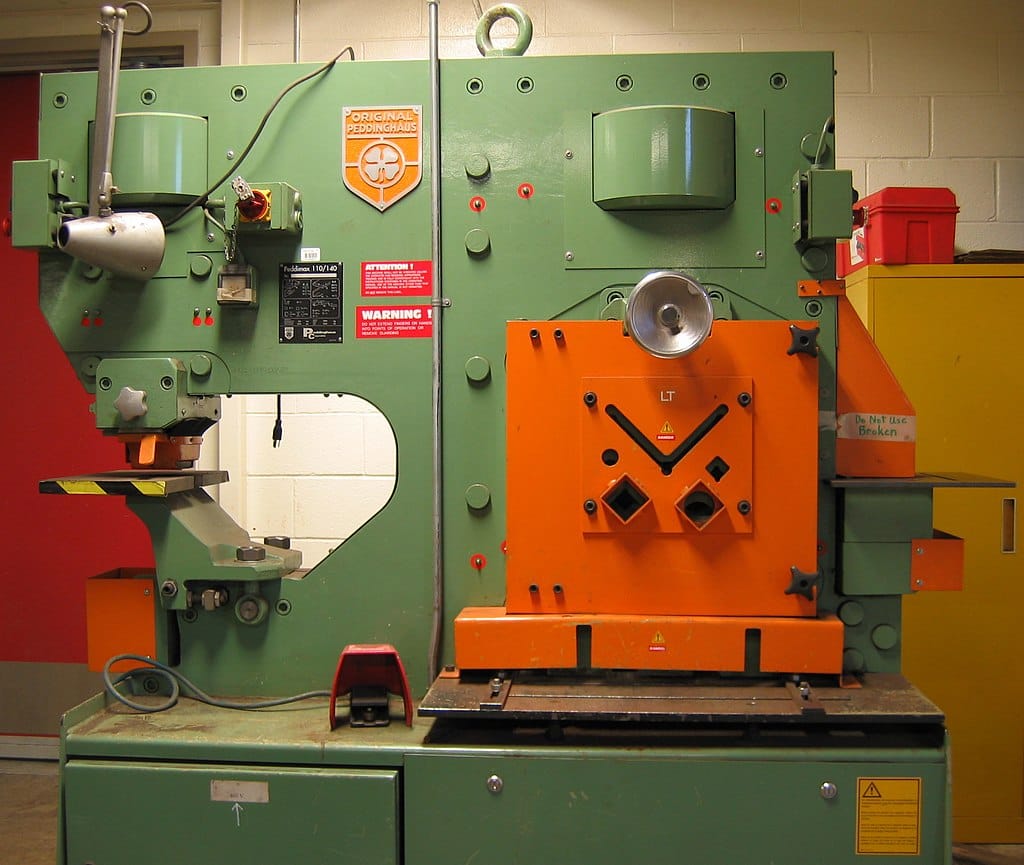
The global iron and steel machinery market has witnessed steady expansion, driven by rising industrialization, infrastructure development, and technological advancements in metal processing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the metal forming machinery market—key to iron and steel production—was valued at USD 81.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2028. This growth is further supported by increasing demand for high-precision machines in automotive, construction, and heavy manufacturing sectors. As global steel production continues to climb, particularly in Asia-Pacific and emerging economies, the need for efficient, automated, and energy-saving iron machines has become critical. In this evolving landscape, leading manufacturers are scaling innovation to deliver robust solutions that enhance productivity and sustainability. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and global reach, the following are the top 10 iron machines manufacturers shaping the future of industrial metal processing.
Top 10 Iron Machines Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Wholesale Industrial Steam Iron Manufacturers, Suppliers
Domain Est. 2003
Website: cnweijie.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in producing more than 100 series of ironing products such as steam iron itself, iron shoes, steam boiler, fusing machine, heat transfer machine….
#2 Eagle Iron Works
Domain Est. 2001
Website: eagleironworks.com
Key Highlights: Eagle Iron Works is a manufacturer that provides heavy duty, robust equipment for washing, classifying, scrubbing, dewatering, mixing and tailings ……
#3 GMP Ironers
Domain Est. 2020
Website: gmp-ironers.com
Key Highlights: GMP Ironers is a flatwork ironer and laundry equipment supplier and the leading European ironer manufacturer. Discover more….
#4 West Point Industries:
Domain Est. 1995
Website: westpoint.com
Key Highlights: West Point Industries is your efficient, single-source vendor for precision iron castings and assemblies, and one of the oldest operating iron foundries in the ……
#5 Scotchman Industries
Domain Est. 1996
Website: scotchman.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture 13 models of hydraulic ironworkers, ranging from 45 to 150 tons in capacity, offered in two distinct styles and available in both single- and ……
#6 Edwards Ironworkers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: edwardsironworkers.com
Key Highlights: 10-day returnsEdwards Manufacturing is your go-to source for quality metalworking equipment. Browse our hydraulic ironworker machines and accessories for sale online….
