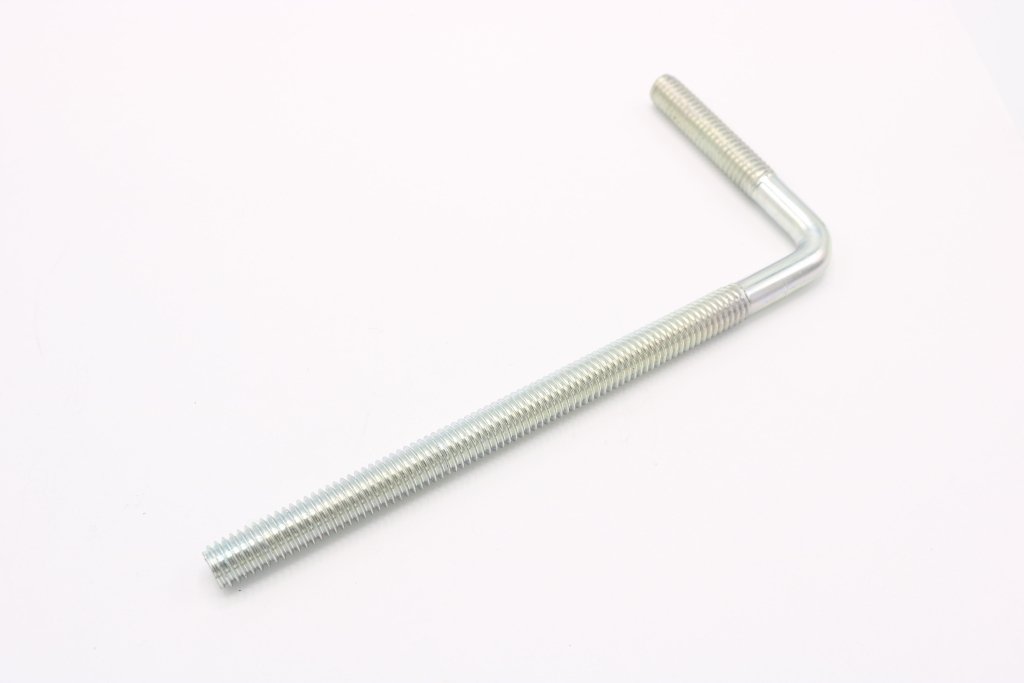
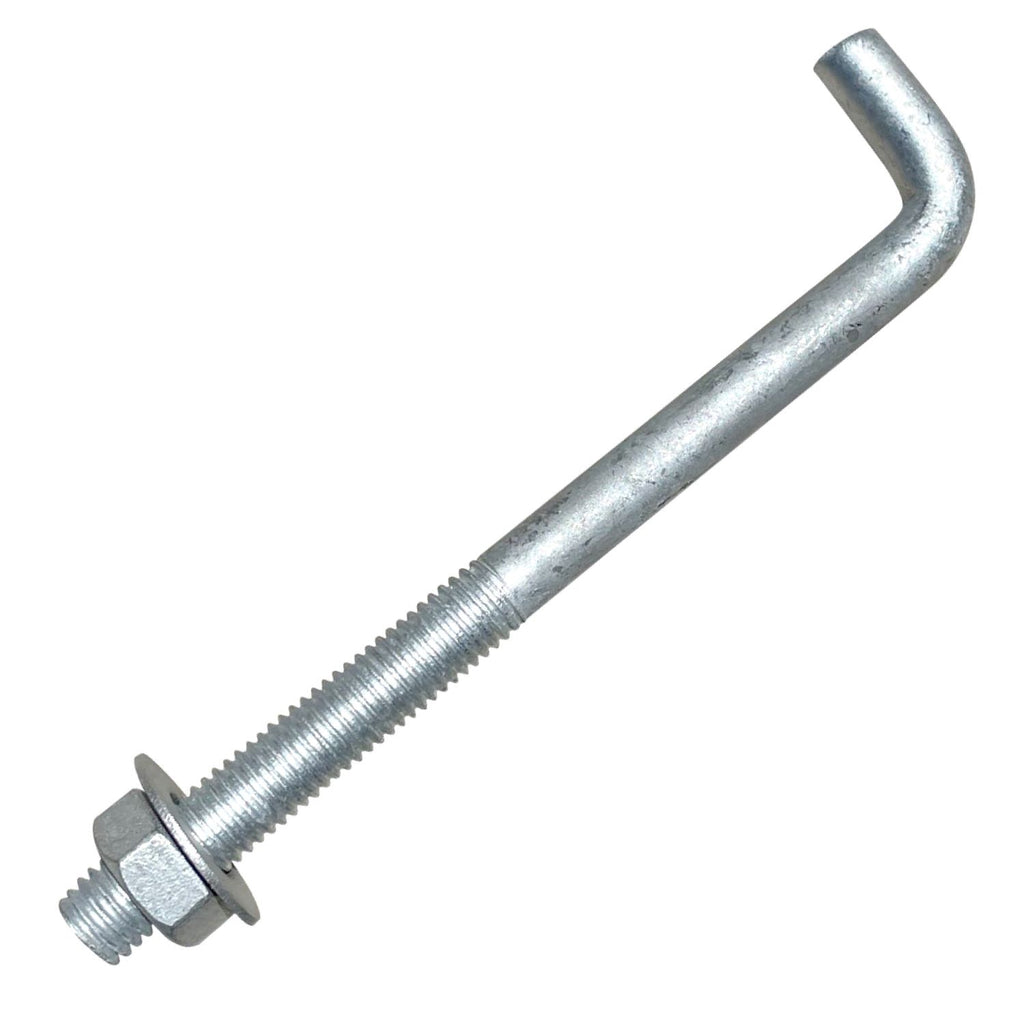
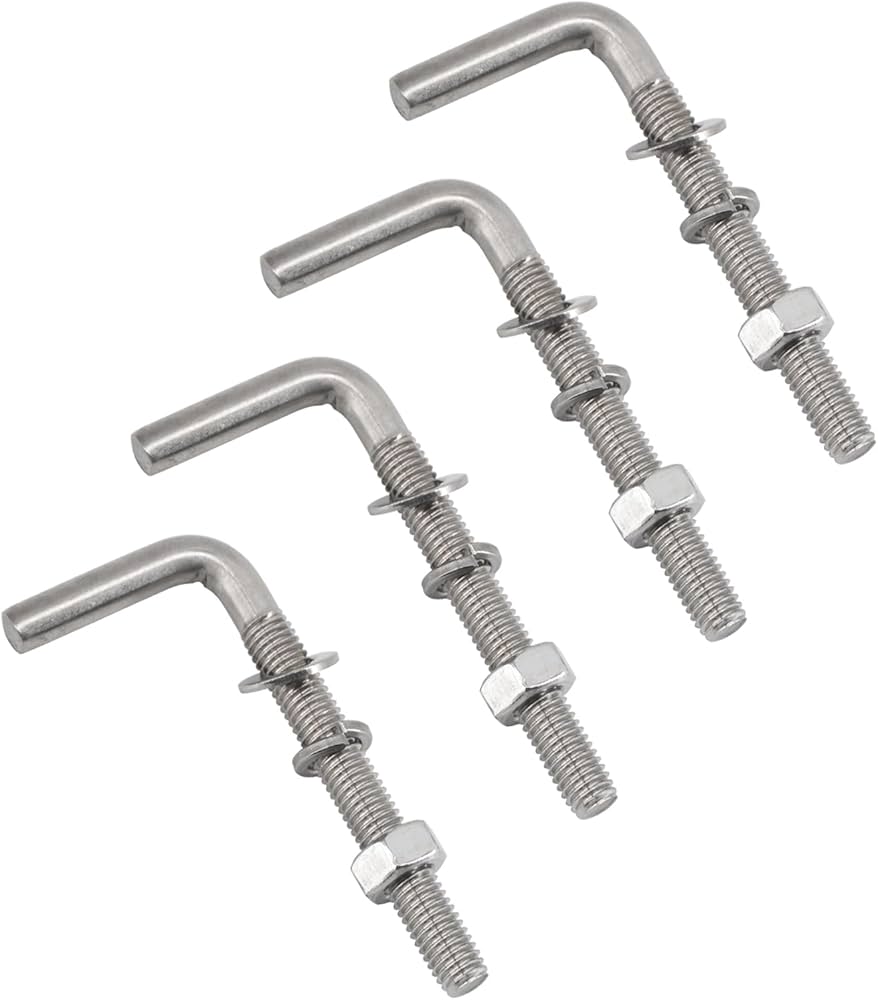
The global fasteners market, driven by robust demand from construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With threaded fasteners like L-bolts—particularly those threaded on both ends—playing a critical role in structural anchoring and mechanical assembly, the need for high-quality, precision-engineered components has never been greater. As infrastructure investments rise and industrial automation expands, especially across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, manufacturers specializing in L-bolts are scaling production with tighter tolerances and enhanced material durability. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that Asia-Pacific dominates both production and consumption, propelled by rapid urbanization and government-backed construction initiatives. In this evolving landscape, identifying top-performing L-bolt manufacturers ensures reliability, compliance, and supply chain resilience for OEMs and contractors alike.
