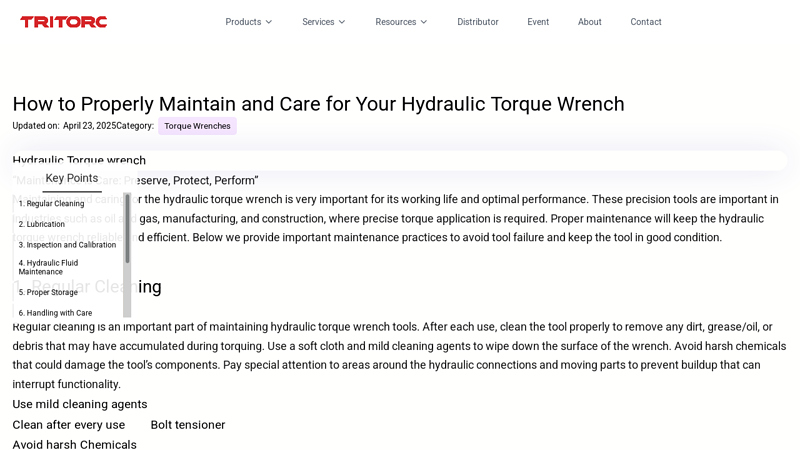
The global hydraulic torque tools market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision and efficiency in industrial maintenance, oil & gas operations, and heavy machinery assembly. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global torque tools market—which includes hydraulic variants—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. Hydraulic torque wrenches, in particular, are gaining traction due to their ability to deliver consistent, high-torque output with minimal reaction force, enhancing safety and accuracy in critical bolting applications. With industries prioritizing reliability and compliance with tightening standards, manufacturers specializing in hydraulic torque solutions are seeing heightened demand across energy, construction, and manufacturing sectors. This growing momentum underscores the importance of identifying the top performers shaping the industry, based on innovation, market reach, and technological advancement.
Top 7 Hydraulic Torque Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 HYTORC
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hytorc.com
Key Highlights: Revolutionizing industrial bolting with innovative tools, technology, and solutions that enhance safety, precision, and efficiency. HYTORC has been trusted ……
#2 BMF Torque Wrench Co.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bmftorquewrench.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of hydraulic torque wrenches for heavy industrial applications, apply torque ranging from 600 to 200000 ft-lbs….
#3 Hydraulic Torque Wrench
Domain Est. 1997
Website: torcup.com
Key Highlights: The most unique and recognizable square drive hydraulic torque wrench. Ergonomically shaped to handle every socket drive application….
#4 WREN hydrauli;hydraulic torque wrench manufacturing;hydraulic …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: wrenchina.com
Key Highlights: WREN is a modern manufacturer with professional to design,produce and sell Hydraulic Tools.WREN often exports Hydraulic Torque Wrench,Hydraulic Cylinder and ……
#5 TorsionX
Domain Est. 2013
Website: torsionx.com
Key Highlights: Powerful and reliable when your job demands it. TorsionX offers a full line of torque pumps and associated equipment available for purchase or rent….
#6 How to Properly Maintain and Care for Your Hydraulic Torque Wrench
Domain Est. 2013
Website: tritorc.com
Key Highlights: How to Properly Maintain and Care for Your Hydraulic Torque Wrench · 1. Regular Cleaning · 2. Lubrication · 3. Inspection and Calibration · 4….
#7 Hydraulic torque wrench for industry
Domain Est. 2013
Website: hytorcatlantique.fr
Key Highlights: Hytorc France has been the leader in bolting solutions and hydraulic clamping systems for the industry for more than 10 years on the French market….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Hydraulic Torque

2026 Market Trends for Hydraulic Torque
Increased Automation and Integration in Industrial Applications
The hydraulic torque tools market is expected to see substantial growth driven by the rising demand for automation across manufacturing, oil & gas, automotive, and construction sectors. By 2026, more companies are anticipated to integrate smart hydraulic torque tools into automated assembly lines and maintenance systems. These tools, equipped with IoT connectivity and data feedback capabilities, will enable real-time torque monitoring, enhance process consistency, and support predictive maintenance—improving overall operational efficiency and reducing human error.
Growing Emphasis on Precision, Safety, and Compliance
Regulatory standards and safety requirements in critical industries are becoming more stringent, particularly in sectors like aerospace, energy, and heavy machinery. Hydraulic torque tools offer high precision and repeatability, essential for ensuring bolted joint integrity and preventing failures. By 2026, demand will be further fueled by the need to comply with international standards such as ISO 5393 and API specifications. Manufacturers will increasingly adopt smart hydraulic torque wrenches with digital calibration and audit trails to meet traceability and safety compliance mandates.
