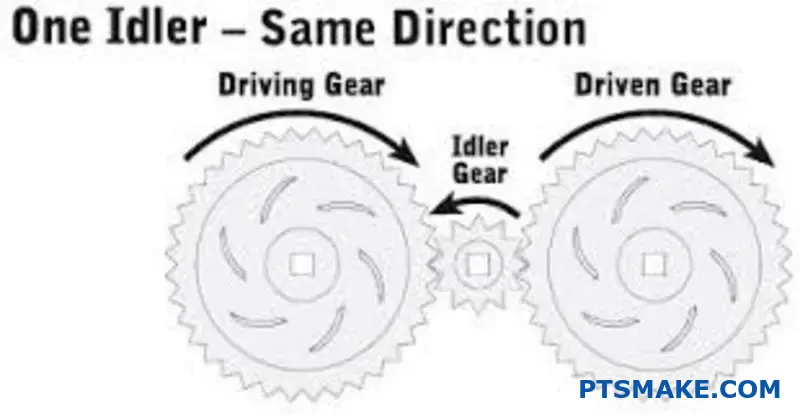
The global idler gear market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, and power transmission sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global gear and gear product market—including idler gears—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated value of USD 98.5 billion by 2028. This expansion is fueled by advancements in transmission technologies, rising automotive production—particularly in Asia-Pacific—and the growing need for efficient power transmission systems in industrial automation. Idler gears, which play a crucial role in adjusting drive alignment and torque distribution in mechanical systems, are becoming increasingly vital in maintaining operational efficiency across equipment used in manufacturing, transportation, and energy sectors. With this backdrop, identifying leading manufacturers who combine innovation, precision engineering, and global reach is essential for OEMs and suppliers aiming to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Top 8 Idler Gear Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
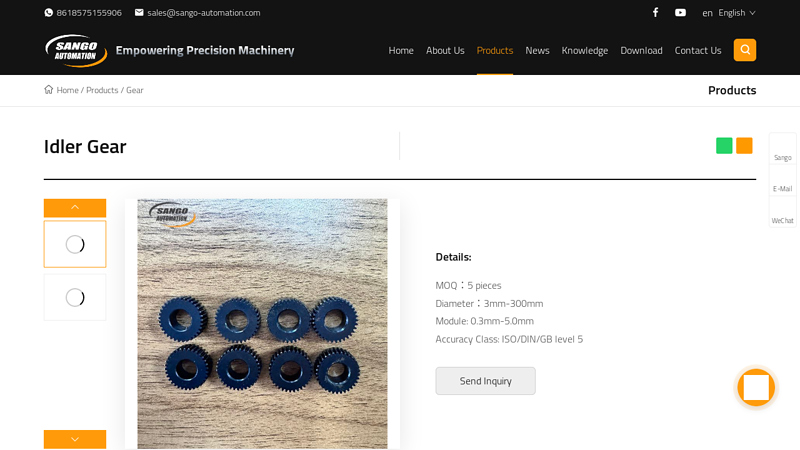
#1 China Idler Gear Manufacturers, Suppliers
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sango-automation.com
Key Highlights: Find professional idler gear manufacturers and suppliers in China here. With 10 years’ experience, we warmly welcome you to wholesale high quality idler ……
#2 idler gear Suppliers and Factory
Website: ggn-gear.com
Key Highlights: GRANGIN is one of the most professional bevel gears manufacturers and suppliers in China. Our factory offer high quality bevel gears made in China with ……
#3 Idler Gear for high
Domain Est. 2001
Website: manufacturer.hzpt.com
Key Highlights: From transmission systems to timing belts, idler gears help maintain proper tension, minimize backlash, and ensure efficient power transfer in ……
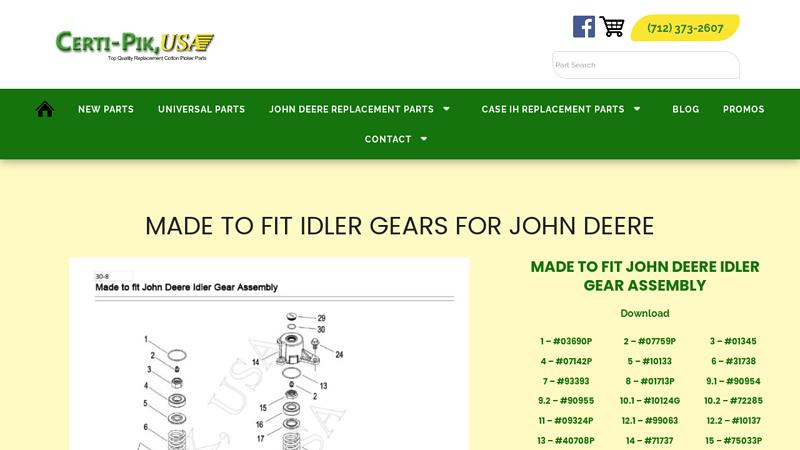
#4 Universal Idler Gears
Domain Est. 2001
Website: certipik.com
