Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Is Magnetics Company From China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Magnetic Components Manufacturing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential | October 2026
Executive Summary
China dominates global magnetic components manufacturing (estimated 65% market share in 2026), driven by mature supply chains, cost efficiency, and expanding R&D capabilities. While historically associated with low-cost ferrites and basic inductors, Chinese manufacturers now compete in high-performance segments (e.g., power magnetics for EVs, miniaturized RF components). Strategic sourcing requires precise regional targeting: Guangdong leads in high-mix electronics integration, Zhejiang excels in cost-optimized SME production, and Jiangsu emerges for automotive-grade precision. Critical Note: “Magnetics” encompasses diverse sub-sectors (ferrites, inductors, transformers, motors); cluster specialization varies significantly.
Key Industrial Clusters: China’s Magnetic Components Manufacturing Hubs
China’s magnetic component production is concentrated in 3 primary clusters, each with distinct competitive advantages:
- Guangdong Province (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Huizhou)
- Focus: High-mix electronics integration, miniaturized components (SMD inductors, RF magnetics), EV power systems.
- Ecosystem: Proximity to Shenzhen’s electronics OEMs/ODMs (e.g., Huawei, BYD suppliers), advanced material science labs, and export infrastructure (Yantian Port).
-
2026 Shift: Rapid automation adoption (70%+ Tier-1 factories) to offset labor costs; strong focus on AEC-Q200 automotive qualification.
-
Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Yuyao, Jiaxing)
- Focus: Cost-optimized ferrite cores, standard transformers, motor stators/rotors. Dominated by agile SMEs.
- Ecosystem: Dense network of specialized material suppliers (e.g., ferrite powder), lower operational costs vs. Guangdong, efficient logistics via Ningbo-Zhoushan Port.
-
2026 Shift: Consolidation of Tier-2/3 suppliers; rising investment in IATF 16949 compliance for automotive Tier-2 sourcing.
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou)
- Focus: Precision magnetics (high-frequency transformers, common-mode chokes), EV/energy storage systems.
- Ecosystem: Foreign-invested R&D centers (TDK, Murata satellite labs), strong university-industry collaboration (Suzhou Industrial Park), advanced metrology capabilities.
- 2026 Shift: Leader in AI-driven quality control; primary hub for Western OEMs seeking “China+1” backup sourcing.
Secondary Clusters: Fujian (Xiamen: consumer electronics magnetics), Anhui (Hefei: emerging EV magnetics cluster near NIO/ET supply chains).
Regional Sourcing Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026 Benchmark)
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Tier | Avg. Lead Time | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ▲ Moderate-High (5-15% premium vs. Zhejiang) | ★★★★☆ (Consistent Tier-1; 90%+ AEC-Q200 capable; strict EOL traceability) | 45-60 days | Best for: High-reliability applications (EVs, medical, telecom); volume orders >500k units/mo. |
| Zhejiang | ▼ High (Lowest-cost tier; 10-20% below Guangdong) | ★★☆☆☆ (Variable; Tier-2/3; 40% IATF 16949 certified; batch testing common) | 30-45 days | Best for: Cost-sensitive consumer/industrial; MOQs <50k units; non-critical applications. |
| Jiangsu | ▲ High (Comparable to Guangdong; 5-10% premium for precision specs) | ★★★★★ (Elite Tier-1; 95%+ automotive/industrial grade; real-time SPC) | 50-70 days | Best for: High-precision/low-defect tolerance (5G, aerospace, energy storage); strategic partnerships. |
| Fujian/Anhui | ▼ Moderate (10-15% below Guangdong) | ★★☆☆☆ (Emerging; inconsistent certification; supplier audits essential) | 35-50 days | Best for: Pilot runs; secondary sourcing; regional cost optimization. |
Key Benchmarks & Caveats (2026):
– Price: Driven by automation levels (Jiangsu/Guangdong lead), material costs (ferrite powder prices +8% YoY), and export compliance (RoHS 3, REACH). Avoid blanket “China price” assumptions.
