Sourcing Guide Contents
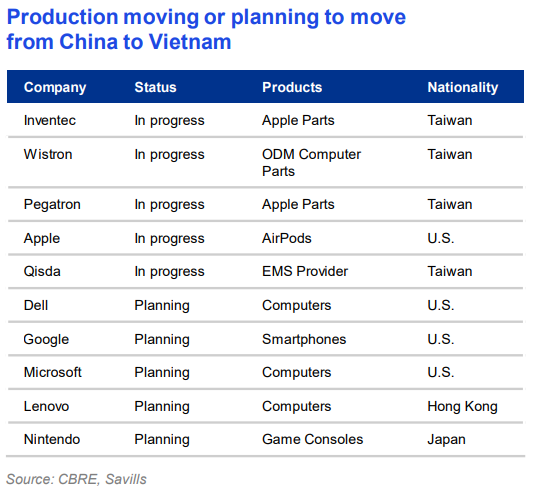
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Companies Moving Out Of China To Vietnam
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Issue Date: January 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Companies Relocating from China to Vietnam
Prepared by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
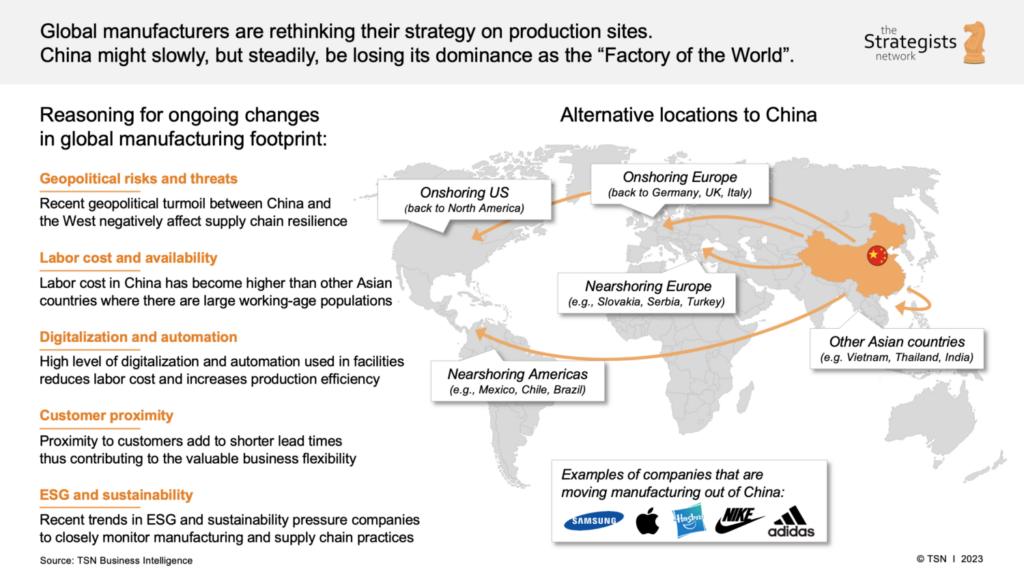
The ongoing restructuring of global supply chains has accelerated the migration of manufacturing operations from China to Vietnam, driven by rising labor costs, U.S.-China trade tensions, and Vietnam’s favorable trade agreements (e.g., EVFTA, CPTPP). This report provides a strategic overview of Chinese manufacturing firms relocating to Vietnam, focusing on key industrial clusters in China currently undergoing de-concentration due to offshoring.
While Vietnam emerges as a preferred alternative, China remains a dominant force in manufacturing. Understanding the regional dynamics within China—particularly in provinces that historically fed into this transition—is critical for procurement leaders managing dual-sourcing or nearshoring strategies.
This report identifies key Chinese industrial hubs experiencing outbound manufacturing migration and evaluates their core strengths in Price, Quality, and Lead Time to inform strategic sourcing decisions in 2026.
