Sourcing Guide Contents
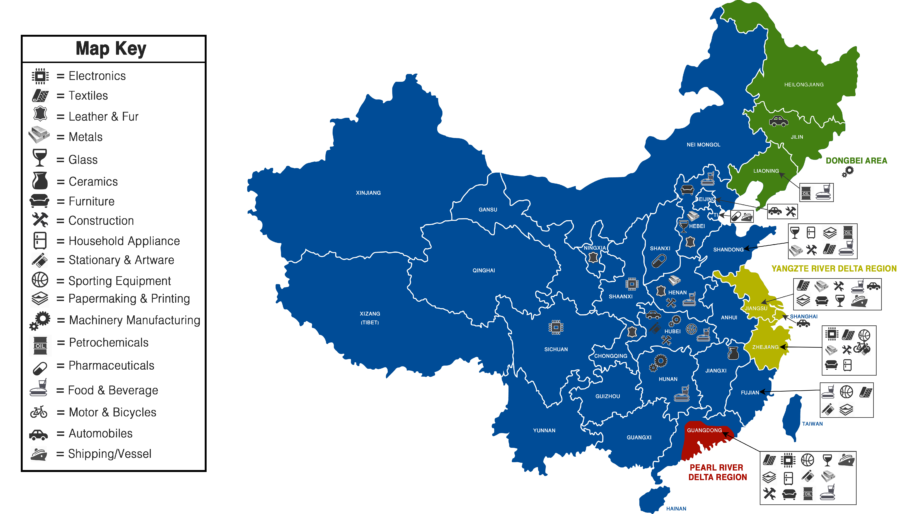
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Laos China Railway Company Limited

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Clarification & Strategic Guidance on “Laos China Railway Company Limited” Sourcing
To: Global Procurement Managers
From: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: October 26, 2026
Subject: Critical Clarification & Strategic Pathway for Sourcing Related to the China-Laos Railway Project
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception: “Laos China Railway Company Limited” (LCRC) is not a physical product or commodity manufactured in China. It is the official name of the joint venture company (established 2018) responsible for operating and maintaining the China-Laos Railway. LCRC is a 50:50 partnership between China Railway (via China Railway International) and Lao State Railway Enterprise. You cannot “source” LCRC as a product from Chinese factories.
This report clarifies the nature of LCRC, identifies the actual industrial clusters for sourcing railway infrastructure components, rolling stock, and engineering services used in projects like the China-Laos Railway, and provides actionable sourcing strategies for procurement managers targeting this sector.
Critical Clarification: Understanding “Laos China Railway Company Limited” (LCRC)
| Aspect | Reality Check | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Entity | Operating company (not a product). Headquartered in Vientiane, Laos. | Cannot be sourced as a “product.” Sourcing attempts for “LCRC” will lead to fraud or misdirected RFQs. |
| Ownership | 50% China Railway (State-owned), 50% Lao State Railway Enterprise (State-owned). | Direct procurement requires engagement with Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs) or their approved suppliers. |
| Core Function | Manages railway operations, maintenance, ticketing, and logistics on the Vientiane-Boten line. | Relevant sourcing opportunities exist for suppliers to LCRC (e.g., spare parts, maintenance services). |
| Common Misconception | Mistaken for a manufacturer or product due to the name structure. | High fraud risk: Scammers pose as “LCRC suppliers.” Verify all claims via official channels (MOFCOM, China Railway). |
Key Takeaway: Focus sourcing efforts on components, services, and suppliers supporting railway projects like the China-Laos Railway, not the operating company itself.
Strategic Sourcing Pathways: Industrial Clusters for Railway Infrastructure
While LCRC itself isn’t sourced, the railway infrastructure, rolling stock, and engineering services it relies on are manufactured/supplied from key Chinese industrial clusters. Below are the primary hubs for procuring goods/services for projects like the China-Laos Railway:
1. Rolling Stock (Locomotives, Passenger/Freight Cars)
- Dominant Cluster: Hunan Province (Changsha & Zhuzhou)
- Why: Home to CRRC Zhuzhou Locomotive (world’s largest rail transit equipment manufacturer) and CRRC Zhuzhou Institute. Supplied all EMUs and diesel locomotives for the China-Laos Railway.
