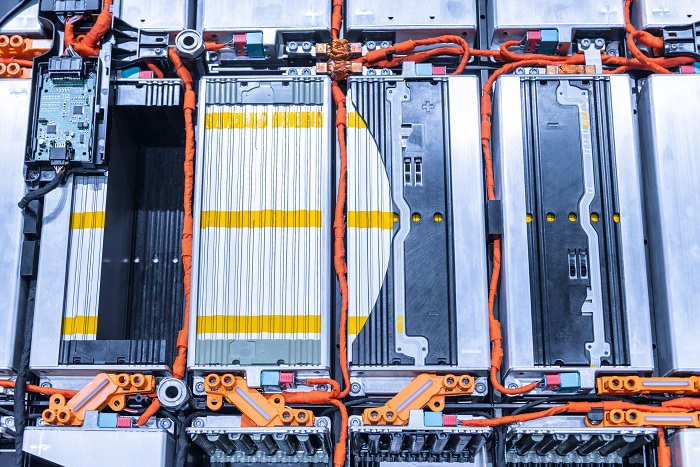
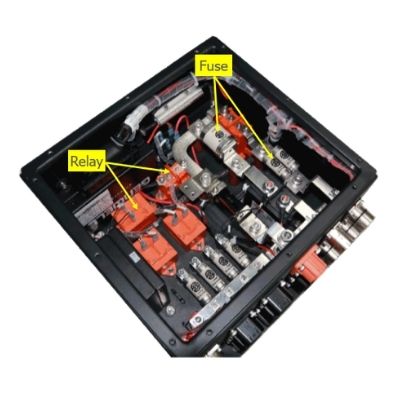
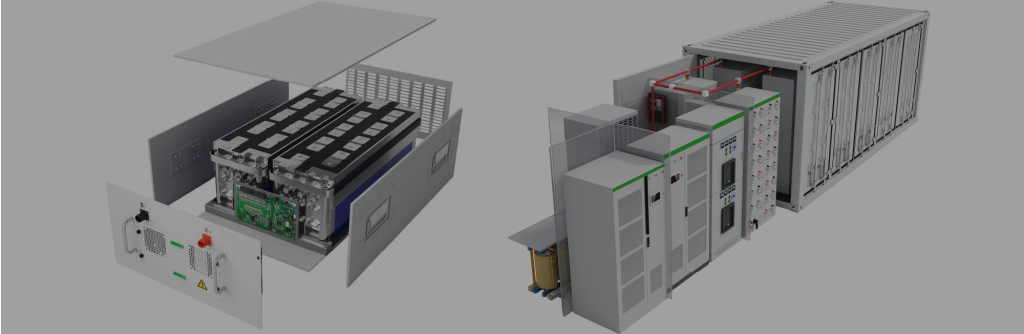
The global junction box battery market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and energy storage solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global solar charge controller and related component market—of which junction box batteries are a critical part—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global energy storage systems market will expand at a CAGR of 18.4% during the same period, further fueling the need for reliable, integrated components like junction box batteries. As solar and battery technologies continue to advance, manufacturers are innovating to improve efficiency, safety, and durability within compact, modular units. With these trends shaping the industry, identifying the top manufacturers becomes essential for developers, contractors, and energy firms seeking high-performance solutions. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 9 junction box battery manufacturers leading the charge in technology, scalability, and market presence.
Top 9 Junction Box Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 East Penn Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eastpennmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: We are the world’s largest single-site lead-acid battery manufacturer. Explore reliable energy solutions for automotive, industrial, ……
#2 KDM Battery Junction Box, The Reliable Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2018
Website: kdmsteel.com
Key Highlights: KDM is a professional manufacturer and producer of battery junction box in China. Producing most durable and long life span junction boxes….
#3 Hawker Powersource, Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hawkerpowersource.com
Key Highlights: We craft custom motive power battery and charger solutions for Class l, ll, and lll trucks to empower and enhance each customer’s unique daily operations….
#4 Discover Energy Systems
Domain Est. 2024
Website: discoverenergysys.com
Key Highlights: Discover lithium batteries and power electronics are independently certified to the highest safety, performance, and reliability standards….
