The global laser annealing market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for advanced semiconductor manufacturing, flat-panel displays, and emerging applications in microelectronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser annealing market was valued at USD 482 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 720 million by the end of the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of excimer and solid-state lasers in precision annealing processes, particularly in next-generation logic and memory device fabrication. As semiconductor nodes continue to shrink and demand for low-temperature processing increases, manufacturers are investing heavily in high-throughput, high-precision laser annealing systems. In this competitive landscape, a select group of global manufacturers leads in innovation, reliability, and market reach—shaping the future of advanced materials processing.
Top 10 Laser Annealing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
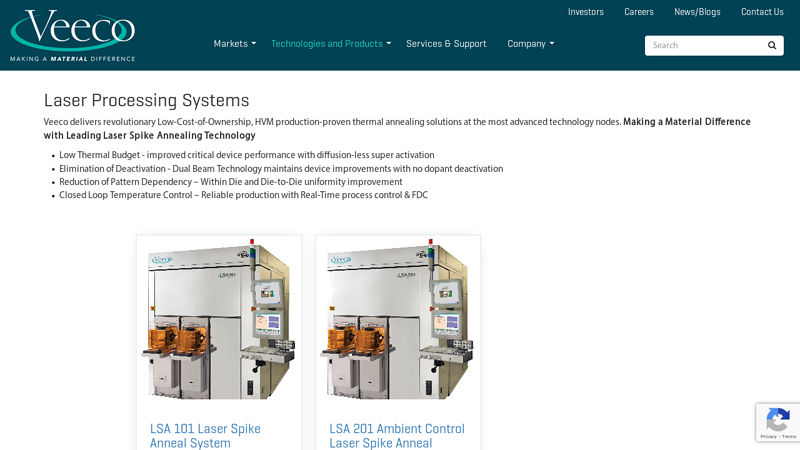
#1 Laser Processing Systems
Domain Est. 1995
Website: veeco.com
Key Highlights: Laser Processing Systems. Veeco has developed revolutionary technology products to enable thermal annealing solutions at the most advanced technology nodes….
#2 Laser Annealing Technology
Domain Est. 1999
Website: tjslasers.com
Key Highlights: Discover laser annealing technology for permanent, high-contrast marking that maintains surface integrity across critical industries like medical, ……
#3 Explore Laser Annealing Solutions
Domain Est. 2006
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Laser annealing allows manufacturers to create markings on metal, plastic and other materials without disrupting the surface. It is most effective on steel, ……
#4 Laser Annealing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: keyence.com
Key Highlights: Laser annealing is a common marking method that uses a powerful laser to create controlled heat on the surface of a material….
#5 Laser Marking
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mecco.com
Key Highlights: What is Laser Annealing? Laser annealing refers to localized heating that changes the color of the material being heated depending on temperature of the heat….
#6 Annealing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Annealing is a laser marking procedure used to gently apply long-lasting markings to metals. No material is removed in the process….
#7 IPG Photonics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#8 Processes Laser Annealing
Domain Est. 1999
Website: fobalaser.com
Key Highlights: Annealing marking is when an oxide layer is created on ferrous metals (iron, steel, high-grade steel) and titanium through localized heating….
#9 Laser Annealing Machining
Domain Est. 2000
Website: permanentmarking.com
Key Highlights: Laser annealing is an advanced material processing technique used to create high-contrast markings on metals like steel and stainless steel….
#10 Laser Annealing for Monolithic Magnetic Sensors
Domain Est. 2021
Website: lasersensorformation.com
Key Highlights: The award-winning microVEGA™ xMR system provides high-throughput laser annealing for monolithic magnetic sensor formation….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Laser Annealing

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Laser Annealing
As the semiconductor and advanced display industries continue to evolve toward higher performance, miniaturization, and energy efficiency, laser annealing is poised to play a pivotal role in manufacturing processes by 2026. The global laser annealing market is expected to experience robust growth, driven by technological advancements, rising demand for advanced flat-panel displays and next-generation semiconductors, and the increasing adoption of flexible and transparent electronics.
