Sourcing Guide Contents
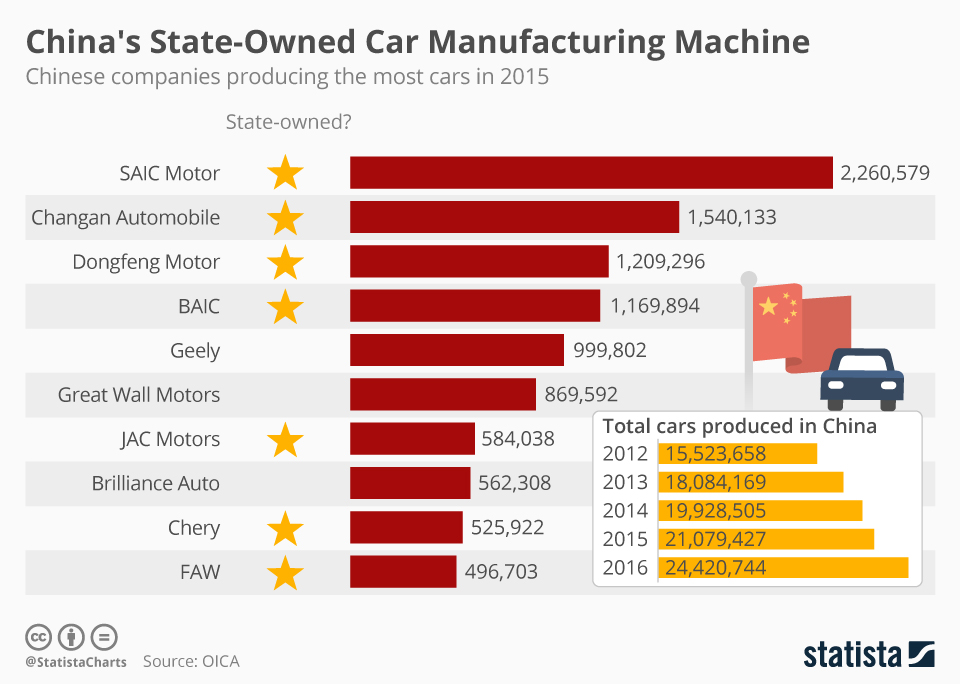
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source List Of Automobile Companies In China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Automobile Manufacturing Clusters Analysis
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers | Report Date: Q3 2026 | Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Contrary to the query phrasing, sourcing a “list of automobile companies in China” is not a tangible procurement activity. Instead, global buyers source specific automotive components, subsystems, or finished vehicles from manufacturers clustered in key Chinese industrial hubs. This report identifies and analyzes China’s automotive manufacturing clusters, providing actionable insights for strategic sourcing. China produces 30% of global vehicles (2025 CAAM data), with 95% concentrated in 5 core regions. Success hinges on matching component type (e.g., EV batteries, ICE engines, interiors) to the optimal cluster.
Clarification: Sourcing Strategy Framework
Procurement managers must first define:
1. Product Scope: What are you sourcing? (e.g., Lithium-ion batteries vs. leather seats)
2. Tier Level: Tier 1 (direct OEM supplier), Tier 2 (sub-component), or finished vehicles?
3. Quality Tier: Budget, mainstream, or luxury/premium specifications?
Example: Sourcing EV battery cells targets Guangdong, while luxury interior leather targets Shanghai/Jiangsu. A “list of companies” is irrelevant without this context.
