The global insulated building blocks market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient construction materials and increasingly stringent building energy codes. According to Grand View Research, the global insulation materials market was valued at USD 64.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by government initiatives promoting green building practices and the construction sector’s shift toward sustainable, high-performance materials. Insulated concrete forms (ICFs) and other insulated masonry systems are playing a pivotal role in this trend, offering superior thermal performance, noise reduction, and structural durability. As a result, manufacturers of insulated building blocks are scaling innovation and production to meet growing demand across residential, commercial, and industrial applications. In this evolving landscape, the following nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technological advancement, product reliability, and market reach to shape the future of energy-efficient construction.
Top 9 Insulated Building Blocks Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 THERMOBLOCK® ICF
Domain Est. 2023
Website: thermoblockicf.com
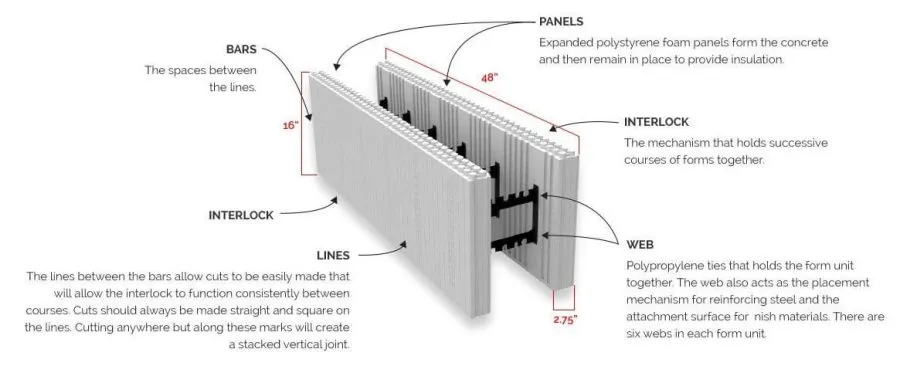
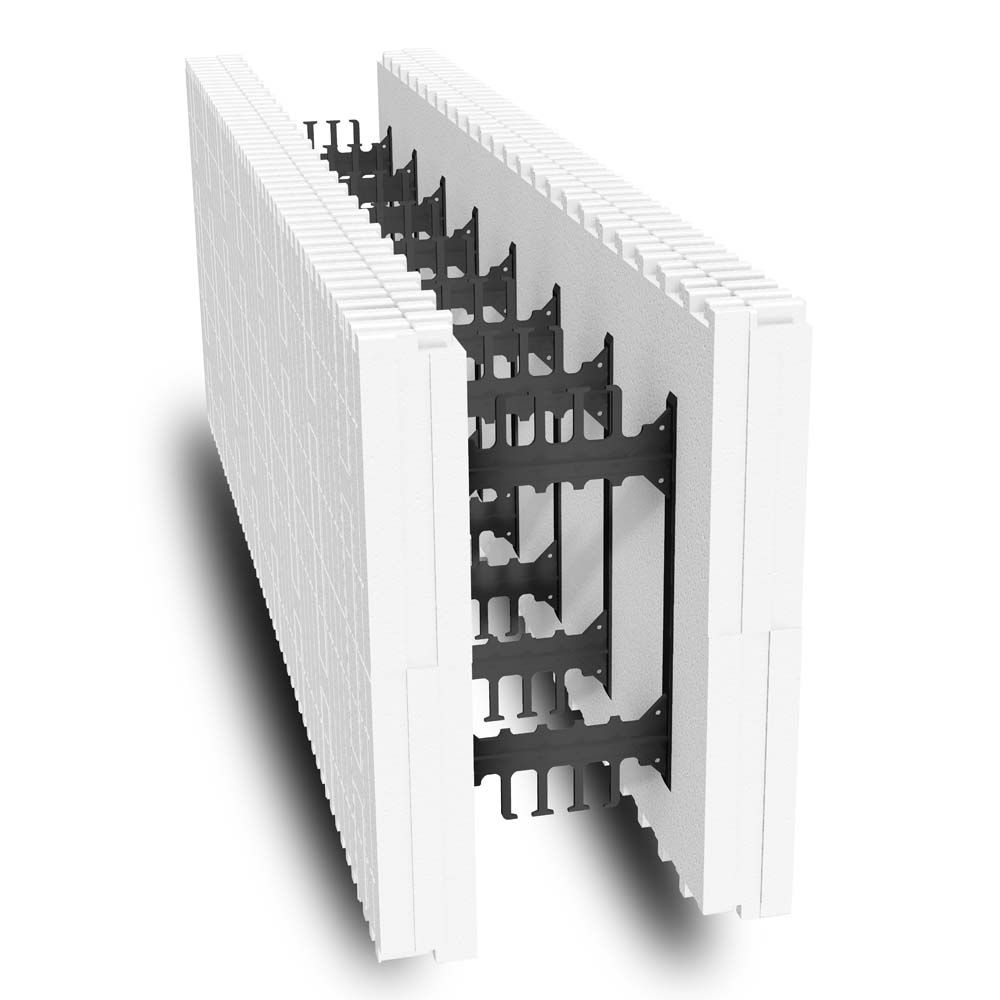
Key Highlights: An extremely high strength ICF building framework for commercial, industrial and residential wall systems. ThermoBlock construction translates to improved ……
#2 Insulated Concrete Forms
Domain Est. 1997
Website: quadlock.com
Key Highlights: ICFs for walls, floors & roofs are used to form bunker-strong, CIP reinforced concrete buildings and they stay in place to provide world-class insulation….