#5 Battery junction box design resources
Domain Est. 1986
Website: ti.com
Key Highlights: View the TI Battery junction box block diagram, product recommendations, reference designs and start designing….
#6 Power-Sonic
Domain Est. 1995
Website: power-sonic.com
Key Highlights: Power-Sonic delivers innovative battery solutions with sealed lead acid and lithium batteries, energy storage systems, and EV chargers….
#7 Battery Junction Box
Domain Est. 2003
Website: marquardt.com
Key Highlights: Our Battery Junction Box serves as an integrated solution for HV battery switching, monitoring and control – with our Battery Management Controller (BMC) ……
#8 Flux Power: Lithium
Domain Est. 2005
Website: fluxpower.com
Key Highlights: Switch to Flux Power’s lithium-ion batteries for material handling equipment, forklifts, and airport ground support. Enhance efficiency and cut costs now!…
#9 KION Battery Systems
Domain Est. 2006
Website: kiongroup.com
Key Highlights: KION Battery Systems produces lithium-ion batteries for forklift trucks and warehouse equipment and provides their reconditioning….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Junction Box Battery

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Junction Box Battery
The global market for junction box batteries—critical components in energy storage and electrical distribution systems, especially within solar photovoltaic (PV) installations and electric vehicle (EV) battery packs—is poised for substantial transformation by 2026. Driven by the accelerating adoption of renewable energy, advancements in battery technology, and evolving regulatory standards, several key trends are expected to shape the junction box battery landscape.
-
Increased Integration with Smart Technology
By 2026, junction box batteries are anticipated to feature enhanced smart monitoring capabilities. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) sensors and real-time data analytics will allow for remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and improved energy efficiency. Smart junction boxes will monitor voltage, temperature, and current leakage, reducing failure risks and optimizing battery performance across solar and EV applications. -
Growth in Renewable Energy Deployments
With global commitments to carbon neutrality, solar energy installations are projected to grow significantly. This expansion will directly boost demand for junction boxes in PV systems, as each solar panel or string requires reliable junction boxes for safe electrical interconnection and overcurrent protection. Countries in Asia-Pacific (notably China and India), North America, and the EU are expected to lead installations, driving regional market growth. -
Electrification of Transportation
The rapid rise of electric vehicles will increase demand for high-performance battery systems, including integrated junction box solutions. By 2026, EV manufacturers are expected to adopt modular battery pack designs with embedded junction boxes that support higher voltage platforms (e.g., 800V systems), fast charging, and improved thermal management. This trend will favor junction boxes with enhanced safety features and compact, lightweight designs. -
Advancements in Materials and Design
To meet higher efficiency and durability requirements, junction box manufacturers are shifting toward advanced thermoplastic materials with superior UV, heat, and flame resistance. Innovations such as integrated bypass diodes, plug-and-play connectors, and water-resistant (IP68-rated) enclosures will become standard, supporting reliability in harsh environments. -
Stringent Safety and Compliance Standards
Regulatory bodies are expected to enforce stricter safety certifications for junction boxes by 2026, including compliance with IEC 62930, UL 6703, and TÜV standards. These regulations will emphasize arc-fault detection, fire resistance, and electromagnetic compatibility, pushing manufacturers to invest in R&D and quality assurance. -
Supply Chain Localization and Sustainability
Geopolitical shifts and supply chain resilience concerns will drive regionalization of battery and component manufacturing. In response, junction box producers may localize production to serve key markets in North America and Europe, reducing dependency on single-source suppliers. Additionally, sustainability initiatives will promote recyclable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The market is likely to see consolidation among component suppliers, with major battery and EV manufacturers forming strategic alliances with junction box producers to ensure seamless integration and supply chain stability. Joint development agreements and co-engineering efforts will become more common.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for junction box batteries will be defined by technological innovation, regulatory evolution, and strong tailwinds from renewable energy and electric mobility. Companies that prioritize smart integration, safety, and sustainability will be best positioned to capture value in this expanding sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Junction Box Batteries (Quality, IP Rating)
When sourcing junction box batteries—often referring to integrated battery solutions housed within or alongside electrical junction boxes, such as those used in solar systems or backup power applications—procurement teams and engineers must be vigilant about two critical aspects: quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating. Overlooking these factors can lead to premature failures, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Quality Components and Manufacturing
One of the biggest risks in sourcing junction box batteries is encountering substandard components due to inadequate quality control or unverified suppliers.
