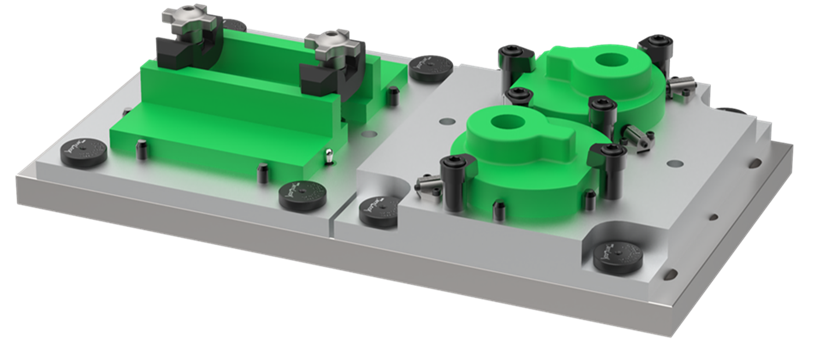
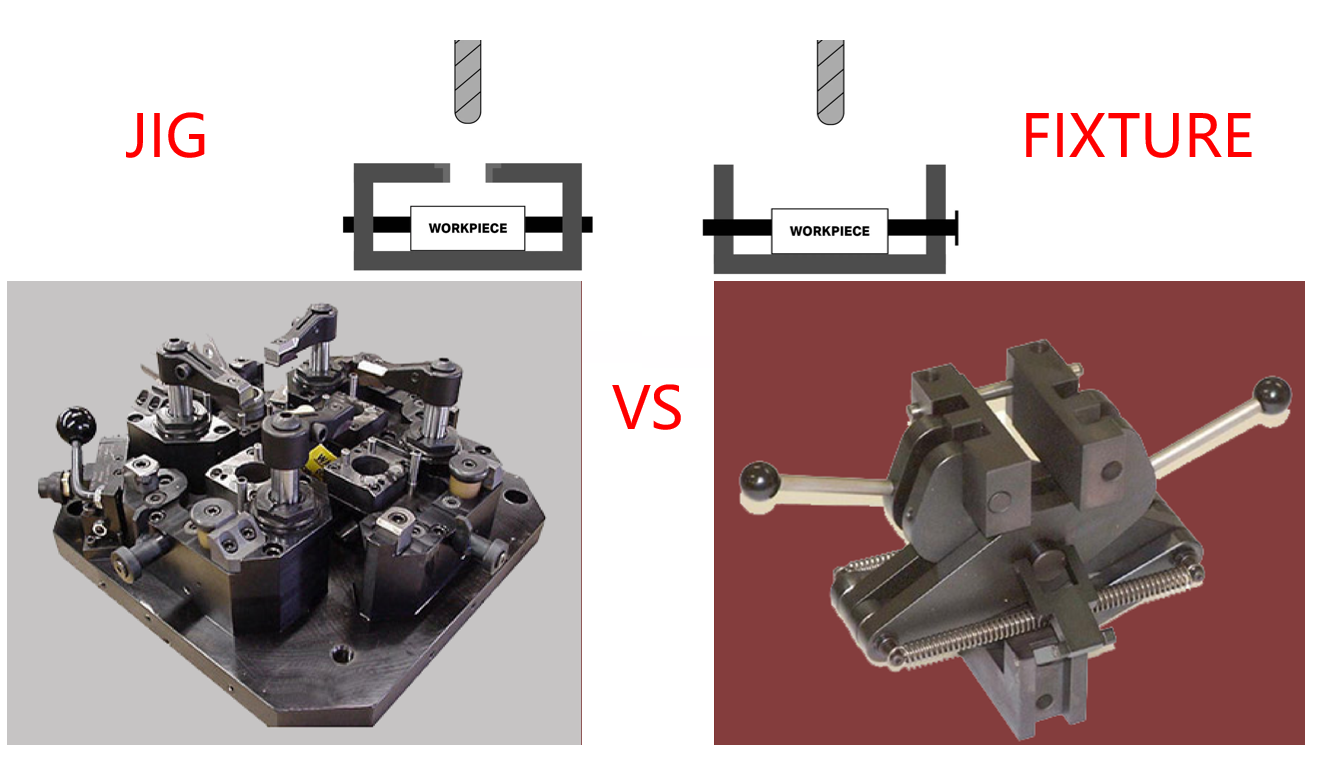
The global jig and fixture tooling market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision, repeatability, and efficiency in manufacturing processes across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global jig and fixture market was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.3% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of automation, advanced materials, and modular tooling systems that reduce setup time and improve production throughput. As manufacturers seek to optimize operational performance and maintain competitive advantage, the role of high-quality jig and fixture solutions has become increasingly critical. In this context, a select group of leading manufacturers have emerged, combining engineering expertise, innovation, and scalable production capabilities to meet evolving industry demands. Below is a data-informed overview of the top 8 jig and fixture tooling manufacturers shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 8 Jig And Fixture Tooling Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Fixture Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pjfinc.com
Key Highlights: Precision Jig & Fixture (PJF) is a full-service inspection fixture and custom tooling manufacturer. PJF offers 5 axis machining services for all industries….