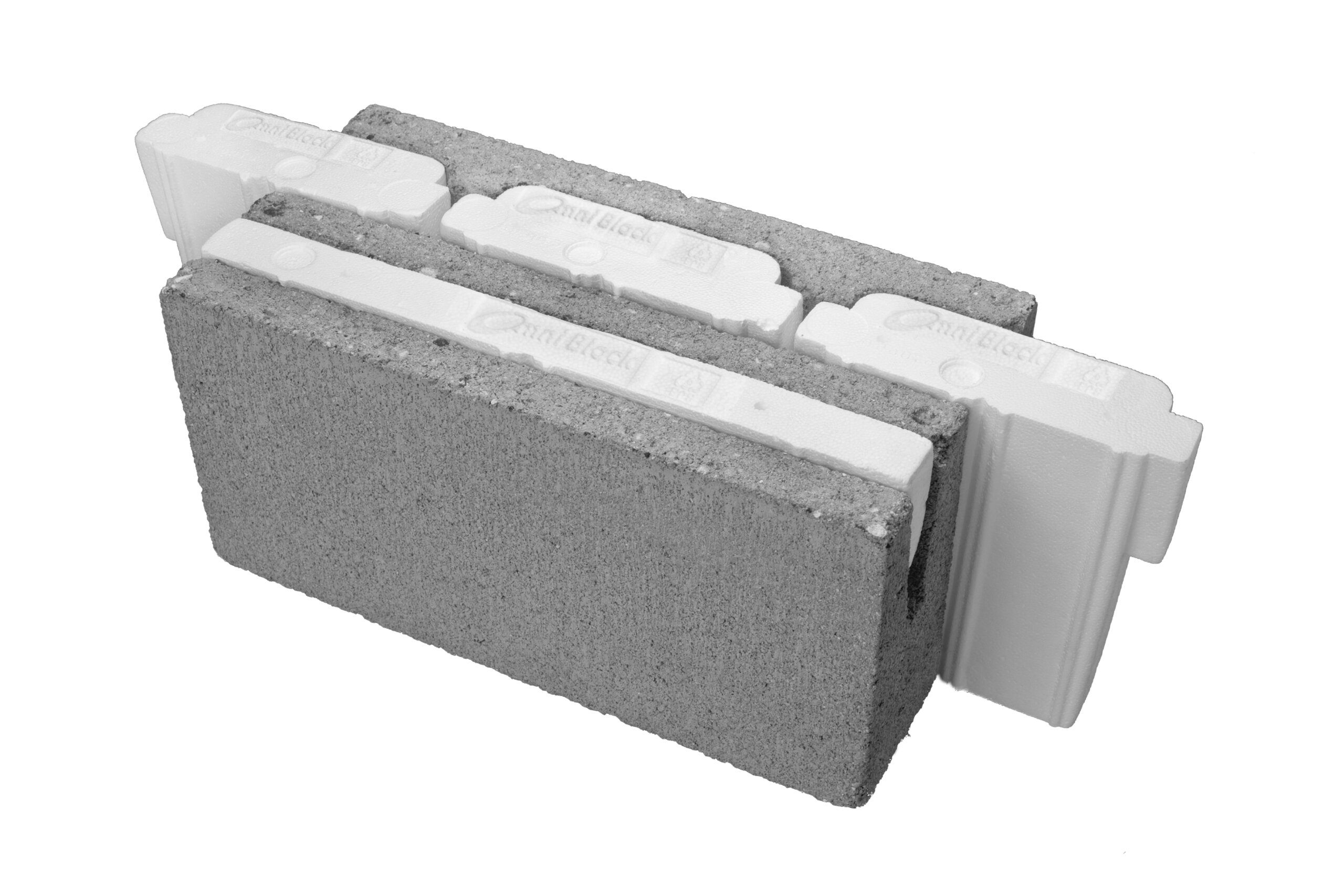
#3 Omniblock
Domain Est. 1997
Website: omniblock.com
Key Highlights: Omni Block – an insulated Concrete Block. The best thermally efficient building system on the market today!…
#4 LiteForm
Domain Est. 1997
Website: liteform.com
Key Highlights: LiteForm specializes in manufacturing folding, preassembled insulating concrete form (ICF) systems and a range of related products….
#5 BuildBlock Insulating Concrete Forms (ICFs) Building Systems
Domain Est. 2003
Website: buildblock.com
Key Highlights: BuildBlock has a complete ICF solution for projects of any size or complexity. Form sizes from 4′′-12′′+, floor and roof decking, bucking, and more….
#6 Fire
Domain Est. 2016
Website: theperfectblock.com
Key Highlights: The Perfect Block is an insulated composite concrete form (ICCF) made of a blend of recycled expanded polystyrene (EPS), also known as Styrofoam, Portland ……
#7 Gablok
Domain Est. 2018 | Founded: 2019
Website: gablok.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 2019, Gablok offers a revolutionary insulated timber-frame construction method. Aiming to simplify construction and offer a simple, high-performance ……
#8 The Hemp Block Company Ltd
Domain Est. 2020
Website: hempblock.co.uk
Key Highlights: Hemp blocks, made from the versatile and renewable hemp plant, offer numerous benefits that go beyond traditional construction materials….
#9 Discover the 7
Domain Est. 2024
Website: buildmonolith.com
Key Highlights: ICF stands for Insulated Concrete Forms, a modern construction system that combines reinforced concrete with insulating foam blocks. These blocks remain in ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Insulated Building Blocks

2026 Market Trends for Insulated Building Blocks
Accelerated Adoption Driven by Global Sustainability Mandates
By 2026, stringent global building energy codes and net-zero carbon regulations will significantly boost demand for insulated building blocks (IBBs). Countries in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia-Pacific are expected to enforce stricter thermal performance standards, making IBBs a cost-effective compliance solution. The integration of IBBs into green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM will further incentivize their use in both residential and commercial construction.
Technological Innovation and Material Advancements
Manufacturers will increasingly invest in R&D to enhance the thermal efficiency, structural strength, and fire resistance of IBBs. Expect wider adoption of next-generation insulating cores using aerogels, vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), and bio-based foams. Additionally, smart IBBs embedded with sensors for real-time thermal monitoring could emerge in high-end markets, adding value through building performance analytics.
Growth in Prefabrication and Modular Construction
The rising popularity of off-site and modular construction methods will favor IBBs due to their precision, ease of assembly, and inherent insulation properties. The alignment of IBBs with design-for-manufacture-and-assembly (DfMA) principles will drive their integration into factory-built housing solutions, reducing construction timelines and labor costs—especially in urban and labor-constrained markets.
