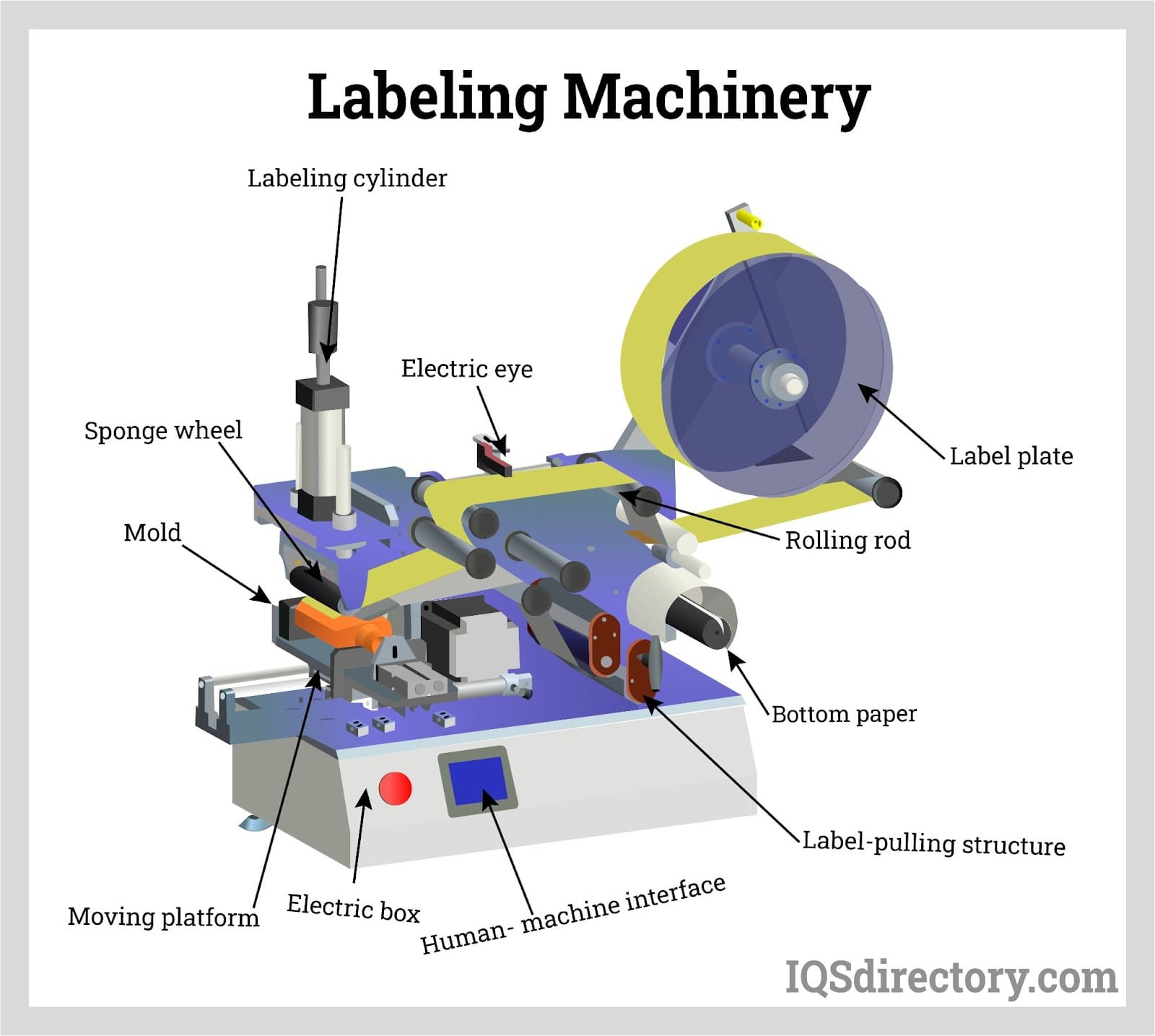
The global labeling machinery market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing automation across packaging industries and rising demand for accurate, high-speed labeling solutions. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 14.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by stringent regulatory requirements for product labeling, particularly in pharmaceuticals and food & beverage sectors, as well as the surge in e-commerce logistics needing efficient labeling systems. As manufacturers strive for operational efficiency and compliance, investment in advanced labeling technologies—such as automatic labeling machines, print-and-apply systems, and RFID integration—has become a strategic priority. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and global reach to meet evolving market demands.