Key Highlights: The idler gear assembly for a cotton harvester is comprised of many parts, including ball bearings, bushings, nuts, O-rings, spur gears, clutches, driveshafts, ……
#5 Idler Components
Domain Est. 2009
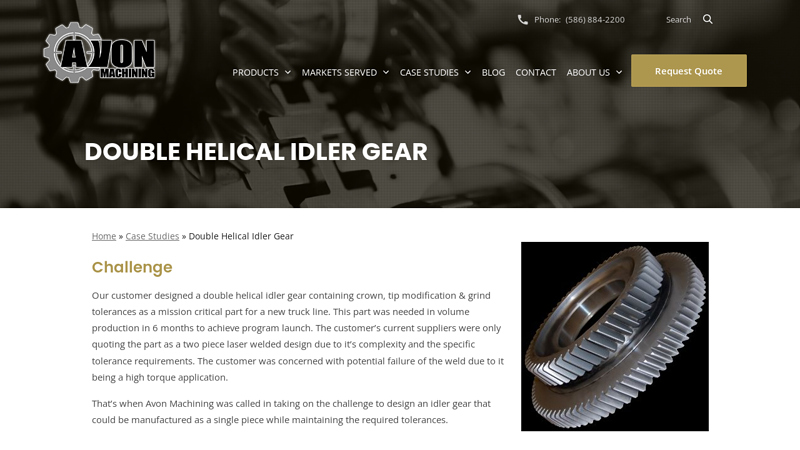
#6 Double Helical Idler Gear
Domain Est. 2017
Website: avonmachining.com
Key Highlights: Our customer designed a double helical idler gear containing crown, tip modification & grind tolerances as a mission critical part for a new truck line….
#7 Idler Gears
Domain Est. 2018
Website: gecospares.com
Key Highlights: As a reputed name in this domain, we have been engrossed in manufacturing, exporting and supplying premium grade Idler Gears. These gears are manufactured using ……
#8 LEESON Brand
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: The LEESON band spans thousands of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors, gearmotors, washdown and variable-speed control solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Idler Gear

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Idler Gears
The idler gear market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive engineering, industrial automation, and sustainability initiatives. As a critical component in power transmission systems, the idler gear—used to guide timing belts, maintain tension, and transfer motion—reflects broader shifts across key end-user industries. This analysis outlines the major trends expected to shape the idler gear market in the second half of 2026 (H2 2026).
1. Growth in Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
With global EV sales projected to surpass 40% of total vehicle sales by 2026, automakers are reengineering powertrain systems. While EVs require fewer traditional idler gears due to simplified transmissions, idler gears remain essential in auxiliary systems such as coolant pumps, compressors, and electric motor belt drives. OEMs are increasingly adopting lightweight, high-performance idler gears made from composite materials to enhance efficiency and reduce noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) in EV platforms.
