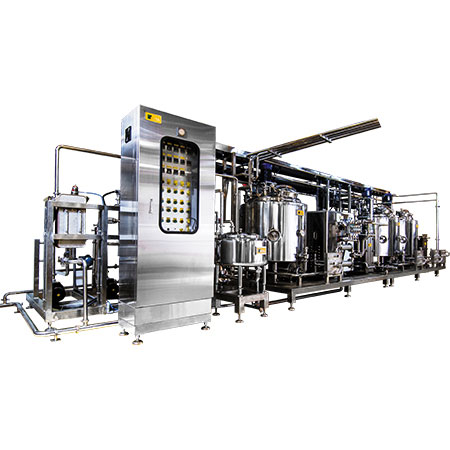
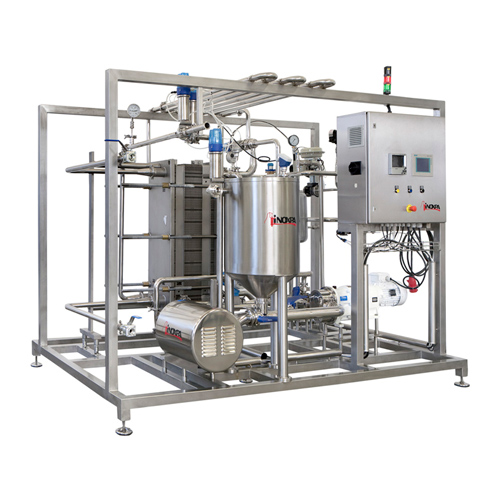
The global food and beverage industry is witnessing a surge in demand for safe, shelf-stable liquid products, driving widespread adoption of High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) pasteurization systems. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global pasteurization equipment market was valued at USD 42.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, driven by stringent food safety regulations and rising consumer awareness. HTST technology, known for its ability to eliminate pathogens while preserving nutritional quality and flavor, has become a cornerstone in dairy, juice, and beverage processing. With this growing demand, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and scalability. The following analysis identifies the top 10 HTST pasteurization manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement and global reach.
Top 10 Htst Pasteurisation Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Custom High
Domain Est. 1996
Website: csidesigns.com
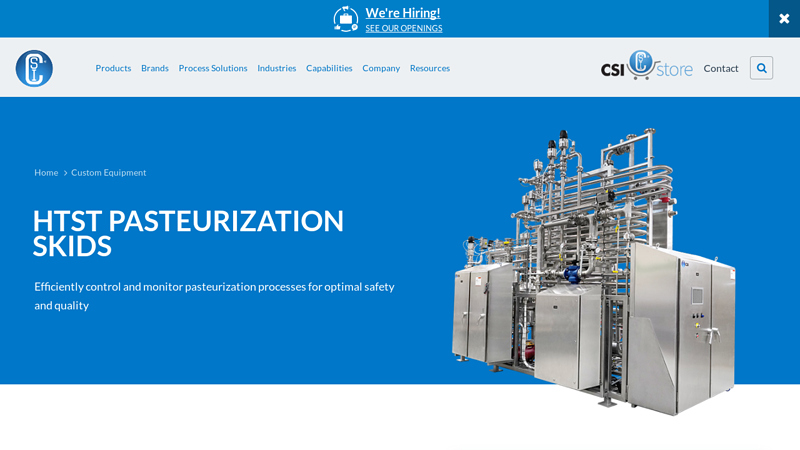
Key Highlights: Central States Industrial (CSI) makes process sanitary processing equipment and systems, including custom HTST pasteurization skids and stainless steel …Missing: pasteurisation …
#2 Pasteurization systems (HTST)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jcs.com
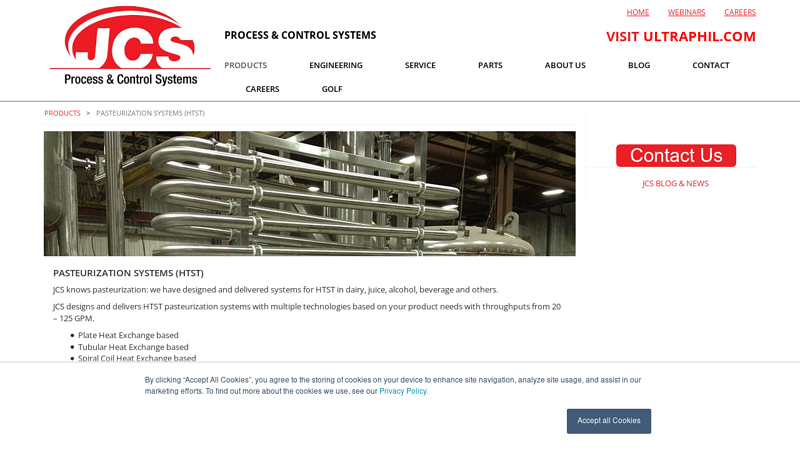
Key Highlights: JCS designs and delivers HTST pasteurization systems with multiple technologies based on your product needs with throughputs from 20 – 125 GPM.Missing: pasteurisation manufacturer…
#3 HTST system for ice cream production
Domain Est. 1999
Website: teknoice.com
Key Highlights: The Teknomix HTST (High Temperature Short Time) is a solution for industrial ice cream mix preparation in large quantities….