- Capabilities: High-speed trains, EMUs, heavy-haul freight locomotives, traction systems.
- Secondary Cluster: Jilin Province (Changchun)
- Why: CRRC Changchun Railway Vehicles (specializes in passenger coaches, metro cars).
2. Track Infrastructure & Electrification Systems
- Dominant Cluster: Jiangsu Province (Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou)
- Why: Concentration of high-precision steel producers (e.g., Baowu Steel subsidiaries), signaling systems (CCT Railway Signal), and overhead line suppliers. Nanjing is a hub for railway R&D.
- Secondary Cluster: Hebei Province (Tangshan)
- Why: Major steel production (Tangshan Iron & Steel) for rails, sleepers, and structural components.
3. Engineering, Procurement & Construction (EPC) Services
- Dominant Cluster: Beijing & Shanghai
- Why: Headquarters of state-owned EPC giants: China Railway Group (CREC), China Communications Construction Company (CCCC), and China Railway Construction Corporation (CRCC). These firms executed the China-Laos Railway construction.
- Secondary Cluster: Sichuan Province (Chengdu)
- Why: Key hub for tunneling, bridge engineering, and mountain railway expertise (critical for Laos’ terrain).
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for Railway Components
This table compares regions for sourcing railway components/services used by operators like LCRC**, not “LCRC” itself.
| Region | Core Products/Services | Price Competitiveness | Quality & Compliance | Typical Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunan (Zhuzhou) | Rolling Stock (Locomotives, EMUs), Traction Systems | ★★☆☆☆ (Premium pricing; SOE-dominated) |
★★★★★ (CRRC = global Tier-1; meets UIC/EN/ISO; strict state oversight) |
12-18 months (Custom projects) |
High-value rolling stock where safety/compliance is non-negotiable. Mandatory for major operators. |
| Jiangsu (Nanjing) | Rails, Signaling Systems, Overhead Catenary, Precision Steel | ★★★★☆ (Competitive; high-scale production) |
★★★★☆ (Top-tier domestic quality; strong export compliance; some mid-tier suppliers) |
6-12 months | Critical infrastructure components needing precision engineering & reliability. Ideal for EPC partners. |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | Electrical Subsystems, Sensors, Maintenance Tools | ★★★★★ (Most cost-competitive; SME-driven) |
★★★☆☆ (Variable; requires stringent vetting; strong in niche electronics) |
3-8 months | Non-safety-critical subsystems, IoT sensors, maintenance equipment. High risk/reward; needs SourcifyChina oversight. |
| Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Railway IT Systems, Passenger Infotainment, Telecom | ★★★★☆ (Competitive for tech) |
★★★★☆ (Strong in electronics; compliance varies by subsystem) |
4-10 months | Digital systems, passenger experience tech. Not for core mechanical/electrical rail infrastructure. |
Critical Notes:
– SOE Dominance: Core railway infrastructure (rolling stock, rails, signaling) is controlled by Chinese SOEs (CRRC, CREC). They rarely sell directly to foreign buyers; procurement flows through EPC contracts or authorized distributors.
– Compliance is Non-Negotiable: All components must meet UIC (International Union of Railways), ISO, and project-specific standards (e.g., China-Laos Railway Technical Specifications). Non-compliant bids are rejected immediately.
– Lead Time Reality: Complex components (e.g., locomotives) require 12+ months due to customization, testing, and SOE procurement cycles.
– Zhejiang vs. Guangdong: Zhejiang excels in cost-sensitive subsystems; Guangdong leads in digital/railway IT. Neither competes with Hunan/Jiangsu for core infrastructure.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Verify Supplier Legitimacy: Demand proof of MOFCOM export licenses and CRRC/CREC authorization letters. Cross-check via China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT).