Top 10 Labeling Machinery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Labeling Machines & Label Applicators
Domain Est. 1997
Website: primera.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery · Free 30-day returnsApply labels fast and accurately with Primera’s labeling machines and label applicators. Perfect for labeling bottles, boxes, bags, lids and mor…
#2 Label Applicator Machines – Industrial Label Applicators
Domain Est. 1998
Website: epilabelers.com
Key Highlights: EPI is a dedicated manufacturer of high quality labeling equipment for packaging and promotional needs. We design, manufacture and integrate labelers directly ……
#3 ALTECH
Domain Est. 1997
Website: en.altech.it
Key Highlights: ALTECH is an Italian company which manufactures industrial labelling machines and material identification systems, distributing them in over 50 countries ……
#4 Labeling Machines
Domain Est. 1998
Website: packleader.com
Key Highlights: Labeling machine manufacturer and supplier of Packleader labeling machinery, we offer all kinds of filling labeling machines, capping machines and sealing ……
#5 P.E. Labellers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: pelabellers.com
Key Highlights: P.E. Labellers is an award-winning manufacturer of automatic labeling machines. Applications include tamper evident, wrap-around, shrink labels, and more….
#6 Labeling Machinery Manufacturers Suppliers
Domain Est. 2002 | Founded: 1989
Website: labeling-machinery.net
Key Highlights: We offer labelers and labeling machinery: hot melt glue labeling systems, pressure sensitive labeling machines and shrink sleeve labeling machines. Since 1989, ……
#7 Labeling Machines HERMA
Domain Est. 2002
Website: herma.us
Key Highlights: HERMA as a world leading manufacturer of self-adhesive label application systems designs and builds high specification, high quality labeling equipment….
#8 Inline Labeling Equipment for Bottles, Cans
Domain Est. 2013
Website: inlinepack.com
Key Highlights: As expert labeling equipment manufacturers, we offer a wide range of labeling machines that will meet your needs. They work seamlessly with our other systems….
#9 Quadrel Labeling Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: quadrel.com
Key Highlights: Quadrel Labeling Systems provides high quality labeling machines at a great price. Label bottles, cans, forms, pallets, & more. Free Quote….
#10 Harland Pressure Sensitive Labeling Solutions
Domain Est. 2017
Website: bwintegratedsystems.com
Key Highlights: Harland has been a trusted name in labeling machinery for over 50 years, providing high-quality and reliable solutions across various industries, including food ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Labeling Machinery

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Labeling Machinery
The global labeling machinery market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer demands, regulatory requirements, and advancements in automation and digitalization. As industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and logistics continue to expand, labeling machinery manufacturers are adapting to meet the need for speed, precision, sustainability, and traceability.