Top 10 L-Bolt Threaded Both Ends Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 The Official ARP Web Site
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arp-bolts.com
Key Highlights: ARP started applying technology to race fastener design and manufacturing in 1968. We’ll discuss five components of fastener technology in detail….
#2 Portland Bolt
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1912
Website: portlandbolt.com
Key Highlights: Portland Bolt has manufactured and distributed the highest-quality anchor bolts and nonstandard construction fasteners since 1912….
#3 L&H Threaded Rods Corp.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: lhrods.com
Key Highlights: L&H Threaded Rods Corp. is a Threaded Rod and U-Bolt Manufacturer. We support the heavy-duty aftermarket industry by providing innovative products and services….
#4 Bent Anchor Bolt Distributor
Domain Est. 2001
Website: dalecompany.com
Key Highlights: The Dale Company is a bent anchor bolt distributor that manufactures high-quality, galvanized and stainless steel L shaped bolts used in structural, concrete ……
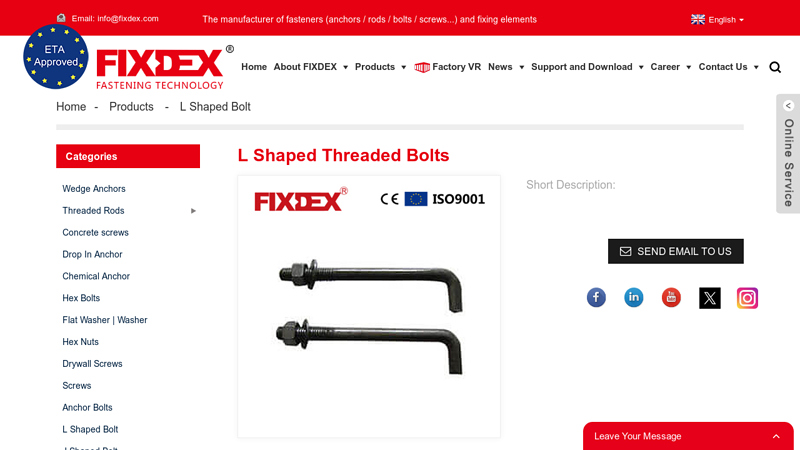
#5 l shaped threaded bolts
Domain Est. 2015
Website: fixdex.com
Key Highlights: l shaped threaded bolts Finish: ZINC, Plain, customized, Black Material: Stainless Steel, Steel Place of Origin: Handan,China Brand….
#6 Anchor Bolts. Steel Fabrication. Galvanizing.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: maddenbolt.com
Key Highlights: Madden Bolt – Competitively priced anchor bolts, miscellaneous steel fabrication & galvanizing services all under one roof, providing end-to-end solutions….