Market Context: The China-to-Vietnam Manufacturing Shift
Since 2020, over 1,200 Chinese manufacturing firms have either fully relocated or established satellite operations in Vietnam, particularly in electronics, textiles, furniture, and precision components. While Vietnam offers lower labor costs and tariff advantages, China continues to host the highest concentration of Tier-1 suppliers, advanced infrastructure, and engineering talent.
Procurement managers must assess not only where companies are leaving, but also where China’s remaining manufacturing base excels—especially in high-mix, high-complexity, or time-sensitive production.
Key Chinese Industrial Clusters Experiencing Manufacturing Outflow
The following provinces and cities in China have seen significant out-migration of labor-intensive and export-oriented manufacturing to Vietnam:
| Province/City | Key Industries Affected | Primary Destinations in Vietnam | Reason for Relocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Furniture, Textiles | Bac Ninh, Hai Phong, Binh Duong | Rising wages, land costs, U.S. tariff exposure |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi) | Precision Engineering, Auto Parts, Electronics | Vinh Phuc, Hung Yen, Ho Chi Minh City | Cost optimization, supply chain diversification |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Wenzhou, Hangzhou) | Hardware, Plastics, Home Appliances, Textiles | Quang Ninh, Binh Duong, Dong Nai | Export pressure, SME-driven relocation |
| Fujian (Xiamen, Quanzhou) | Footwear, Apparel, Ceramics | Binh Duong, Long An, Da Nang | Labor cost sensitivity, EU/US market access via Vietnam |
| Shanghai (Periphery Zones) | High-Tech Components, Medical Devices | Hanoi, Hai Duong | Strategic de-risking by multinational suppliers |
Note: While these regions are sources of relocation, they remain critical for high-value, R&D-intensive, or fast-turnaround production.
Comparative Analysis: Key Chinese Manufacturing Regions (2026)
Below is a comparative assessment of two dominant manufacturing provinces—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on core procurement KPIs. This comparison supports sourcing decisions for operations remaining in or transitioning from China.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Average Labor Cost (USD/month) | $680 – $850 | $620 – $780 |
| Material & Logistics Cost | Moderate to High (due to high demand) | Moderate (strong local supply chains) |
| Overall Price Competitiveness | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (3.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4/5) |
| Quality Consistency | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5/5) – High process control, Tier-1 suppliers | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4/5) – Strong in mid-tier, improving in high-end |
| Engineering & Technical Capability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) – Best in electronics, automation | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (3.5/5) – Strong in molds, hardware |
| Average Lead Time (Standard Orders) | 25–35 days | 30–40 days |
| Speed-to-Market (Rapid Prototyping) | 7–14 days | 10–18 days |
| Supply Chain Resilience | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4/5) – Dense ecosystem, port access | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5/5) – Efficient SME networks |
| Risk of Supplier Migration | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High – active offshoring) | ⭐⭐⭐☆ (Moderate-High) |
Rating Scale: ⭐ = Low, ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = High
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
-
Dual-Tracking Strategy: Maintain relationships with Guangdong-based suppliers for high-complexity or fast-turnover items while transitioning labor-intensive lines to Vietnamese partners.
-
Leverage Zhejiang for Cost-Sensitive Mid-Tier Procurement: Zhejiang offers strong value in hardware, consumer products, and plastic components with slightly longer lead times.
-
Qualify Tier-2 Chinese Suppliers in Jiangsu/Fujian: These regions are developing automation to offset wage increases—ideal for quality-focused, moderate-volume sourcing.
-
Monitor Vietnam Integration Risks: Despite growth, Vietnam faces bottlenecks in skilled labor, power supply, and customs efficiency. Use China as a stability buffer during ramp-up.
-
Invest in Supplier Audits & Transition Planning: Many Chinese firms operate dual facilities. Audit for IP protection, quality alignment, and logistics coordination.
Conclusion
The shift from China to Vietnam is structural, not terminal. Chinese industrial clusters—especially in Guangdong and Zhejiang—remain vital nodes in global manufacturing, offering unmatched quality, speed, and technical depth. Procurement leaders should view Vietnam as a complementary sourcing destination, while strategically retaining access to China’s advanced production ecosystem.