#7 End Wrought Iron Machines
Domain Est. 2000
Website: nargesa.com
Key Highlights: The PC16 and NF70 hot forging machines shape, flatten, roll, and form the tips of ornamental bars. They can create all types of tips—flat, pyramidal, ……
#8 Iron
Domain Est. 2021
Website: iron-rhino.com
Key Highlights: It has an operating capacity of 3000 lbs. with a machine weight of 7200 lbs. With an Aux Flow of 24.8GPM this machine can run most attachments with ease. The ……
#9 Iron Machine Tool
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ironmachinetool.com
Key Highlights: Iron Machine Tool supplies CNC machines, EDM machines, and precision milling solutions. Get expert support and request a quote for customized manufacturing ……
#10 Franklin Iron
Domain Est. 2023
Website: franklinironfoundry.com
Key Highlights: At Franklin Iron, we pride ourselves in providing customers high-quality ductile iron castings with exception service at competitive prices….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Iron Machines

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Iron Machines
While “Iron Machines” could refer to a specific company or a broad category of industrial machinery made from iron/steel, this analysis interprets the term as representing the broader heavy machinery and industrial equipment sector (e.g., construction, mining, agricultural, manufacturing machinery) where iron and steel remain fundamental materials. Here’s an analysis of key market trends expected to shape this sector in 2026:
1. Sustainability and Electrification Drive Innovation
- Zero-Emission Mandates: Stricter global emissions regulations (e.g., EU Stage V, potential US Tier 5) will accelerate the shift towards electrification. By 2026, expect significant growth in battery-electric (BEV) and hydrogen fuel cell (FCEV) heavy machinery, particularly for urban construction, mining, and indoor applications. Major manufacturers (Caterpillar, Komatsu, Volvo CE) will have expanded their electric fleets.
- Circular Economy Focus: Increased demand for remanufactured, refurbished, and recycled components. Manufacturers will invest in take-back programs, designing machines for easier disassembly and part reuse to reduce material waste and carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Materials: Exploration and pilot use of low-carbon steel (produced via hydrogen-based DRI or CCUS) in machine manufacturing will gain traction, driven by corporate ESG commitments and potential carbon border adjustments (e.g., EU CBAM).
2. Digitalization and Automation Become Standard
- Advanced Telematics & IoT: Ubiquitous machine connectivity will enable real-time monitoring of health, usage, location, and performance. This data fuels predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Fleet management platforms will be essential.
- AI-Powered Optimization: AI algorithms will move beyond diagnostics to prescriptive analytics, optimizing machine operation (e.g., fuel efficiency, bucket fill), scheduling, and site logistics. Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Mine Planning software will deepen.
- Autonomy Expansion: While fully autonomous sites remain niche, increased levels of automation (Level 3-4) – like automated dozing, grading, and loading – will become commercially viable and more common in controlled environments (mines, quarries, large infrastructure projects).
3. Resilience and Supply Chain Restructuring
- Nearshoring/Regionalization: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and lessons from recent disruptions will push manufacturers towards regionalized supply chains. Expect increased investment in manufacturing and sourcing closer to key markets (NAFTA, EU, Asia-Pacific) to mitigate risks, even at higher cost.
- Critical Material Security: Focus will intensify on securing supplies of rare earth elements, lithium, and cobalt essential for electric motors and batteries, driving partnerships and recycling initiatives.
- Inventory Buffering: Companies will maintain higher strategic inventory levels for critical components to buffer against future shocks.
4. Labor Shortages Fuel Technology Adoption
- “Labor Saver” Technology: Persistent skilled labor shortages in construction and mining will be a primary driver for adopting automation, remote operation, and user-assist technologies (e.g., grade control, machine control). Machines will be designed for easier operation by less experienced personnel.
- Focus on Operator Experience: Enhanced cabs, intuitive interfaces (touchscreens, voice control), and improved ergonomics will be key differentiators to attract and retain operators.
5. Growth in Infrastructure and Green Energy Projects
- Government Stimulus: Continued global investment in renewable energy infrastructure (wind farms, solar plants, grid upgrades), water management, and transportation networks (especially in North America under IIJA/IRA and Europe under the Green Deal) will drive demand for earthmoving, lifting, and specialized machinery.
- Urbanization & Electrification: Growth in urban centers will require machinery for vertical construction, tunneling, and utility work, often favoring compact and zero-emission models.
6. Consolidation and Ecosystem Competition
- Industry Consolidation: The high R&D costs for electrification, automation, and digitalization may lead to further M&A activity, as smaller players struggle to keep pace.