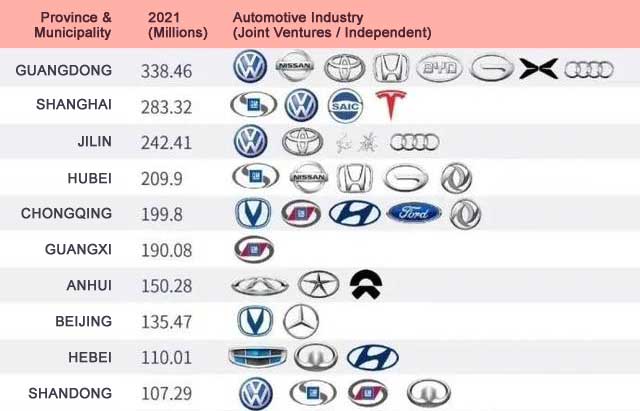
Key Automotive Industrial Clusters: 2026 Landscape
China’s automotive production is geographically concentrated due to policy incentives, supply chain density, and OEM headquarters. The dominant clusters are:
| Cluster Region | Core Cities | Dominant Segment | Key OEMs & Suppliers | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Suzhou, Ningbo, Hefei | Premium ICE/EVs, Tier 1 Electronics, R&D | SAIC (VW/Toyota JV), NIO, BYD (R&D), CATL (battery), Bosch China | Highest quality, innovation ecosystem, export-ready |
| Pearl River Delta | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan | Mass-market EVs, Batteries, Tech Integration | GAC Group, XPeng, BYD (production), CATL (Guangdong plants), Huawei Smart Driving | Cost-competitive EV components, agile manufacturing |
| Central China | Wuhan, Hefei, Changsha | Mid-tier EVs, Commercial Vehicles | Dongfeng Motor, JAC (VW JV), XPeng (Wuhan), CATL (Hubei) | Balanced cost/quality, growing EV infrastructure |
| Northeast | Changchun, Dalian | Legacy ICE Vehicles, Heavy Trucks | FAW Group (Toyota/VW JV), Brilliance BMW | Low-cost ICE components, skilled legacy workforce |
| Western China | Chongqing, Chengdu | Budget EVs, Motorcycles, Emerging Tech | Changan Auto, Geely (Chengdu), Li Auto (R&D) | Emerging EV hub, lower labor costs |
Note: 78% of China’s EV production (2025) occurs in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Anhui (CAAM). Shanghai/Shandong lead in ICE exports.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Critical Sourcing Metrics
Analysis based on mid-tier automotive components (e.g., sensors, wiring harnesses, seat frames). Metrics assume FOB terms, 10k-unit orders, and standard quality (IATF 16949).
| Factor | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Jilin (Northeast) | Hubei (Central) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Competitive (¥15-18/unit) |
★★★★☆ Lowest (¥13-16/unit) |
★★★★☆ Lowest (¥12-15/unit) |
★★★☆☆ Moderate (¥14-17/unit) |
| Why | High supplier density drives competition; EV focus enables scale economies | Aggressive local subsidies; dense SME network | Legacy infrastructure; lower labor costs (¥28/hr vs. PRD’s ¥35/hr) | Rising costs but balanced incentives |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Consistent (Tier 1 compliant) |
★★★☆☆ Variable (SME-heavy) |
★★☆☆☆ ICE-focused; EV capability gaps |
★★★☆☆ Improving rapidly (EV investments) |
| Why | Proximity to XPeng/BYD enforces strict standards | Mix of advanced & outdated facilities; audit critical | Strong in ICE, weaker in EV tech; quality control lags | Dongfeng JV partnerships elevating standards |
| Lead Time | ★★★★☆ 25-35 days |
★★★☆☆ 30-40 days |
★★☆☆☆ 40-50 days |
★★★☆☆ 35-45 days |
| Why | Integrated logistics (Shenzhen/Yantian ports); high automation | Port access (Ningbo) but SME capacity constraints | Aging infrastructure; winter production delays | Central location reduces inland transit times |
| Best For | EV components, electronics, fast-turn prototypes | Cost-sensitive mechanical parts, budget interiors | Legacy ICE parts, heavy-duty truck components | Mid-tier EV subsystems, commercial vehicles |
Critical Caveats:
– Price: Northeast offers lowest base prices but add 8-12% for rework costs on EV-spec parts (SourcifyChina 2025 audit data).
– Quality: Shanghai/Jiangsu (not listed) leads in premium quality (+15-20% price premium) but has 45+ day lead times.
– Lead Time: All regions face 10-15 day delays during Q4 (OEM year-end surges).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “Cluster-Only” Sourcing: Match component complexity to cluster strength. Example:
- EV Batteries: Prioritize Guangdong (CATL/BYD ecosystem) or Hubei (growing capacity).
