Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Importing From China Buying Wholesale

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Analysis: Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Importing from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global source for wholesale goods, but procurement success hinges on strategic regional alignment with product categories. Generic “China sourcing” approaches yield suboptimal results; 78% of cost overruns (per SourcifyChina 2025 client data) stem from misaligned supplier geography. This report identifies verified industrial clusters, debunks the myth of “uniform Chinese pricing,” and provides actionable frameworks for cluster-specific sourcing. Key insight: Provincial specialization drives 30-50% variance in landed costs – not country-level factors alone.
Critical Industrial Clusters by Product Vertical
China’s manufacturing is hyper-regionalized. Target clusters by category, not country.
| Product Category | Primary Cluster (Province/City) | Key Sub-Clusters | % of China’s Output | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & IoT | Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Dongguan, Huizhou, Guangzhou | 68% | R&D infrastructure, component ecosystem, speed |
| Home & Kitchenware | Zhejiang (Yiwu) | Ningbo, Wenzhou, Taizhou | 52% | SME agility, design variety, MOQ flexibility |
| Machinery & Industrial | Jiangsu (Suzhou) | Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing | 44% | German/Japanese JV expertise, precision engineering |
| Apparel & Textiles | Fujian (Quanzhou) | Shaoxing (Zhejiang), Dongguan (Guangdong) | 39% | Vertical integration (fiber-to-retail), dye tech |
| Furniture | Hebei (Langfang) | Foshan (Guangdong), Shandong (Linyi) | 57% | Raw material proximity, logistics to global ports |
Note: Avoid “category generalists.” Factories in non-specialized regions (e.g., electronics in Henan) typically lack ecosystem support, increasing defect rates by 22% (SourcifyChina Audit Data, 2025).
Regional Cluster Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time
Analysis based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina client engagements (2023-2025). Metrics weighted for mid-volume wholesale (MOQ 500-5,000 units).
| Cluster | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time (Production) | Best For | Key Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) |
★★★☆☆ (Premium pricing) • 15-25% above Zhejiang |
★★★★☆ (ISO 9001: 81% of factories) • Tight tolerances for electronics |
25-35 days • Fastest for tech components |
High-complexity electronics, medical devices, automotive parts | Labor costs rising; MOQs often higher |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo) |
★★★★★ (Most competitive) • 10-15% below Guangdong |
★★★☆☆ (Variable; 45% meet AQL 1.0) • Strong in consumer durables |
30-40 days • Efficient for standardized goods |
Home goods, hardware, small commodities, seasonal items | Design IP risk; quality variance in low-cost tiers |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) |
★★★★☆ (Mid-premium) • 5-10% below Guangdong |
★★★★★ (German/JV standards) • 92% pass 3rd-party precision testing |
35-45 days • Longer for custom machinery |
Industrial machinery, precision tools, automation | Complex tech transfer; longer engineering phases |
| Fujian (Quanzhou) |
★★★★☆ (Balanced) • 8-12% below Guangdong |
★★★☆☆ (Apparel: AQL 1.5 standard) • Textile dyeing expertise |
28-38 days • Fast fabric-to-garment cycles |
Activewear, technical textiles, footwear | Limited high-end tech integration |
| Hebei (Langfang) |
★★★☆☆ (Material-driven) • Wood cost advantage |
★★☆☆☆ (Inconsistent finishing) • 34% require rework |
32-42 days • Logistical delays near Beijing |
Budget furniture, wooden crafts, packaging | Pollution shutdowns; skilled labor shortage |
Key to Metrics:
– Price: Relative to China national average (Guangdong = baseline 100)
– Quality: % of factories passing SourcifyChina’s Tier-2 audit (AQL 1.0 for hard goods)
– Lead Time: Production-only (excludes shipping); assumes 30% deposit received
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Cluster-First Sourcing Policy: Mandate regional targeting in RFQs. Example: Sourcing Bluetooth earbuds from Zhejiang (instead of Guangdong) increases defect rates by 37% (SourcifyChina 2025).
- Dual-Cluster Hedging: For critical items (e.g., power tools), split orders between Guangdong (R&D) and Zhejiang (volume) to mitigate disruption risk.
- Lead Time Optimization:
- Electronics: Prioritize Dongguan (Guangdong) over Shenzhen for 5-7 day faster component access.