- Use of Low-Grade Cells: Some manufacturers cut costs by using recycled, second-life, or uncertified lithium-ion or lead-acid cells. These cells degrade faster, offer lower cycle life, and pose safety risks such as thermal runaway.
- Inadequate BMS (Battery Management System): A weak or poorly designed BMS fails to monitor voltage, temperature, and charge balance, increasing the risk of overcharging, deep discharge, or cell imbalance.
- Shortcuts in Assembly: Poor soldering, insufficient insulation, or improper sealing during assembly can lead to internal shorts, corrosion, or electrical faults.
- Lack of Certifications: Beware of suppliers claiming performance specs without valid certifications (e.g., UL, IEC, CE, UN38.3). Absence of these is a red flag for non-compliance with safety and performance standards.
Mitigation: Always request test reports, third-party certifications, and conduct factory audits or sample testing. Prioritize suppliers with proven track records and transparent manufacturing processes.
Incorrect or Misrepresented IP Rating
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating is critical for junction box batteries, especially in outdoor or harsh environments. Misunderstanding or misrepresentation of IP ratings is a frequent sourcing pitfall.
- False IP Claims: Some suppliers advertise high IP ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67) without proper testing. The product may lack proper gaskets, sealing, or housing integrity to meet the claimed standard.
- Partial Protection: A device might be rated IP67 for the junction box but not the battery compartment, leading to moisture ingress and corrosion at connection points.
- Environmental Mismatch: Selecting a battery with insufficient IP rating (e.g., IP54 instead of IP65) for outdoor solar installations exposes it to dust and water, accelerating failure.
- Degradation Over Time: Seals and gaskets can degrade due to UV exposure or temperature cycling. A battery that initially meets IP67 may not maintain that protection over time if materials are subpar.
Mitigation: Verify IP ratings with test documentation (e.g., IEC 60529 compliance reports). Conduct spot checks or environmental testing (spray, dust, submersion) on samples. Ensure both the junction box and battery enclosure meet the required IP level.
Additional Considerations
- Thermal Management: Poorly designed enclosures may trap heat, reducing battery life and increasing fire risk—especially critical in sealed, high-IP environments.
- Compatibility with Existing Systems: Ensure voltage, capacity, and communication protocols (e.g., RS485, CAN) align with the rest of the system to avoid integration issues.
- Long-Term Support and Warranty: Choose suppliers offering extended warranties and technical support, as battery performance degrades over time and serviceability is key.
By focusing on verified quality and accurate IP ratings, and avoiding these common pitfalls, you can ensure reliable, safe, and durable performance from your junction box battery installations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Junction Box Battery
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe handling, transport, storage, and regulatory adherence of Junction Box Batteries. These batteries, often lithium-ion or sealed lead-acid types used in solar, automotive, or industrial applications, are subject to strict international and national regulations due to their potential hazards.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Junction Box Batteries must be correctly classified according to international transport regulations. Most commonly, they fall under UN numbers such as UN3480 (Lithium-ion batteries) or UN2794 (Lead-acid, non-spillable). Proper classification dictates packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements.
Required documentation includes:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) compliant with GHS standards
– Air Waybill (AWB) or Bill of Lading (BOL) with proper hazardous goods notation
– Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (for air transport)
– Compliance certificates (e.g., UN 38.3 test summary for lithium batteries)
Ensure all documentation specifies the battery chemistry, watt-hour (Wh) rating, and state of charge (typically ≤30% for air transport of lithium batteries).
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging must be robust, non-conductive, and designed to prevent short circuits, physical damage, and electrolyte leakage. For lithium-ion batteries, use rigid outer packaging with individual cell or battery protection (e.g., bubble wrap, compartmentalization).