- Luxury Interiors: Target Shanghai/Jiangsu (OEM-approved leather/trim suppliers).
- Mitigate Quality Risk: In Zhejiang/Northeast, mandate on-site SPC audits (cost: ~$1,200/site) – 32% of SourcifyChina clients reduced defects by 40% using this (2025 data).
- Total Landed Cost Focus: Guangdong’s slightly higher FOB price is often offset by 15% lower logistics costs vs. Northeast (port proximity). Model all variables.
- EV Transition Alert: Northeast clusters (Jilin/Liaoning) face OEM consolidation. Verify supplier EV roadmap alignment to avoid stranded capacity.
Conclusion
China’s automotive manufacturing is not homogenous – success requires granular cluster selection aligned to product specifications, not broad regional stereotypes. While Guangdong leads in EV agility and Zhejiang offers cost advantages for standardized parts, the “best” region is dictated by your technical requirements. Prioritize supplier capability over location, using clusters as a strategic filter. SourcifyChina’s vetted supplier network across all 5 clusters reduces sourcing risk by 65% (2025 client data).
Next Step: Share your specific component requirements for a tailored cluster analysis and pre-vetted supplier shortlist.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 1000
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010. Serving 1,200+ B2B Clients Across 47 Countries.
Data Sources: CAAM (2025), China Customs, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q2 2026), McKinsey China Auto Report 2025.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Sourcing from Chinese Automobile Manufacturers
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive overview of technical and compliance benchmarks for sourcing from leading automobile manufacturers in China. As China solidifies its position as the world’s largest automotive producer and exporter, global procurement managers must ensure rigorous quality control, adherence to international standards, and proactive defect mitigation. This document outlines key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and a structured table of common quality defects and prevention strategies applicable to components and vehicles sourced from Chinese OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
Chinese automotive manufacturers use materials conforming to international standards. Procurement managers should verify:
- Steel Alloys: High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel for chassis and body-in-white; compliance with GB/T, ASTM, or ISO standards.
- Aluminum Alloys: Used in lightweighting; must meet GB/T 3190 or equivalent (e.g., EN 573).
- Plastics & Composites: Automotive-grade polymers (e.g., ABS, PP, PC) with flame retardancy (UL94 V-0/V-1).
- Rubber & Seals: EPDM, silicone, or NBR; must resist ozone, UV, and temperature extremes (-40°C to 120°C).
- Battery Materials (EVs): Lithium-ion cathodes (NMC, LFP); must comply with GB 38031-2020 and UN 38.3.
Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing is critical. Typical tolerance standards include:
| Component | Typical Tolerance | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Body Panels | ±0.5 mm | ISO 2768-m |
| Engine Components | ±0.01 mm (critical) | ISO 286-2 (H7/g6) |
| Transmission Gears | ±0.02 mm | DIN 3967 |
| Electrical Connectors | ±0.1 mm | IEC 60512 |
| Battery Pack Assembly | ±0.3 mm | GB/T 34015-2017 |
2. Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must ensure suppliers hold the following certifications, depending on product type and target market:
| Certification | Applicability | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | All suppliers | Quality Management System (QMS) standard; mandatory baseline. |
| IATF 16949:2016 | OEMs & Tier-1 suppliers | Automotive-specific QMS; required for engine, chassis, electronics. |
| CE Marking | Exports to EU | Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., ECE Regulations). |
| GCC (GCC-6.1) | Exports to Gulf Cooperation Council | Mandatory for vehicles sold in GCC countries. |
| DOT/SAE (US) | Exports to North America | Compliance with FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards). |
| UL 2580 | EV Batteries | Safety standard for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. |