#4 HTST/UHT Pasteurization, Sterilization and Aseptic Filling
Domain Est. 1997
Website: microthermics.com
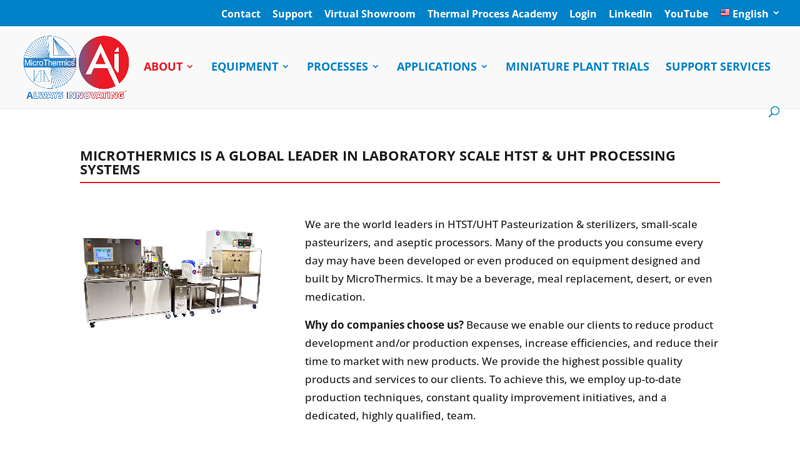
Key Highlights: We are the world leaders in HTST/UHT Pasteurization & sterilizers, small-scale pasteurizers, and aseptic processors. Many of the products you consume every ……
#5 HTST Pasteurization Systems & Equipment
Domain Est. 1998
Website: heritage-equipment.com
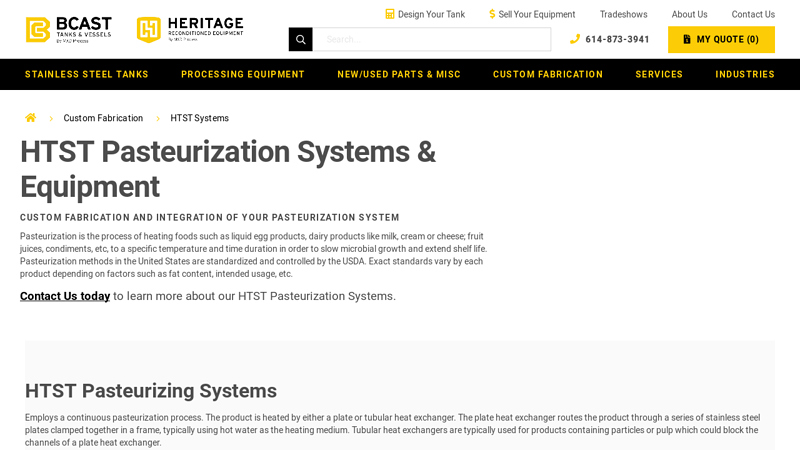
Key Highlights: Heritage Equipment’s custom HTST Pasteurization Systems and Pasteurization Equipment will suit all of your fluid processing needs. Call for a quote today!…
#6 HTST Pasteurization Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ipec-inc.com
Key Highlights: IPEC High Temperature Short Time (HTST) Pasteurization Systems heat and hold solutions at a specific temperature and time to ensure complete inactivation of ……
#7 A&B Pasteurizers/HTST Systems
Domain Est. 2002
Website: jbtc.com
Key Highlights: If you need a reliable machine to sterilize your dairy goods, check out our custom High Temperature Short Time (HTST) pasteurization systems….
#8 High temperature short time (HTST) pasteurization systems
Domain Est. 2002
Website: inspection.canada.ca
Key Highlights: The following provides recommended practices for high temperature short time (HTST) pasteurization of dairy products….