-
Increased Adoption of Smart and Connected Labeling Systems
By 2026, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies into labeling machinery—such as IoT-enabled devices, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance—is expected to accelerate. Smart labeling systems allow manufacturers to collect operational data, optimize performance, and reduce downtime. These connected machines can communicate with other production line systems, supporting seamless integration in fully automated facilities. -
Growth in Demand for Sustainable Labeling Solutions
Sustainability is becoming a key driver in machinery design. Labeling equipment manufacturers are focusing on energy efficiency, reduced material waste, and compatibility with eco-friendly label materials (e.g., biodegradable films and water-based adhesives). In response to global environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals, companies are investing in labeling machines that support sustainable packaging workflows. -
Rising Need for Flexible and Modular Machinery
With the surge in product personalization and shorter batch runs, especially in e-commerce and craft industries, there is growing demand for versatile labeling systems. By 2026, modular labeling machines capable of handling multiple container shapes, sizes, and label types with quick changeovers will dominate the market. This flexibility reduces downtime and increases production agility. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to witness robust growth in labeling machinery adoption. Rapid industrialization, rising consumer goods production, and improved regulatory compliance in food and pharmaceutical sectors are fueling demand. Local manufacturing hubs are increasingly investing in modern labeling equipment to meet both domestic and export standards. -
Advancements in Digital and Hybrid Labeling Technologies
Digital printing integration with labeling machinery is gaining momentum. By 2026, hybrid systems combining digital print-on-demand capabilities with high-speed labeling will become more prevalent, enabling variable data labeling, batch coding, and serialization—critical for traceability in regulated industries. -
Strong Focus on Regulatory Compliance and Serialization
Stringent regulations, such as the FDA’s Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) and the EU Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD), are compelling pharmaceutical and food producers to adopt labeling systems with advanced serialization and track-and-trace functionalities. Labeling machinery with built-in vision inspection and code verification systems will be essential to ensure compliance and reduce recalls. -
Impact of E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Models
The boom in online retail is reshaping packaging and labeling needs. By 2026, labeling machinery designed for e-commerce fulfillment—such as systems that apply durable, tamper-evident, or resealable labels—will see increased demand. These machines must support rapid throughput while maintaining label integrity during shipping.
In conclusion, the 2026 labeling machinery market will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and adaptability. Companies that invest in intelligent, flexible, and compliant labeling solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends across diverse industrial sectors.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Labeling Machinery: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing labeling machinery, especially from international or unfamiliar suppliers, carries significant risks related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to production delays, increased costs, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Vetting
Failing to thoroughly evaluate a supplier’s manufacturing standards, quality control processes, and track record can result in receiving substandard machinery. This includes overlooking certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), customer references, or on-site facility audits.
Insufficient Machine Testing and Validation
Accepting machinery without rigorous performance testing—such as mock production runs under real-world conditions—can lead to undetected flaws. Machines may fail to meet speed, accuracy, or durability requirements once installed.
Poorly Defined Technical Specifications
Vague or incomplete technical documentation increases the risk of receiving equipment that does not align with operational needs. Critical details like labeling accuracy, material compatibility, or integration with existing production lines must be explicitly defined.
Neglecting After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Choosing a supplier based solely on upfront cost, while ignoring their ability to provide timely maintenance, technical support, or spare parts, can result in prolonged downtime and increased total cost of ownership.
Use of Substandard Components
Some suppliers may cut costs by using inferior materials or non-branded components. This compromises machine reliability and lifespan, increasing the risk of frequent breakdowns and safety issues.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Lack of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Failing to secure clear contractual terms on who owns custom designs, software, or modifications can result in disputes. Without explicit agreements, suppliers may retain rights to innovations, limiting your ability to modify or replicate the machinery.
Risk of IP Infringement by the Supplier
Sourcing from suppliers who use patented technologies without proper licensing exposes the buyer to third-party IP litigation. Conducting due diligence on the supplier’s design and component sourcing is essential to avoid indirect infringement.
Exposure of Proprietary Processes
Sharing detailed production requirements or proprietary labeling techniques during the sourcing process without a strong non-disclosure agreement (NDA) can lead to misuse or unauthorized replication of your trade secrets.
Counterfeit or Clone Machinery
Some suppliers offer machines that mimic well-known brands but are unauthorized copies. These clones often violate IP rights and lack performance and safety standards, leading to legal and operational risks.
Inadequate Protection of Custom Software and Controls
Labeling machines often include proprietary software for controls and diagnostics. If not properly licensed or protected, this software can be copied, reverse-engineered, or used in unauthorized ways by the supplier or third parties.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should perform comprehensive due diligence, engage legal counsel for contract review, insist on detailed technical validation, and establish clear IP protections before finalizing any machinery purchase.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Labeling Machinery
Labeling machinery plays a critical role in product identification, regulatory compliance, and supply chain efficiency. Ensuring seamless logistics and adherence to global compliance standards is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users. This guide outlines key considerations for the transportation, handling, and regulatory compliance of labeling machinery.