1. Rising Demand in Semiconductor Manufacturing
By 2026, laser annealing technologies—particularly millisecond laser annealing (MSLA) and solid-phase crystallization (SPC) using excimer lasers—are anticipated to become increasingly critical in advanced semiconductor fabrication. With the industry pushing beyond the 3nm node and exploring gate-all-around (GAA) and complementary FET (CFET) architectures, precise thermal control during doping and crystallization processes is essential. Laser annealing offers localized, ultra-fast thermal processing with minimal thermal damage to surrounding materials, making it ideal for sub-5nm node manufacturing. Foundries such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel are expected to expand their use of laser-based annealing to improve dopant activation and reduce junction leakage.
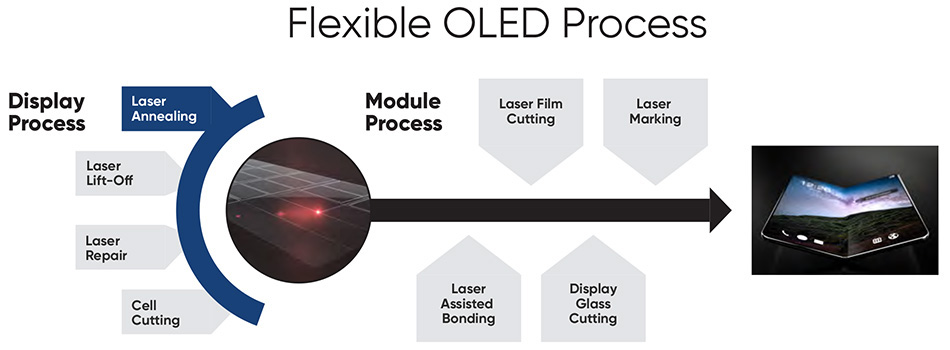
2. Expansion in Display Technologies
The flat-panel display sector, especially low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and oxide semiconductor backplanes for OLED and micro-LED displays, will remain a dominant application area for laser annealing. As consumer electronics demand high-resolution, energy-efficient, and foldable displays, manufacturers are relying more on excimer laser annealing (ELA) to convert amorphous silicon into polycrystalline silicon with superior electron mobility. By 2026, innovations in large-area and roll-to-roll laser annealing systems are expected to support the production of flexible and transparent displays, particularly for foldable smartphones, wearables, and augmented reality (AR) devices.
3. Technological Innovations and Equipment Advancements
Laser source development, including higher repetition rates, improved beam uniformity, and enhanced energy efficiency, will drive wider adoption. Companies such as Gigaphoton, Cymer (an ASML company), and Coherent are expected to lead in delivering high-power, stable excimer and solid-state lasers tailored for industrial annealing applications. Integration with machine learning for real-time process monitoring and optimization will also enhance yield and throughput in high-volume manufacturing environments.
4. Growth in Emerging Applications
Beyond semiconductors and displays, laser annealing is gaining traction in photovoltaics (especially perovskite and tandem solar cells), 2D materials processing (e.g., graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides), and flexible electronics. These applications benefit from the non-contact, selective heating capabilities of lasers, enabling precise material modification without damaging substrates. By 2026, pilot production lines incorporating laser annealing for next-gen solar cells and bio-integrated sensors are expected to scale, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific—led by China, South Korea, and Taiwan—will continue to dominate the laser annealing market due to its concentration of semiconductor foundries and display manufacturers. Government initiatives supporting domestic semiconductor self-reliance, especially in China, are expected to boost investments in advanced fabrication tools, including laser annealing systems. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see growth driven by R&D in quantum computing, photonics, and advanced packaging, where laser annealing supports novel material integration.
6. Challenges and Outlook
Despite its advantages, the high capital cost of laser annealing equipment and the complexity of process integration remain barriers to widespread adoption, particularly for small- and medium-sized enterprises. However, as tool reliability improves and production volumes increase, costs are expected to decline gradually by 2026. Additionally, sustainability concerns may prompt development of more energy-efficient laser systems and eco-friendly manufacturing workflows.
Conclusion
By 2026, the laser annealing market is projected to expand significantly, fueled by the convergence of semiconductor scaling, display innovation, and emerging applications in clean energy and flexible electronics. With ongoing advancements in laser technology and process integration, laser annealing will transition from a niche enabler to a mainstream manufacturing solution across high-tech industries.