#2 Jigs & Fixtures
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fetusa.com
Key Highlights: FET Engineering provides precision Jigs & Fixtures solutions to assist in meeting manufacturing goals: repeatability, consistency, & time reduction….
#3 Jig & Fixture Manufacturer & Design Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mahutatool.com
Key Highlights: We provide custom jig and fixture tooling solutions tailored to specific needs, whether for milling, surface grinding or specialized operations. Our expertise ……
#4 Jigs And Fixture Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2009
Website: mddesignwi.com
Key Highlights: MD Design and Automation is a jig and fixture manufacturer—experienced in building and supplying machining tools to clients all over the US, South America, ……
#5 Great Lakes Jig & FIXTURE
Domain Est. 2010
Website: gljf.us
Key Highlights: Great Lakes Jig & Fixture, LLC has been building quality checking fixtures for manufacturers in the automotive, aerospace and medical industries for over Twenty ……
#6 to Kreg Tool
Domain Est. 1999
Website: kregtool.com
Key Highlights: There’s a new pocket hole jig in town. The kregjig Rebel is a battery powered pocket hole jig on Kreg’s new Ionic Drive system of tools….
#7 Tools & Jig Fixture
Domain Est. 2000
Website: siamdial.com
Key Highlights: Tools & Jig Fixture CNC CNC (Computer Numerical Control) process involves the automation of machine tools through computer programming….
#8 Turnkey Fixtures/Jigs/Tooling Manufacturing Design Services
Domain Est. 2004
Website: ktmsolutions.com
Key Highlights: KTM Solutions builds turnkey fixture, jig, and tooling manufacturing systems that are built to facilitate reliable and safe product manufacturing….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Jig And Fixture Tooling
2026 Market Trends for Jig and Fixture Tooling
The jig and fixture tooling market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, increased automation, and evolving industry demands. These specialized tools—critical for ensuring precision, repeatability, and efficiency in production processes—are adapting to the needs of modern industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. This analysis explores the key trends expected to shape the jig and fixture tooling market in 2026.
Rising Adoption of Smart and Modular Fixturing Systems
One of the most prominent trends by 2026 is the growing shift toward smart and modular jig and fixture systems. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting modular tooling platforms that offer flexibility, rapid reconfiguration, and reduced setup times. Integrated with sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, smart fixtures provide real-time feedback on alignment, pressure, and wear, enabling predictive maintenance and improved quality control. This trend is particularly strong in high-mix, low-volume production environments where adaptability is crucial.
Integration with Advanced Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
As Industry 4.0 continues to reshape manufacturing, jig and fixture tooling are becoming integral components of connected production ecosystems. By 2026, expect widespread integration of tooling systems with digital twins, CAD/CAM software, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). This enables seamless data flow from design to production, allowing for faster prototyping, error reduction, and enhanced traceability. Cloud-based tooling management platforms will also gain traction, facilitating remote monitoring and optimization of tooling assets across global supply chains.
Growth in Lightweight and Composite Material Applications
The expanding use of lightweight materials—such as carbon fiber composites, aluminum alloys, and advanced polymers—in aerospace and automotive sectors is influencing jig and fixture design. Traditional steel fixtures are being replaced with lighter, non-marring alternatives made from composite materials or aluminum to avoid damaging sensitive workpieces. Customized, low-clamp-force fixtures will be in higher demand to accommodate the unique handling requirements of these materials without compromising precision.