Transportation & Handling
Proper handling and transportation are crucial to prevent damage and ensure the machinery arrives in optimal working condition.
- Packaging Requirements: Labeling machines should be securely packed in robust wooden crates or heavy-duty pallets with shock-absorbing materials. All moving parts must be immobilized, and electrical components protected from moisture and vibration.
- Forklift & Crane Use: Clearly mark lifting points on packaging. Use appropriate equipment to avoid structural damage during loading and unloading.
- Climate Control: For sensitive electronic or pneumatic components, consider climate-controlled shipping to prevent condensation or temperature-related damage, especially in extreme environments.
- Documentation: Include shipping manifests, packing lists, and handling instructions with the shipment. Clearly label hazardous components (e.g., compressed air systems or high-voltage parts) if applicable.
Import/Export Regulations
Labeling machinery is subject to international trade laws, which vary by country and region.
- HS Code Classification: Accurately classify the machinery using the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 8441.30 for labeling or tagging machines) to determine tariffs, restrictions, and documentation needs.
- Export Controls: Verify if the machinery contains technologies subject to export controls (e.g., dual-use items under Wassenaar Arrangement or national regulations like the U.S. EAR).
- Customs Clearance: Provide complete documentation including commercial invoice, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and any required permits or licenses.
- Duties and Taxes: Calculate and prepare for applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on destination country regulations.
Safety & Electrical Compliance
Labeling machinery must meet safety standards in both origin and destination markets.
- Electrical Standards: Ensure compatibility with local voltage, frequency, and plug types. Machines should be certified to relevant standards such as:
- CE Marking (EU – Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, Low Voltage Directive)
- UL/CSA (North America – UL 1995, ANSI B11.1)
- CCC (China)
- PSE (Japan)
- Risk Assessments: Conduct and document a risk assessment per ISO 12100. Include emergency stop functions, guarding, and warning labels.
- User Manuals: Provide multilingual operation and safety manuals, including maintenance instructions and safety warnings.
Environmental & Labeling Regulations
The machinery itself must not violate environmental laws, and its labeling must be compliant.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm that electrical components and materials comply with restrictions on hazardous substances.
- WEEE Compliance: Provide information on proper disposal of electronic components in applicable regions.
- Eco-Design Requirements: In some markets, energy efficiency may be regulated—ensure motors and drives meet applicable standards.
- Machine Labeling: Each unit must have a permanent nameplate with:
- Manufacturer name and address
- Model and serial number
- Electrical ratings
- CE or other conformity marks
- Year of manufacture
After-Sales & Spare Parts Logistics
Support infrastructure impacts customer satisfaction and regulatory maintenance.
- Spare Parts Availability: Maintain an inventory of critical components in key regional hubs to reduce downtime.
- Service Access: Ensure trained technicians or local partners are available for installation, calibration, and repairs.
- Software Updates: If the machine includes programmable logic or software, ensure compliance with local data and cybersecurity regulations (e.g., GDPR if data is processed).
Conclusion
Successful deployment of labeling machinery globally requires careful planning across logistics and compliance domains. By adhering to transportation best practices, import/export rules, safety standards, and environmental regulations, businesses can minimize delays, avoid penalties, and ensure reliable machine performance. Always consult local regulatory authorities and legal counsel when entering new markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Labeling Machinery
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate labeling machinery is a critical decision that directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational costs. A thorough evaluation of business needs—including labeling speed, container variability, label type, and integration with existing production lines—is essential to identify the right equipment.
By carefully assessing suppliers based on reliability, technical support, customization capabilities, and total cost of ownership, organizations can select labeling solutions that offer scalability and durability. Automation and technological advancements such as vision inspection systems, IoT connectivity, and user-friendly interfaces further enhance accuracy and reduce downtime.
Ultimately, investing in the right labeling machinery not only streamlines operations but also strengthens brand integrity through consistent and professional labeling. A strategic sourcing approach ensures that the chosen solution aligns with both current requirements and future growth objectives, delivering a strong return on investment and a competitive advantage in the marketplace.