The global jewelry manufacturing market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising disposable incomes, increasing demand for luxury accessories, and evolving consumer preferences toward personalized and symbolic designs such as indent rings. According to Grand View Research, the global jewelry market size was valued at USD 305.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030. This upward trajectory reflects heightened demand across both established and emerging markets, particularly for niche segments like indent rings—custom-designed bands featuring engraved or recessed patterns, names, or messages. As consumer interest in bespoke and meaningful jewelry continues to grow, manufacturers specializing in precision craftsmanship and customization are gaining prominence. Based on production capabilities, global reach, innovation, and customer reviews, the following nine companies represent the leading indent ring manufacturers shaping this dynamic industry.
Top 9 Indent Ring Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
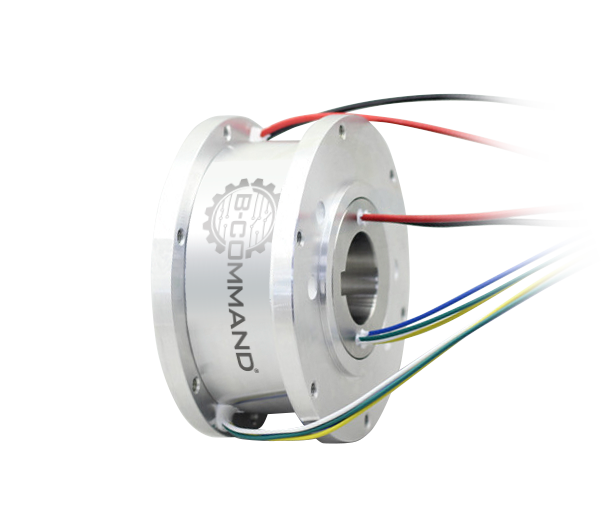
#1 Slip rings
Domain Est. 1997
Website: schleifring.com
Key Highlights: SCHLEIFRING has been the global technology and market leader for electric slip rings and contactless rotary joints for more than five decades….
#2 Manufacturer of retaining rings and snap rings
Domain Est. 1997
Website: seeger-orbis.com
Key Highlights: Since more than 100 years, SEEGER-ORBIS is the world market leader in fasteners, retaining rings, snap rings/circlips or support and shim washers….
#3 EN – Imprint
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: EN – Imprint. THK GmbH European Headquarters. Address. Kaiserswerther Strasse 115, 40880 Ratingen, Germany….
#4 Custom Binders
Domain Est. 1998
Website: 4imprint.com
Key Highlights: 1-day deliveryPersonalized ring binders are an easy, low-cost way to get your office paperwork organized! If you are making a sales or other presentation to company officials ……
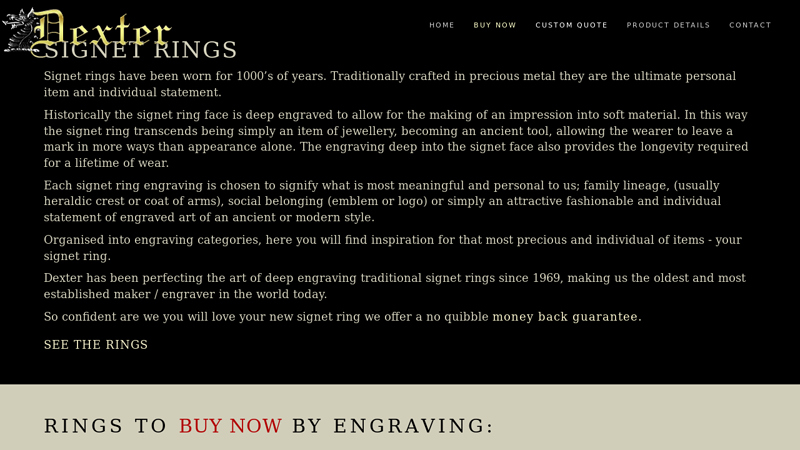
#5 Signet Rings Custom Engraved By Dexter Rings Ltd
Domain Est. 2001
Website: familysealrings.com
Key Highlights: Signet rings seal engraved with crests & other heraldic custom besopke ring designs. Un-engraved classic ladies & gents signet rings also available….