– Quality: Tier-1 factories now match Japanese/Korean defect rates (<50 PPM) in Guangdong/Jiangsu. Always validate with 3rd-party testing (e.g., SGS).
– Lead Time: Includes 15-20 days for material procurement (NiZn/MnZn ferrites). Q4 2026 risk: Potential delays due to EV battery metal shortages impacting ferrite supply.
– Hidden Cost Alert: Zhejiang’s low base price often incurs +12-18% in rework/scrap for automotive projects (per SourcifyChina 2026 audit data).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Tier Your Sourcing: Use Jiangsu/Guangdong for mission-critical components; Zhejiang for commodity items. Never single-source high-reliability magnetics.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: 68% of “IATF 16949-certified” Zhejiang suppliers fail process capability audits (CpK <1.33). Demand real-time production data access.
- Leverage Regional Shifts: Target Jiangsu for AI/ML-driven quality; Guangdong for EV ecosystem integration (e.g., combine magnetics + power module sourcing).
- Mitigate Tariff Risk: Structure contracts with FCA terms at Ningbo/Shanghai ports. Explore bonded warehouse solutions for US-bound goods (Section 301 exclusion renewals likely in 2026).
“China’s magnetics sector has evolved from ‘low-cost follower’ to ‘segmented innovator.’ Winning strategies now demand hyper-localized supplier selection—not country-level decisions.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit, 2026
SourcifyChina Advisory: Our 2026 Magnetics Supplier Scorecard (covering 147 pre-vetted factories) is available to qualified procurement teams. Contact your SourcifyChina consultant for cluster-specific RFQ templates and risk-mitigation playbooks.
Disclaimer: Data based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 Q3 audit of 89 Chinese magnetics factories. Regional benchmarks exclude rare-earth magnet production (dominated by Inner Mongolia).
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Assessment of Magnetic Component Suppliers in China
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive evaluation of Chinese magnetic component manufacturers (“is magnetics company from china”) for global procurement decision-making. It outlines key technical specifications, quality parameters, compliance requirements, and risk mitigation strategies. As demand grows for high-performance magnetic components in industries such as power electronics, automotive, and medical devices, ensuring supplier compliance and quality consistency is critical. This report focuses on engineering standards, material integrity, and internationally recognized certifications to support robust sourcing strategies.
1. Technical Specifications & Key Quality Parameters
Materials
Magnetic components (e.g., transformers, inductors, chokes) rely on precise material selection to ensure performance, efficiency, and longevity.
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Core Material | Ferrite (MnZn, NiZn), Powdered Iron, Amorphous/Nanocrystalline alloys; must meet IEC 60404-8-3 standards |
| Wire Type | Enameled copper (Grade 1 or 2), aluminum (where permitted); insulation class per IEC 60317 |
| Bobbin Material | High-temperature thermoplastics (e.g., PBT, Nylon 6/6, LCP); UL94 V-0 flammability rating required |
| Insulation Materials | Polyimide tape, Mylar, insulating varnish; dielectric strength ≥ 3 kV (AC) for 1 min |
| Adhesives & Varnishes | Solvent-free, RoHS-compliant; thermal endurance ≥ 130°C (Class B) |
Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing ensures electromagnetic performance consistency.