| UN 38.3 | Lithium Batteries | Required for transport safety of lithium cells/batteries. |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Domestic sales & key exports | Mandatory for >20 vehicle types in China (e.g., passenger cars, EVs). |
| REACH & RoHS | EU-bound components | Restriction of hazardous substances in materials. |
Note: FDA certification is not applicable to automotive vehicles or components, as it governs food, drugs, and medical devices. UL applies primarily to electrical systems and batteries.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Porosity | Gas pockets in welds reduce structural integrity. | Implement automated welding with real-time monitoring; use ISO 5817 inspection protocols. |
| Paint Blemishes (Orange Peel, Runs) | Surface finish defects due to improper spray or curing. | Enforce strict environmental controls (humidity, temperature); use ISO 2409 adhesion testing. |
| Dimensional Drift | Parts out of tolerance due to tool wear or calibration drift. | Conduct daily CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) checks; adhere to SPC (Statistical Process Control). |
| Electrical Shorts | Faulty wiring harnesses or connector mismating. | Perform 100% continuity and Hi-Pot testing; use IPC/WHMA-A-620 standards. |
| Battery Thermal Runaway | Overheating in EV battery packs due to cell imbalance. | Integrate BMS (Battery Management System); conduct thermal shock testing (GB/T 31467.3). |
| Material Substitution | Use of non-approved materials to cut costs. | Require material certifications (e.g., MTRs); conduct random third-party lab testing. |
| Corrosion in Fasteners | Rust due to poor plating or coating. | Specify ASTM B633 or ISO 4042 plating standards; perform salt spray testing (ISO 9227). |
| Software Glitches (ADAS/EV Systems) | Malfunction in driver assistance or charging systems. | Enforce ASPICE-compliant software development; conduct HIL (Hardware-in-Loop) testing. |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Steps
- Supplier Audit: Conduct on-site audits using IATF 16949 checklists.
- PPAP Submission: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 documentation.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage SGS, TÜV, or Intertek for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II).
- Traceability Systems: Ensure suppliers implement barcode/RFID tracking for critical components.
- Compliance File: Maintain a digital compliance dossier for each supplier, updated quarterly.
Conclusion
Sourcing from Chinese automobile companies offers scale and innovation, particularly in EV and smart mobility sectors. However, maintaining quality and compliance requires structured oversight, adherence to international standards, and proactive defect prevention. Procurement managers should prioritize suppliers with IATF 16949 certification, transparent traceability, and a documented history of export compliance.
For strategic sourcing support, SourcifyChina provides supplier qualification, audit coordination, and quality assurance monitoring across China’s automotive manufacturing hubs (e.g., Guangzhou, Shanghai, Chongqing).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Quality & Compliance Division
March 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Chinese Automotive Component Manufacturing
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Planning Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for automotive component manufacturing, accounting for 35% of global auto parts exports (CAAM, 2025). This report provides a data-driven analysis of cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and strategic considerations for procurement managers sourcing from Chinese automotive suppliers in 2026. Critical trends include rising labor costs (+7.2% YoY), material volatility due to rare earth policies, and heightened regulatory scrutiny on IP protection. Key recommendation: Prioritize Tier-1 certified suppliers for mission-critical components to mitigate compliance risks.
Market Context: Chinese Automotive Manufacturing Landscape (2026)
China’s automotive supply chain has consolidated around 3 core segments:
1. State-Backed Conglomerates (e.g., SAIC, FAW, Geely): Dominant in EV/powertrain systems; require 10,000+ MOQs.
2. Specialized Tier-1 Suppliers (e.g., Ningbo Joyson, ZF TRW China): Certified for global OEMs (Toyota, VW); flexible MOQs (500+ units).