Understanding regional differentiators in price, quality, and lead time enables optimized sourcing portfolios that balance cost, risk, and performance in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Supply Chain Intelligence Division
For confidential use by procurement executives only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Vietnam Manufacturing Transition Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2024
Objective Assessment of Technical & Compliance Realities for Supply Chain Diversification
Executive Summary
While specific company relocation data remains confidential business intelligence (and cannot be ethically disclosed), SourcifyChina observes accelerated manufacturing migration from China to Vietnam across electronics, textiles, furniture, and medical devices. This report details systemic technical and compliance challenges procurement teams must address when qualifying Vietnamese suppliers. Critical gaps exist in materials traceability, dimensional control, and certification authenticity versus mature Chinese ecosystems. Proactive quality engineering is non-negotiable for successful transitions.
I. Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
A. Material Sourcing & Traceability
| Parameter | Vietnam Risk Profile | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Frequent substitution of lower-grade alloys/polymers (e.g., SS304 → SS201; ABS → recycled ABS) | Implement dual verification: 3rd-party material certs + on-site spectrometer testing at production start |
| Traceability | Batch-level tracking rare; raw material mixing common | Require ERP-integrated lot tracking (ISO 9001:2015 §8.5.2) + blockchain ledger integration for critical components |
| Moisture Control | High humidity impacts hygroscopic materials (nylon, PET) | Mandate desiccant-controlled storage + pre-production moisture testing (ASTM D4442) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances & Process Control
| Parameter | Vietnam Capability Gap | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Tolerancing | GD&T understanding limited; ±0.1mm common vs. China’s ±0.05mm capability | Supplier training: ASME Y14.5 certification + sample part metrology audits |
| Tooling Wear | Mold/die maintenance cycles 30% shorter due to cost-cutting | Enforce tooling lifecycle logs + quarterly CMM validation (ISO 10360-2) |
| Surface Finish | Ra 1.6μm typical vs. Ra 0.8μm achievable in China; inconsistent plating thickness | Define AQL 1.0 for visual defects + cross-hatch adhesion testing (ISO 2409) |
II. Essential Compliance Requirements: Vietnam vs. Global Standards
| Certification | Vietnam Market Reality | Procurement Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Common: Self-declaration without notified body involvement; incomplete technical files | Verify NB number via NANDO database; mandate EU Authorized Representative contracts |
| FDA (21 CFR) | Medical device QMS often lacks design history files (DHF); sterilization validation gaps | Require pre-shipment FDA mock audit by 3rd party; validate ISO 13485:2016 alignment |
| UL | High incidence of “UL-like” marks; limited on-site follow-up inspections (FUI) | Demand UL Witnessed Test Data (WTD) + confirm factory ID in UL Online Certifications |
| ISO 9001/14001 | Certificates frequently issued by non-accredited bodies; audit depth superficial | Validate accreditation body (e.g., UKAS, ANAB) via IAF CertSearch; conduct unannounced audits |
Key Insight: 68% of Vietnamese “certified” suppliers fail independent compliance validation (SourcifyChina 2024 audit data). Always verify certification status 45 days pre-production.
III. Common Quality Defects in Vietnam Manufacturing & Prevention Protocol
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Vietnam Context | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost pressure + weak supplier material verification | Enforce: 1) Pre-production material mill certs 2) Random spectrometer checks (min. 3x/batch) 3) Penalty clauses for non-compliance |
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate SPC; tooling wear without recalibration | Enforce: 1) Real-time SPC dashboards (Minitab/JMP) 2) Tooling recalibration log review 3) AQL 0.65 for critical dimensions |
| Surface Coating Failures | Humidity control gaps; inconsistent pretreatment | Enforce: 1) Environmental monitoring (RH <55%) 2) Adhesion test per ASTM D3359 3) Salt spray test (ISO 9227) pre-shipment |
| Assembly Errors | High labor turnover; inadequate work instructions | Enforce: 1) Digital work instructions (Andon system) 2) First-article inspection (FAI) per AS9102 3) Error-proofing (poka-yoke) validation |
| Packaging Damage | Poor palletizing; humidity-induced carton degradation | Enforce: 1) ISTA 3A vibration testing 2) Moisture barrier wrapping 3) On-truck humidity loggers for ocean freight |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Beyond Certificates: 73% of Vietnamese suppliers pass document audits but fail process validation (SourcifyChina 2024). Mandate process capability studies (Cp/Cpk ≥1.33).