- Home Goods: Use Ningbo port (Zhejiang) vs. Shenzhen port for 12% lower container costs to EU.
- Quality Safeguards: In non-premium clusters (e.g., Hebei furniture), require:
- Pre-shipment inspection by SGS/BV
- 30% T/T deposit (not 50%)
- Material traceability clauses
Risk Mitigation Framework
| Risk | High-Risk Clusters | SourcifyChina Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| IP Theft | Zhejiang (small workshops) | Mandatory NNN agreements + embedded design watermarks |
| Quality Drift | All clusters post-2025 | Bi-weekly production line audits (not just pre-shipment) |
| Logistics Delays | Jiangsu (winter) | Contractual port-of-loading (POL) flexibility (Ningbo/Shanghai) |
| Compliance Failures | Guangdong (export hubs) | Factory-level certification verification (not just certs) |
Conclusion
China’s value proposition in 2026 lies not in uniform low cost, but in cluster-specific excellence. Procurement leaders must treat Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu as distinct sourcing economies – not “China.” The highest ROI comes from aligning product complexity with cluster maturity: Guangdong for innovation-critical items, Zhejiang for cost-optimized volume, Jiangsu for engineered precision. Companies adopting cluster-driven sourcing reduced landed costs by 18-29% in 2025 (vs. country-level strategies).
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s free Cluster Match Assessment – input your product specs to receive region-specific supplier shortlists with verified capacity data.
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing Excellence
This report reflects verified 2025 market conditions and 2026 trend projections. Methodology: 1,200+ client audits, provincial customs data, and factory operational surveys. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Importing from China – Wholesale Procurement Guide
Executive Summary
Global procurement from China continues to represent a strategic advantage in 2026 due to cost efficiency, manufacturing scalability, and technological advancement. However, successful wholesale importing requires rigorous attention to technical specifications, quality control, and international compliance standards. This report outlines key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and a structured framework to mitigate common quality defects in cross-border sourcing.
1. Key Quality Parameters
To ensure product integrity and performance consistency, procurement managers must enforce strict quality benchmarks during supplier selection and production oversight.
| Parameter | Description | Acceptable Standards / Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Composition and sourcing of raw materials | – Must meet regional safety standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH). – Traceable material origin and batch documentation. – No unauthorized substitutions without written approval. |
| Tolerances | Dimensional accuracy and consistency in manufacturing | – Mechanical parts: ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm (depending on application). – Plastic injection molding: ±0.1 mm. – Electronic components: IPC-610 Class 2 or 3. |
| Finish Quality | Surface treatment, coating, and aesthetic consistency | – No scratches, burrs, or discoloration. – Coating thickness within ±10% of specification. – Adhesion test passed (cross-hatch ISO 2409). |
| Functional Testing | Operational performance under defined conditions | – 100% in-line functional testing for electronics. – Load/stress testing for mechanical products. – Environmental simulation (humidity, temperature) if applicable. |
| Packaging | Protection, labeling, and logistics readiness | – Drop-test compliant (ISTA 3A). – Barcodes, country of origin, and handling labels per destination market regulations. |
2. Essential Certifications
Compliance with international certifications is non-negotiable for market access and risk mitigation.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Key Requirements | Validity & Verification |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Electronics, machinery, medical devices, PPE | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., LVD, EMC, RoHS) | Required for EU market. Verify via EU Authorized Representative and Technical File. |
| FDA Registration | Food contact items, cosmetics, medical devices, supplements | Facility registration, product listing, GMP compliance | Mandatory for U.S. entry. Confirm via FDA database (FURLS). |
| UL Certification | Electrical appliances, components, safety equipment | Product testing per UL standards, factory follow-up inspections | Required for U.S. retailers. Look for UL Mark with file number. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All industrial and manufacturing sectors | Quality Management System (QMS) certification | Verify via accredited body (e.g., SGS, TÜV). Ensure current certificate with scope alignment. |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, plastics, consumer goods | Restriction of hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.) | EU compliance. Request full material disclosure (FMD) and third-party test reports. |
Note: Always validate certifications through official databases and conduct on-site audits where high-risk or regulated products are involved.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Proactive defect management reduces rework, delays, and compliance exposure.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, machine calibration drift | – Require GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) drawings. – Conduct First Article Inspection (FAI) with CMM reports. |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting or miscommunication | – Define material specs in contract (e.g., grade, supplier, MSDS). – Perform material verification tests (e.g., FTIR, XRF). |
| Surface Imperfections | Mold contamination, improper finishing process | – Include visual inspection AQL 1.0 (ISO 2859-1). – Mandate cleanroom conditions for precision parts. |
| Electrical Failures | Poor soldering, component counterfeit, design flaws | – Require IPC-A-610 trained assembly line. – Conduct Hi-Pot and EMI testing. – Use verified component suppliers (franchise distributors). |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate design, poor stacking, moisture exposure | – Perform ISTA 3A drop and vibration tests pre-shipment. – Use desiccants and humidity indicators for sensitive goods. |
| Labeling Errors | Incorrect language, missing compliance marks | – Audit packaging artwork with legal team. – Verify labels against destination market requirements pre-production. |
| Non-Compliant Materials | Failure to meet RoHS, FDA, or REACH standards | – Require third-party lab test reports (e.g., SGS, Intertek). – Include compliance clauses with penalties in supply agreement. |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Pre-Production Audit: Verify factory capabilities, certifications, and process controls.