Regional Expansion and Emerging Market Penetration
While Europe remains a dominant market, significant growth is anticipated in North America and parts of Asia-Pacific, including China, India, and Southeast Asia. Government housing initiatives, urbanization, and rising energy costs will expand IBB adoption in developing economies. Localized manufacturing hubs will emerge to reduce logistics costs and meet regional demand.
Supply Chain Resilience and Cost Optimization
By 2026, supply chain stabilization post-pandemic and geopolitical disruptions will lead to more consistent raw material availability. Producers will focus on circular economy practices, such as incorporating recycled plastics and industrial byproducts into block production, improving sustainability profiles and reducing costs over time.
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The IBB market will experience increased competition, prompting mergers and partnerships between material suppliers, construction firms, and technology providers. Smaller innovators may be acquired by larger building materials conglomerates seeking to expand their sustainable product portfolios, leading to greater standardization and market maturity.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Insulated Building Blocks (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing insulated building blocks—such as Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs) or Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)—can offer significant benefits in energy efficiency and construction speed. However, buyers often encounter critical challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid costly delays, performance failures, or legal disputes.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing insulated building blocks is inconsistent product quality. Suppliers, particularly in low-cost manufacturing regions, may use inferior materials—such as lower-density expanded polystyrene (EPS), weak concrete reinforcement, or subpar adhesives—leading to compromised thermal performance, structural integrity, and durability. Buyers may receive blocks that do not meet specified R-values, compressive strength, or fire resistance standards. Without rigorous third-party testing and certification (e.g., ASTM, ICC-ES), there is a high risk of performance failure in real-world applications.
Lack of Standardization and Certification
Many suppliers, especially smaller or regional manufacturers, fail to adhere to internationally recognized building standards. Sourcing blocks without proper certification can lead to code compliance issues, rejected inspections, and liability risks. It is crucial to verify that products are tested and listed with independent agencies and comply with local building codes. Assuming similar appearance equates to equivalent performance is a common mistake.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Insulated building block designs often involve patented interlocking systems, insulation configurations, or manufacturing processes. Sourcing from unauthorized or generic manufacturers may result in the use of counterfeit or IP-infringing products. This exposes the buyer and project stakeholders to legal action, shipment seizures, and reputational damage. Always confirm that the supplier has legitimate rights to produce and sell the design, especially when sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement.
Inadequate Technical Support and Warranty Coverage
Low-cost suppliers may offer limited technical documentation, installation guidance, or warranty support. If blocks fail prematurely or do not integrate well with other building systems, the lack of post-purchase support can lead to expensive remediation. Verify warranty terms and ensure the supplier provides engineering support and installation training.
Supply Chain and Logistics Challenges
Insulated blocks are bulky and fragile, making transportation and storage difficult. Poor logistics planning can result in damaged goods or project delays. Additionally, inconsistent batch production may lead to color, dimension, or performance variations over time, affecting the final build quality.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: audit suppliers, request product test data, verify IP ownership, and prioritize certified, reputable manufacturers—even if initial costs are higher. Investing in quality and compliance upfront prevents far greater expenses and legal complications down the line.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Insulated Building Blocks
Overview of Insulated Building Blocks
Insulated Building Blocks (IBBs) are modern construction materials designed to combine structural strength with thermal insulation. Typically made from expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), or polyurethane foam, these blocks are often reinforced with concrete or used as permanent formwork. Their use promotes energy efficiency, reduced construction time, and improved building performance.
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe and legal transportation, storage, and use of IBBs in construction projects.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
International and National Standards
Insulated Building Blocks must comply with regional building codes and material standards. Common standards include:
- Europe: EN 13163 (for thermal insulation products of rigid cellular plastics, including EPS and XPS), CE Marking under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) 305/2011.
- United States: ASTM C578 (Standard Specification for Rigid, Cellular Polystyrene Thermal Insulation), compliance with the International Building Code (IBC) and International Energy Conservation Code (IECC).
- Canada: CAN/ULC S701 for foam plastic building insulation.
- Australia/New Zealand: AS/NZS 4859.1 (Materials for the thermal insulation of buildings).
Manufacturers and importers must ensure products carry appropriate certification and documentation.
