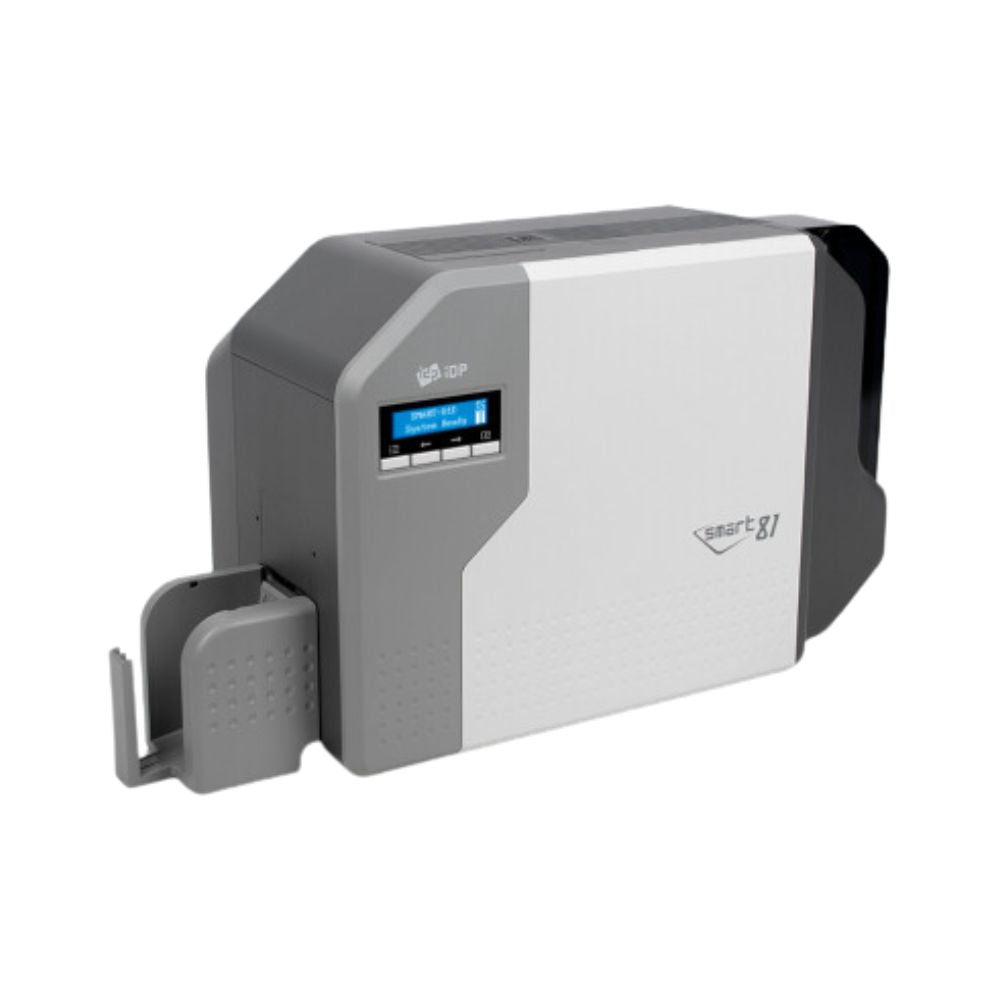
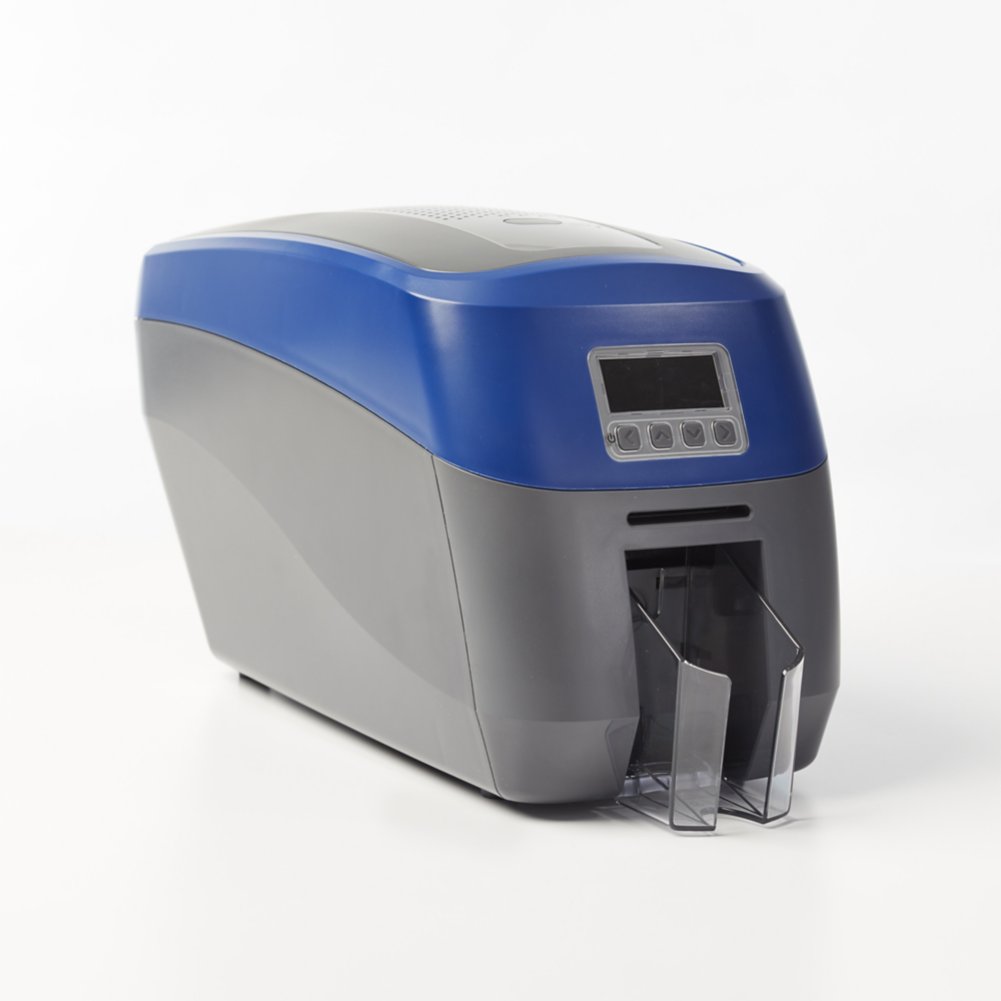
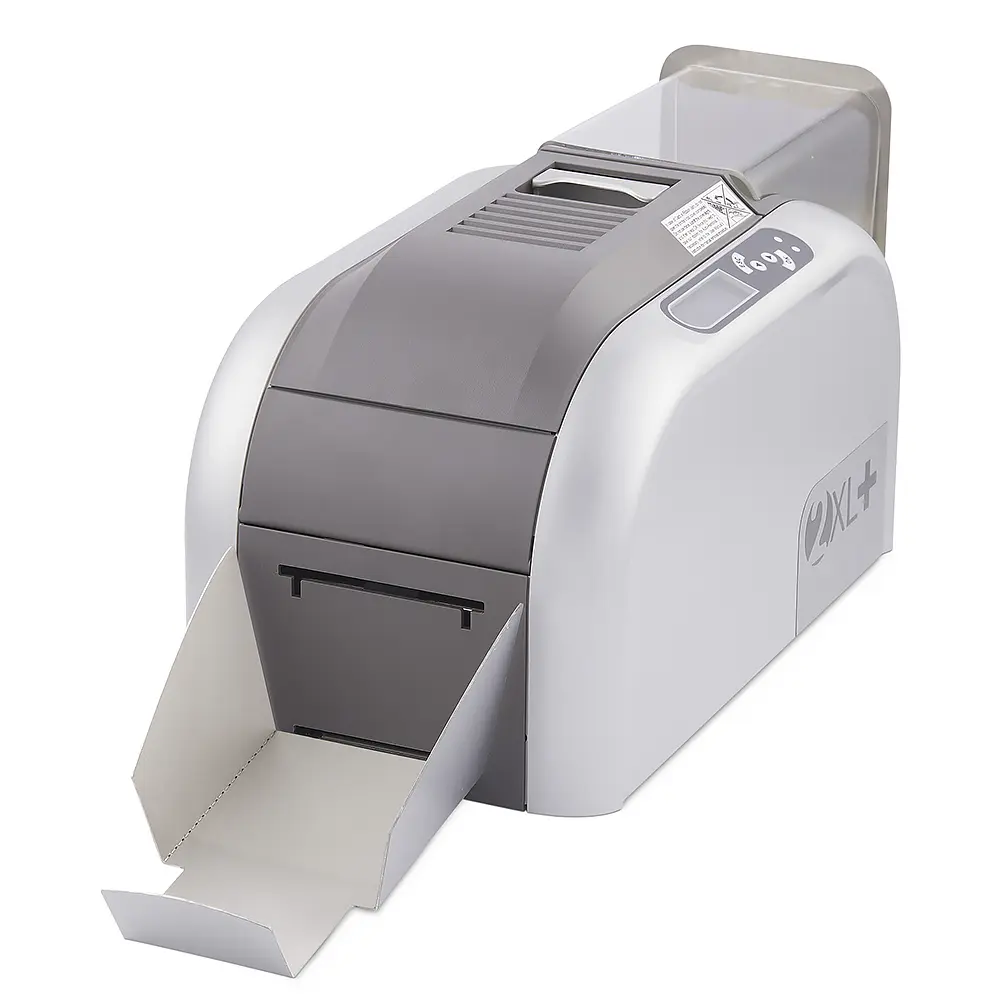
The global ID card printer market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for secure identification across government, corporate, and educational sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.45 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing adoption of ID cards for access control, employee verification, and national ID programs, alongside advancements in printing technologies such as RFID integration and high-resolution color printing. As security and identity management become top priorities worldwide, manufacturers are innovating rapidly to deliver durable, efficient, and scalable ID card printing solutions. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, setting industry benchmarks in performance, reliability, and technological innovation.
Top 10 Id Printer Card Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Card Printers
Domain Est. 2005
Website: hidglobal.com
Key Highlights: Our selection of card printers range from entry-level printers to the industry’s most sophisticated, industrial printing, laser engraving and encoding solutions ……
#2 Photo ID Printers and Technology by IDP Americas
Domain Est. 2013
Website: idpamericas.com
Key Highlights: At IDP Americas, we specialize in photo ID technology and high-quality printers for various applications. Choose us for your card printing needs today….