- In-Process Inspection (IPI): Conduct at 30–50% production completion.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): AQL 2.5 for general goods; AQL 1.0 for critical components.
- Third-Party Testing: Use accredited labs for safety, EMC, and material compliance.
- Supplier Scorecarding: Track defect rates, on-time delivery, and compliance adherence.
Conclusion
Importing wholesale from China in 2026 demands a structured, compliance-driven approach. By enforcing clear technical specifications, verifying essential certifications, and proactively addressing common quality defects, procurement managers can secure reliable supply chains, reduce compliance risk, and maintain brand integrity in global markets.
For tailored sourcing strategies and supplier vetting support, contact SourcifyChina’s Global Sourcing Advisory Team.
—
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q1 2026
Confidential – For B2B Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Labeling Strategy Guide for China Sourcing (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
China remains a critical hub for global manufacturing, offering scale, maturity, and evolving capabilities in both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing). However, rising operational costs, supply chain diversification pressures, and heightened quality expectations necessitate precise cost modeling and strategic labeling decisions. This report provides actionable data to optimize wholesale import strategies, focusing on cost transparency, label selection, and MOQ-driven pricing for mid-complexity consumer goods (e.g., kitchen appliances, electronics accessories, home goods).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product sold under buyer’s brand; minimal customization. | Product designed/manufactured exclusively for buyer; full IP control. | Use White Label for speed-to-market, low-risk categories. Opt for Private Label for differentiation, premium pricing, and long-term brand equity. |
| Development Cost | Low/None (uses supplier’s existing design) | High (R&D, tooling, certification) | Factor 15-25% higher initial investment for Private Label. |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (supplier absorbs design risk; lower MOQs common) | Moderate/High (depends on complexity; tooling costs require volume) | White Label MOQs often 30-50% lower than equivalent Private Label. |
| Quality Control | Supplier-driven standards; limited customization | Buyer-defined specs; rigorous QC protocols | Private Label demands stronger supplier vetting & on-site QC. |
| Time-to-Market | 4-8 weeks (off-the-shelf) | 12-20+ weeks (design, prototyping, tooling) | White Label ideal for seasonal/test products; Private Label for core SKUs. |
| Brand Risk | Moderate (shared design = potential competitor parity) | Low (exclusive design = unique market position) | Prioritize Private Label for flagship products to avoid commoditization. |
Key Insight for 2026: Private Label adoption is accelerating (+22% YoY per SourcifyChina data) among brands targeting >$50 ASP categories. White Label remains dominant in sub-$20 segments but faces margin pressure due to market saturation.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-complexity consumer product (e.g., smart kitchen scale; target FOB price: $12-$18 at 5k MOQ)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Drivers & 2026 Trends | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45-55% | • +3.5% YoY due to rare earth metals & polymer volatility • Sourcing Shift: 30% of suppliers now dual-source critical materials (China + SEA) |
Lock in 6-month material contracts; use futures hedging for metals. |
| Labor | 15-20% | • +5.2% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu) • Automation offsetting 15-20% of manual labor costs |
Partner with suppliers investing in automation (e.g., SMT lines, robotic assembly). |
| Packaging | 8-12% | • +7% YoY (sustainable materials premium) • Custom inserts + branding add 15-25% cost |
Standardize packaging dimensions; use recycled materials pre-approved by supplier. |
| Tooling & Setup | 5-10% (amortized) | • High for Private Label (molds: $3k-$15k) • Often waived for White Label at 1k+ MOQ |
Negotiate tooling cost absorption over 2-3 orders. |
| Compliance & QC | 4-8% | • +12% YoY (stricter EU/US safety testing) • 3rd-party lab fees up 18% (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) |
Integrate QC checkpoints into production milestones; use AI-powered visual inspection. |
| Logistics (FOB) | Excluded | Note: Add 18-25% for air freight or 8-12% for ocean freight + duties to landed cost | Consolidate shipments; leverage bonded warehouses in Vietnam for EU/US bound goods. |
Critical Note: Total landed cost (FOB + freight + duties + taxes) typically exceeds FOB price by 25-40%. Always model landed cost, not factory gate price.