Expansion of Additive Manufacturing in Tooling
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is revolutionizing jig and fixture production by enabling rapid, cost-effective creation of custom tooling. By 2026, more manufacturers will adopt in-house 3D printing for prototyping and end-use fixtures, reducing lead times and inventory costs. Materials such as high-strength polymers and metal alloys suitable for printing are making printed jigs and fixtures viable for high-precision and high-load applications, further accelerating adoption.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Considerations
Environmental sustainability is emerging as a key driver in tooling design and selection. By 2026, manufacturers will prioritize reusable, recyclable, and energy-efficient jig and fixture solutions. Modular systems that extend tooling lifespan and reduce waste will be favored. Additionally, companies will seek suppliers with sustainable manufacturing practices, including reduced carbon footprints and responsible material sourcing.
Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical shifts and supply chain disruptions have prompted a reevaluation of manufacturing localization. In 2026, regional hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific will see increased investment in domestic jig and fixture production to enhance supply chain resilience. Nearshoring and onshoring trends will drive demand for localized tooling solutions, especially in industries requiring high precision and quick turnaround times.
Workforce Skill Transformation
With the increasing complexity of smart and automated tooling systems, the demand for skilled professionals in digital manufacturing, robotics, and system integration will rise. By 2026, continuous training and upskilling programs will become essential for maintaining a competitive workforce capable of designing, operating, and maintaining advanced jig and fixture systems.
In conclusion, the 2026 jig and fixture tooling market will be defined by innovation, digital integration, and adaptability. Companies that embrace modular design, smart technologies, and sustainable practices will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities across diverse industrial sectors.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Jig and Fixture Tooling: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Quality Control Leading to Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing jig and fixture tooling—especially from low-cost or offshore suppliers—is inconsistent quality. Poor material selection, inadequate machining tolerances, and substandard assembly practices can result in tooling that fails prematurely or introduces variation into the manufacturing process. Without strict quality control protocols and clear specifications, companies risk production downtime, increased scrap rates, and compromised product quality.
Inadequate Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Suppliers may deliver jigs and fixtures that technically meet the design criteria but are not optimized for actual production environments. This includes poor ergonomics, difficult maintenance access, or failure to account for thermal expansion and wear. These oversights can reduce throughput, increase operator fatigue, and shorten tool life, ultimately undermining the efficiency gains the tooling was meant to achieve.
Lack of Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
When sourcing externally, especially internationally, there is a significant risk of IP theft or unauthorized replication. Jigs and fixtures often embody proprietary manufacturing processes and design know-how. Without robust legal agreements—such as non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), clear ownership clauses, and restrictions on tooling duplication—companies may find their designs copied or sold to competitors.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive documentation, including CAD files, inspection reports, material certifications, and assembly instructions. This lack of traceability complicates quality audits, maintenance, and potential rework. It also creates challenges when trying to reproduce the tooling or transfer it to another supplier, increasing long-term operational risk.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Sourcing decisions often focus on up-front cost without considering long-term support. Some suppliers may be unable or unwilling to provide spare parts, repairs, or design updates. This can lead to extended downtime when components wear out or break, especially if the tooling is custom and not easily replaceable.
Failure to Validate Supplier Capabilities and Experience
Choosing a supplier based solely on price or speed, without verifying their expertise in precision tooling, can lead to costly mistakes. Suppliers unfamiliar with tight tolerance requirements or specific industry standards (e.g., automotive, aerospace) may deliver tooling that does not meet functional or regulatory demands. Conducting site audits and requesting samples or references is critical to mitigate this risk.
Absence of Clear Acceptance Criteria and Testing Protocols
Without predefined acceptance tests—such as first-article inspections, functional trials, or load testing—companies may accept tooling that appears correct but performs poorly under real-world conditions. Establishing clear performance benchmarks and validation steps before full acceptance helps ensure reliability and alignment with production needs.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Jig and Fixture Tooling
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for managing jig and fixture tooling throughout its lifecycle, from design and procurement to deployment, maintenance, and disposal. Proper adherence ensures operational efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance.