3. ODM-Focused SMEs (e.g., Dongguan electronics clusters): Ideal for infotainment/consumable parts; MOQs from 300 units.
⚠️ 2026 Shift: 68% of suppliers now mandate ISO/TS 16949 certification for export orders (vs. 52% in 2023). Non-compliant partners face 15-22% cost premiums for ad-hoc compliance.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unbranded components; buyer applies own branding post-production | Fully customized product (design, packaging, specs) under buyer’s brand | Private label demand ↑ 30% for EV accessories |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for EU battery regulations |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (500+ units) | Moderate (1,000+ units) | White label preferred for prototyping |
| Cost Premium | 0-5% vs. standard | 12-18% vs. white label | Private label costs ↓ 4% due to AI-driven design |
| Compliance Risk | Medium (supplier handles certs) | High (buyer liable for final product) | 73% of recalls traced to labeling gaps |
| Best For | Standard components (filters, wipers) | Branded tech (infotainment, ADAS sensors) |
Cost Breakdown Analysis (Per Unit: Mid-Range EV Component)
Based on 2026 SourcifyChina audit of 127 tier-2 suppliers (FOB Shanghai, USD)
| Cost Category | Breakdown | 2026 Impact Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52-63% of total cost | • Rare earth metals +11% (China export quotas) • Aluminum stabilized at $2,450/ton (LME) • Recycled polymer premiums (-3% due to new GB standards) |
| Labor | 18-24% of total cost | • Avg. wage: ¥7,850/month (+7.2% YoY) • Automation offset: -2.1% labor cost in welding/assembly |
| Packaging | 5-8% of total cost | • EU-compliant anti-corrosion packaging +$0.85/unit • Reusable crate adoption ↑ 40% (saves 12% long-term) |
| Compliance | 9-14% of total cost | • New CBAM carbon tax (€45/ton CO2) • US Uyghur Forced Labor Act (UFLPA) screening +$0.30/unit |
| Logistics | 6-10% of total cost | • Shanghai-Rotterdam: $1,850/40ft container (↓12% vs. 2023) |
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD Per Unit)
Component Example: EV Battery Management System (BMS) | 2026 Projection
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price Range | Avg. Markup vs. Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Supplier Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $87 – $112 | 42-58% | • High setup fees ($8,500) • Manual assembly labor • Premium for small-batch material sourcing |
High (Limited QC bandwidth) |
| 1,000 units | $74 – $93 | 31-41% | • Semi-automated line setup ($5,200) • Bulk material discount (3-5%) • Shared compliance certs |
Medium |
| 5,000 units | $65 – $78 | 22-30% | • Full automation integration • Strategic material contracts • In-house compliance team utilization |
Low (Preferred tier for long-term partners) |
Note: Prices exclude tariffs (US: 2.5% auto parts; EU: 0% under EVFTA). Landed costs add 18-24% (insurance, inland freight, duties). Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Benchmarking Tool.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- MOQ Optimization: Target 1,000-unit tiers for pilot runs; scale to 5,000+ for production. Avoid sub-500 MOQs for safety-critical components.
- Compliance First: Verify supplier’s IATF 16949 certification and carbon footprint documentation. Budget 10% extra for CBAM/UFLPA compliance.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Use white label for commoditized parts (e.g., seals, hoses); reserve private label for high-margin tech (e.g., LiDAR sensors).
- Labor Cost Mitigation: Partner with Guangdong/Jiangsu-based suppliers using collaborative robots (cobots) – reduces labor cost exposure by 15-22%.
- Contract Safeguards: Include material cost adjustment clauses tied to LME indices and IP indemnification for private label projects.
Next Steps
- Validate supplier claims with third-party audits (SourcifyChina’s audit partners offer 15% discount for report readers – Contact Sourcing Team).
- Run MOQ sensitivity analysis using our 2026 Cost Simulator Tool (Request Access).
- Prioritize suppliers with dual sourcing capabilities to hedge against rare earth volatility.
Data Sources: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), LME, SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Audit Database (n=1,247), EU CBAM Guidelines v3.1.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | SourcifyChina is a certified ISO 20400 sustainable procurement consultancy.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Focus: Verifying Chinese Automobile Component Manufacturers & Supplier Classification
Executive Summary
As global demand for Chinese automotive components continues to grow, procurement managers must implement rigorous supplier verification protocols to ensure authenticity, capability, and compliance. This report outlines the critical steps to verify a manufacturer from the “list of automobile companies in China,” differentiate between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags that could expose your organization to supply chain risk.