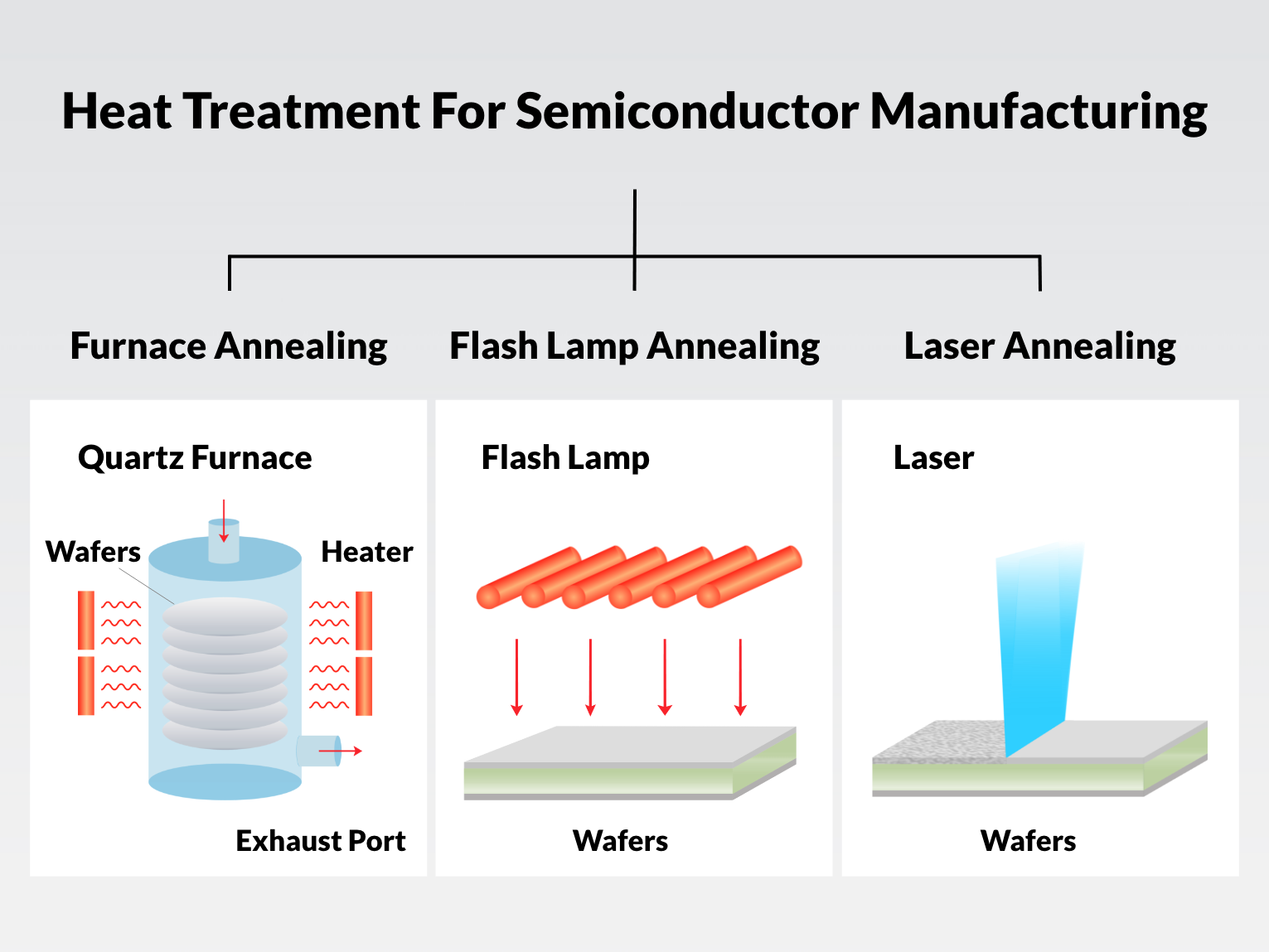
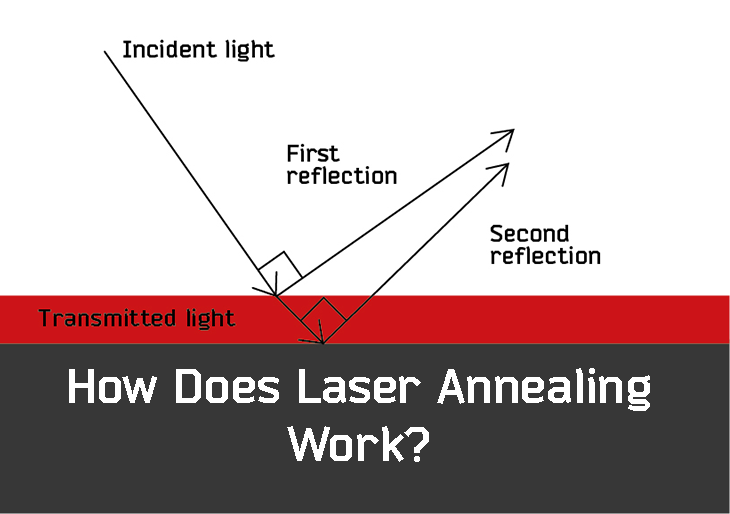
H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Annealing Technology – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing Laser Annealing (LA) technology—whether as equipment, process development, or integrated services—presents significant challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to project delays, compromised performance, legal disputes, and loss of competitive advantage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Process Repeatability
Laser Annealing performance is highly sensitive to laser parameters (wavelength, pulse duration, fluence), beam profile, and environmental conditions. Sourcing from vendors with inadequate process control or insufficient metrology can result in non-uniform annealing, leading to device yield loss and reliability issues. -
Lack of Standardized Qualification Metrics
Unlike established processes such as rapid thermal annealing (RTA), LA lacks universally accepted quality benchmarks. Buyers may struggle to evaluate vendor claims without clear metrics for crystal quality, dopant activation, defect density, or surface morphology. -
Insufficient Integration with Downstream Processes
Laser Annealing must interface seamlessly with pre- and post-anneal steps (e.g., deposition, lithography, etching). Sourcing equipment or services without considering integration compatibility can result in particle contamination, stress-induced defects, or thermal mismatch. -
Limited Expertise in Vendor Support
LA requires specialized knowledge in laser physics, materials science, and semiconductor processing. Vendors with weak technical support may fail to troubleshoot process drift or optimize annealing for specific materials (e.g., Si, Ge, III-V compounds). -
Hidden Maintenance and Downtime Costs
High-power lasers and optical components degrade over time. Vendors may understate maintenance requirements or lack robust service networks, leading to unexpected downtime and increased cost of ownership.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