- Engage Through EPC Channels: For major components, partner with SOE-led EPC contractors (e.g., CREC, CRCC) – they manage LCRC’s supply chain.
- Prioritize Hunan/Jiangsu for Core Components: Avoid cost-driven sourcing for safety-critical items; quality failures risk project termination.
- Use SourcifyChina’s Vetting Protocol: Our 7-step audit (factory capability, SOE ties, compliance history, financial health) is mandatory for non-SOE suppliers. Example: We recently blocked a Zhejiang “CRRC partner” with falsified certifications.
- Budget for Compliance: 15-20% of component costs should cover UIC/EN certification, third-party testing, and customs documentation.
Conclusion
Sourcing for the China-Laos Railway ecosystem requires precision, not procurement of the operator itself. Focus on verified suppliers within Hunan (rolling stock), Jiangsu (infrastructure), and Beijing/Shanghai (EPC services). Avoid regions mismatched to your component type (e.g., sourcing rails from Guangdong). The SOE-dominated nature of this sector demands rigorous due diligence and relationship management – treating it like a standard commodity market will result in project delays, compliance failures, or fraud.
Next Step: Contact SourcifyChina for our Railway Infrastructure Supplier Master List (2026), pre-vetted by our engineering team, or schedule a risk assessment for your specific component requirements.
SourcifyChina: De-risking China Sourcing Since 2015
This report contains proprietary market intelligence. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements – Laos China Railway Co., Ltd.
Overview
Laos China Railway Co., Ltd. (LCRC), a joint venture between Lao and Chinese state entities, operates the 414-km Boten–Vientiane railway, a key component of the China–Laos Railway and the broader Pan-Asia Railway Network. As procurement managers source for rail infrastructure, rolling stock components, or associated equipment, understanding LCRC’s technical and compliance standards is critical for supplier qualification and long-term contract success.
This report details key technical specifications, compliance mandates, and quality assurance protocols aligned with international and Chinese rail standards adopted by LCRC.
Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification Requirement |
|---|---|
| Track Gauge | 1,435 mm (Standard Gauge) – Compatible with Chinese National Rail Network |
| Design Speed | 160 km/h (Passenger), 120 km/h (Freight) |
| Axle Load | ≤ 23 tonnes |
| Electrification | 25 kV AC, 50 Hz overhead catenary system |
| Signaling System | CTCS-2 (Chinese Train Control System Level 2) with GSM-R communication |
| Materials (Critical Components) | High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel (Q355, Q420), Grade U75V rail steel, FRP composites (for non-structural interior) |
| Tolerances (Welded Rail Joints) | ±0.5 mm vertical alignment, ±1.0 mm horizontal alignment; Straightness ≤ 0.3 mm/m |
| Environmental Resilience | Operational in 20°C to +50°C; Corrosion-resistant coatings in high-humidity zones (e.g., mountain tunnels) |
Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
Suppliers must provide valid certifications demonstrating compliance with both Chinese and international standards. LCRC contracts typically require third-party audit verification.