#7 L
Domain Est. 2001
Website: madar.com
Key Highlights: Each L-Bolt is supplied as a convenient kit with two hexagonal nuts and one washer, ready for embedding into concrete foundations to secure structural elements ……
#8 Anchor Bolts
Domain Est. 2006
Website: atlrod.com
Key Highlights: Order Anchor Bolts Made to Your Requirements. We manufacture anchor bolts with cut or rolled threads on one or both ends to fit your exact needs. Available ……
#9 L-Shaped Anchor Bolts & Epoxy ~ Bulk Orders
Domain Est. 2020
Website: boltcraftmfg.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $1,000At BoltCraft Manufacturing, we provide durable L shaped anchor bolts for construction projects. Whether you’re securing heavy machinery, reinforcing struct…
#10 l shaped threaded bolts
Domain Est. 2023
Website: l_shaped_threaded_bolts.ytbolt.com
Key Highlights: In essence, a Threaded L bolt features a 90-degree bend giving it an L shape, with threading typically on one end, allowing it to be firmly screwed into place….
Expert Sourcing Insights for L-Bolt Threaded Both Ends
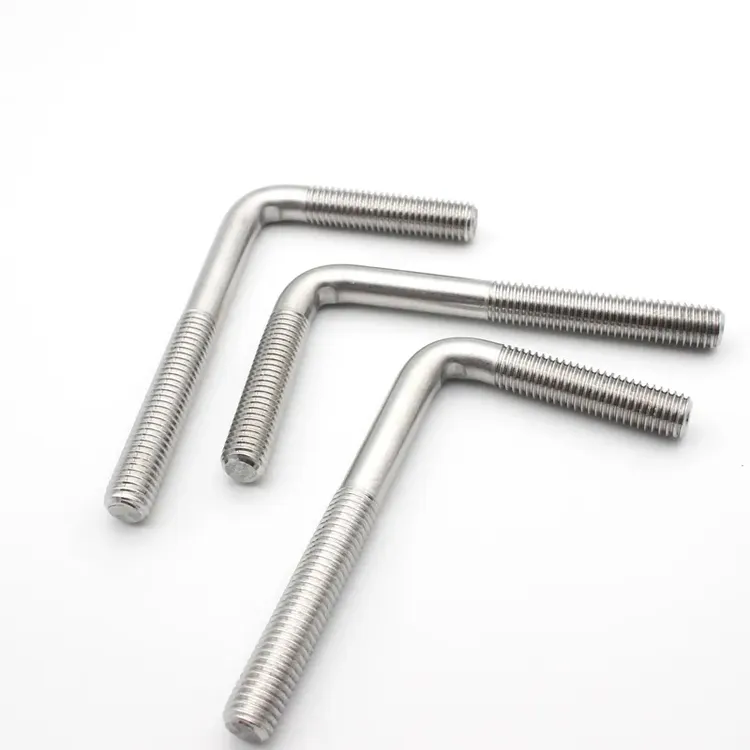

H2: 2026 Market Trends for L-Bolt Threaded Both Ends
The L-bolt threaded on both ends, a specialized fastener valued for its high tensile strength and dual-threaded functionality, is poised for steady growth and transformation in 2026. Driven by infrastructure expansion, evolving construction methodologies, and industrial modernization, the market is expected to reflect several key trends shaped by regional dynamics, material innovation, and supply chain resilience.
1. Infrastructure-Led Demand Surge
Governments worldwide—particularly in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia—are accelerating investments in public infrastructure (bridges, highways, railways, and urban transit). L-bolts threaded on both ends are essential in precast concrete connections, structural steel anchoring, and seismic retrofitting. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and similar EU and Indian initiatives will directly boost procurement, making infrastructure the largest end-use segment by 2026.
2. Growth in Prefabricated and Modular Construction
The construction industry’s shift toward off-site manufacturing and modular building techniques favors standardized, high-precision fasteners. L-bolts with dual threading offer flexibility in alignment and load distribution during modular component assembly. As modular construction gains traction in residential, commercial, and healthcare projects, demand for L-bolts will rise proportionally, particularly in urban centers with labor shortages and tight timelines.
3. Material and Coating Innovations for Durability
With increasing focus on longevity and sustainability, demand for corrosion-resistant L-bolts is rising. High-strength carbon steel remains dominant, but adoption of weathering steel (e.g., ASTM A588) and duplex stainless steel variants is growing—especially in coastal or chemically aggressive environments. Advanced coatings like Dacromet, Geomet, and hot-dip galvanizing will become standard in premium applications, driven by green building standards (e.g., LEED) and lifecycle cost analysis.