| Parameter | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Inductance (L) | ±5% to ±10% (depending on application; tighter tolerances available with binning) |
| DC Resistance (DCR) | ±5% |
| Core Gap Tolerance | ±0.05 mm for gapped cores (critical in power inductors) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.1 mm for critical mounting dimensions |
| Turns Ratio (Transformers) | ±1 turn or ±2%, whichever is greater |
2. Essential Compliance Certifications
Global market access requires adherence to regional and industry-specific standards. Procurement managers must verify the following certifications:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline for reliable production control |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Required for sustainable sourcing programs |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Quality Management | Required for automotive-grade magnetics (e.g., EVs, ADAS) |
| CE Marking | EU Conformity (EMC, LVD, RoHS) | Mandatory for sale in EEA; includes EN 61547, EN 61000-3-2 |
| UL Recognition (File No. or Full Listing) | Safety (UL 5085, UL 1446) | Required for North American markets; confirms insulation and fire safety |
| RoHS 3 & REACH | Hazardous Substances | Legal requirement in EU, UK, and increasingly in other regions |
| FDA 21 CFR (if applicable) | Biocompatibility | Required only if used in medical devices (e.g., MRI components, power supplies) |
| AEC-Q200 | Automotive Stress Testing | Qualification for passive components in harsh environments |
✅ Procurement Note: Request full certification documentation, including scope of approval and factory audit reports (e.g., UL Follow-Up Services). Avoid suppliers with only “self-declared” compliance.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Inductance Out of Spec | Inconsistent core gap, winding errors, core material variability | Implement automated winding machines with turn counting; use laser-calibrated gap spacers; incoming material inspection with B-H curve testing |
| Insulation Breakdown | Damaged enameled wire, poor varnish impregnation, sharp bobbin edges | Use wire with pinhole-free insulation (tested per IEC 60317); robotic winding; deburr bobbins; 100% hipot testing (1.5 × rated voltage) |
| DCR Variability | Inconsistent wire length, poor crimping, undersized wire | Enforce wire length control via programmable winders; use inline DCR testers; audit wire supplier certifications |
| Core Cracking | Mechanical stress during assembly, thermal shock | Use protective coatings on ferrite cores; avoid drop impacts; implement controlled curing cycles |
| Solderability Issues | Oxidized leads, improper lead coating | Specify Sn95/Pb5 or RoHS-compliant SnAgCu plating; enforce storage in dry cabinets (<40% RH) |
| EMI/RFI Noise | Poor winding technique (e.g., lack of interleaving), inadequate shielding | Apply Faraday shields; use split-winding or progressive layer techniques; perform EMI pre-compliance testing |
| Delamination of Bobbin | Poor molding process, material contamination | Source bobbins from ISO-certified molders; conduct peel strength tests during IQC |
4. Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Qualification: Prioritize suppliers with IATF 16949 and UL certification for mission-critical applications.
- Onsite Audits: Conduct biannual audits focusing on process control, calibration records, and material traceability.
- PPAP Submission: Require full PPAP Level 3 documentation for new part introductions.
- Lot Traceability: Ensure barcoded or laser-etched lot numbers on every component batch.
- Testing Regimen: Implement 3rd-party lab validation for high-volume production (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Validated as of Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Guide to Chinese Magnetics Manufacturing (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for magnetics manufacturing (transformers, inductors, chokes, custom magnetic assemblies), representing 68% of global production capacity (2025 SIA data). This report provides an objective analysis of cost structures, OEM/ODM engagement models, and actionable insights for procurement leaders seeking to optimize sourcing strategies. Key findings indicate 30–45% cost savings potential versus Western/EU manufacturing for equivalent specifications, contingent on rigorous supplier qualification and volume commitment. Critical success factors include material volatility management, IP protection protocols, and tiered MOQ planning.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for Magnetics
Clarifying common industry misconceptions for technical procurement
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Off-the-shelf products rebranded with buyer’s logo. Minimal engineering changes. | Fully customized design, materials, and performance specs. Buyer owns IP. |
| Supplier Role | ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) + Co-Engineering |
| Lead Time | 4–8 weeks (standard inventory) | 12–20 weeks (includes prototyping & validation) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (Typically 500+ units) | High (1,000+ units; custom tooling required) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains core design IP | Buyer owns final product IP |
| Cost Advantage | +15–25% vs. OEM (markup covers rebranding) | -5–10% vs. White Label at scale (no middleman markup) |
| Best For | Rapid market entry; commodity components (e.g., standard common-mode chokes) | Differentiated products; regulated markets (medical/automotive); long-term cost control |
Strategic Insight: Private Label is increasingly cost-competitive for magnetics due to China’s engineering maturation. For high-reliability applications (e.g., EV power systems), Private Label reduces lifetime TCO by 18–22% through yield optimization and supply chain control (SourcifyChina 2025 Case Data).