- Platform Wars: Competition will shift beyond the machine itself to integrated ecosystems – the combination of hardware, software (telematics, fleet management, optimization), financing, and service. Success will depend on seamless integration and data value.
In summary, the Iron Machines market in 2026 will be defined by a fundamental transformation: driven by environmental imperatives, technological leaps, and economic pressures. Success will belong to companies that aggressively embrace electrification and digitalization, build resilient supply chains, leverage data for efficiency, and position themselves as providers of sustainable, automated solutions within expanding infrastructure and energy transition markets. The traditional “iron” machine will increasingly be a sophisticated, connected, and often zero-emission platform.
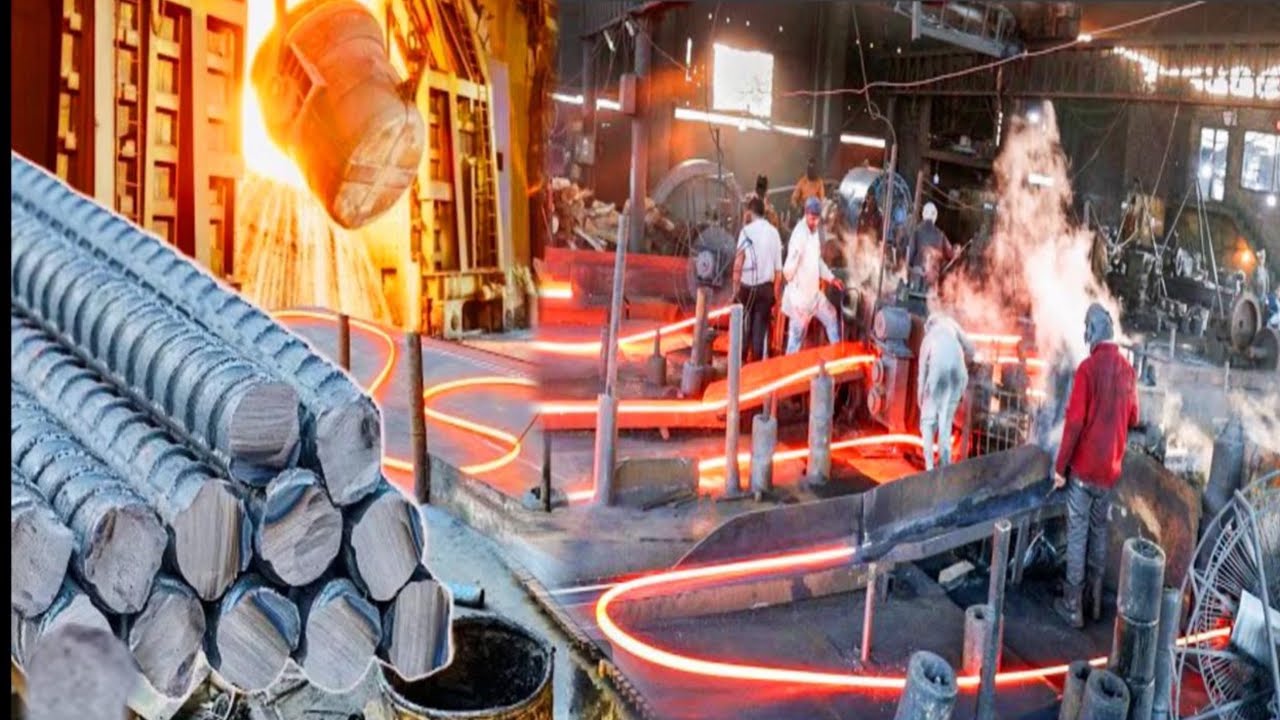

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Iron Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing iron machines—such as industrial machinery, heavy equipment, or fabricated metal components—presents significant challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Specifications
A common issue is receiving iron components that do not meet specified grades (e.g., cast iron vs. ductile iron) or chemical compositions. Suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials to cut costs, leading to premature failure under stress or in corrosive environments. Always verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and conduct third-party testing when necessary.
2. Poor Manufacturing Tolerances and Finishes
Iron machines often require precise engineering. Inadequate attention to dimensional accuracy, surface finish, or heat treatment can result in misaligned parts, increased wear, or reduced machine lifespan. Ensure detailed technical drawings are provided and conduct pre-shipment inspections to validate compliance.
3. Lack of Robust Quality Control Processes
Some suppliers, especially in low-cost regions, may lack certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001). Without documented QC procedures, batch inconsistencies become likely. Audit potential suppliers’ facilities and review their quality controls before committing to large orders.