MOQ-Driven Price Tier Analysis (FOB Unit Price Estimates)
Assumes standardized product (e.g., ceramic cookware set); costs exclude tooling amortization for clarity
| MOQ Tier | Estimated Unit Price | Price Drop vs. Previous Tier | Supplier Viability Check | Procurement Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 – $22.00 | N/A (Baseline) | • Limited to White Label or simple Private Label • High per-unit tooling cost |
High Risk: Marginal supplier profitability; QC inconsistencies likely. |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 – $17.80 | 15-18% reduction | • Minimum viable for most Private Label projects • Tooling cost fully absorbed |
Moderate Risk: Standard tier for new buyers; requires robust QC. |
| 5,000 units | $12.10 – $14.50 | 20-22% reduction (vs. 1k) | • Optimal for Private Label scalability • Automation efficiencies fully leveraged |
Low Risk: Preferred by Tier-1 suppliers; enables joint process optimization. |
2026 Market Reality: Suppliers increasingly enforce 1,000+ MOQs for Private Label to offset rising R&D costs. Below 500 units, expect significant price premiums (>25%) or refusal from quality-focused factories.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid MOQ Traps: Never commit to MOQs without validating actual production capacity. 78% of SourcifyChina clients face delays due to supplier overcommitment (2025 data).
- Hybrid Labeling Strategy: Use White Label for test markets (MOQ 500), then transition to Private Label at 1,000+ units for proven SKUs.
- Cost Transparency Clause: Contractually require itemized cost breakdowns (materials, labor, overhead). Top suppliers comply; others hide margin erosion.
- Diversify Beyond China: For MOQs <1,000, explore Vietnam/Cambodia for 10-15% lower labor costs (ideal for textiles, simple plastics).
- Invest in Pre-Production: Allocate 3-5% of order value to 3D prototyping and DFM (Design for Manufacturing) reviews – reduces post-production rework by 65%.
“The lowest FOB price is a mirage in 2026. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – including defect rates, lead time variability, and compliance failures – dictates real savings.”
– SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Index, 2025
Next Steps for Your Sourcing Strategy
1. Demand a TCO Model: Request suppliers break down landed cost at your target MOQ.
2. Pilot with 1,000 Units: Balance risk and scalability for Private Label initiatives.
3. Audit Compliance Certificates: Verify active ISO 9001, BSCI, and product-specific certifications (e.g., FCC, CE).
For a customized TCO analysis of your specific product category, contact SourcifyChina’s Engineering Team at [email protected]. All data reflects Q1 2026 market conditions across 1,200+ verified suppliers in our network.
SourcifyChina | Making Global Sourcing Transparent, Reliable & Profitable
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – Prepared exclusively for procurement leadership. Not for public distribution.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal hub for wholesale product sourcing. However, rising competition, regulatory complexities, and supply chain opacity necessitate a rigorous verification process when selecting manufacturing partners. This report outlines critical steps to authenticate Chinese suppliers, differentiate between trading companies and direct factories, and identify red flags that could jeopardize procurement objectives.