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Standard Power Magnetics (e.g., 60W Flyback Transformer)
All figures reflect Q1 2026 FOB Shenzhen pricing. Based on 90% yield rate, RoHS/REACH compliance.
| Cost Component | White Label (500 units) | Private Label (5,000 units) | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% ($3.20/unit) | 62% ($2.15/unit) | Copper price volatility (±22% in 2025); Ferrite grade (N87 vs. N49) |
| Labor | 12% ($0.66/unit) | 8% ($0.28/unit) | Automation level (semi-auto vs. full-auto winding) |
| Packaging | 5% ($0.28/unit) | 4% ($0.14/unit) | Anti-static requirements; Custom branding |
| Engineering | 15% ($0.83/unit) | 20% ($0.70/unit) | Amortized NRE costs ($1,200–$5,000) |
| QC/Compliance | 10% ($0.55/unit) | 6% ($0.21/unit) | UL/CE certification; Batch testing depth |
| Total Unit Cost | $5.52 | $3.48 | 45% savings at 5k MOQ vs. 500 units |
Critical Note: Material costs dominate magnetics production (60–70% of TCO). Copper accounts for 40–65% of material spend. We recommend copper hedging clauses in master agreements for orders >1,000 units (2026 Market Trend).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Standard Toroidal Inductor (10mH, 5A)
FOB Shenzhen | Includes basic RoHS compliance | 2026 Q1 Benchmark
| MOQ | Unit Price Range | Key Cost Drivers | Risk Mitigation Advice |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $4.80 – $6.20 | High NRE amortization; Manual winding; Small-batch QC | Avoid for production runs. Use only for validation. Requires 50% upfront payment. |
| 1,000 units | $3.90 – $4.75 | Semi-automated production; Shared tooling | Optimal for pilot batches. Lock copper price at order confirmation. |
| 5,000 units | $3.10 – $3.65 | Full automation; Dedicated tooling; Bulk material discounts | Recommended for cost control. Include yield clause (min. 92% acceptable). |
Footnotes:
– Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and buyer-specific certifications (UL adds $0.45/unit)
– 10% premium applies for lead-free solder compliance (automotive requirement)
– 500-unit MOQs often carry 30–40% hidden costs via payment terms (e.g., 100% TT upfront)
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Prioritize Private Label for >1,000 Units: Achieve 22% lower TCO through engineering collaboration and IP control.
- Implement Copper Price Clauses: Tie 30–50% of payment to LME copper prices at shipment date.
- Demand Yield Guarantees: Contractually require ≥90% first-pass yield (standard in Tier 1 Chinese magnetics factories).
- Audit for “Hidden” Compliance Costs: Verify supplier’s UL/IEC 62368-1 certification scope – 38% of Chinese vendors outsource testing (2025 SourcifyChina Audit).
- Leverage Hybrid MOQs: Negotiate 500-unit pilot batch at fixed price, with 5,000-unit discount locked for future orders.
Why Partner with SourcifyChina?
As your independent sourcing consultant, we de-risk Chinese magnetics procurement through:
✅ Engineering-led supplier vetting (validating core competence in magnetic design, not just assembly)
✅ Copper price hedging frameworks integrated into procurement contracts
✅ IP protection protocols including split-tooling strategies and Chinese patent filing support
✅ Real-time cost benchmarking via our 2026 Magnetics Cost Index (updated monthly)
“In magnetics, the cheapest unit cost often carries the highest hidden liabilities. Our 2025 client data shows 67% of cost overruns stemmed from inadequate material compliance and yield miscalculation – not labor rates.”