4. Inadequate Testing and Validation
Iron machines should undergo performance, stress, and endurance testing. Suppliers may skip these steps to expedite delivery. Insist on witnessing factory acceptance tests (FAT) or receiving test reports to confirm reliability under real-world conditions.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Design IP
When sourcing custom iron machines, there’s a risk that suppliers replicate your designs for other customers or sell them independently. Without clear contractual ownership, your proprietary designs may be compromised. Use comprehensive IP clauses in contracts to specify that all designs, molds, and tooling remain your exclusive property.
2. Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Suppliers may reverse engineer your equipment to create similar products. This is especially prevalent when tooling or prototypes are left in the supplier’s possession. Implement strict access controls, use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and retrieve or destroy proprietary tools after production.
3. Infringement of Third-Party Patents
The sourced machine might inadvertently infringe on existing patents, exposing your business to litigation. Conduct due diligence on the design and require suppliers to warrant that their products do not violate any third-party IP rights.
4. Weak Contractual Protections
Generic procurement contracts often lack specific IP safeguards. Ensure agreements explicitly cover IP ownership, confidentiality, permitted use of designs, and post-contract obligations (e.g., return of technical data). Legal review prior to signing is essential.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier vetting, including site audits and reference checks.
- Require material and process certifications with each shipment.
- Use third-party inspection services for quality validation.
- Draft clear, jurisdiction-specific contracts with strong IP clauses.
- Register critical designs and patents in relevant markets.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can protect their investments, maintain product integrity, and reduce long-term supply chain risks when sourcing iron machines.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Iron Machines
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for the import, export, handling, and transportation of Iron Machines. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integrity.
Scope and Applicability
This guide applies to all Iron Machines products, including industrial machinery, components, and spare parts, across all global operations involving manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, and customer delivery.
Regulatory Compliance
All shipments of Iron Machines must comply with applicable international, national, and regional regulations, including but not limited to:
– Export Controls: Adherence to EAR (Export Administration Regulations), ITAR (if applicable), and sanctions lists (OFAC, UN, EU).
– Customs Compliance: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification, proper documentation (commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin), and compliance with destination country import regulations.
– Product Standards: Machines must meet safety and environmental standards such as CE (EU), UL (USA), CCC (China), or other local certifications as required.
– Environmental Regulations: Compliance with RoHS, REACH, and WEEE directives for applicable components.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- All Iron Machines must be packaged to withstand international transit, including moisture, vibration, and impact protection.
- Standardized labeling must include:
- Product name, model, and serial number
- Net and gross weight
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
- Export control classification number (ECCN) if applicable
- Barcodes for inventory tracking
Transportation and Shipping
- Use approved freight forwarders with experience in heavy machinery logistics.
- Select transport mode (air, sea, or land) based on urgency, cost, and machine specifications.
- Oversized or heavy machinery must be accompanied by special permits and routing approvals.
- Real-time shipment tracking is required for all international orders.
Documentation Management
Maintain complete and accurate records for a minimum of five years, including:
– Commercial invoices
– Bill of lading / air waybill
– Export declarations
– Certificates of conformity and origin
– End-user statements (when required)
All documents must be stored digitally with secure access and audit trails.
Import and Export Procedures
- Conduct pre-shipment compliance checks using internal screening tools against restricted party lists.
- Submit accurate export declarations via AES (Automated Export System) or equivalent national systems.
- Coordinate with customs brokers at destination for timely clearance and duty assessment.
- Notify customers of any import obligations (e.g., local inspections, taxes).
Risk Management and Insurance
- All shipments must be insured against loss, damage, and delay.
- Perform risk assessments for high-value or high-risk destinations.
- Establish contingency plans for customs delays, port congestion, or geopolitical disruptions.
Training and Accountability
- Logistics and compliance personnel must receive annual training on export controls, customs regulations, and internal procedures.
- Designate a Compliance Officer responsible for audits, recordkeeping, and regulatory updates.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
- Conduct internal audits at least annually to verify compliance with this guide.
- Address non-conformities promptly and implement corrective actions.
- Review and update this guide biannually or as regulations change.
By following this Logistics & Compliance Guide, Iron Machines ensures the secure, legal, and efficient movement of products worldwide while maintaining the highest standards of corporate responsibility.
In conclusion, sourcing iron machines requires a strategic and well-informed approach that balances cost, quality, reliability, and long-term value. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities, adherence to industry standards, reputation, and after-sales support. Conducting thorough due diligence—such as requesting product certifications, reviewing client testimonials, and performing site visits—can mitigate risks associated with performance and durability. Additionally, considering factors like energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and scalability ensures that the sourced machines align with operational goals and sustainability objectives. By leveraging market research, establishing strong supplier relationships, and staying updated on technological advancements, organizations can make informed procurement decisions that enhance productivity and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.