4. Regional Manufacturing Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions post-pandemic have prompted OEMs and contractors to prioritize regional sourcing. In 2026, expect increased production of L-bolts in nearshore facilities (e.g., Mexico for North America, Eastern Europe for the EU) and domestic manufacturing in key markets like India and Vietnam. This localization trend enhances delivery reliability and reduces logistics costs, benefiting regional suppliers.
5. Digitalization and Smart Fastening Integration
While L-bolts themselves remain mechanical components, the broader fastening ecosystem is embracing digitization. By 2026, leading manufacturers may integrate IoT-enabled traceability (e.g., QR codes or RFID tags) for quality assurance and compliance tracking in critical infrastructure. Additionally, BIM (Building Information Modeling) adoption will drive demand for standardized L-bolts with precise digital specifications, reducing errors in prefabrication.
6. Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations will push manufacturers toward energy-efficient production and recyclable materials. Steel recycling rates already exceed 90%, but suppliers will increasingly highlight carbon footprint data and invest in low-emission forging and threading processes. End-users in ESG-conscious sectors (e.g., public projects, green buildings) will favor suppliers with verifiable sustainability certifications.
Conclusion
By 2026, the L-bolt threaded on both ends market will be characterized by infrastructure-driven volume growth, technological adaptation, and a stronger emphasis on durability and sustainability. Manufacturers who invest in material innovation, regional supply chains, and digital integration will capture the greatest share of this resilient and essential fastener segment.
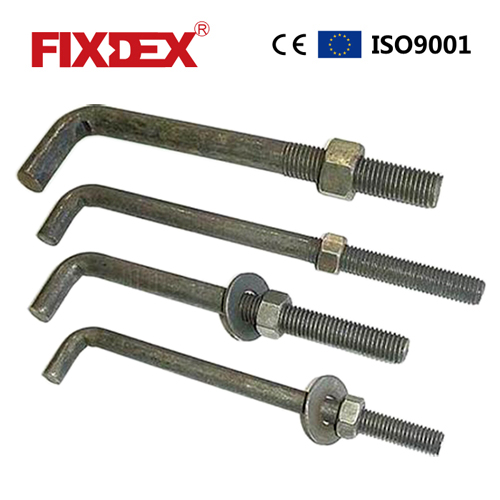

Common Pitfalls Sourcing L-Bolt Threaded Both Ends (Quality, IP)
Sourcing L-bolts threaded on both ends, especially with specific quality and Ingress Protection (IP) requirements, presents several common challenges that can lead to project delays, safety issues, or increased costs if not properly addressed.
Unclear or Inconsistent Quality Specifications
One of the most frequent pitfalls is ambiguity in defining “quality.” Buyers may specify only broad standards like “high strength” or “stainless steel” without referencing recognized international or industry standards (e.g., ASTM A193, ISO 898-1, or DIN 931). This lack of specificity can result in suppliers delivering bolts that technically meet a material grade but fall short in critical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance. Additionally, inconsistent heat treatment or poor thread rolling practices can compromise structural integrity, especially in load-bearing applications.
Inadequate Material and Corrosion Resistance for Intended Environment
Even when stainless steel is specified (e.g., A2 or A4), sourcing pitfalls arise when the environment demands higher corrosion resistance than the material provides. For example, using A2 (304) stainless in marine or chlorinated environments may lead to pitting or crevice corrosion over time. Buyers may overlook the need for higher-grade materials like A4 (316) stainless or duplex steels, particularly when IP ratings suggest exposure to moisture or chemicals. Failing to match material selection with operational conditions undermines both durability and safety.
Misunderstanding or Overlooking Thread Quality and Tolerances
Thread precision is critical for proper fit, preload, and performance. Sourcing bolts with poorly formed threads—such as those with rolled threads that lack proper root radii or have dimensional inaccuracies—can lead to thread stripping, galling, or inconsistent torque application. Many low-cost suppliers may not adhere to thread tolerance standards (e.g., 6g for external threads per ISO 965), resulting in fitment issues or reduced fatigue life under cyclic loading.