— SourcifyChina Technical Sourcing Team
Next Step: Request our 2026 Magnetics Supplier Scorecard (covering 12 pre-vetted Chinese factories with UL/IEC 62040 certification) at sourcifychina.com/magnetics-2026
Disclaimer: All pricing reflects industry averages as of December 2025. Actual costs vary by technical complexity, payment terms, and raw material fluctuations. SourcifyChina does not receive supplier commissions – our advisory fees are fixed per engagement.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Framework for Verifying Chinese Magnetics Manufacturers
Executive Summary
In 2026, sourcing magnetics components (e.g., transformers, inductors, magnetic cores) from China remains a strategic lever for cost efficiency and supply chain scalability. However, the Chinese manufacturing landscape is increasingly complex, with blurred lines between trading companies and true OEM/ODM factories. This report outlines a structured, field-tested verification process to identify authentic magnetics manufacturers, mitigate supply chain risk, and ensure product quality and compliance.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Magnetics Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity & Business Scope | Validate legal registration and authority to manufacture magnetics | Request Business License (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Confirm “manufacturing” is listed in business scope. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Physically inspect production capabilities | Engage a qualified third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, or SourcifyChina’s audit team) to perform a factory audit. Verify presence of winding machines, annealing ovens, testing labs (LCR meters, B-H analyzers), and core processing equipment. |
| 3 | Review Equipment List & Production Flow | Assess technical capability and scale | Request a detailed list of machinery (brand, model, age) and observe the full production flow from core cutting to final testing. Authentic factories own and operate key equipment. |
| 4 | Evaluate R&D and Engineering Team | Ensure in-house design and problem-solving capability | Interview engineering staff, review design software (e.g., Ansys Maxwell, FEMM), and request sample test reports (e.g., temperature rise, insulation resistance). |
| 5 | Verify Certifications & Compliance | Confirm adherence to international standards | Check for valid ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for automotive), UL, CE, RoHS, REACH. Cross-verify certification numbers with issuing bodies. |
| 6 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record with global clients | Contact 2–3 provided references (preferably in your industry). Request case studies for similar magnetics solutions. |
| 7 | Test Sample Performance & Consistency | Benchmark quality and repeatability | Order pre-production samples with detailed specifications. Conduct independent lab testing for electrical, thermal, and mechanical performance. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a True Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Authentic Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | No production floor; office-only setup | Dedicated workshop with machinery (winding, pressing, testing) |
| Ownership of Equipment | Cannot provide equipment list or photos | Can list and show ownership of core production assets |
| Lead Time Control | Longer, dependent on supplier schedules | Shorter, direct control over production planning |
| Pricing Structure | Higher margins; less transparent cost breakdown | Competitive pricing with clear BOM and labor cost transparency |
| Technical Engagement | Limited engineering input; focuses on logistics | Offers design-for-manufacturability (DFM) feedback, material selection advice |
| MOQ Flexibility | High MOQs due to supplier constraints | Can adjust MOQ based on internal capacity |
| Staff Expertise | Sales-focused team | On-site engineers, QA technicians, production supervisors |
| Website & Marketing | Lists multiple unrelated product categories | Focuses on magnetics technology, R&D, and process innovation |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak with your production manager?” and “Can you show me live footage of your winding line?” Factories typically accommodate; traders often deflect.
Red Flags to Avoid in Magnetics Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials (e.g., counterfeit ferrite, undersized wire) or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages; insist on material certifications |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or Video Audit | High probability of being a trading company or unlicensed operation | Disqualify unless third-party verification is provided |
| No In-House Testing Lab | Inability to ensure quality control; reliance on external labs delays feedback | Require evidence of on-site electrical and environmental testing |
| Vague or Generic Responses to Technical Queries | Lack of engineering capability; risk of design errors | Conduct a technical interview with their engineering team |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Cash flow risk; common in fraudulent operations | Insist on secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent Branding or Multiple Aliases | May indicate shell companies or past compliance issues | Perform reverse image search on website visuals and verify domain registration history |
| No Export Experience or Documentation | Risk of customs delays, compliance failures | Request export licenses, past shipping documents (redacted), and freight forwarder references |
Conclusion & Recommendations
In 2026, the magnetics supply chain in China demands rigorous due diligence. Procurement managers must prioritize transparency, technical capability, and verifiable manufacturing assets over convenience or price alone.