#3 Identity (ID) Card Printers
Domain Est. 1994
Website: entrust.com
Key Highlights: Explore our range of instant ID card printer options, including features like tactile impression, lamination, UV printing, and more….
#4 ID Card Printers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: zebra.com
Key Highlights: Zebra card and badge printers make it easy to connect, create and print high quality, durable cards for a variety of applications….
#5 ID card printers by Magicard
Domain Est. 1997
Website: magicard.com
Key Highlights: Magicard offers a range of ID printers to exceed every user’s requirements. Whatever you need: low cost to high security printing solutions….
#6 Evolis
Domain Est. 1999
Website: evolis.com
Key Highlights: Evolis, global leader in badge and card printer solutions, designs, manufactures and sells plastic cards and ID badges printers….
#7 IDville
Domain Est. 2001
Website: idville.com
Key Highlights: Shop IDville for cost effective ID card solutions. You can get ID printing supplies, accessories and printer systems shipped on the same day you order!…
#8 ID Wholesaler provides top
Domain Est. 2002
Website: idwholesaler.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $100 30-day returnsID Wholesaler provides top-quality ID card printers, badge accessories & supplies. Shop from top trusted brands with expert support & fast shi…
#9 ID Badges & Cards
Domain Est. 2003
Website: alphacard.com
Key Highlights: AlphaCard carries a wide range of professional ID card printers and supplies from the industry’s top brands including Magicard, Datacard, Zebra, Fargo, and ……
#10 IDSecurityOnline
Domain Est. 2009
Expert Sourcing Insights for Id Printer Card

2026 Market Trends for ID Printer Cards
The global market for ID printer cards is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising security demands, and expanding applications across industries. As organizations prioritize secure identification, personalized access, and digital integration, ID printer cards are evolving beyond traditional plastic credentials into smart, data-rich tools. This analysis explores key trends shaping the ID printer card market in 2026, focusing on technology, demand drivers, regional developments, and competitive dynamics.
Advancements in Smart Card Technology
One of the most influential trends in 2026 is the widespread adoption of smart ID printer cards embedded with RFID, NFC, and biometric sensors. These cards support multifunctional capabilities, including contactless access, digital payments, and real-time authentication. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating secure microchips that comply with ISO/IEC 14443 and FIPS 201 standards, enhancing data encryption and resistance to cloning. The shift toward smart cards is particularly evident in government-issued IDs, corporate badges, and higher education campuses.