-
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Development
When co-developing LA processes with vendors, contracts often fail to clarify IP ownership. Ambiguity can result in disputes over who owns improvements, process recipes, or integration methods—potentially blocking internal scaling or product commercialization. -
Risk of Infringing Third-Party Patents
Laser Annealing is a mature field with extensive patent portfolios held by major equipment manufacturers and research institutions. Sourcing solutions without freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis may expose buyers to infringement claims, especially in areas like excimer laser designs or mask-based annealing techniques. -
Inadequate Protection of Trade Secrets
Process recipes (e.g., multi-shot annealing sequences, temperature ramp profiles) often constitute critical trade secrets. Vendors may not have sufficient confidentiality safeguards, risking exposure during joint development or equipment servicing. -
Overreliance on Proprietary Black-Box Systems
Some vendors offer LA tools with closed software and locked process parameters. While convenient, this limits process transparency and control, making it difficult to innovate, qualify, or transfer processes internally—effectively ceding long-term IP control to the vendor. -
Global IP Enforcement Variability
Sourcing from international vendors introduces complexities in IP enforcement. Jurisdictional differences in patent law and weak IP protection in certain regions increase the risk of unauthorized replication or technology leakage.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough technical due diligence, including on-site process audits and sample testing.
- Demand transparent service level agreements (SLAs) and detailed maintenance plans.
- Engage legal counsel early to define IP ownership, licensing terms, and confidentiality in contracts.
