The global machine tool market, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. Within this expanding landscape, the lathe machine segment plays a pivotal role, with the headstock—housing the spindle and drive system—being a critical component determining performance, accuracy, and durability. As industries increasingly prioritize automation and high-speed machining, demand for advanced lathe headstocks has surged. Mordor Intelligence estimates the machine tools market to exceed USD 140 billion by 2028, fueled by technological advancements and regional industrialization, particularly in Asia-Pacific. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of reliable headstock manufacturers capable of delivering innovation, precision, and robust engineering. In this context, the following list highlights the top 10 lathe headstock manufacturers shaping the future of turning technology.
Top 10 Lathe Headstock Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Sherline
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sherline.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture the world’s most complete line of precision milling machines, lathes, and chucker lathes (also known as Mini or Micro Mills and Lathes)….
#2 CITIZEN MACHINERY CO., LTD.
Website: cmj.citizen.co.jp
Key Highlights: The lineup of products from Citizen Machinery, the world’s top market share holder in the world of CNC automatic lathes….
#3 Company
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1961
Website: iemca.com
Key Highlights: Since 1961, IEMCA designs and manufactures automatic bar feeders for lathes. IEMCA’s range includes bar feeder solutions for every lathe type. (US / US)…
#4 TAIG Tools
Domain Est. 1999
Website: taigtools.com
Key Highlights: At TAIG Tools we manufacture precision desktop Milling Machines, Lathes (otherwise known as Micro Mills and Micro Lathes) and a complete line of accessories….
#5 Swiss-type lathes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tornos.com
Key Highlights: Swiss-type lathes | Sliding headstock lathes ; Swiss DT 10, Ø 10 mm, 6 ; Swiss DT 13 HP, Ø 13 mm, 5 ; Swiss DT 13 S · Ø 13 mm, 5 ; Swiss DT 26 HP, Ø 25.4 mm, 5/6….
#6 Star Micronics GB
Domain Est. 2001
Website: stargb.com
Key Highlights: Leading UK supplier of CNC sliding and fixed headstock lathes. Star Micronics GB is the leading provider of CNC sliding head (Swiss-type) lathe solutions ……
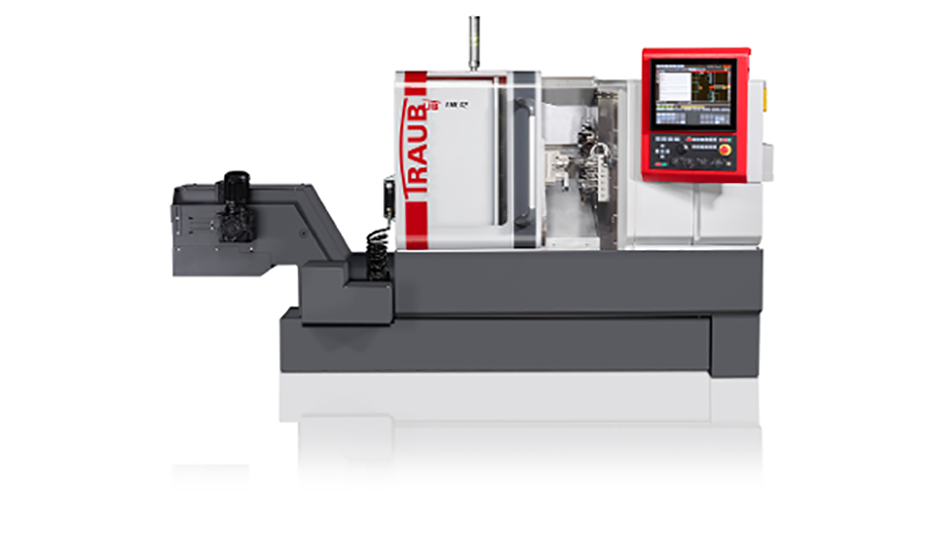
#7 TRAUB
Domain Est. 2001
Website: index-group.com
Key Highlights: CNC sliding headstock machines from TRAUB are designed for exact and productive manufacturing of long and slim parts with a maximum diameter of 32 mm. The ……
#8 Manual Lathe
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sunmaster-cnc.com
Key Highlights: SUN MASTER offers various manual metal lathe machines divided into several categories by different sizes and different applications, such as geared head, ……
#9 Lathe Headstock Spindle
Domain Est. 2012
Website: en.okada-china.com
Key Highlights: Okada Intelligence focuses on the design, development and production of Lathe Headstock Spindle, Bt50 Spindle, Headstock In Lathe Machine, ……
#10 WEILER
Website: weiler.de
Key Highlights: WEILER Precision Lathes: Lathes Made in Germany. Whether for industry, craftsmanship or training: WEILER stands for highest quality in metalworking for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lathe Headstock

2026 Market Trends for Lathe Headstock
The global lathe headstock market is poised for dynamic transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industrial demands, and strategic shifts in manufacturing. Key trends shaping the market include:
Advancements in Smart and Connected Headstocks
By 2026, integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI-driven monitoring systems into lathe headstocks will become mainstream. Smart headstocks equipped with embedded sensors will enable real-time condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization. This shift enhances machine uptime, reduces unplanned downtime, and supports Industry 4.0 initiatives across automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering sectors.