Advancements in Smart and Connected Tools
Technological innovation will play a pivotal role in shaping the 2026 landscape. Hydraulic torque tools are evolving into intelligent systems with embedded sensors, wireless communication (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi), and cloud-based data management platforms. These advancements allow for remote monitoring, automatic documentation of torque values, and integration with enterprise asset management (EAM) systems. This digital transformation supports Industry 4.0 initiatives and will be a key differentiator for tool providers aiming to capture market share.
Shift Toward Lightweight and Ergonomic Designs
As workplace safety and operator fatigue become focal points, manufacturers are investing in lighter, more ergonomic hydraulic torque tools. By 2026, expect to see wider adoption of composite materials and compact hydraulic systems that reduce tool weight without compromising power. These improvements enhance usability in confined spaces and repetitive tasks, particularly in wind energy and offshore platforms, where accessibility and operator safety are critical.
Expansion in Renewable Energy and Infrastructure Projects
The global push toward renewable energy—especially wind power—will significantly influence demand for hydraulic torque tools. Wind turbine installations and maintenance require high-torque, reliable tools for blade and tower assembly. With continued investments in infrastructure and clean energy, the hydraulic torque market is projected to benefit from sustained project pipelines through 2026, particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Considerations
Although hydraulic systems are powerful, environmental concerns are prompting innovations in energy efficiency and fluid management. By 2026, manufacturers may focus on developing closed-loop hydraulic systems, energy recovery mechanisms, and biodegradable hydraulic fluids to align with corporate sustainability goals. While electric tools are gaining traction in some segments, hydraulic solutions will retain dominance in high-torque applications due to their superior power density and reliability.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Hydraulic Torque Tools (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing hydraulic torque tools—especially from lower-cost manufacturing regions—presents significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key challenges to consider:
1. Substandard Materials and Manufacturing
Many low-cost suppliers use inferior materials (e.g., lower-grade steel, subpar seals, or inadequate hydraulic components) to reduce costs. This compromises tool durability, accuracy, and safety. Poor heat treatment, imprecise machining, or lack of quality control during assembly can result in tools that fail under pressure or deliver inconsistent torque output, increasing the risk of equipment damage or workplace accidents.
2. Inaccurate or Unreliable Torque Output
A critical function of hydraulic torque tools is precision. Some sourced tools lack proper calibration or drift over time due to poor internal design. Without traceable calibration certificates or adherence to international standards (e.g., ISO 5393), users cannot trust torque values, potentially leading to under- or over-tightening of critical joints in oil & gas, wind energy, or construction applications.
3. Misrepresentation of Specifications and Performance
Suppliers may exaggerate torque capacity, cycle life, or operating pressure in marketing materials. Tools advertised as “equivalent to” or “compatible with” leading OEMs (e.g., Hytorc, Enerpac) often fail to meet the same performance benchmarks. Buyers may unknowingly receive underperforming tools that don’t meet project requirements.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement
A major risk is sourcing tools that infringe on patented designs or trademarks. Some manufacturers produce near-identical copies of branded hydraulic wrenches or pumps, violating IP rights. Purchasing such tools—even unknowingly—can expose the buyer to legal liability, shipment seizures, or forced recalls. Additionally, using counterfeit or cloned tools may void insurance or warranty coverage on associated equipment.
5. Lack of Technical Support and Spare Parts
Low-cost suppliers often lack robust after-sales support, technical documentation, or readily available spare parts. When a tool fails, downtime can be extensive due to long lead times for replacements or lack of local service centers. This undermines operational efficiency and increases total cost of ownership.
6. Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
Reputable hydraulic torque tools comply with safety and performance standards such as ASME B30.1, ISO 17025 (for calibration), or ATEX (for explosive environments). Sourced tools may lack proper certification or third-party testing, making them unsuitable for regulated industries and exposing users to compliance risks.
7. Supply Chain and Traceability Issues
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to verify the origin of components or ensure ethical manufacturing practices. Without traceability, it’s challenging to conduct root cause analysis in case of failure or respond effectively to quality audits.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and sample testing.
- Require documented compliance with relevant standards and traceable calibration.
- Work with legal counsel to assess IP risks and include indemnification clauses in contracts.
- Source from authorized distributors or manufacturers with verifiable IP ownership.