Confusion Between IP Rating and Mechanical Performance
A significant pitfall is conflating IP (Ingress Protection) ratings with mechanical strength or corrosion resistance. IP ratings (e.g., IP67, IP68) define protection against dust and water ingress but do not guarantee material quality or structural performance. Suppliers may market bolts as “IP68-rated” based on sealing at the joint or housing, not the bolt itself. Sourcing decisions based solely on IP claims without verifying mechanical certifications can result in components that resist water but fail mechanically under load.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
High-integrity applications (e.g., in construction, energy, or transportation) require full traceability, including material test reports (MTRs), mill certifications, and compliance documentation. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide certified documentation—such as EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 certificates—poses a major risk. This lack of traceability can lead to non-compliance with regulatory standards and complicate quality audits or failure investigations.
Inconsistent Surface Finishes and Coatings
Surface treatments such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, or Dacromet coatings are often necessary for enhanced corrosion resistance. However, inconsistencies in coating thickness, adhesion, or hydrogen embrittlement relief processes can compromise performance. For threaded components, poor plating can lead to thread galling or increased friction during assembly, affecting torque-tension relationships. Buyers may not specify coating requirements clearly, leading to substandard finishes that degrade prematurely.
Supply Chain Transparency and Counterfeit Risk
Sourcing from unverified suppliers, especially in global markets, increases the risk of counterfeit or substandard fasteners. Bolts may be mislabeled with incorrect grade markings or forged from inferior materials. Without rigorous supplier vetting and third-party inspection, organizations may inadvertently integrate compromised components into critical systems, risking structural failure and liability.
By addressing these pitfalls through detailed specifications, supplier qualification, and independent verification, buyers can ensure the L-bolts they source meet both quality and environmental protection requirements effectively.
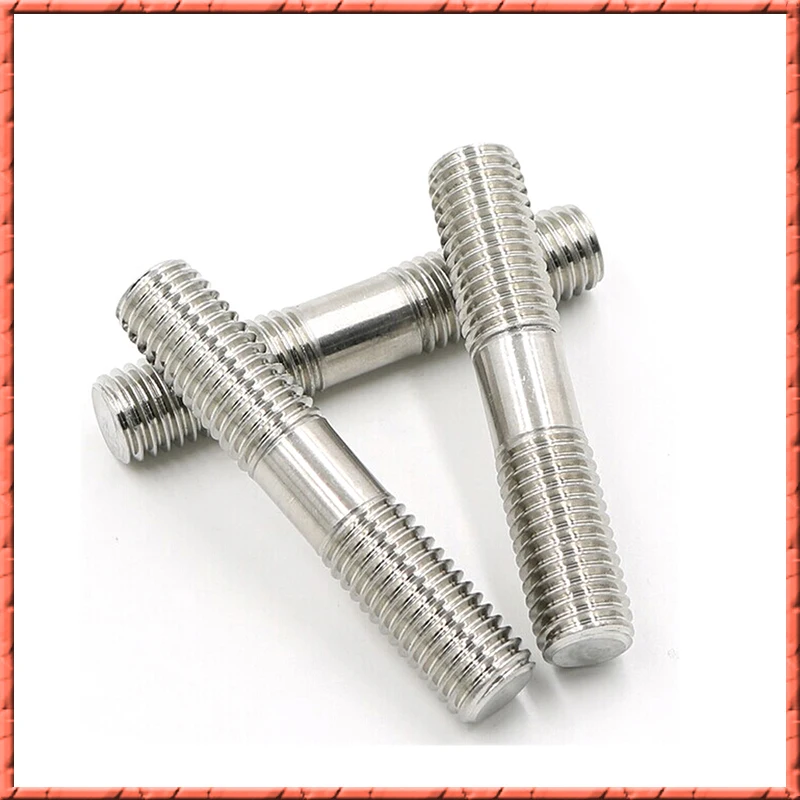

Logistics & Compliance Guide for L-Bolt Threaded Both Ends
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, and use of L-Bolts with threads on both ends. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational safety.