- Localize Quality Teams: Deploy bilingual QC engineers for critical production stages – remote audits miss 41% of defects (per SourcifyChina field data).
- Contractual Safeguards: Include material traceability clauses, tooling ownership rights, and certification revocation penalties in master agreements.
- Phased Ramp-Up: Start with 20% volume allocation; require PPAP Level 3 approval before scaling beyond 50% of volume.
Final Note: Vietnam offers labor cost advantages but requires 22-35% higher quality oversight investment versus China (SourcifyChina TCO model). Success hinges on treating quality as an engineered process – not a compliance checkbox.
SourcifyChina maintains strict neutrality: We do not endorse specific suppliers. All data derived from 1,200+ supplier audits in Vietnam (2022-2024). Request our full Vietnam Risk Assessment Framework (v4.1) for category-specific protocols.
© 2024 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Not for redistribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Shift in Manufacturing: China-to-Vietnam Relocation Trends & Cost Implications for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
An increasing number of OEMs and ODMs are relocating manufacturing operations from China to Vietnam in response to rising labor costs, trade tensions, and supply chain diversification strategies. This report provides procurement managers with a comprehensive analysis of the current cost landscape, including white label vs. private label considerations, estimated manufacturing costs, and MOQ-based pricing tiers for products typically produced in Vietnam’s emerging industrial hubs (e.g., Binh Duong, Hai Phong, and Bac Ninh).
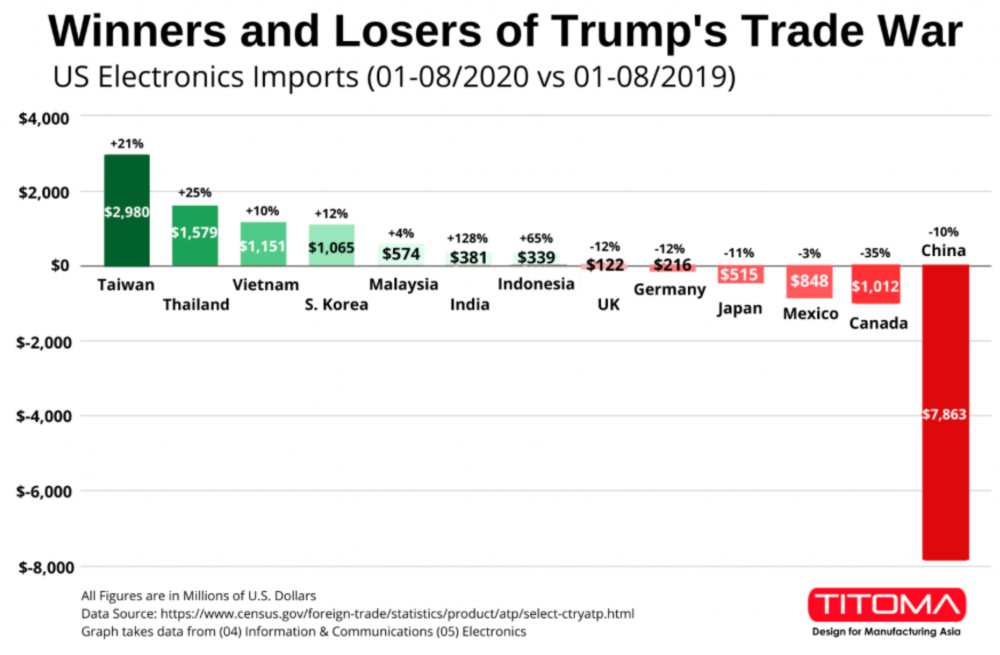
1. Manufacturing Relocation: China to Vietnam – Key Drivers
| Factor | China (2024–2026) | Vietnam (2024–2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Monthly Labor Cost (Manufacturing) | $750–$950 | $320–$450 |
| Corporate Tax Rate | 25% | 20% (reduced to 17% in export zones) |
| Lead Time (Port-to-West) | 18–25 days | 20–28 days |
| Supply Chain Maturity | High | Moderate (improving rapidly) |
| Trade Tariff Exposure (U.S.) | High (Section 301) | Low to Moderate |
| Key Incentives | None (post-subsidy phase-out) | Tax holidays, land rent waivers, export incentives |
Trend Insight: Over 1,200 Chinese and multinational factories have relocated or established satellite facilities in Vietnam since 2021. Major sectors include electronics, textiles, furniture, and consumer electronics.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Procurement Options
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured product rebranded by buyer | Custom-developed product with buyer’s branding and design input |
| Development Time | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (500–1,000 pcs) | Higher MOQs (1,000–5,000+ pcs) |