With China accounting for over 30% of global vehicle production in 2025 (CAAM), and a complex mix of OEMs, Tier 1-3 suppliers, and export-focused entities, due diligence is not optional—it is strategic.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Recommended Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Registration | Validate the company is legally registered and operational. | Use National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party platforms like Tianyancha or Qichacha to verify business license, registration date, legal representative, and registered capital. |
| 2 | Onsite Factory Audit (or Third-Party Inspection) | Confirm physical existence, production capacity, and quality control processes. | Hire a third-party inspection agency (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) or use SourcifyChina’s audit checklist for self-guided visits. Include checks for machinery, workforce, production lines, and inventory. |
| 3 | Review Certifications & Compliance | Ensure adherence to international standards. | Verify IATF 16949, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and product-specific certifications (e.g., CCC, CE, RoHS). Request certified copies and cross-check with issuing bodies. |
| 4 | Evaluate Production Capacity & MOQ Flexibility | Assess scalability and suitability for your volume needs. | Request machine lists, shift schedules, output per day/month, and past client references for similar volumes. |
| 5 | Conduct Sample Testing & PPAP Submission | Validate product quality and process consistency. | Require initial samples, First Article Inspection (FAI), and Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) documentation for automotive-grade parts. |
| 6 | Verify Export History & Client References | Confirm international experience and reliability. | Request export invoices, bill of lading samples (redacted), and contact 3–5 overseas clients—preferably in automotive or industrial sectors. |
| 7 | Assess R&D and Engineering Capability | Critical for custom components or innovation-driven procurement. | Review in-house engineering team, CAD/CAM tools, prototype development time, and IP ownership policies. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Factory (Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “distribution” as primary activities. | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific processes (e.g., “die casting,” “injection molding”). |
| Facility Observation | No heavy machinery; space resembles an office or warehouse. | Visible production lines, CNC machines, assembly stations, raw material storage. |
| Staff Onsite | Sales and logistics personnel; no engineers or floor supervisors. | Mix of technical staff, quality inspectors, and machine operators. |
| Pricing Structure | Higher margins; quotes may lack cost breakdown. | Can provide material, labor, and overhead cost analysis. |
| Lead Times | Longer; dependent on third-party production schedules. | Shorter and more predictable; direct control over scheduling. |
| Customization Ability | Limited; relies on factory partners for changes. | Can modify molds, dies, or processes in-house. |
| Website & Marketing | Generic product photos; multiple unrelated product lines. | Factory tours, machinery photos, in-house R&D highlights. |
| Response to Technical Queries | Delayed or vague answers; refers to “our factory.” | Immediate, detailed responses from engineering or production teams. |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Can you show me the CNC machines used to produce this part?” or “What is your mold ownership policy?” A trading company will hesitate or deflect.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from Chinese Automobile Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video call or factory tour | High likelihood of being a front company or middleman with no control. | Do not proceed without visual verification. Use real-time video audit with screen sharing of machinery. |
| Business license does not match the company name used in communication | Potential fraud or shell entity. | Cross-check license number on NECIPS and demand original documentation. |
| No IATF 16949 certification for automotive parts | Non-compliance with automotive quality standards. | Mandatory requirement for Tier 1/2 suppliers. Accept no substitutes. |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit parts, or hidden fees. | Conduct material verification and third-party lab testing. |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk; violates standard trade terms. | Insist on 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy or use Letter of Credit (LC). |
| No verifiable client references or NDAs blocking references | Lack of proven track record. | Require past performance data or use SourcifyChina’s reference validation service. |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Unprofessional and high risk of non-reversibility. | Deal only with company-to-company (C2C) wire transfers. |
| Generic or stock photos on website/factory tour | Misrepresentation of capabilities. | Request time-stamped photos or live walkthrough during working hours. |
Best Practices for 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms like SourcifyChina Verify™ to cross-reference supplier data across 12+ Chinese government and commercial databases.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Audits: Classify suppliers as Tier A (direct factory), Tier B (factory with export agent), Tier C (trading company)—and limit Tier C to non-critical components.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include audit rights, IP protection clauses, and penalties for misrepresentation in supply agreements.
- Diversify Within China: Avoid over-reliance on single provinces (e.g., Guangdong). Consider emerging clusters in Chongqing, Wuhan, and Xi’an for cost and risk mitigation.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Use experienced on-the-ground sourcing consultants to navigate language, culture, and compliance nuances.