Growing Demand for High-Precision and High-Speed Spindles
Industries requiring micron-level accuracy, such as medical device manufacturing and aerospace components, are pushing demand for headstocks with higher RPM capabilities and improved thermal stability. Manufacturers are focusing on advanced bearing technologies (e.g., ceramic hybrid bearings) and precision cooling systems to minimize thermal deformation and vibration, ensuring consistent part quality.
Increased Adoption in Emerging Economies
Rising industrialization in Asia-Pacific (particularly India, Vietnam, and Indonesia), along with government initiatives promoting domestic manufacturing (e.g., “Make in India”), will drive demand for cost-effective, reliable lathes and headstock components. Localized production and partnerships with regional machine tool builders will be critical for market penetration.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and energy costs are pushing OEMs to design energy-efficient headstock motors and drive systems. By 2026, headstocks featuring regenerative braking, optimized motor designs, and reduced lubrication requirements will gain favor, aligning with broader ESG goals in industrial operations.
Customization and Modular Designs
End-users increasingly demand modular headstock solutions that allow for easy retrofitting and adaptability across different machining tasks. Flexibility in spindle nose configurations, speed ranges, and power outputs enables manufacturers to serve niche applications without investing in entirely new machines.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical uncertainties and past disruptions have prompted a shift toward localized sourcing of critical components. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to diversify supply chains and increase regional production of headstock assemblies to mitigate risks and reduce lead times.
In summary, the 2026 lathe headstock market will be defined by intelligence, precision, sustainability, and adaptability, with innovation centered on enhancing performance while supporting the evolving needs of modern manufacturing ecosystems.
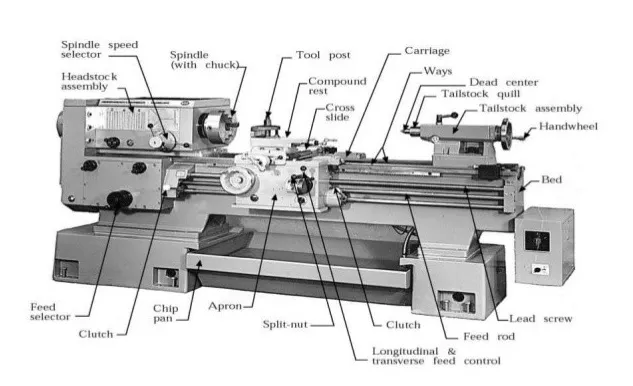
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Lathe Headstock (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a lathe headstock—whether as a component, replacement part, or integrated into a machine—presents several critical challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to performance issues, legal liabilities, and financial losses.
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving headstocks that fail to meet required precision and durability standards. Many suppliers, especially in low-cost manufacturing regions, may lack rigorous quality control processes. This can result in dimensional inaccuracies, improper bearing fits, or substandard materials that compromise spindle runout, thermal stability, and overall machining accuracy. Without clear, detailed technical specifications (including tolerances, material grades, and surface finishes), buyers risk receiving parts that don’t integrate properly or degrade quickly under load.
Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Designs
A significant IP risk arises when sourcing from unverified suppliers who may offer headstocks that mimic branded OEM designs. These products are often reverse-engineered without authorization, infringing on patents, trademarks, or trade secrets. Purchasing such components exposes the buyer to legal action, especially if the final machine is sold commercially. Additionally, counterfeit headstocks typically use inferior materials and manufacturing methods, leading to premature failure and safety hazards.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers should provide full documentation, including material certifications, heat treatment records, and quality inspection reports. However, many vendors—particularly smaller or offshore manufacturers—fail to provide these, making it difficult to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN). Without traceability, it becomes nearly impossible to diagnose failures or defend against liability claims in case of malfunction.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Even if initial samples meet expectations, ongoing production may vary due to inconsistent machining practices, uncalibrated equipment, or lack of process controls. This variability affects critical aspects like bearing preload, gear meshing, and alignment—directly impacting spindle performance and tool life. Suppliers without certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) are more prone to these inconsistencies.