Increased Demand from Enterprise and Government Sectors
Enterprises and public sector institutions are driving demand for high-security ID printer cards. With remote work evolving into hybrid models, organizations require robust identity verification systems. In 2026, the need for secure physical access and workforce management is fueling deployments of on-site ID card printing solutions. Governments are also investing in national digital ID programs, such as digital driver’s licenses and citizen ID cards, further expanding the market. Countries in Europe and North America are leading adoption, while emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are rapidly catching up.
Growth of On-Demand and Portable ID Printing
The trend toward decentralized, on-demand card issuance is accelerating. By 2026, portable and desktop ID printers are becoming more affordable and user-friendly, enabling schools, hospitals, and event venues to produce cards instantly. This reduces lead times, enhances customization, and improves security by minimizing third-party handling. Cloud-connected ID printing platforms now allow remote management of card issuance, supporting scalability and compliance across multi-site operations.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are influencing material choices in ID card manufacturing. In 2026, eco-conscious organizations are opting for biodegradable PVC alternatives, recycled polycarbonate, and compostable card substrates. Printer manufacturers are also introducing energy-efficient models and recyclable ribbon cartridges. These sustainability initiatives are becoming a competitive differentiator, especially among public institutions and corporations with ESG commitments.
Integration with Digital Identity Ecosystems
ID printer cards are no longer standalone physical tools—they are increasingly integrated into broader digital identity ecosystems. In 2026, many organizations link physical ID cards with mobile credentials via companion apps, enabling seamless transitions between physical and digital authentication. This convergence supports unified access control, time-and-attendance tracking, and secure single sign-on (SSO) experiences. Interoperability with platforms like Microsoft Azure AD and Google Workspace is becoming standard.
Regional Market Expansion
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets due to stringent security regulations and high adoption of automated identity systems, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to record the highest growth rate by 2026. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are modernizing public infrastructure and rolling out national ID programs. Meanwhile, the Middle East is investing in smart city projects that rely heavily on secure ID technologies for residents and visitors.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The ID printer card market in 2026 is highly competitive, with key players such as HID Global, Zebra Technologies, Evolis, and Entrust investing in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Innovations include dual-sided printing, holographic overlays, tamper-evident features, and AI-driven card design software. Strategic partnerships between printer manufacturers and cybersecurity firms are also on the rise, aiming to deliver end-to-end identity solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the ID printer card market will be defined by intelligence, security, and integration. The convergence of smart technologies, regulatory demands, and environmental responsibility is reshaping how organizations issue and manage identity credentials. As physical and digital identities continue to merge, ID printer cards will remain a critical component of secure, efficient, and scalable identity ecosystems across industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing ID Printer Cards (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing ID printer cards—such as PVC, smart, or proximity cards—requires careful consideration to avoid compromising security, functionality, and legal compliance. Two major areas where organizations often face challenges are card quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of the following pitfalls can help ensure a reliable and legally sound procurement process.
Poor Material Quality and Durability
One of the most frequent issues is receiving ID cards made from substandard materials. Low-quality PVC or composite layers can lead to warping, cracking, or fading when exposed to heat, moisture, or daily wear. Cards that degrade quickly undermine security and brand image, especially in high-use environments like corporate offices or educational institutions.
Inconsistent Print Receptivity
Not all ID cards are created equal in terms of print performance. Inferior surface coatings may result in poor dye-sublimation or resin printing, causing blurry text, smudged photos, or fading over time. This inconsistency affects the professional appearance and long-term readability of the cards.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Many cheaply sourced cards fail to meet international standards such as ISO/IEC 7810 (size and physical characteristics) or ISO/IEC 14443 (for contactless smart cards). Non-compliant cards may not work reliably with access control systems, leading to integration issues and higher operational costs.
Counterfeit or Unauthorized Smart Chips
Using ID cards with embedded chips (e.g., MIFARE, DESFire) from unauthorized suppliers poses serious IP risks. Some vendors counterfeit branded chips or use cloned firmware, which can violate intellectual property rights and expose the buyer to legal liability. Additionally, counterfeit chips often lack proper security protocols, making systems vulnerable to cloning or data breaches.
Unclear or Missing Licensing Agreements
Reputable chip manufacturers require proper licensing for the use of their technology. Sourcing cards from suppliers who do not provide proof of valid licensing (e.g., NXP’s MIFARE license) can result in non-compliant deployments and potential legal action. Always verify that your supplier is an authorized partner.
Inadequate Data Security and Pre-Programming Risks
Some suppliers pre-program cards or provide default keys and configurations, which can introduce security vulnerabilities. Without proper cryptographic management, these cards may be easily duplicated or intercepted, compromising the entire access control system.