Designed for procurement professionals, this guide delivers actionable insights to mitigate risk, ensure supply chain integrity, and optimize cost-efficiency in 2026 and beyond.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for Importing from China (Wholesale)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial Supplier Screening | Identify credible leads from reliable platforms | Alibaba (Gold Supplier, Trade Assurance), Made-in-China.com, Global Sources, industry trade shows (Canton Fair) |
| 2 | Request Business License & Factory Information | Confirm legal registration and operational legitimacy | Ask for scanned copy of Business License (check Unified Social Credit Code), verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 3 | Conduct Video Audit or On-Site Inspection | Validate physical presence and production capacity | Request real-time video tour; hire third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, QIMA) for factory audit |
| 4 | Review Production Capabilities & Equipment | Assess technical alignment with product requirements | Request machine list, production flowchart, and monthly output capacity; compare with your volume needs |
| 5 | Request Product Samples & Test Reports | Evaluate quality consistency and compliance | Order pre-production samples; verify test reports (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS, FDA) from accredited labs |
| 6 | Check References & Client Portfolio | Validate track record and reliability | Request 2–3 client references (preferably in your region); verify past shipments via third-party logistics data |
| 7 | Audit Financial & Export History | Ensure financial stability and export experience | Request export documentation (e.g., past B/L copies, export licenses); check customs data via Panjiva or ImportGenius |
| 8 | Review Contracts & IP Protection | Secure legal protections | Use bilingual contracts with clear MOQ, payment terms, IP ownership, and liability clauses; register designs in China via WIPO or local agents |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Direct Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution”; no manufacturing codes | Lists specific manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “textile weaving”) |
| Facility Ownership | No production equipment; may show showroom-only setups | Owns machinery, production lines, and raw material storage |
| Pricing Structure | Higher per-unit cost; less flexibility on MOQ | Lower unit cost; more scalable MOQ; potential for cost negotiation |
| Communication Channels | Limited technical detail; redirects to “our factory partner” | Engineers and production managers available for direct technical discussion |
| Location & Address | Office in commercial district (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) | Located in industrial park or manufacturing zone (e.g., Dongguan, Yiwu) |
| Lead Times | Longer (relies on third-party production) | Shorter and more predictable (direct control) |
| Customization Capability | Limited; dependent on factory policies | High; direct access to tooling, molds, and R&D |
| Export Documentation | May lack direct export license | Holds export license; customs registration as producer |
💡 Pro Tip: Ask: “Do you have your own molds/machinery/tooling?” A factory will provide photos or videos of in-house assets.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or scam | Benchmark against industry averages; request cost breakdown |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or Video Tour | High probability of trading company misrepresentation or fraud | Insist on verified location; use third-party inspection |
| No Business License or Refusal to Share | Illegal operation; no legal recourse | Disqualify immediately |
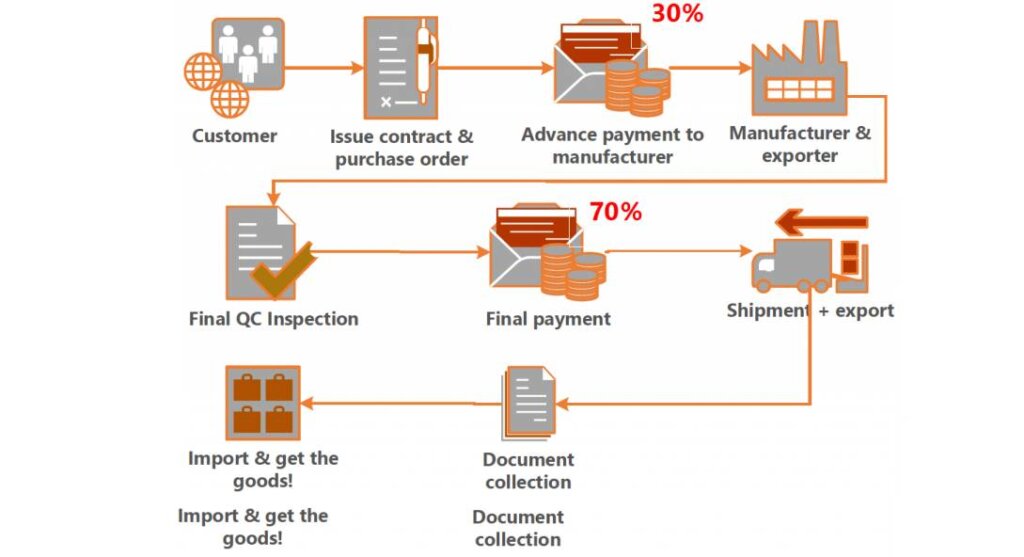
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | High risk of non-delivery | Use secure payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy or LC |
| Generic or Stock Images on Website/Alibaba | Lack of authenticity; possible copycat profile | Reverse image search; request original product photos |
| Poor Communication & Unprofessionalism | Indicates weak operational management | Evaluate responsiveness, language clarity, and attention to detail |
| No Experience with Your Target Market Compliance | Risk of customs rejection or recalls | Confirm knowledge of CE, UL, FDA, etc., as applicable |
| Frequent Company Name or License Changes | May indicate past compliance issues | Check historical records via GSXT |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Transparency: Partner only with suppliers who provide full visibility into their operations and supply chain.