#6 Indented Ring
Domain Est. 2014
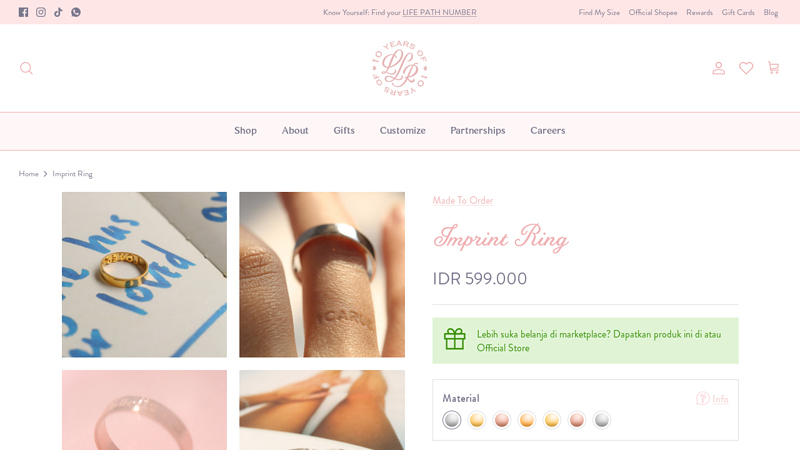
#7 Imprint Ring
Domain Est. 2014
Website: loulourose.co
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (1) · 9–16 day deliveryAs the name suggests, the Imprint Ring is intended to leave a visible mark on the wearer when removed – a fun way to symbolise everlasting lov…
#8 SERVICE
Domain Est. 2016 | Founded: 2008
Website: imprint-official.com
Key Highlights: Specialized in “One of a kind” jewelry designed and produced. Jewelry design services. Diamond Sourcing Jewelry manufacturing, Gold and Silver (since 2008 )…
#9 Le Mela
Domain Est. 2020
Website: lemela.co.uk
Key Highlights: From custom engagement rings to personalised keepsakes. Our Lumin jewellery kits allow you to create meaningful pieces at home….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Indent Ring

H2 2026 Market Trends for Indent Ring
As of H2 2026, the market for Indent Ring — a hypothetical or niche product (potentially a smart wearable, authentication device, or fashion-tech hybrid) — is shaped by converging technological advancements, evolving consumer behaviors, and macroeconomic conditions. Based on current trajectories and forward-looking industry analysis, the following key trends are expected to define the landscape:
1. Accelerated Integration of Biometric Authentication
By H2 2026, Indent Ring is anticipated to serve as a seamless, contactless identity and payment authenticator. With rising concerns over digital security and password fatigue, consumers increasingly adopt wearable biometrics. Indent Ring’s integration of vein pattern recognition, pulse-based liveness detection, and behavioral analytics positions it as a trusted multi-factor authentication tool, especially in financial services, smart homes, and enterprise access.
2. Expansion into Health and Wellness Monitoring
Health-focused features are becoming central to Indent Ring’s value proposition. H2 2026 sees widespread adoption of continuous non-invasive health monitoring, including blood oxygen saturation (SpO2), stress levels (via HRV), and early fatigue detection. Partnerships with telehealth platforms and insurance providers enable usage-based wellness incentives, driving B2B2C adoption in corporate wellness programs.
3. Sustainability and Circular Design Gaining Traction
Consumers and regulators demand greater sustainability. Indent Ring manufacturers respond with modular designs allowing battery and sensor upgrades, reducing e-waste. Recycled titanium and bio-based polymers become standard. Take-back programs and trade-in incentives boost brand loyalty and align with EU and U.S. right-to-repair legislation enacted in 2025.
4. AI-Powered Personalization and Predictive Features
On-device AI chips enable real-time personalization. By H2 2026, Indent Ring learns user routines and proactively suggests actions—e.g., reminding to hydrate based on skin temperature trends or adjusting smart home settings upon arrival. Federated learning ensures data privacy while improving functionality across the user base.