- Perform comprehensive FTO analysis before adopting new LA tools or processes.
- Favor vendors offering modular, open-architecture systems to retain process control and IP rights.
Proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls ensures that Laser Annealing adoption enhances, rather than hinders, technological advancement and competitive positioning.
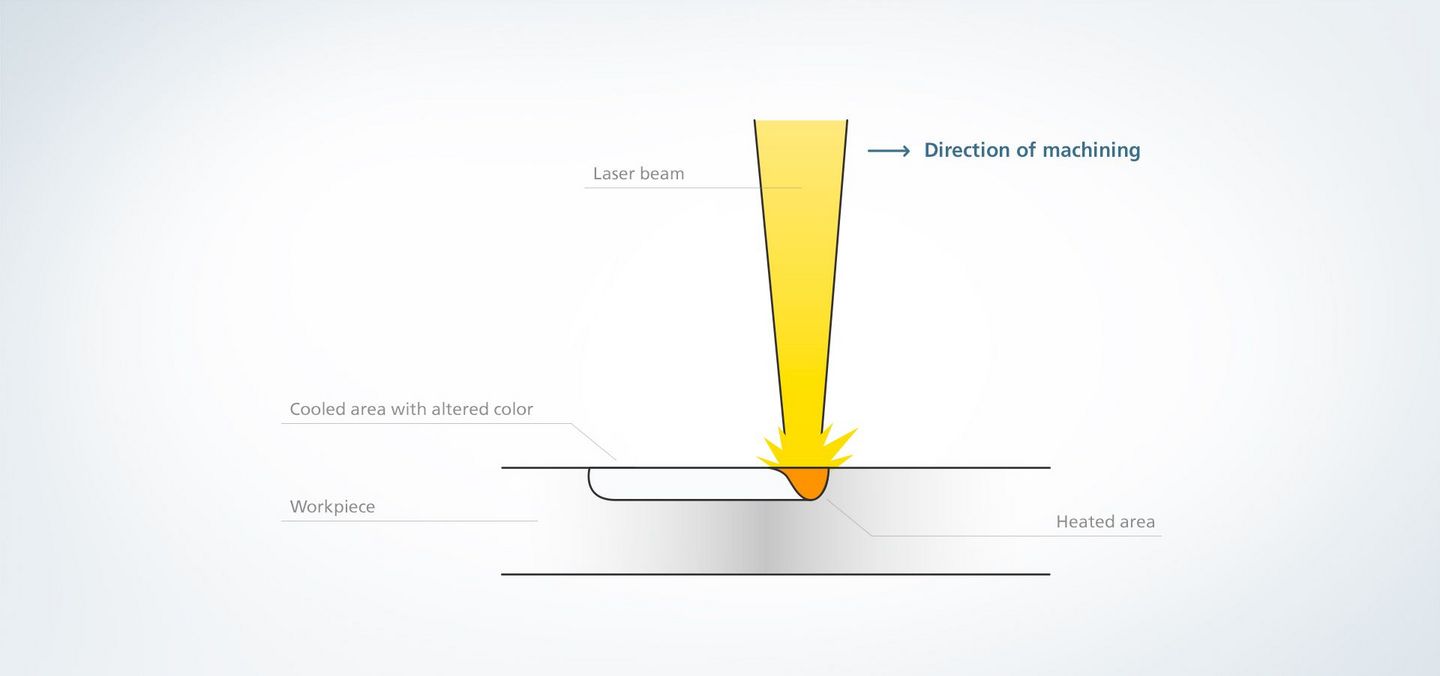
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Laser Annealing
Laser annealing is an advanced semiconductor processing technique used to activate dopants and repair crystal lattice damage without causing thermal stress to surrounding materials. Due to its precision and integration into high-tech manufacturing environments—particularly in semiconductor fabrication—proper logistics and regulatory compliance are essential for safe and efficient operations. This guide outlines key considerations under the H2 category of logistics and compliance.
H2.1 Equipment Transportation & Installation
- Pre-shipment Inspection: Ensure laser annealing systems are securely packaged with shock-absorbing materials and environmental protection (e.g., moisture barriers) to prevent damage during transit.