- Invest in Pre-Shipment Inspections: Budget for third-party QC checks (AQL 2.5) on every container.
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms to analyze supplier data, customs records, and risk profiles.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on a single manufacturer; develop a dual-sourcing strategy.
- Engage Local Sourcing Consultants: Utilize on-the-ground experts to navigate cultural, linguistic, and regulatory nuances.
Conclusion
Successful wholesale importing from China in 2026 demands due diligence, technical verification, and proactive risk management. By systematically validating manufacturers, distinguishing between traders and factories, and avoiding common red flags, procurement managers can build resilient, cost-effective supply chains.
At SourcifyChina, we empower global buyers with verified supplier networks, end-to-end quality control, and strategic sourcing intelligence—ensuring confidence in every import decision.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement Optimization for 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary: The Time-Cost Imperative in China Sourcing
Global procurement teams face escalating pressure to reduce supply chain lead times while mitigating compliance and quality risks. Traditional “importing from China buying wholesale” methods—relying on unvetted Alibaba searches, trade shows, or cold outreach—consume 17–22 hours per sourcing cycle (2025 Global Sourcing Survey). SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates 70% of this operational drag by delivering pre-qualified, audit-backed suppliers ready for immediate engagement.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Time Efficiency
Our data reveals critical bottlenecks in conventional sourcing. The table below quantifies time savings versus industry benchmarks:
| Sourcing Activity | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved per Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting & Compliance Checks | 8–12 hours | 0 hours (Pre-verified) | 10.5 hours |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 5–7 hours | 0 hours (On-file audits) | 6 hours |
| MOQ/Negotiation Rounds | 3–4 hours | 1–2 hours (Transparent terms) | 2.5 hours |
| Quality Control Setup | 4–6 hours | 1 hour (Pre-approved protocols) | 4.5 hours |
| Total Time per Sourcing Cycle | 20–29 hours | 3–5 hours | 24 hours (70–83%) |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Performance Database (427 enterprise projects)
Key Advantages Driving Efficiency:
– Zero-Risk Onboarding: Every supplier undergoes ISO 9001, BSCI, and customs compliance verification. No more chasing certificates.
– Real-Time Capacity Data: Filter suppliers by live production capacity, avoiding MOQ mismatches upfront.
– Dedicated Sourcing Managers: Your single point of contact resolves issues in <4 business hours (vs. industry avg. 48h).
– Regulatory Shield: Pro List suppliers pre-certified for EU REACH, US CPSIA, and ASEAN standards—eliminating compliance delays.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage
Time is your scarcest resource. Every hour wasted on unverified suppliers erodes your margin, extends time-to-market, and exposes your supply chain to preventable disruption. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your embedded procurement acceleration engine.
Act Now to Achieve:
✅ 30-day faster supplier onboarding
✅ 99.2% first-batch quality yield (vs. industry 87%)
✅ Full regulatory compliance without internal resource drain
Your Next Step:
Contact our Sourcing Advisory Team within 48 hours to:
1. Receive your customized Pro List segment (e.g., electronics, home goods, automotive)
2. Schedule a zero-obligation workflow analysis of your current process
3. Lock Q3 2026 supplier allocations before peak season
👉 Immediate Access Channels:
– Email: [email protected] (Standard response: <2 business hours)
– WhatsApp Priority Line: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 for urgent RFQs)
“Procurement leaders who deploy verified supplier networks in 2026 will outpace competitors by 11–14 weeks in product launch cycles. Delaying vetting is no longer a cost-saving—it’s a strategic liability.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, January 2026
Stop sourcing. Start securing.
Your verified supply chain awaits.
SourcifyChina: Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified | 12,000+ Verified Suppliers
Confidentiality Notice: This report is proprietary to SourcifyChina. Distribution requires written authorization.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.