Design and Specification Compliance
All jig and fixture designs must comply with relevant engineering standards (e.g., ISO, ANSI, ASME), internal manufacturing specifications, and client requirements. Design documentation should include tolerance specifications, material certifications, and safety assessments. Use of standardized components and adherence to Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles are mandatory to ensure interchangeability and ease of maintenance.
Procurement and Supplier Management
Jig and fixture tooling must be sourced from certified suppliers with documented quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001). Purchase orders must specify technical requirements, delivery timelines, packaging instructions, and compliance documentation (e.g., material test reports, calibration certificates). Supplier audits and performance evaluations should be conducted annually to ensure ongoing compliance.
Transportation and Handling Logistics
Tooling must be transported using protective packaging to prevent damage during transit. Crates should be labeled with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include unique asset tracking IDs. For international shipments, ensure compliance with customs regulations, including proper Harmonized System (HS) codes, export declarations, and adherence to Incoterms® 2020. Use only logistics partners experienced in handling precision tooling.
Import/Export Compliance
All cross-border movements of jig and fixture tooling must comply with applicable trade regulations, including export controls (e.g., EAR, ITAR if applicable), sanctions, and restricted party screening. Maintain records of export licenses, commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Ensure tools containing dual-use technologies are assessed for compliance prior to shipment.
Receiving and Inspection
Upon receipt, jig and fixture tooling must undergo a formal receiving inspection. Verify against purchase order, packing list, and design specifications. Conduct dimensional checks and functional testing as defined in the acceptance protocol. Document non-conformances and initiate corrective actions through the quality management system (QMS).
Asset Tracking and Inventory Management
Implement a digital asset management system to track location, usage, maintenance history, and calibration status of each jig and fixture. Assign unique identifiers (e.g., barcode/RFID) and update records in real time. Conduct periodic physical inventories to reconcile system data and ensure traceability throughout the tooling lifecycle.
Calibration and Maintenance Compliance
Schedule regular calibration and preventive maintenance per documented procedures and frequency requirements (e.g., monthly, quarterly). Calibration must be performed by accredited labs with traceability to national or international standards (e.g., NIST). Maintain logs of all maintenance, repairs, and modifications, including personnel certifications and parts used.
Workplace Safety and Ergonomics
Ensure all jig and fixture tooling complies with occupational health and safety regulations (e.g., OSHA, local equivalents). Conduct risk assessments for pinch points, sharp edges, and operational hazards. Provide training to operators on safe handling and emergency procedures. Tools must be ergonomically designed to minimize operator strain and fatigue.
Documentation and Record Retention
Maintain a centralized repository for all tooling-related documentation, including design drawings, inspection reports, calibration certificates, maintenance logs, and compliance certifications. Retain records for a minimum of seven years or as required by industry-specific regulations (e.g., aerospace, automotive). Ensure data is backed up and accessible for audits.
End-of-Life and Disposal Procedures
Decommissioned jig and fixture tooling must be evaluated for reuse, resale, or recycling. Dispose of hazardous materials (e.g., cutting fluids, coated metals) in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH). Document disposal methods and retain certificates of destruction or recycling to support compliance audits and sustainability initiatives.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
Conduct internal audits at least annually to verify compliance with logistics and regulatory requirements. Use audit findings, non-conformance reports, and feedback from operations to drive continuous improvement in tooling management processes. Update this guide periodically to reflect changes in regulations, technologies, or business practices.
Conclusion: Sourcing Jig and Fixture Tooling
Sourcing jig and fixture tooling is a critical aspect of ensuring manufacturing efficiency, precision, and repeatability in production processes. A well-structured sourcing strategy balances quality, cost, lead time, and long-term reliability. By carefully evaluating internal capabilities versus outsourcing options, manufacturers can determine whether to produce tooling in-house or partner with experienced external suppliers.
Key considerations in the sourcing decision include design complexity, production volume, material requirements, and desired lead times. Collaborating with trusted suppliers who offer engineering support, use advanced manufacturing technologies, and adhere to quality standards can significantly enhance tooling performance and lifespan. Additionally, establishing clear communication, robust quality control protocols, and long-term partnerships helps mitigate risks and reduce total cost of ownership.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of jig and fixture tooling contributes to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and consistent product quality—driving competitiveness in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment. A strategic, data-driven approach to procurement ensures that tooling solutions align with both immediate production needs and future scalability goals.