- Qualified Carriers: Use logistics providers experienced in handling high-value, sensitive semiconductor equipment. Temperature- and humidity-controlled transport is recommended.
- Site Readiness: Confirm that the receiving facility meets infrastructure requirements:
- Stable power supply with surge protection
- Vibration-isolated foundation
- Cleanroom environment (ISO Class 5 or better, as required)
- Adequate ventilation and exhaust systems
- Installation by Certified Technicians: Only factory-trained engineers should perform installation and calibration to ensure operational safety and regulatory alignment.
H2.2 Regulatory Compliance
- Laser Safety (IEC 60825-1 / ANSI Z136.1):
- Classify the laser system according to output power and wavelength.
- Implement engineering controls (interlocks, beam enclosures) and administrative controls (training, access restriction).
- Post appropriate warning labels and laser hazard signage.
- Electrical Safety (UL, CE, or CSA Certification):
- Verify equipment meets regional electrical safety standards prior to installation.
- Environmental Regulations:
- Comply with local and international standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH) for materials used in equipment components.
- Manage waste generated during maintenance (e.g., used optics, contaminated wipes) per hazardous waste guidelines.
- Workplace Safety (OSHA or Equivalent):
- Conduct risk assessments for laser radiation, electrical hazards, and compressed gases (if used).
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density (OD) rating.
H2.3 Handling of Consumables & Gases
- Gas Supply Logistics (if applicable for assist gases):
- Use only certified gas cylinders with proper labeling and storage (upright, secured, ventilated).
- Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all gases (e.g., N₂, O₂, or specialty mixtures).
- Implement leak detection and emergency shutoff systems.
- Optical Component Maintenance:
- Log and track replacement of lenses, mirrors, and filters.
- Dispose of used optics containing coatings or contaminants per local environmental regulations.
H2.4 Documentation & Auditing
- Compliance Records:
- Maintain logs for:
- Laser safety inspections
- Equipment maintenance and calibration
- Personnel training and certifications
- Incident reports (if any)
- Audit Preparedness:
- Conduct internal audits annually to ensure adherence to ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSAS 18001 (or ISO 45001) standards.
- Be prepared for external audits by regulatory bodies or customers.
H2.5 Training & Operational Protocols
- Operator Certification:
- All personnel must complete laser safety training accredited by an authorized body.
- Refresher courses required annually or after equipment upgrades.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
- Develop and enforce SOPs for startup, operation, shutdown, and emergency response.
- Include lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures for maintenance.
H2.6 Import/Export Compliance (For Cross-Border Shipments)
- Export Controls:
- Verify if the laser annealing system falls under dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR).
- Obtain necessary export licenses for high-power or precision laser systems.
- Customs Documentation:
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Classify equipment using correct HS codes (e.g., 8543.70 for electrical apparatus for semiconductor manufacturing).
H2.7 Emergency Preparedness
- Laser-Related Emergencies:
- Establish protocols for laser misfire, beam exposure, or fire.
- Equip facilities with laser-safe fire extinguishers and emergency power-off switches.
- Spill & Leak Response:
- Provide spill kits for coolant or gas leaks.
- Train staff in emergency shutdown and evacuation procedures.
Adhering to this H2 logistics and compliance framework ensures safe, legal, and efficient deployment and operation of laser annealing systems in semiconductor and advanced manufacturing environments. Regular review and updates to policies are recommended to align with evolving regulations and technological advancements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Laser Annealing:
In conclusion, sourcing laser annealing technology presents a strategic opportunity to enhance semiconductor manufacturing processes with improved precision, reduced thermal damage, and increased throughput. Its ability to enable low-temperature processing while achieving high-quality dopant activation makes it particularly valuable for advanced node fabrication and next-generation devices, including flexible electronics and 3D-integrated circuits. When sourcing laser annealing systems, it is essential to evaluate equipment performance, vendor expertise, cost of ownership, and compatibility with existing production lines. Partnering with established suppliers offering proven technology, strong support, and scalability ensures a reliable integration path. As demand for high-performance, energy-efficient devices grows, investing in laser annealing positions manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, supporting long-term competitiveness in the semiconductor industry.