Supply Chain Opacity and Traceability Issues
Purchasing from unverified or offshore suppliers may obscure the origin of materials and components. Lack of transparency increases the risk of receiving counterfeit products or those produced under unethical conditions, while also complicating warranty claims and technical support.
Short-Term Savings Leading to Long-Term Costs
Opting for the cheapest available cards often results in higher total cost of ownership due to increased failure rates, system incompatibilities, and security incidents. Investing in high-quality, IP-compliant cards from trusted vendors ensures reliability, longevity, and legal safety.
By carefully evaluating both the technical quality and intellectual property legitimacy of ID printer cards, organizations can avoid these common pitfalls and build secure, durable, and compliant identification systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for ID Card Printers
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the procurement, deployment, and operation of ID card printers in organizational settings. Adhering to these guidelines ensures efficient operations, data security, and regulatory adherence.
Procurement and Supplier Management
Ensure all ID card printers are sourced from authorized and reputable suppliers. Verify product authenticity, warranty terms, and service support availability. Evaluate suppliers based on compliance certifications (e.g., ISO standards), data security practices, and sustainability policies. Maintain accurate procurement records for audit and compliance purposes.
Shipping and Handling
Package ID card printers securely to prevent damage during transit. Use anti-static packaging materials and include handling labels (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Track shipments in real time and confirm delivery with signed receipts. Inspect units upon arrival for physical damage or tampering before deployment.
Installation and Deployment
Install ID card printers in secure, access-controlled environments. Follow manufacturer guidelines for setup, including power requirements and connectivity. Ensure network-connected printers are placed behind firewalls and on segmented networks to reduce cyber risks. Document installation details, including location, serial number, and assigned personnel.
Data Security and Privacy Compliance
ID card printers often process personally identifiable information (PII). Ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, depending on jurisdiction and use case. Implement secure data transmission (e.g., encrypted connections), limit access to authorized personnel, and avoid storing cardholder data on printer memory. Use printers with built-in security features like secure erase and tamper detection.
Access Control and User Authentication
Restrict physical and digital access to ID card printers. Employ role-based access controls and require user authentication (e.g., login credentials, smart cards) before operation. Maintain audit logs of card printing activity, including user, timestamp, and card details, to support accountability and investigations.
Environmental and Regulatory Standards
Ensure ID card printers comply with environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and ENERGY STAR standards where applicable. Dispose of used printer components (e.g., ribbons, cards, cartridges) according to local e-waste and recycling regulations. Maintain compliance documentation for audits.
Maintenance and Servicing
Schedule regular maintenance to ensure optimal printer performance and longevity. Only authorized technicians should perform repairs or maintenance. When equipment is serviced off-site, ensure data sanitization procedures are followed and service providers are bound by confidentiality agreements.
End-of-Life Management
Decommission ID card printers securely at end-of-life. Perform a factory reset or use certified data-wiping tools to erase all stored data. Physically destroy storage components if necessary. Recycle or dispose of the device through certified e-waste handlers and retain disposal certificates for compliance records.
Training and Policy Enforcement
Train personnel on proper use, security protocols, and compliance requirements related to ID card printing. Enforce organizational policies regarding card issuance, data handling, and incident reporting. Conduct periodic audits to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion on Sourcing an ID Card Printer
Sourcing an ID card printer is a strategic decision that significantly impacts the efficiency, security, and professionalism of an organization’s identification system. After evaluating various factors such as print technology (direct-to-card vs. retransfer), printer durability, print quality, security features, software compatibility, and budget considerations, it is evident that selecting the right printer requires a balance between functionality and long-term value.
For organizations requiring high-volume, durable, and secure ID cards—such as corporations, educational institutions, or government agencies—investing in a reliable, secure, and scalable ID card printer is essential. Features like lamination, encoding (magnetic stripe, smart chip, or RFID), and tamper-resistant printing enhance the security and longevity of issued ID cards.
Additionally, considering ongoing costs—including replacement ribbons, cleaning kits, and maintenance—is crucial for cost-effective operation. Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer warranties, technical support, and access to genuine consumables further ensures sustained performance.
In conclusion, a well-researched decision in sourcing an ID card printer not only improves operational efficiency but also strengthens organizational security and credibility. By aligning the printer’s capabilities with specific use-case requirements, organizations can achieve a reliable, secure, and professional ID card issuance process for years to come.