#9 HTST Pasteurizer
Domain Est. 2006
Website: inoxpausa.com
Key Highlights: HTST pasteuriser is designed for the thermal treatment of milk and dairy products as well as other food products as soft drinks and juices….
#10 HTST Pasteurisation
Domain Est. 2013
Website: hysysco.com
Key Highlights: Hysysco help dairy processors by designing, building, installing and commissioning fully automated HTST Pasteurisation plant. Whether you’re processing 2,000 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Htst Pasteurisation

H2: 2026 Market Trends for HTST Pasteurization
As the global food and beverage industry evolves in response to consumer demands, regulatory standards, and technological advancements, High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) pasteurization remains a critical process—particularly in the dairy, juice, and liquid egg sectors. By 2026, several key market trends are expected to shape the adoption, innovation, and expansion of HTST pasteurization systems.
1. Rising Demand for Minimally Processed Foods
Consumers are increasingly favoring products perceived as fresh, natural, and minimally processed. HTST pasteurization aligns with this trend by offering effective microbial reduction while preserving the sensory and nutritional qualities of products better than traditional high-heat methods. This balance supports its continued use in premium dairy (e.g., organic milk), cold-pressed juices, and plant-based beverages, driving market growth.
2. Expansion in Plant-Based and Alternative Beverages
The booming plant-based milk and beverage market (including almond, oat, soy, and pea-based drinks) is a major growth driver for HTST systems. These products require pasteurization to ensure safety and extend shelf life without compromising taste. By 2026, increasing production capacity in this sector will likely lead to higher investments in HTST technology tailored for low-viscosity, non-dairy liquids.
3. Regulatory and Food Safety Compliance
Global food safety standards are becoming stricter, particularly in emerging markets. HTST pasteurization meets regulatory requirements (such as those from the FDA, EU Food Safety Authority, and Codex Alimentarius) for pathogen reduction in liquid foods. As governments enforce compliance, especially in developing regions, demand for standardized HTST systems is expected to rise.
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Focus
Manufacturers are under pressure to reduce carbon footprints and operational costs. Modern HTST systems incorporate heat recovery units, advanced controls, and IoT-enabled monitoring to optimize energy use. By 2026, energy-efficient and smart HTST pasteurizers will gain market share, supported by sustainability certifications and corporate ESG goals.
5. Automation and Digital Integration
The integration of automation, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance in HTST systems will accelerate. By leveraging Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and AI analytics, dairy and beverage processors can improve process consistency, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance. This shift toward smart processing is a defining trend for 2026.
6. Regional Market Growth
While North America and Europe remain mature markets for HTST technology, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to see the highest growth rates by 2026. Rising urbanization, improved cold chain infrastructure, and increasing dairy consumption in countries like India, China, and Brazil will boost demand for reliable pasteurization solutions.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
Leading equipment suppliers (e.g., Tetra Pak, GEA, Alfa Laval) are focusing on modular, scalable HTST systems that cater to small to mid-sized producers. Innovations such as compact designs, faster clean-in-place (CIP) systems, and compatibility with ultra-high temperature (UHT) hybrid processes will enhance flexibility and market penetration.
Conclusion
By 2026, the HTST pasteurization market will be shaped by consumer preferences for fresh-like products, the expansion of alternative beverages, stringent food safety regulations, and a strong push toward automation and sustainability. These trends will drive both technological innovation and geographic expansion, reinforcing HTST as a cornerstone of safe and high-quality liquid food processing worldwide.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing HTST Pasteurization Equipment (Quality, IP)
When sourcing High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) pasteurization systems, businesses must navigate several critical pitfalls related to equipment quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these areas can lead to operational inefficiencies, regulatory non-compliance, and legal risks.
Poor Equipment Quality and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues is sourcing HTST systems made with substandard materials or inadequate manufacturing practices. Low-quality stainless steel (e.g., non-316L grade) can corrode over time, leading to contamination risks and product spoilage. Inconsistent heat exchanger plate thickness or poor weld integrity may compromise temperature control and food safety. Buyers should verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and ensure compliance with food-grade standards like 3-A Sanitary Standards and ASME BPE.
Inadequate Validation and Performance Testing
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive validation documentation, such as heat distribution studies, hold tube residence time verification, or microbial log-reduction validation. Without proper documentation, the equipment may not meet regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 120 for juice or 21 CFR Part 113 for low-acid foods). Always require performance qualification (PQ) and factory acceptance testing (FAT) before shipment.