Fire Safety Regulations
IBBs may require fire-retardant additives and protective cladding to meet fire performance standards:
- Fire resistance ratings must align with local building codes (e.g., ASTM E84 or EN 13501-1 for surface burning characteristics).
- On-site storage must follow fire safety protocols—keep away from ignition sources and ensure proper separation from flammable materials.
Environmental and Chemical Compliance
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Ensure low or zero VOC emissions, especially for interior applications.
- REACH (EU) and TSCA (USA): Confirm that chemical components (e.g., blowing agents in foam) comply with environmental and health regulations.
- Recycling and Disposal: Provide end-of-life handling instructions in line with local waste management laws.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Packaging Standards
- Blocks should be tightly bundled on pallets using stretch wrap or strapping to prevent shifting during transit.
- Use moisture-resistant wrapping to avoid water damage, especially for foam-based blocks.
- Label each package with product type, batch number, fire rating, insulation value (R-value), and handling instructions.
Handling Procedures
- Use forklifts or pallet jacks for loading and unloading; avoid dragging or dropping blocks.
- Train site personnel on proper handling to prevent compression damage or edge chipping.
- Store blocks horizontally on flat, dry surfaces to avoid warping.
Transportation Logistics
Mode of Transport
- Road: Most common for regional distribution. Use enclosed or covered trucks to protect from rain, UV exposure, and wind.
- Sea: For international shipping; blocks must be palletized and protected against humidity and salt air. Use desiccants if necessary.
- Rail: Suitable for bulk shipments over long distances—ensure secure strapping and weather protection.
Load Securing and Stacking
- Follow ISO and national load securement standards (e.g., EUMOS for Europe).
- Stack height should not exceed manufacturer recommendations to avoid bottom-layer compression.
- Separate shipments with dunnage or edge protectors to prevent damage.
Documentation and Tracking
- Include commercial invoices, packing lists, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and certificates of conformity with each shipment.
- Use barcodes or RFID tags for traceability.
- Maintain digital records for compliance audits and warranty claims.
On-Site Storage and Inventory Management
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, covered area, elevated off the ground (e.g., on pallets) to prevent moisture absorption.
- Protect from direct sunlight to avoid UV degradation of polymer components.
- Limit exposure time to weather during construction phases.
Inventory Control
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to reduce material aging risks.
- Regularly inspect stock for damage, moisture, or pest infestation.
- Keep detailed logs of delivery dates, batch numbers, and locations on site.
Quality Assurance and Inspection
Pre-Delivery Checks
- Conduct quality inspections at the manufacturing facility or warehouse prior to shipment.
- Verify dimensions, density, R-value, and labeling accuracy.
On-Site Acceptance
- Inspect deliveries upon arrival for damage or deviations from order specifications.
- Reject non-compliant or damaged materials and document issues.
Third-Party Certification
- Engage accredited laboratories to test samples periodically for compliance with thermal, mechanical, and fire performance standards.
Conclusion
Efficient logistics and strict compliance are essential for maximizing the performance and safety of Insulated Building Blocks. Adhering to regulatory standards, implementing proper handling and storage protocols, and maintaining accurate documentation ensure that IBBs contribute effectively to sustainable, code-compliant construction projects worldwide. Always consult local authorities and certified engineers to confirm project-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Insulated Building Blocks
In conclusion, sourcing insulated building blocks presents a strategic opportunity to enhance energy efficiency, reduce long-term operational costs, and support sustainable construction practices. These high-performance materials combine structural integrity with superior thermal insulation, contributing to improved building envelope performance and reduced environmental impact. When selecting suppliers, considerations such as product quality, compliance with local building codes and energy standards, cost-effectiveness, and delivery reliability are critical to ensuring project success.
Engaging with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who offer technical support, warranties, and proven track records in the market can significantly mitigate risks and ensure consistent performance. Additionally, evaluating the full lifecycle benefits—such as reduced heating and cooling demands and increased occupant comfort—further underscores the value of investing in quality insulated building blocks.
Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy that balances performance, cost, and sustainability will enable builders, developers, and designers to deliver high-efficiency buildings that meet modern environmental and regulatory demands.