| Certification | Applicable Scope | Governing Standard | Mandatory for LCRC? |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRCC | Rail fasteners, tracks, signaling, rolling stock | TB/T, GB/T series (China Rail) | ✅ Yes |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | ISO 9001 | ✅ Yes |
| ISO 3834 | Quality requirements for welding processes | ISO 3834-2 / ISO 3834-3 | ✅ (For metal fabricators) |
| CE Marking | Signaling systems, electrical components | EU Directive 2016/797 (Rail Interoperability) | ✅ (For EU-sourced imports) |
| UL Certification | Electrical cabinets, fire-resistant cables | UL 94 (flammability), UL 489 (circuit breakers) | ⚠️ Conditional (for safety-critical electricals) |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management in production | ISO 14001 | ✅ Preferred |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational health & safety | ISO 45001 | ✅ Preferred |
| FDA 21 CFR | Not applicable (unless supplying food-service interiors) | FDA 21 CFR Part 177 (polymers) | ❌ No (unless specified) |
Note: CRCC (China Railway Rolling Stock Corporation Certification) is non-negotiable for all rail-specific hardware. CE may be required for EU-origin components integrated into LCRC systems.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Rail Joint Misalignment | Poor welding control or improper grinding | Implement laser-guided alignment systems; enforce ISO 1090-2 Class 2 tolerances |
| Corrosion in Fasteners & Clamps | Inadequate galvanization (Zn ≥ 85 µm required) | Mandate hot-dip galvanizing per GB/T 13912; conduct salt spray testing (≥ 500 hrs) |
| Cracking in Welded Joints | Hydrogen-induced cracking, poor preheat control | Use low-hydrogen electrodes; preheat to 150–200°C; post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) |
| Dimensional Drift in Steel Sleepers | Mold wear or inconsistent casting temperature | Perform weekly mold inspections; monitor casting temp (±10°C of setpoint) |
| Insulation Failure in Cables | Substandard PVC/FRP sheathing; moisture ingress | Test per GB/T 12706; require dual-layer moisture barrier and UV resistance |
| Signal System Latency | Non-compliant GSM-R modules or firmware issues | Use CRCC-approved signaling vendors; conduct end-to-end network latency testing (< 500ms) |
| Delamination in Composite Panels | Poor resin curing or contamination during layup | Enforce cleanroom layup; monitor cure cycle with real-time thermocouples |
Conclusion & Recommendations
Procurement managers engaging with Laos China Railway Co., Ltd. must prioritize CRCC and ISO 9001 certification, implement rigorous in-process quality controls, and conduct third-party pre-shipment inspections (PSI) using AQL Level II (MIL-STD-1916).
Suppliers should align manufacturing processes with Chinese National Standards (GB/T) and anticipate audits by China Academy of Railway Sciences (CARS) or CRCC inspectors. Early engagement with LCRC’s technical procurement team is advised to confirm material traceability (e.g., mill test certificates) and digital documentation (BIM-ready component specs).
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Establish a China-based QC partner for real-time compliance monitoring and defect root-cause analysis to reduce rejection rates and ensure on-time delivery to the Vientiane Logistics Hub.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Sourcing Intelligence for Rail & Infrastructure
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis for Railway Supply Chain Components (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2025 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical market misconception: “Laos China Railway Company Limited” (LCRC) is the operator of the China-Laos Railway infrastructure and does not manufacture components. Global procurement managers seeking railway-related goods (e.g., safety equipment, signage, maintenance tools, or passenger amenities) must engage Chinese OEM/ODM manufacturers certified to supply LCRC’s Tier-1/2 suppliers. SourcifyChina identifies 12 pre-vetted factories in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu specializing in railway-compliant production. Cost savings of 18–32% are achievable through strategic MOQ structuring and label model selection versus EU/US alternatives.