- Prioritize long-term reliability and safety over initial cost savings.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure they source hydraulic torque tools that are safe, reliable, and legally compliant.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Hydraulic Torque Tools
Overview
Hydraulic torque tools are precision equipment used in industrial applications such as oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing for applying controlled torque to fasteners. Due to their high-pressure operation and critical safety role, proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential throughout their lifecycle—from manufacturing to end use.
Transportation and Handling
Hydraulic torque tools require careful handling during shipping and transport to prevent damage and ensure operator safety.
– Packaging: Use manufacturer-approved crates or cases with foam inserts to protect hydraulic components, hoses, and control units.
– Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” labels. Include any hazardous material indicators if applicable (e.g., residual hydraulic fluid).
– Hazardous Materials: While most tools are non-hazardous, associated fluids (e.g., hydraulic oil) may be regulated. Confirm fluid classification under IATA, IMDG, or DOT regulations before air, sea, or ground transport.
– Temperature Control: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures during transit, which can degrade seals and hoses. Store and transport in environments between 0°C and 40°C (32°F–104°F).
Import/Export Compliance
International movement of hydraulic torque tools must adhere to customs and trade regulations.
– HS Codes: Classify tools under Harmonized System (HS) codes such as 8467.89 (hand tools with self-contained electric or non-electric motors). Confirm with local customs authorities.
– Export Controls: Check for dual-use or military applicability under regulations like the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulation. Most industrial torque tools are EAR99 and unrestricted, but verify based on specifications.
– Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/airway bill. Include technical specifications to support classification.
– Certifications: Some countries require conformity assessments (e.g., CE marking for the EU, UKCA for the UK, or GOST-R for Russia). Ensure tools meet regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Hydraulic torque tools must meet safety and performance standards in the jurisdictions where they are used.
– Pressure Equipment Directive (PED): In the EU, tools operating above 0.5 bar may fall under PED 2014/68/EU. Verify CE marking and EU Declaration of Conformity.
– OSHA and ANSI Standards (USA): Follow OSHA 29 CFR 1910 for workplace safety. Comply with ANSI B107.36-2017 for performance and safety requirements of hydraulic torque tools.
– ATEX/IECEx: In explosive atmospheres (e.g., oil refineries), use tools certified for hazardous locations under ATEX (EU) or IECEx standards.
– Calibration and Traceability: Maintain regular calibration with documentation traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST in the U.S.). Calibration intervals should align with manufacturer recommendations or industry best practices (typically annually).
Maintenance and Operational Compliance
Proper maintenance ensures continued compliance and tool reliability.
– Inspection Regime: Conduct routine visual and functional checks for leaks, hose integrity, and pressure accuracy.
– Record Keeping: Maintain logs for calibration, repairs, and safety inspections. Required for audits and ISO 9001/14001 compliance.
– Operator Training: Ensure personnel are trained in safe operation, emergency shutdown procedures, and PPE requirements (e.g., eye protection, gloves).
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
Environmental regulations govern end-of-life handling.
– Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE): In the EU, hydraulic tools with electronic controls may fall under WEEE Directive 2012/19/EU. Dispose through certified e-waste channels.
– Hydraulic Fluid Disposal: Used or spilled hydraulic oil must be treated as hazardous waste in many regions. Follow EPA (USA) or equivalent local guidelines for containment and recycling.
– Recycling: Salvage metal components and return hoses/fittings to certified recyclers.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for hydraulic torque tools involve careful transport planning, adherence to international trade rules, alignment with regional safety standards, and disciplined maintenance. Proactive compliance minimizes delays, ensures workplace safety, and supports sustainable operations. Always consult local regulations and manufacturers for tool-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Hydraulic Torque Tools:
Sourcing hydraulic torque tools requires a strategic approach that balances performance, reliability, cost, and long-term service support. These tools are critical in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and heavy manufacturing, where precision, safety, and efficiency in bolted joint applications are paramount. After evaluating key factors such as tool accuracy, pressure capacity, ease of maintenance, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 5393), and supplier reputation, it becomes evident that partnering with a reputable supplier offering certified equipment and technical support is essential.
Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond the initial purchase price—ensures better value, factoring in durability, calibration services, spare parts availability, and training. Investing in high-quality hydraulic torque tools not only enhances operational safety and efficiency but also reduces downtime and minimizes the risks of joint failure.
In conclusion, successful sourcing involves thorough supplier vetting, alignment with industry requirements, and a focus on long-term reliability. By prioritizing quality and support over short-term savings, organizations can ensure precise, repeatable torque application and maintain the integrity of critical bolting operations.