Lack of Traceability and Component Sourcing Transparency
Counterfeit or untraceable components—such as pumps, valves, sensors, and PLCs—can undermine system reliability and food safety. Reputable suppliers should provide full traceability for critical parts and use OEM-sourced components. Sourcing from unknown manufacturers may lead to compatibility issues and void warranties.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing HTST systems from unauthorized or offshore manufacturers can expose buyers to IP infringement claims. Some suppliers replicate patented heat exchanger designs, control algorithms, or sanitary fittings without licensing. This not only poses legal liability but may also result in equipment seizure or recall. Always verify that the supplier holds proper licenses or owns the IP for the technology used.
Insufficient Documentation and Lack of As-Built Drawings
Many suppliers provide incomplete technical documentation, missing critical items like piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), control schematics, or sanitation procedures. Without accurate as-built drawings and operation manuals, maintenance, troubleshooting, and regulatory audits become significantly more difficult.
Hidden Costs from Poor Design or Integration Challenges
Systems designed without proper hydraulic or thermal modeling may require costly retrofits for integration into existing lines. Undersized regenerative sections or poorly located sensors can reduce efficiency and increase energy consumption. Ensure the supplier conducts a site-specific engineering review and provides a detailed scope of supply.
Absence of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Choosing suppliers without local service networks or long-term spare parts commitments can lead to extended downtime. Verify service response times, availability of critical spares, and whether firmware/software updates are supported—especially for proprietary control systems.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—prioritizing quality verification, demanding complete documentation, and ensuring IP compliance—companies can mitigate risks and secure reliable, compliant HTST pasteurization systems.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for HTST Pasteurisation
Overview of HTST Pasteurisation
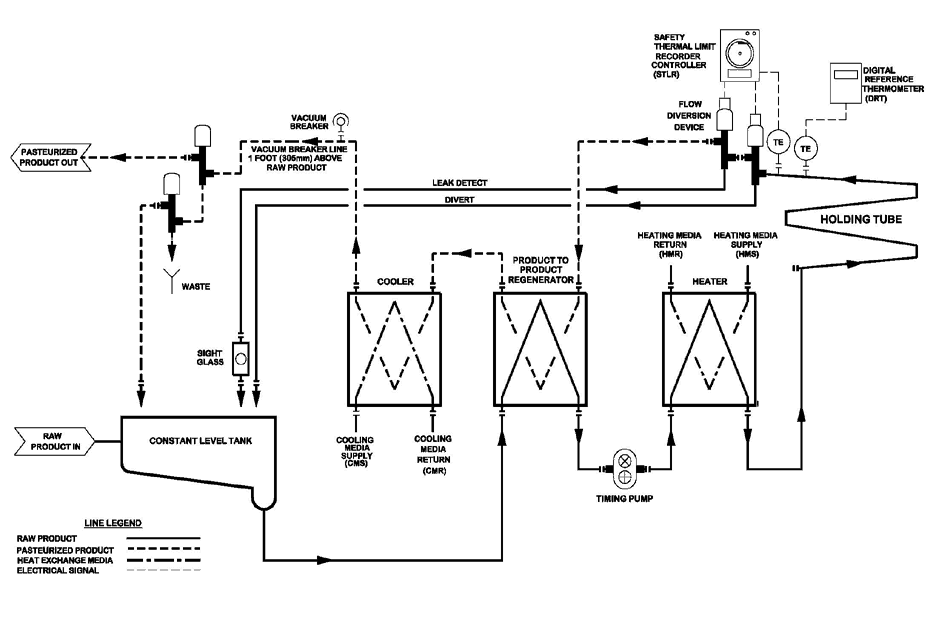
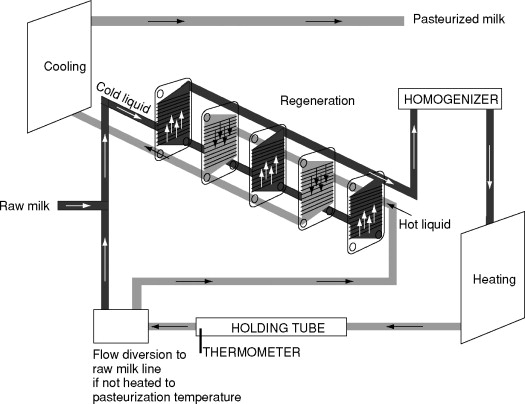
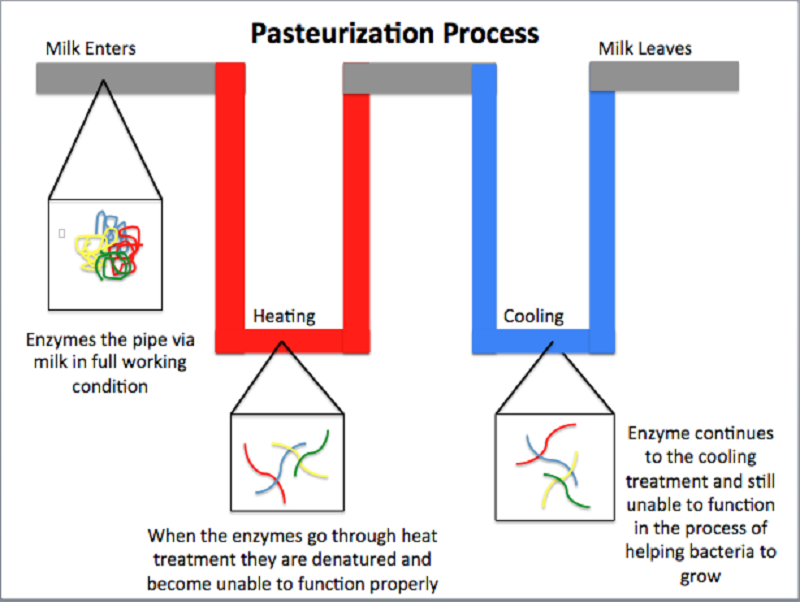
High-Temperature Short-Time (HTST) pasteurisation is a continuous thermal process used primarily in the dairy and beverage industries to destroy pathogenic microorganisms and extend shelf life. This method involves heating the product to a minimum temperature of 72°C (161°F) for at least 15 seconds, followed by rapid cooling. Adhering to strict logistical and regulatory standards ensures product safety, quality, and legal compliance.
Equipment and Facility Requirements
All HTST systems must be installed in a controlled environment with adequate space for operation, maintenance, and sanitation. Equipment must include:
