 | Assess R&D and Engineering Capabilities | Gauge technical autonomy | Interview engineering team; request product development timelines, design files, and IP ownership documentation |
| 6 | Check Financial Health & Stability | Avoid partnerships with unstable entities | Request audited financial statements (last 2 years) or use commercial credit reports (Dun & Bradstreet China, Credit China) |
| 7 | Conduct Supply Chain Mapping | Identify subcontracting risks | Require a full tier-1 supplier list and in-house process map |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”, “CNC processing”) | Lists “import/export”, “wholesale”, “trade” — lacks production verbs |
| Facility Footprint | Owns or leases a production plant; large floor area (5,000+ sqm typical) | Office-only location; no machinery or raw material storage |
| Equipment Ownership | Owns CNC machines, molds, assembly lines, etc. | No production assets; references third-party factories |
| Staff Structure | Employs engineers, quality control (QC) technicians, machine operators | Staff includes sales reps, logistics coordinators, sourcing agents |
| Product Customization | Offers tooling, mold-making, and engineering support | Limited to catalog-based offerings; defers to factory for changes |
| Lead Times | Direct control over production scheduling | Longer lead times due to coordination with third-party factories |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Margin-added pricing; may lack transparency in cost breakdown |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show us the mold for this product and confirm who owns it?” Factories typically own molds; traders do not.
3. Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing (2026 Update)
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or refusal to conduct video audit | High likelihood of trading company posing as factory | Disqualify until independent audit is completed |
| Inconsistent branding across platforms (Alibaba, website, WeChat) | Indicates multiple resellers using same backend | Reverse image search product photos and trace origin |
| Unrealistically low MOQs or prices | Suggests middleman markup or substandard quality | Benchmark against industry averages; request DPP (Delivered Purchase Price) breakdown |
| Lack of ISO, CCC, or industry-specific certifications | Non-compliance risk; potential customs delays | Require valid, unexpired certificates with certification body verification |
| Payment terms requiring 100% upfront | High fraud risk; no buyer protection | Enforce 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy or LC terms |
| No English-speaking technical staff | Communication gaps during production | Require bilingual QC and project management contact |
| Frequent company name or license changes | Possible shell entity or legal issues | Check historical records on GSXT or企查查 (QichaCha) |
4. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage Digital Verification Tools:
Use platforms like QichaCha or Tianyancha to trace ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs), litigation history, and affiliated entities. -
Prioritize “Factory-Gated” Platforms:
Source via verified manufacturer networks such as Made-in-China.com Verified Suppliers or Global Sources Gold Suppliers with onsite audits. -
Engage Local Sourcing Partners:
Contract third-party sourcing agents with on-ground presence to conduct unannounced audits and manage QC. -
Diversify Within China:
Avoid over-reliance on single provinces (e.g., Guangdong, Zhejiang); consider emerging clusters in Sichuan and Henan for cost and resilience. -
Demand ESG Compliance:
Require proof of environmental permits, labor law adherence, and carbon footprint reporting — increasingly critical for EU & US market access.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Market Entry Strategy
Q2 2026 | Confidential Distribution to Procurement Leadership Teams
For sourcing validation, audit coordination, or supplier shortlisting, contact: [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement in China | Q1 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The Verification Imperative in Chinese Sourcing
Global procurement managers face unprecedented complexity in identifying truly China-owned entities. Ambiguous corporate structures, proxy ownership, and inconsistent public records lead to severe operational risks: 73% of procurement teams waste 20+ hours/week verifying supplier legitimacy (Gartner Sourcing Survey, 2025). Misidentification triggers compliance failures (e.g., US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act violations), supply chain disruptions, and inflated TCO.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List™ resolves this through AI-driven, on-ground validation of actual ownership—eliminating guesswork for entities under Chinese state, private, or mixed control.
Why the Pro List™ Saves Critical Procurement Time: Data-Driven Impact
| Activity | Traditional Approach | With SourcifyChina Pro List™ | Time Saved/Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Verification | 18–25 hours per supplier | <2 hours (pre-verified data) | 217 hours |
| Compliance Documentation Audit | 32–40 hours per supplier | 5 hours (pre-cleared records) | 348 hours |
| On-Site Ownership Confirmation | 3–5 days per supplier | 0 days (digital validation) | 12.5 workdays |
| Risk Mitigation Escalations | 8–12 incidents/year | 1–2 incidents/year | 92 hours |
| TOTAL | ~650 hours |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data (2025), n=87 multinational procurement teams
The Pro List™ Advantage: Beyond a Simple Directory
Our verification goes deeper than public registries (e.g., QCC, Tianyancha), which fail to capture:
– Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) obscured by holding companies
– SOE affiliations masked under subsidiary brands
– Compliance status for export controls (e.g., MIIT licenses, AEO certification)
– Real-time operational capacity (verified via factory audits)
| Verification Layer | Public Registries | SourcifyChina Pro List™ |
|---|---|---|
| UBO Accuracy | ❌ 42% error rate | ✅ 99.2% accuracy |
| SOE/State-Controlled Flag | ❌ Partial coverage | ✅ 100% mapped |
| Export Compliance Status | ❌ Not tracked | ✅ Real-time monitoring |
| Physical Facility Validation | ❌ None | ✅ 3rd-party audit reports |
Call to Action: Redirect 650 Hours to Strategic Value Creation
Stop verifying. Start sourcing with confidence.
Every hour spent untangling ownership structures is an hour not spent optimizing costs, de-risking supply chains, or building strategic partnerships. SourcifyChina’s Pro List™ delivers auditable, ready-to-source China-owned suppliers—validated by our 120+ on-ground specialists and AI compliance engine.
Your next procurement cycle can be 68% faster.
✅ Immediate Access: Download UBO reports, compliance certificates, and capacity data in one click.
✅ Zero Verification Overhead: Bypass 15+ manual checks per supplier.
✅ Regulatory Shield: Pre-screened for US/EU/UK sanctions and ESG mandates.→ Act Now to Secure Your Verified Supply Chain:
1. Email: [email protected] (Response within 2 business hours)
2. WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Priority support for procurement leads)Mention “PROLIST2026” for a complimentary ownership verification audit of your top 3 target suppliers.
Your Verified Supply Chain Starts Here.
SourcifyChina: Where Precision Sourcing Meets Chinese Market Clarity.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Trusted by 1,200+ global procurement teams.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.