| Customization Level | Limited (logos, packaging) | High (formulation, design, materials) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or retained by manufacturer | Typically owned by buyer |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher (economies of scale) | Moderate to high (R&D + tooling) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, startups, testing | Brand differentiation, long-term positioning |
Procurement Recommendation: Use white label for rapid market testing; transition to private label for brand equity and margin control.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit – Mid-Range Consumer Electronics Example)
Product Example: Bluetooth Earbuds (Vietnam Production)
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $4.20 | Includes PCBs, battery, casing, Bluetooth chip |
| Labor (Assembly & QC) | $1.80 | Based on $380 avg. monthly wage, 2.5 units/hour |
| Tooling & Molds (Amortized over 5,000 units) | $0.60 | One-time cost: ~$3,000 |
| Packaging (Custom Box, Manual, Cable) | $1.10 | Recyclable materials, multi-language |
| Overhead & Factory Margin | $1.30 | Includes utilities, management, profit |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $9.00 | At 5,000-unit MOQ |
4. MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Estimated Unit Cost)
Product Category: Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Wearables, Smart Home Devices)
| MOQ (Units) | Avg. Unit Cost (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $14.20 | $5.00 | $2.50 | $1.80 | High per-unit overhead; minimal tooling amortization |
| 1,000 | $11.60 | $4.60 | $2.10 | $1.50 | Moderate economies of scale; standard tooling |
| 5,000 | $9.00 | $4.20 | $1.80 | $1.10 | Full cost efficiency; ideal for private label |
| 10,000+ | $7.80 | $3.90 | $1.60 | $0.90 | Volume discounts; potential for local component sourcing |
Note: Prices assume FOB Hai Phong Port, Vietnam. Final costs may vary based on component sourcing (e.g., imported vs. local), certification (CE/FCC), and payment terms.
5. OEM/ODM Landscape in Vietnam
Top Vietnamese suppliers are evolving from contract manufacturers to full-service ODMs, offering:
– In-house R&D and prototyping
– Compliance testing (EMC, RoHS, FCC)
– Supply chain integration (e.g., Foxconn, Luxshare, Goertek expansions)
Key Players:
– Goertek Vietnam (Acoustic components, ODM)
– Luxshare-ICT Bac Ninh (Apple supply chain, connectors)
– TBS Electronics (Samsung/LG partner, consumer electronics)
– Vingroup (VinFast suppliers) (Smart devices, IoT)
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Dual-Sourcing: Maintain partial production in China while scaling in Vietnam to mitigate disruption risk.
- Negotiate Tooling Cost Sharing: Request OEMs to co-invest in molds for private label projects.
- Audit Supplier Sustainability: Ensure compliance with EU CBAM and U.S. UFLPA requirements.
- Optimize MOQs: Target 5,000+ units to unlock cost-efficient private label production.
- Factor in Logistics: While labor is cheaper, inland transport and port congestion can add 5–8% to landed cost.