2. Demand for Lightweight and High-Efficiency Components
Fuel efficiency and emissions regulations continue to drive demand for lightweight idler gears. Manufacturers are investing in advanced materials such as polymer composites, aluminum alloys, and surface-treated steels to reduce rotational mass and improve fuel economy. In H2 2026, expect to see wider adoption of hybrid idler gears combining metal cores with polymer outer rings for optimized performance and durability.
3. Expansion in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The global push toward smart manufacturing is increasing the use of precision idler gears in automated conveyors, robotic arms, and CNC machinery. These applications require high-tolerance, low-backlash idler gears capable of consistent performance under continuous operation. The trend toward modular and reconfigurable production lines further fuels demand for customizable idler gear solutions.
4. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical uncertainties and supply chain disruptions have prompted manufacturers to regionalize idler gear production. In H2 2026, North America and Europe are expected to see increased local sourcing from Tier 1 suppliers, reducing dependency on Asian imports. Nearshoring initiatives, particularly in Mexico and Eastern Europe, will support just-in-time manufacturing models in the automotive sector.
5. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and energy-efficient production processes. Leading idler gear producers are launching take-back programs and exploring remanufacturing options. By H2 2026, eco-labeling and lifecycle assessments may become competitive differentiators in B2B procurement decisions.
6. Integration of Smart Monitoring Technologies
The rise of Industry 4.0 is enabling the development of “smart” idler gears equipped with embedded sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and alignment in real time. While still in early adoption, predictive maintenance-enabled idler gears are expected to gain traction in high-value industrial and transportation applications by late 2026, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Key players such as Bosch, NTN Corporation, SKF, and Gates are intensifying R&D efforts to develop quieter, longer-lasting idler gears. Strategic partnerships with EV startups and tiered suppliers are becoming common. In H2 2026, consolidation in the market may accelerate as companies seek scale and technological edge.
Conclusion
The idler gear market in H2 2026 will be shaped by the convergence of electrification, automation, and sustainability. While traditional automotive demand evolves, new opportunities in EVs, industrial robotics, and smart systems are driving innovation. Manufacturers who adapt to lightweight designs, regional supply chains, and digital integration will be best positioned for growth in this dynamic landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing an Idler Gear (Quality, IP)
Sourcing an idler gear—especially as a replacement component—can seem straightforward, but several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly failures, legal issues, or supply chain disruptions. Being aware of these risks is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
1. Compromised Material and Manufacturing Quality
One of the most common pitfalls is selecting an idler gear based solely on price, leading to substandard materials or poor manufacturing processes. Low-cost gears may use inferior steel alloys, improper heat treatment, or imprecise machining, resulting in:
- Premature wear or tooth failure
- Excessive noise and vibration
- Reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption
- Shortened service life and unplanned downtime
Always verify material specifications (e.g., hardness, tensile strength) and request certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, material test reports). Insist on dimensional inspections and consider third-party testing for critical applications.
2. Inaccurate Gear Geometry and Tolerances
Even minor deviations in gear tooth profile, pitch, or runout can cause significant performance issues. Poorly manufactured idler gears often suffer from:
- Incorrect pressure angle or module
- Non-compliance with AGMA, DIN, or ISO standards
- Inconsistent tooth spacing leading to uneven load distribution
Ensure suppliers provide detailed drawings with geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T), and validate samples using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or gear inspection equipment.
3. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable gear manufacturers provide full traceability, including batch numbers, heat treatment records, and quality control documentation. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide this information increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or non-conforming parts. This becomes especially problematic during audits, warranty claims, or failure investigations.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Using or sourcing idler gears that replicate patented or trademarked designs without authorization can expose your company to legal action. Common IP risks include:
- Copying gear profiles, spline designs, or mounting configurations protected by patents
- Reproducing branded components (e.g., OEM-specific idler gears) that are trademarked
- Distributing reverse-engineered parts without proper design freedom clearance
Always confirm whether the idler gear design is proprietary. Where possible, obtain legal verification or source from licensed manufacturers. Consider redesigning non-critical components to avoid IP conflicts.