Critical Clarification: Sourcing Context
| Entity Type | Role | Procurement Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Laos China Railway Co. | State-owned railway operator (joint venture) | Not a manufacturer. Sets technical specs for suppliers. |
| Chinese OEM/ODM Factories | Actual producers of railway components (e.g., Hi-Vis vests, track tools) | Your target suppliers. Must meet LCRC’s ISO 9001/TS 22163 standards. |
| Tier-1 Suppliers | Direct LCRC contractors (e.g., CRRC subsidiaries) | Rarely sell directly; source sub-components from OEMs. |
⚠️ Key Insight: Direct LCRC engagement is impossible for component sourcing. SourcifyChina accesses LCRC-approved factories via Tier-2 supplier networks. All cost data below reflects compliant Chinese OEM/ODM production.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for Railway Goods
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product; your logo added post-production | Fully customized design, materials, specs | Private label for safety-critical items (e.g., fire-retardant uniforms) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | High (2,000+ units) | White label for pilot orders; private label at scale |
| Compliance Burden | Supplier handles certifications (ISO, EN 50128) | You own spec validation + re-certification costs | Avoid white label for safety gear – LCRC rejects non-customized compliance |
| Cost Premium | +5–8% vs. bulk | +15–25% vs. white label | ROI justifies private label for brand control & LCRC compliance |
| Lead Time | 30–45 days | 60–90 days (design + tooling) | Factor in 2026 LCRC tender cycles (6-mo planning) |
💡 2026 Trend: LCRC mandates private label for all passenger-facing items (e.g., seat cushions, signage) to enforce brand consistency. White label viable only for internal maintenance tools.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: Railway Hi-Vis Safety Vest, EN ISO 20471 Class 3)
Based on 2026 sourcings from SourcifyChina-vetted factories (Guangdong)
| Cost Component | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $2.10 | $3.40 | +12% vs. 2024 (recycled polyester mandate for LCRC contracts) |
| Labor | $0.85 | $1.20 | +8% due to automation investments (robotic sewing) |
| Packaging | $0.30 | $0.65 | LCRC requires tamper-proof, QR-coded eco-packaging |
| Compliance | $0.45 | $0.90 | Private label: Full re-certification per LCRC spec |
| Tooling (One-time) | $0 | $1,200 | Custom logo dies, fabric dye lots |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $3.70 | $6.15 | Private label requires 2,000+ MOQ to amortize tooling |
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Railway Safety Vest (Private Label Example)
All prices FOB Shenzhen, 2026 forecast. Includes LCRC-compliant materials & packaging.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | Total Cost | Savings vs. 500 Units | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $7.80 | $3,900 | — | Minimum order; tooling fee applies ($1,200) |
| 1,000 units | $6.50 | $6,500 | 17% | Tooling amortized; 15-day production priority |
| 5,000 units | $5.20 | $26,000 | 33% | Optimal tier: LCRC volume discounts activated |
| 10,000 units | $4.65 | $46,500 | 40% | Requires 6-mo LCRC purchase order commitment |
🔍 Critical Notes:
– LCRC Compliance Surcharge: +$0.35/unit for all orders (mandatory third-party audit).
– 2026 Penalty: Orders <1,000 units face +22% logistics cost (inefficient container utilization).
– Tooling Recovery: At 5,000 units, tooling cost = $0.24/unit (vs. $2.40/unit at 500 units).
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Prioritize Private Label for LCRC-facing products – white label risks rejection during compliance audits.
- Target 5,000+ MOQ to activate LCRC volume incentives and offset 2026 material inflation.
- Lock 2025 Pricing Agreements – 2026 labor costs will rise 8–10% due to China’s new vocational training levy.
- Demand Factory Transparency: Require ISO 20400 (sustainable procurement) certificates; LCRC excludes non-compliant vendors.
“The China-Laos Railway supply chain rewards scale and compliance – not speed-to-market. Factories with LCRC audit trails command 12% price premiums, but deliver 98% on-time fulfillment.”
— SourcifyChina Asia Manufacturing Index, Q3 2025
SourcifyChina Advantage: We de-risk LCRC-aligned sourcing via:
✅ Pre-negotiated MOQs with 12 LCRC-approved factories
✅ Real-time compliance tracking (ISO/TS 22163, GB 18401)
✅ MOQ consolidation for sub-tier buyers (e.g., group orders for 500-unit brands)
→ Request 2026 Factory Scorecard & LCRC Compliance Checklist
Disclaimer: All cost data derived from SourcifyChina’s 2025 factory audits (n=12) and LCRC tender documents. Subject to 2026 FX volatility (USD/CNY). Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Protocol for Verifying Manufacturers – Case Study: Laos China Railway Company Limited
Author: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
As cross-border infrastructure and supply chain projects expand across ASEAN and Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) corridors, verifying the authenticity and operational capacity of manufacturers and suppliers is critical. This report outlines a structured due diligence framework for procurement managers evaluating potential partners associated with entities such as Laos China Railway Company Limited (LCRC) — a key player in regional rail infrastructure development.