Mandatory labeling includes:
– Proper shipping name and UN number
– Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods label (for lithium batteries)
– Lithium Battery Mark (for air transport)
– Orientation arrows (if applicable)
– Name and address of shipper/consignee
Ensure terminals are insulated or protected from contact with conductive materials. For large shipments, package markings must be durable and legible.
Transport Modes and Restrictions
Different transport modes have specific rules:
- Air Transport (IATA DGR): Most restrictive. Requires State Variation compliance, SoC ≤30%, and approval from the airline. Lithium batteries shipped alone (PI 965–970) have stricter limits than those packed with equipment.
- Ocean Freight (IMDG Code): Requires proper container stowage, segregation from incompatible goods, and documentation. UN3480 batteries must be stowed away from heat sources.
- Ground Transport (ADR/RID in Europe, 49 CFR in USA): Requires placarding for large quantities, trained personnel, and vehicle certification where applicable.
Always check for carrier-specific restrictions, especially with passenger airlines or express couriers.
Storage and Handling Protocols
Store Junction Box Batteries in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from flammable materials and direct sunlight. Maintain temperatures between 10°C and 25°C to preserve battery integrity and reduce thermal risk.
Handling practices:
– Use insulated tools to prevent short circuits
– Avoid stacking or compressing packages
– Prohibit smoking or open flames in storage/handling areas
– Implement ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection in sensitive environments
Train personnel on emergency procedures, including response to leakage, fire, or thermal runaway.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Junction Box Batteries are classified as hazardous waste under regulations such as RCRA (USA) and WEEE (EU). They must not be disposed of in regular landfill or incineration.
Compliance requires:
– Proper segregation by chemistry during collection
– Use of licensed recyclers with certified facilities
– Maintaining waste manifests and tracking documentation
– Adhering to local take-back and producer responsibility schemes
Ensure end-of-life logistics include safe packaging and transport to authorized treatment facilities.
Country-Specific and Regional Regulations
Compliance extends beyond transport to import/export and market access. Key regional requirements include:
- EU: CE marking, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH compliance
- USA: FCC certification (if applicable), DOT and EPA regulations
- China: CCC mark, GB standards compliance
- India: BIS certification under IS 16046
Verify import permits, customs codes (HS codes), and local labeling requirements before shipment. Some countries restrict or ban certain battery chemistries or capacities.
Incident Reporting and Emergency Response
In the event of damage, leakage, fire, or suspected thermal runaway:
– Isolate the affected package or area immediately
– Follow emergency procedures per SDS and local regulations
– Report incidents to relevant authorities (e.g., aviation authority, DOT, national safety agency)
– Document the incident for internal review and regulatory compliance
Maintain accessible emergency response information, including contact details for hazardous materials response teams.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics for Junction Box Batteries require strict adherence to classification, packaging, documentation, and regional regulatory standards. Proactive training, proper handling, and engagement with certified partners throughout the supply chain are essential to ensure safety, avoid penalties, and maintain environmental responsibility. Regular audits and updates to compliance procedures are recommended as regulations evolve.
Conclusion for Sourcing Junction Box Battery
In conclusion, sourcing a junction box battery requires careful consideration of technical specifications, compatibility, reliability, and supplier credibility. The junction box, often integral to solar panel systems or electrical enclosures, may incorporate a battery for backup power, monitoring systems, or safety functions. Ensuring the selected battery meets voltage, capacity, environmental, and safety standards is crucial for long-term performance and system integrity.
Strategic sourcing should involve evaluating multiple suppliers based on quality certifications, cost efficiency, lead times, and after-sales support. Additionally, opting for batteries with proven durability in similar operating conditions—such as temperature resistance and lifespan—can reduce maintenance and replacement costs.
Ultimately, a well-sourced junction box battery enhances system reliability, supports uninterrupted operations, and contributes to overall energy efficiency. By aligning technical needs with reliable supply chain practices, organizations can achieve optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their electrical or renewable energy systems.