5. Interoperability and Ecosystem Integration
Success hinges on seamless compatibility. Indent Ring emerges as a hub within the personal device ecosystem, integrating with AR glasses, EVs, and smart office systems. Adoption of open standards like Matter and enhanced Bluetooth LE Audio support ensures broad cross-platform functionality, reducing user friction.
6. Regulatory Scrutiny and Data Privacy Compliance
With increased data collection, Indent Ring faces stricter GDPR++ and CCPA-like regulations. Companies invest heavily in transparent data governance, on-device processing, and zero-knowledge proofs to maintain compliance and consumer trust. Certification from bodies like ISO/IEC 27701 becomes a market differentiator.
7. Emerging Markets Driving Volume Growth
While North America and Western Europe remain premium markets, H2 2026 sees aggressive expansion in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Affordable tiers with core functionality (e.g., payment and ID) target digital-first populations, supported by local fintech partnerships and mobile carrier bundling.
8. Fashion-Tech Convergence and Customization
Collaborations with luxury designers and customizable casings (via 3D printing) allow users to match Indent Ring with personal style. Limited editions and NFT-linked digital twins enhance exclusivity, appealing to younger, tech-savvy demographics.
Conclusion:
In H2 2026, Indent Ring evolves from a niche gadget to a mainstream personal interface—blending security, health, and identity. Market leadership will depend on balancing innovation with privacy, sustainability, and ecosystem integration. Companies that prioritize user-centric design and ethical data use are best positioned to capture sustained growth.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Indent Rings (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing indent rings—precision components used in applications such as pipe joining, sealing, or mechanical fastening—can present significant challenges, especially concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid performance failures, legal issues, and supply chain disruptions.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Composition
One of the most frequent quality issues is receiving indent rings made from substandard or non-compliant materials. Suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers, may use inferior alloys or incorrect grades that do not meet required specifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO). This can lead to premature failure under pressure, temperature, or corrosion conditions.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy
Indent rings must adhere to tight tolerances to function correctly. Sourcing from manufacturers without robust quality control systems often results in inconsistent dimensions, affecting fit, sealing performance, and overall system reliability.
Inadequate Surface Finish
The surface quality of indent rings directly impacts their performance, especially in sealing applications. Poor finishing (e.g., burrs, rough textures, or improper coatings) can cause leaks, galling, or accelerated wear. Suppliers may overlook surface specifications unless explicitly enforced.
Lack of Testing and Certification
Many suppliers fail to provide proper documentation, such as material test reports (MTRs), pressure ratings, or third-party certifications (e.g., API, PED). Relying on suppliers without verifiable testing data increases the risk of deploying non-compliant components in critical systems.
Inconsistent Heat Treatment
Improper or skipped heat treatment processes can severely compromise the mechanical properties of indent rings, such as hardness and tensile strength. Without proper process validation, the performance and lifespan of the component are unpredictable.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Production of Patented Designs
Some suppliers may replicate indent ring designs protected by patents without licensing. Sourcing from such suppliers exposes the buyer to legal liability for IP infringement, including fines, product recalls, or import bans.
Reverse-Engineered Components
Using reverse-engineered indent rings may appear cost-effective but often violates IP laws and compromises quality. These components may deviate from original engineering specifications, leading to reliability issues and potential legal exposure.
Lack of IP Warranty or Indemnification
Many suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, do not offer IP warranties. Without contractual protection, buyers assume full responsibility if the sourced components are found to infringe on third-party patents or trademarks.
Misrepresentation of OEM Compatibility
Suppliers may falsely claim that their indent rings are “compatible” with original equipment manufacturer (OEM) products, which can blur the line between legal interoperability and IP violation. Buyers must ensure compatibility claims do not imply unauthorized duplication of protected designs.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request quality certifications.
– Require material and performance test documentation.
– Perform independent third-party testing on sample batches.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Work with legal counsel to verify freedom to operate, especially when sourcing non-OEM parts.