Product Overview
L-Bolts (also known as L-shaped anchor bolts) threaded on both ends are fasteners used primarily in construction and industrial applications to anchor structural supports, equipment, or machinery to concrete. One leg is embedded in concrete, while the threaded ends protrude for securing with nuts and washers. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, or galvanized steel, with varying strength grades (e.g., ASTM A307, A354, or F1554).
Packaging & Handling
- Packaging: L-Bolts should be packaged in labeled bundles secured with steel or plastic strapping. Use moisture-resistant wrapping or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper for corrosion protection, especially for carbon steel.
- Labeling: Each bundle must include product details: size, material grade, finish (e.g., hot-dip galvanized), quantity, and compliance markings.
- Handling: Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts with soft slings) to avoid damage. Avoid dragging or dropping bundles to prevent thread damage or deformation.
Storage Requirements
- Store indoors in a dry, ventilated area to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Elevate bundles off the floor using pallets or racks to avoid moisture contact.
- Segregate by size, grade, and finish to prevent mix-ups and contamination.
- Limit exposure to salt, chemicals, or high humidity environments, especially for non-stainless variants.
Transportation Guidelines
- Secure loads on trucks or containers to prevent shifting during transit.
- Protect threads using plastic or metal caps where applicable.
- Comply with national and international transport regulations for metal cargo (e.g., IMDG Code for sea freight, ADR for road in Europe).
- Provide a packing list and shipping documents detailing contents, weight, and hazardous classifications (if applicable—typically non-hazardous).
Regulatory Compliance
- Material & Performance Standards:
- Ensure bolts meet recognized standards such as ASTM A307 (Grade B), ASTM A354 (Grade BD), or ASTM F1554 (Grades 36, 55, 105).
- Certification (mill test reports) must be available upon request.
- Coating Compliance:
- Hot-dip galvanized bolts must comply with ASTM A153.
- Mechanical galvanizing must meet ASTM B695.
- RoHS & REACH (EU):
- Confirm absence of restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in plating or coatings.
- LEED & Green Building Standards:
- Use of recyclable materials and sustainable production practices may support project certifications.
Import/Export Documentation
- Provide commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/airway bill.
- Include a certificate of compliance or conformance (CoC).
- For U.S. imports: Harmonized System (HS) code 7318.15 (threaded rods/anchor bolts).
- Check destination country regulations; some require third-party testing or certification (e.g., CCC in China, INMETRO in Brazil).
Quality Assurance & Traceability
- Maintain traceability from raw material to finished product via heat lot numbers.
- Conduct periodic inspections for thread accuracy, dimensional conformity, and surface finish.
- Retain quality records for minimum of 5 years (or per contractual requirement).
Safety & Installation Compliance
- Provide end-users with installation instructions, including torque specifications and embedment depth.
- Warn against overtightening, which may cause thread stripping or bolt failure.
- Recommend use of appropriate washers and nuts meeting complementary standards (e.g., ASTM A563).
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Recyclable at end-of-life; steel content is fully recoverable.
- Dispose of packaging materials in accordance with local waste regulations.
- Avoid littering on construction sites; damaged or excess bolts should be collected for recycling.
Contact & Support
For compliance documentation, technical data sheets (TDS), or material safety data sheets (SDS—though typically not required for inert metal fasteners), contact the manufacturer or supplier directly. Always verify specifications prior to use in critical structural applications.
Conclusion on Sourcing L-Bolt (Threaded on Both Ends):
Sourcing an L-bolt with threads on both ends requires careful consideration of specifications such as material grade, thread type and size, overall dimensions, and applicable standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, or DIN). After evaluating multiple suppliers and manufacturing options, it is evident that reputable industrial fastener suppliers or custom metal fabrication companies can reliably provide these specialized bolts. While standard L-bolts are commonly available, dual-end threaded variants may require customization, potentially affecting lead times and cost. To ensure quality and compatibility, it is recommended to source from certified suppliers with proven track records in producing structural or mechanical fasteners. Proper documentation, including material test reports and dimensional drawings, should accompany the order to meet project requirements and compliance standards. In summary, with clear technical specifications and due diligence in supplier selection, sourcing L-bolts threaded on both ends is feasible and can be executed efficiently for intended applications in construction, manufacturing, or engineering projects.