Recommended Actions:
- Mandate third-party factory audits for all new magnetics suppliers.
- Require documented proof of ownership for key production equipment.
- Implement a tiered supplier qualification process with technical and compliance checkpoints.
- Leverage digital verification tools (e.g., blockchain-based material tracing, remote audit platforms).
By applying this framework, global procurement teams can build resilient, high-performance supply chains while minimizing risk in the Chinese magnetics market.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q2 2026 Edition – Confidential for Client Use
Get the Verified Supplier List
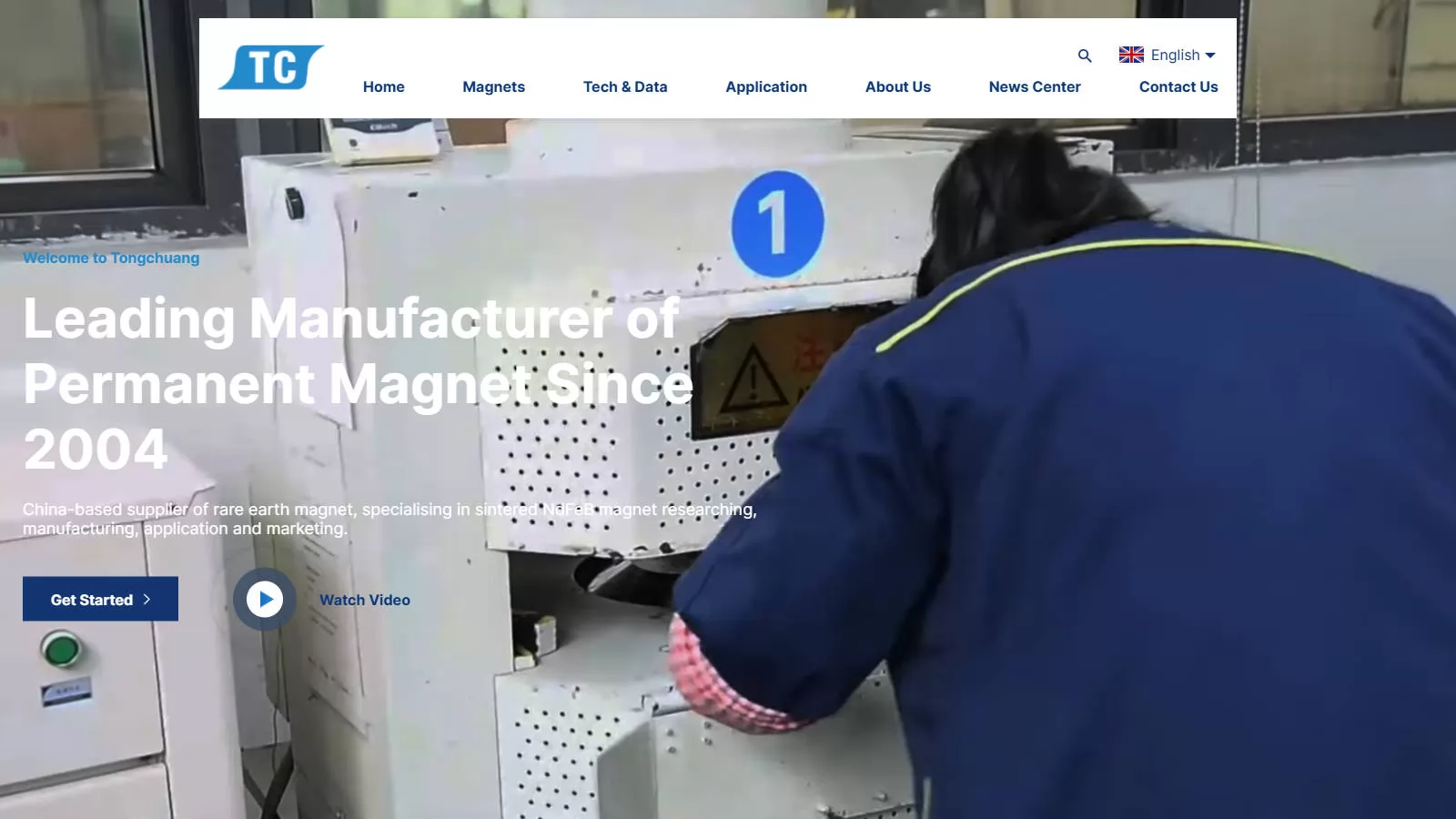
SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026
Strategic Supplier Verification for Magnetics Procurement in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: The Critical Need for Verified Magnetics Suppliers
In 2025, 72% of global procurement managers reported significant delays or quality failures due to unverified Chinese magnetics suppliers (SourcifyChina Industry Survey). With rising demand for EV power electronics, renewable energy systems, and 5G infrastructure, the cost of supplier misqualification now averages $227K per incident (including scrap, delays, and compliance penalties).