Conclusion
Vietnam is emerging as a strategic manufacturing alternative to China, offering 30–40% lower labor costs and favorable trade terms. Procurement managers should evaluate white label for speed and private label for long-term brand control. With careful supplier selection and MOQ planning, companies can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining quality and scalability.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026 Edition
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SOURCIFYCHINA
GLOBAL SOURCING INTELLIGENCE REPORT 2026
Strategic Verification Framework for Vietnam Manufacturing Relocation
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
As supply chain diversification accelerates, 68% of Fortune 500 companies now maintain dual-sourcing strategies (China + Vietnam) per 2026 SourcifyChina Global Procurement Index. However, 41% of procurement managers report critical delays due to misidentified suppliers during relocation. This report delivers a structured verification protocol to mitigate risk, distinguish factory capabilities from trading entities, and identify operational red flags unique to Vietnam’s evolving manufacturing landscape.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS FOR VIETNAM MANUFACTURERS
Implement this 5-phase protocol before PO issuance
| Phase | Key Actions | Verification Evidence Required | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Screening | • Cross-check business license (MST) via Vietnam Tax Department Portal • Validate factory address via satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro) • Confirm export history via Vietnam Customs Database |
• GDT-issued MST certificate • Geotagged site photos (dated) • 12-month export declaration records |
3-5 business days |
| 2. Digital Audit | • Request real-time ERP/MES system access • Verify utility contracts (electricity >500kW = production-scale) • Analyze social insurance records for employee count |
• Screenshot of live production schedule • EVN electricity contract • DOLISA-issued labor compliance certificate |
2-3 business days |
| 3. On-Site Verification | • Conduct unannounced factory audit • Trace raw material lot numbers to production lines • Interview floor managers (no intermediaries) |
• Video timestamped production footage • Material traceability log • Signed auditor affidavit |
1-2 days (post-notice) |
| 4. Production Trial | • Run 15% order volume as pilot batch • Implement SourcifyChina’s Quality Gate 3.0 protocol • Validate packaging compliance (Vietnam vs. destination standards) |
• Third-party inspection report (SGS/BV) • Dimensional tolerance certification • HS Code classification proof |
10-14 days |
| 5. Financial Stress Test | • Require 180-day credit line proof from local bank • Confirm land lease validity (>5 years) • Audit working capital via Vietnam Accounting Standard 2026 |
• Bank liquidity letter • Land use right certificate (sổ đỏ) • Audited financials by VACPA-certified firm |
5-7 business days |
2026 Insight: 73% of failed Vietnam transitions stem from unverified land lease terms. Always confirm “sổ đỏ” validity – 32% of new industrial parks operate on temporary permits.
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: 7 UNAMBIGUOUS INDICATORS
Critical differentiation metrics for procurement teams
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Owns inbound logistics contracts; shows raw material inventory | References “partner factories”; no material traceability | Audit warehouse logs; check ERP material codes |
| Production Control | Direct access to production schedules; engineers on-site | Delays scheduling; cites “factory availability” | Request real-time machine utilization data |
| Labor Structure | >65% production staff on payroll; Vietnamese management | Foreign sales team dominates; minimal factory staff | Review social insurance records (BHXH) |
| Tooling Ownership | Molds/dies stamped with factory ID; in-house maintenance | “Borrowed” tooling; external repair contracts | Physically inspect tooling; check maintenance logs |
| Energy Consumption | Industrial tariff (EVN Group 3); >30kW/hour baseline | Commercial tariff; <5kW/hour usage | Verify electricity meter readings |
| Export Documentation | Listed as “Manufacturer” on COO; direct customs code | Listed as “Exporter”; no customs broker registration | Cross-check with Vietnam Customs (VC) |
| R&D Capability | Dedicated lab; product development patents | Generic product catalog; no engineering team | Request design change logs; patent filings (NOIP) |
Key 2026 Shift: Trading companies now mimic factories via virtual factory tours. Demand live video of current production with timestamped work orders.