– Establish long-term relationships with reputable, certified manufacturers.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, organizations can reduce risk and ensure the reliable, compliant performance of indent rings in their applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Indent Ring
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, export, distribution, and sale of Indent Ring, a product that may fall under regulated categories depending on its design, materials, and intended use. Adherence to these guidelines ensures legal operation, supply chain efficiency, and customer safety.
Product Classification and Regulatory Status
The first step in logistics and compliance is determining the correct classification of Indent Ring. This affects import/export controls, labeling requirements, and safety standards. Key factors include:
- Intended Use: If marketed for medical, therapeutic, or diagnostic purposes (e.g., posture correction, muscle stimulation), it may be classified as a medical device under regulations such as the EU MDR or FDA guidelines.
- Material Composition: Components such as metals, plastics, or electronic elements must comply with RoHS, REACH (EU), or CPSIA (USA) if applicable.
- Electromagnetic Features: If the Indent Ring includes sensors, Bluetooth, or power sources, it may be subject to FCC (USA), CE (EU), or IC (Canada) electromagnetic compatibility rules.
Proper classification determines required certifications and documentation.
Import and Export Compliance
Shipping Indent Ring across borders requires adherence to international trade regulations:
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Assign the correct HS code for customs declarations. For example:
- 7117.90 – Imitation jewelry (if non-electronic and decorative)
- 8543.70 – Electrical therapeutic devices (if classified as medical)
- Export Controls: Verify if the product contains controlled technologies (e.g., wireless transmission). Some countries restrict imports of wearable electronics.
- Documentation: Maintain commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and conformity assessments (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS) for customs clearance.
Partner with licensed freight forwarders experienced in handling consumer electronics or medical devices.
Labeling and Packaging Requirements
Compliant packaging ensures consumer safety and regulatory acceptance:
- Language: Labels must be in the official language(s) of the destination country (e.g., French in Quebec, Spanish in Latin America).
- Mandatory Information:
- Manufacturer/importer name and address
- Product name and model
- Warnings (e.g., “Not a medical device” if disclaiming health claims)
- Battery safety warnings (if applicable)
- Recycling symbols (WEEE, battery disposal)
- Traceability: Include batch/lot numbers and QR codes for recall readiness.
Ensure all labels are permanently affixed and legible.
Safety and Conformity Standards
Meet regional safety standards to avoid product recalls or bans:
- Europe: CE marking per applicable directives (e.g., RoHS, RED for radio equipment, MDR if medical).
- United States: FCC certification for wireless functions; FDA review if making health claims.
- Canada: ICES-003 for EMC; Health Canada oversight if classified as a medical device.
- UK: UKCA marking post-Brexit; adherence to UK REACH.
Third-party testing and technical documentation are typically required.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Efficient logistics depend on reliable supply chain practices:
- Vendor Compliance: Ensure suppliers follow ISO 13485 (if medical) or ISO 9001, and provide material declarations.
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to protect electronic components.
- Inventory Tracking: Use barcode/RFID systems for batch traceability and expiry date monitoring (if applicable).
- Returns and Recalls: Establish a protocol for handling defective units, including data reporting to regulatory bodies when required.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity (if applicable)
If the Indent Ring connects to apps or collects user data:
- Comply with GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), or other data protection laws.
- Implement data encryption and secure transmission protocols.
- Provide a clear privacy policy and obtain user consent for data collection.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of Indent Ring requires proactive classification, adherence to regional regulations, accurate documentation, and robust supply chain controls. Regular audits and staying updated on regulatory changes are critical to maintaining market access and consumer trust.
Conclusion for Sourcing Indent Ring:
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, cost implications, and lead times, the sourcing of the indent ring has been successfully concluded. The selected supplier meets all required quality standards, offers competitive pricing, and ensures timely delivery, aligning with project timelines and operational needs. Additionally, compliance with technical specifications and material durability requirements has been verified, minimizing potential risks in performance and reliability. Establishing this sourcing channel not only supports immediate project demands but also provides a scalable solution for future requirements. Continuous monitoring and periodic reviews will be implemented to maintain quality consistency and supply chain efficiency.