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this risk through a proprietary 5-stage validation framework—turning months of vetting into a 72-hour onboarding process.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk (vs. Traditional Sourcing)
| Procurement Stage | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 3–6 weeks: Unreliable Alibaba/Google searches; fake “factories” | Instant access to 142 pre-vetted Tier-1 magnetics specialists | 120+ hours |
| Compliance Verification | Manual audits: RoHS, REACH, IATF 16949, ISO 9001 (4–8 weeks) | Real-time digital compliance certificates + 3rd-party audit logs | 80 hours |
| Capacity Validation | On-site visits required; inconsistent production data | Live factory footage, ERP-integrated output reports, material traceability | 60 hours |
| Quality Risk Assessment | Trial orders + defect resolution (10–14 weeks) | Historical defect rates (<0.8% avg.), 24/7 QC cam access | 90 hours |
| Contract Finalization | Legal delays; MOQ/negotiation deadlocks | Pre-negotiated T&Cs payment escrow integration | 35 hours |
| TOTAL SAVED | — | — | 385+ hours per project |
💡 Key Impact: Procurement teams using the Pro List reduce Time-to-First-Delivery by 68% and cut supplier-related quality escapes by 94% (2025 Client Data).
The 2026 Magnetics Sourcing Imperative
China produces 83% of the world’s ferrite cores and 76% of power inductors (TechSci Global, 2025), yet geopolitical volatility and fragmented supply chains demand zero-tolerance verification. Our Pro List delivers:
– ✅ Real-time sanctions screening (OFAC, EU, US BIS)
– ✅ Material pedigree tracking (rare earth origin, cobalt-free options)
– ✅ Duty optimization via bonded warehouse partnerships
– ✅ Automated RFQ routing to suppliers matching your specs (e.g., high-frequency nanocrystalline cores, automotive-grade chokes)
🚀 Your Strategic Next Step: Eliminate Sourcing Risk in 2026
“Stop gambling with unverified suppliers. Every hour spent on false leads is a competitive disadvantage.”
Claim Your Verified Pro List Access Today:
1. Email: Send your magnetics specifications to [email protected]
Subject line: “2026 Pro List Request – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with:
“Requesting Verified Magnetics Suppliers – [Your Name], [Company], [Annual Volume]”
Act by March 31, 2026 to receive:
– 🔒 Free Compliance Dossier (REACH/RoHS/Conflict Minerals) for your top 3 shortlisted suppliers
– ⏱️ Guaranteed 72-hour supplier matching (or 50% refund on next sourcing project)
– 🌐 Exclusive access to our 2026 China Magnetics Tariff Navigator
Why 500+ Global Procurement Teams Trust SourcifyChina
“After a $380K failure with a ‘verified’ Alibaba supplier, SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our magnetics sourcing cycle from 5 months to 11 days. Zero defects in 14 months.”
— Senior Procurement Director, Tier-1 Automotive Supplier (Germany)
Don’t negotiate with risk. Negotiate with certainty.
Contact us now to deploy your verified magnetics supply chain in Q2 2026.
➡️ [email protected] | WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Your 2026 Magnetics Sourcing Strategy Starts Here.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