Hidden IP Licensing Obligations
Some headstock designs incorporate patented technologies (e.g., specific bearing arrangements, damping systems, or gearbox configurations). Even if a supplier provides a technically sound unit, the end-user may unknowingly violate IP rights when using or reselling the machine. Failing to conduct due diligence on IP clearance—or assuming the supplier has handled licensing—can result in costly legal disputes.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Warranty Enforcement
Low-cost headstock suppliers may offer limited technical support or warranties that are difficult to enforce internationally. If quality issues arise post-purchase, resolving them can be time-consuming and expensive, especially if spare parts or expert service are unavailable locally.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should vet suppliers thoroughly, demand full technical and compliance documentation, conduct on-site audits if possible, and consult legal experts to ensure IP compliance—particularly when integrating headstocks into commercial machinery.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lathe Headstock
Overview
This guide outlines the logistics procedures and compliance requirements for the safe, efficient, and legal handling, transportation, and use of a lathe headstock—whether as a standalone component or part of a complete lathe machine. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational safety, regulatory compliance, and equipment longevity.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging and handling are essential to prevent damage during storage and transit.
– Use custom-fitted wooden crates or heavy-duty steel frames to secure the headstock.
– Apply anti-corrosion coatings and include desiccants to protect against moisture.
– Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and weight specifications.
– Use lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, overhead cranes) with appropriate slings; never lift by attached components such as gears or motor mounts.
Transportation Requirements
Ensure safe and compliant movement of the headstock across supply chains.
– Secure the headstock with straps or bolting within the transport vehicle to prevent shifting.
– Comply with local and international freight regulations (e.g., IMDG for sea, ADR for road in Europe).
– For oversized shipments, obtain necessary permits and use escort vehicles if required.
– Maintain environmental controls (temperature, humidity) for precision components during long hauls.
Import/Export Compliance
Adhere to international trade laws when shipping across borders.
– Verify Harmonized System (HS) code for lathe components (e.g., 8466.30 for machine tool parts).
– Obtain required export licenses, especially for high-precision or dual-use machinery.
– Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and bill of lading.
– Comply with International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR) if applicable.
Safety & Regulatory Standards
Ensure the headstock meets applicable safety and performance standards.
– Comply with ISO 230 (Acceptance tests for machine tools) and ISO 16016 (Safety of machine tools).
– In the EU, ensure CE marking per the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC.
– In the U.S., follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910.212 (General requirements for all machines).
– Include user manuals with risk assessments and safety instructions in local languages.
Installation & Operational Compliance
Follow manufacturer and regulatory guidelines during setup and use.
– Conduct alignment checks and vibration analysis during installation.
– Ensure proper grounding and electrical compliance (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60204-1 internationally).
– Train operators on emergency stops, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and maintenance routines.
– Maintain logs for inspections, repairs, and safety audits.
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
Manage end-of-life headstocks responsibly.
– Recycle metals (cast iron, steel, aluminum) in accordance with local waste regulations.
– Dispose of lubricants and greases as hazardous waste per EPA or equivalent bodies.
– Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in Europe for electronic components.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate records to support compliance and traceability.
– Keep copies of inspection certificates, calibration reports, and conformity declarations.
– Store shipping documents, customs filings, and safety data sheets (SDS) for at least 7 years.
– Use asset tracking systems (e.g., barcodes, RFID) for lifecycle management.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and strict compliance with safety, trade, and environmental regulations are critical for the responsible handling of lathe headstocks. By following this guide, organizations can ensure uninterrupted operations, avoid legal penalties, and promote workplace safety.
In conclusion, sourcing a lathe headstock requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, material quality, compatibility with existing machinery, and supplier reliability. It is essential to prioritize durability, precision, and performance to ensure optimal machining results and minimize downtime. Whether opting for OEM parts, aftermarket alternatives, or custom fabrication, due diligence in vendor selection, cost analysis, and adherence to industry standards will significantly impact the long-term efficiency and reliability of the lathe system. Proper sourcing not only enhances machine performance but also contributes to improved safety, reduced maintenance costs, and extended equipment lifespan.