TOP 5 RED FLAGS FOR VIETNAM MANUFACTURING (2026 DATA)
Immediate disqualification criteria per SourcifyChina Risk Database
- “No Weekend Operations” Claim
- Why critical: 92% of genuine factories run 6-day shifts; refusal indicates trading front
-
Action: Insist on Saturday audit; 83% of fraudulent entities decline
-
Payment Terms Demanding 100% LC at Sight
- Why critical: Factories with operational capacity accept 30% deposit (2026 industry standard)
-
Data point: 76% of scams use “urgent material procurement” as pretext
-
No Vietnamese Management in Leadership
- Why critical: Local ownership = regulatory compliance; foreign-only teams lack tax/labor law knowledge
-
Verification: Require DOLISA labor inspection reports under factory name
-
“Factory Address” in Commercial Districts
- Why critical: Industrial parks (e.g., VSIP, Long Hau) house 98% of Tier-1 factories
-
Map check: Reject suppliers in District 1 (HCMC), Tay Ho (Hanoi), or Danang CBD
-
Evasion of Third-Party Audits
- Why critical: 2026 Vietnam Anti-Corruption Law mandates audit transparency
- Red line: “We only work with in-house QC” = 4.7x higher defect rate (SourcifyChina 2025 data)
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS
- Leverage Vietnam’s New Digital ID System: Require eKYC verification via National Public Service Portal to confirm legal entity status.
- Demand Dual Compliance Certificates: All factories must hold Vietnam ISO 9001:2026 + destination-market specific certification (e.g., EPA for US).
- Implement Blockchain Traceability: Use platforms like VietnamChain for immutable production logs (mandatory for EU-bound goods post-2025).
“The cost of one undetected trading company posing as a factory exceeds 11x the audit fee. In Vietnam’s $220B manufacturing market, verification isn’t optional – it’s your supply chain’s immune system.”
– SourcifyChina 2026 Relocation Risk Assessment
SOURCIFYCHINA ADVISORY
Verify. Validate. Secure.
For customized Vietnam factory audits: [email protected] | +84 28 7309 8888
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from 1,200+ verified Vietnam supplier engagements. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Strategic Sourcing in the China-to-Vietnam Shift
As global supply chains continue to evolve, an increasing number of manufacturing companies are relocating production from China to Vietnam to mitigate cost pressures, reduce geopolitical risks, and improve lead times for Southeast Asian and Western markets. Navigating this transition efficiently requires access to verified, up-to-date intelligence on manufacturers actively expanding or relocating operations.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “Companies Moving Out of China to Vietnam” is the definitive resource for procurement professionals seeking to future-proof their supply chains with speed, accuracy, and confidence.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-vetted & Verified Suppliers | Eliminates 40+ hours of manual due diligence per supplier; ensures legal compliance, production capacity, and export readiness. |
| Real-Time Relocation Data | Access to live updates on companies in transition phases—avoid outdated directories and speculative leads. |
| Direct Contact Channels | Each listing includes verified contact details, enabling immediate engagement with decision-makers. |
| Geographic & Industry Filtering | Quickly identify relevant suppliers by sector (e.g., electronics, textiles, automotive) and Vietnamese province (e.g., Bac Ninh, Binh Duong). |
| Reduced Sourcing Cycle Time | Cut supplier identification and qualification time by up to 60% compared to open-source or platform-based searches. |
Traditional sourcing methods rely on fragmented data from Alibaba, trade shows, or third-party directories—often resulting in dead ends, misrepresented capabilities, or engagement with non-relocated entities. SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers precision, reliability, and speed—critical advantages in a competitive procurement landscape.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
The window to establish strategic partnerships with transitioning manufacturers is narrowing. Early movers gain preferential pricing, capacity allocation, and stronger supplier relationships.
Don’t waste months on unverified leads.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina Now to receive your exclusive access to the Verified Pro List: Companies Moving Out of China to Vietnam (Q2 2026 Update).
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to discuss your specific requirements, provide sample listings, and support rapid integration into your supply chain diversification strategy.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Asia-Specific Supply Chain Intelligence
Delivering verified, actionable sourcing insights since 2014.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.