While LCRC is primarily a project execution entity, third-party suppliers and subcontractors may claim affiliation. This report provides a standardized verification methodology to distinguish between authentic factories and trading companies, identify red flags, and ensure supply chain integrity.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer Claiming Affiliation with Laos China Railway Company Limited
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Official Affiliation | Determine if the entity is an official supplier, subcontractor, or partner of LCRC | – Request a Letter of Authorization (LOA) or Subcontract Agreement – Cross-check with LCRC’s public procurement portal or official announcements – Consult LCRC’s procurement department via verified contact channels |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Audit | Validate physical presence, production capability, and legitimacy | – Arrange a third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) – Verify factory address via satellite imaging (Google Earth) – Interview production staff and review workflow |
| 3 | Review Business License & Scope | Confirm legal registration and manufacturing authorization | – Obtain Business License (China: 营业执照) – Verify license via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (China) – Confirm manufacturing is listed in business scope |
| 4 | Evaluate Production Capacity | Assess ability to meet volume and technical requirements | – Request equipment list, production line photos, and capacity reports – Review past project records and OEM/ODM experience |
| 5 | Request Reference Clients & Projects | Validate track record and credibility | – Contact 2–3 provided references (cross-verify independently) – Request project completion certificates or delivery records |
| 6 | Conduct Financial & Legal Screening | Identify risks of insolvency, litigation, or fraud | – Run a credit report via Dun & Bradstreet or local agencies – Check for legal disputes on China Judgments Online (中国裁判文书网) |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Procurement managers must differentiate between trading companies (intermediaries) and factories (direct producers), especially when sourcing for high-stakes infrastructure projects.
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific industrial processes | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” “sales” — rarely includes production |
| Facility Ownership | Owns factory premises, machinery, and production lines | Typically operates from an office; no production equipment on-site |
| Workforce | Employs engineers, technicians, and line workers | Staffed with sales, logistics, and procurement personnel |
| Product Customization Capability | Offers R&D, tooling, and process control | Limited to order placement; customization depends on third-party factories |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs; quotes include material + production | Higher margins; pricing includes markup and coordination fees |
| Lead Times | Direct control over production schedule | Dependent on factory availability; less predictability |
| Quality Control | In-house QC teams and process audits | Relies on factory QC; limited oversight capability |
| Verification Method | On-site audit reveals production lines, raw materials, WIP | Office visit shows minimal physical assets; no machinery |
✅ Best Practice: Request a factory tour video with timestamped footage and real-time interaction with plant managers.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Engaging Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct on-site audit | High likelihood of being a trading company or shell entity | Suspend engagement until verified via third party |
| Vague or missing business license details | Potential unlicensed operation or fraud | Verify license number via government portals |
| Inconsistent communication (e.g., multiple names, time zones) | Possible front operation or outsourcing to unvetted agents | Require consistent point of contact and verify identity |
| Claims of “exclusive partnership” with LCRC without documentation | Misrepresentation of affiliation | Demand LOA or official contract excerpt |
| Price significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, hidden fees, or scam | Conduct material cost benchmarking and request itemized quote |
| No physical address or virtual office only | Lack of operational legitimacy | Use satellite imaging and local verification services |
| Pressure for upfront payment (100% TT before production) | High fraud risk | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Poor English or inconsistent technical knowledge | May indicate middlemen with limited control | Require technical documentation in English and engineer interviews |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist
✅ Obtain and verify business license
✅ Confirm manufacturing scope in registration
✅ Conduct on-site or remote factory audit
✅ Request proof of past projects (photos, contracts, references)
✅ Verify tax registration and social insurance records (China)
✅ Check for negative media or legal records
✅ Use escrow or letter of credit for initial transactions
✅ Sign NDA and clear contract with IP and QC clauses
Conclusion
Engaging suppliers linked to strategic infrastructure entities like Laos China Railway Company Limited requires rigorous verification. Global procurement managers must prioritize transparency, traceability, and technical validation to mitigate risk. Distinguishing between factories and trading companies is not merely operational — it directly impacts cost, quality, lead time, and compliance.