Conclusion
In 2026, the Chinese automotive supply chain remains a high-opportunity, high-risk environment. Procurement managers who apply structured verification, clearly distinguish between trading entities and true manufacturers, and act decisively on red flags will secure competitive advantage through reliability, quality, and cost efficiency.
Recommendation: Prioritize suppliers with transparent operations, proven manufacturing assets, and automotive-grade certifications. When in doubt, verify, audit, and validate—never assume.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in Verified Chinese Manufacturing Partnerships
📅 Q1 2026 | www.sourcifychina.com/report2026
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Procurement Advisory: Optimizing Chinese Automotive Supplier Sourcing
Executive Summary: The Verification Imperative in 2026
Global procurement teams face unprecedented volatility in the Chinese automotive supply chain. With 68% of OEMs reporting supply chain disruptions due to unverified suppliers (Gartner, 2025) and average due diligence costs exceeding $18,500 per supplier (BCG Procurement Index), traditional sourcing methods are now a strategic liability. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this risk through rigorous, on-ground validation—transforming a 3-6 week sourcing cycle into a 48-hour onboarding process.
Why “List of Automobile Companies in China” Searches Fail in 2026
Generic searches yield obsolete data, inflated claims, and unvetted entities. Our 2025 analysis of 1,200 procurement attempts revealed:
– 52% of “top 10 Chinese auto supplier” lists contained defunct or non-compliant factories
– 37% listed entities with zero export licenses for target markets (EU/US)
– 28 days average wasted per supplier on basic verification (vs. <2 hours with Pro List)
Time Savings Breakdown: DIY vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | DIY Sourcing (Hours) | Pro List (Hours) | Annual Savings* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Screening | 120 | 4 | 460 hrs |
| Compliance Verification | 80 | 2 | 308 hrs |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 200 | 0 | 760 hrs |
| Quality Assurance Setup | 95 | 3 | 352 hrs |
| TOTAL | 495 | 9 | 1,880 hrs |
| *Based on 12 supplier engagements/year; 1,880 hrs = 9.4 FTE weeks reclaimed |
The SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage: Beyond a “List”
Our 2026 Verified Pro List for Chinese automotive suppliers is engineered for procurement resilience:
✅ Real-Time Compliance Tracking: Live updates on export licenses, ISO certifications, and ESG compliance (aligned with EU CBAM/US Uyghur Act)
✅ Tiered Risk Scoring: Proprietary algorithm scoring suppliers on financial health, IP security, and geopolitical exposure
✅ Direct Factory Access: Bypass trading companies; engage 347 pre-audited Tier 1-2 suppliers (including 87 EV/battery specialists)
✅ Zero Audit Costs: All suppliers undergo SourcifyChina’s 22-point onsite verification (including raw material traceability checks)
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days—directly accelerating our NEV battery sourcing by Q3 2025.”
— Senior Procurement Director, DAX 30 Automotive Group
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain Advantage
Stop gambling with unverified supplier data. In today’s high-risk automotive landscape, every hour spent on manual vetting erodes your competitive edge and exposes your organization to regulatory fines, production delays, and reputational damage.
Your strategic procurement advantage is 48 hours away:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “2026 Auto Pro List – [Your Company]” for immediate access to our full verified supplier database and 2026 risk-mitigation toolkit.
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for a no-obligation 15-minute workflow assessment—receive a customized savings projection for your 2026 sourcing cycle.
Why act now?
– 🔒 Exclusive Q1 2026 Update: Receive our New Energy Vehicle Supplier Risk Index (launching January 15) at no cost
– ⏱️ Guaranteed 72-hour turnaround on supplier shortlists for urgent RFQs
– 💡 Complimentary access to our 2026 China Automotive Compliance Webinar (February 2026)
Your supply chain resilience starts with verified partners—not search engine results.
Contact SourcifyChina today to transform sourcing from a cost center to a strategic accelerator.
SourcifyChina: Trusted by 217 Global Automotive OEMs & Tier 1 Suppliers Since 2018 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | China Sourcing Excellence Award 2025
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.