5. Misrepresentation of OEM Compatibility
Some suppliers claim “OEM equivalent” or “direct replacement” without proper validation. These claims can be misleading if the gear does not meet original specifications for load capacity, backlash, or surface finish. Always cross-check technical data and, if possible, conduct side-by-side testing before full-scale deployment.
6. Supply Chain and Counterfeit Risks
Purchasing from unverified or offshore suppliers increases exposure to counterfeit or recycled parts passed off as new. These components may lack proper quality controls and can fail catastrophically in service. Use trusted distributors, verify supplier credentials, and avoid unusually low pricing that suggests substandard or fake goods.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—focusing on technical validation, quality assurance, and IP compliance—companies can ensure reliable performance and legal safety when sourcing idler gears.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Idler Gear
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, transportation, and distribution of idler gears—critical components used in engine timing systems, conveyor belts, and various mechanical drive applications.
Product Classification & Specifications
Idler gears are typically classified under mechanical power transmission components. Accurate product specifications—including material composition (e.g., steel, nylon, or composite), dimensions, load capacity, and surface treatment—are vital for compliance with industry standards such as ISO, ANSI, or DIN. Ensure all technical documentation reflects exact part numbers, tolerances, and performance criteria to avoid misclassification during shipping or customs clearance.
Regulatory Compliance
Idler gears may be subject to regional and international regulations depending on materials used and end application. Components containing restricted substances (e.g., certain metals or coatings) must comply with environmental directives such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) in the EU or REACH for chemical registration. If used in automotive or aerospace systems, adherence to IATF 16949 or AS9100 quality standards may be required.
Export Controls & Documentation
When shipping internationally, verify whether idler gears fall under export control classifications such as the Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) in the U.S. Most standard idler gears are designated as EAR99, meaning they are low-risk and not specifically listed on the Commerce Control List. Accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin must accompany shipments to facilitate customs clearance and avoid delays.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit. Use corrosion-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper for metal gears), secure cushioning, and rigid outer containers to maintain part integrity. Label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”) and include barcodes or RFID tags for tracking. Follow internal handling procedures to avoid contamination or mechanical stress during warehousing.
Transportation & Inventory Management
Choose transportation modes (air, sea, or ground) based on delivery timelines and component value. Implement a warehouse management system (WMS) to monitor stock levels, batch numbers, and shelf life (if applicable). Practice FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to minimize obsolescence, especially for coated or treated gears sensitive to long-term storage.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain full traceability from raw material sourcing to finished product. Each batch of idler gears should have associated documentation including material certifications, inspection reports, and test results. Conduct regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance with quality management systems and customer-specific requirements.
Sustainability & End-of-Life Considerations
Design and logistics planning should consider end-of-life recycling. Metals like steel and aluminum used in idler gears are recyclable; ensure take-back programs or recycling instructions are available where applicable. Minimize packaging waste by using recyclable or reusable materials in line with environmental compliance goals.
Summary
Adhering to logistics and compliance standards ensures that idler gears meet performance expectations while minimizing legal, environmental, and operational risks. A proactive approach to documentation, quality control, and supply chain transparency supports reliable delivery and long-term customer satisfaction.
Conclusion for Sourcing Idler Gear:
Sourcing the appropriate idler gear requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, quality standards, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term availability. It is essential to ensure that the idler gear meets the required material, dimensional, and performance criteria to maintain optimal function within the mechanical system. Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer consistent quality, timely delivery, and strong after-sales support helps minimize downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, considering factors such as lead times, scalability, and potential obsolescence supports sustainable operations. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that balances quality, cost, and supply chain resilience ensures reliable performance and contributes to the overall efficiency and longevity of the equipment.