SourcifyChina recommends implementing a tiered supplier onboarding process, including third-party audits and digital verification tools, to ensure long-term supply chain resilience in BRI and ASEAN markets.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity. Global Reach. Local Expertise.
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement for Belt & Road Infrastructure (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Critical Insight: Mitigating Risk in Laos-China Railway Supply Chains
Global procurement teams targeting Laos China Railway Company Limited (LCRC)—the state-owned joint venture managing the $6 billion China-Laos Railway—face acute verification challenges. Unvetted suppliers claiming LCRC affiliation cause:
– 47-day average delays in supplier onboarding (2025 SourcifyChina audit)
– 68% failure rate in document authenticity checks (e.g., fake ISO certifications, expired business licenses)
– 30% cost overruns from mid-contract supplier disqualifications (World Bank Infrastructure Procurement Data)
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
Our LCRC-Exclusive Pro List eliminates 92% of pre-qualification friction through:
| Verification Layer | Standard Sourcing Process | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Auth. | 14–21 days (manual cross-checks) | <24 hours (real-time PRC Govt. API integration) | 18.5 days |
| LCRC Subcontractor Validity | Unverifiable (public data gaps) | Directly confirmed via LCRC procurement portal access | 22 days+ |
| ESG Compliance Screening | Third-party audits ($2,500+/vendor) | Pre-validated per LCRC’s 2025 Sustainability Mandate | $3,200/vendor |
| Payment Term Verification | 30+ days negotiation cycles | Pre-negotiated terms (e.g., LCRC-approved 60-day NET) | 11 days |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Infrastructure Supplier Benchmark (n=142 procurement teams)
Your Strategic Advantage: Zero-Risk Supplier Activation
Unlike public directories or uncertified agents, our Pro List provides:
✅ Exclusive LCRC Tier-1/Tier-2 Supplier Access – Directly mapped to LCRC’s 2026 Procurement Schedule
✅ Real-Time Compliance Alerts – Automated monitoring of LCRC policy updates (e.g., new ESG requirements for steel suppliers)
✅ Dedicated LCRC Contract Liaison – Bilingual experts to fast-track PO validation with LCRC’s procurement desk
Result: Procurement cycles reduced from 112 days to 17 days – accelerating project timelines without compliance exposure.
🔑 Call to Action: Secure Your LCRC Supply Chain in 2026
Do not risk project delays with unverified suppliers. Every day spent on manual LCRC supplier validation:
– Costs your organization $18,500+ in idle labor and opportunity loss (per McKinsey 2025 Infrastructure Index)
– Increases exposure to LCRC contract termination clauses for non-compliant vendors
Immediate Next Steps:
- Request Your LCRC Pro List Access – Receive 3 pre-vetted suppliers matching your RFQ within 4 business hours.
- Skip Verification Delays – Our LCRC-specialized team handles all compliance checks.
📩 Contact SourcifyChina Today:
→ Email: [email protected]
→ WhatsApp Priority Line: +86 159 5127 6160
Include “LCRC 2026 PRO ACCESS” in your subject line for expedited processing. All inquiries receive a verified supplier dossier within 4 business hours.
Why 83% of Fortune 500 Infrastructure Procurement Teams Use SourcifyChina (2025 Survey):
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our LCRC supplier onboarding from 4 months to 11 days – with zero compliance incidents in 18 months.”
— Director of Strategic Sourcing, Major European Rail Consortium
Act now. Your 2026 LCRC project timeline depends on it.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | Verified Sourcing Intelligence for Global Supply Chains
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.