– A precision temperature control system with automatic recording
– Flow diversion valve (FDV) to prevent under-processed product from entering the distribution stream
– Regeneration, heating, and cooling sections with efficient heat exchange
– A timing pump or flow control device to ensure proper hold time
Facilities must comply with local health and safety codes and be certified by relevant food safety authorities.
Raw Material Handling and Storage
Raw materials (e.g., milk, juice) must be received, stored, and handled under strict temperature control (typically ≤4°C or 39°F). Suppliers must provide certification of compliance with food safety standards (e.g., Grade A milk standards in the U.S.). All incoming materials must be inspected for temperature, odor, and signs of contamination before processing.
Process Monitoring and Control
Continuous monitoring is essential during HTST pasteurisation:
– Temperature must be recorded at the outlet of the heating section at least every 15 seconds
– Flow rate and pressure differentials must be monitored to ensure proper hold time and prevent product bypass
– The flow diversion valve must be tested daily for proper operation
Automated data logging systems must store records for a minimum of 60 days and be accessible for regulatory audits.
Recordkeeping and Documentation
Accurate and complete records are required for compliance with food safety regulations (e.g., FDA Pasteurized Milk Ordinance, EU Regulation (EC) No 852/2004):
– Daily logs of time-temperature parameters
– Calibration records for thermometers and sensors (calibrated at least annually)
– Maintenance logs for critical equipment
– Cleaning and sanitation schedules (CIP – Clean-in-Place)
All records must be retained for a minimum of two years and available upon request by regulatory agencies.
Personnel Training and Hygiene
Operators must be trained in:
– HTST system operation and emergency shutdown procedures
– Sanitation protocols and allergen control
– Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and personal hygiene
Training records must be maintained, and staff must undergo refresher training at least annually. Personnel must wear appropriate protective clothing and follow handwashing and hygiene protocols.
Cleaning and Sanitation
HTST systems must undergo Clean-in-Place (CIP) procedures after each production run or at least every 24 hours. CIP sequences typically include:
– Pre-rinse with water
– Alkaline wash (e.g., 1–2% NaOH at 75–85°C)
– Intermediate rinse
– Acid wash (e.g., nitric or phosphoric acid) to remove mineral deposits
– Final sanitizing rinse (e.g., peracetic acid or chlorine-based sanitizer)
Verification of cleaning effectiveness must be conducted via ATP swab testing or microbiological analysis.
Product Testing and Quality Assurance
Post-pasteurisation, finished products must undergo:
– Phosphatase test (for milk) to confirm adequate pasteurisation
– Microbiological testing for pathogens (e.g., Listeria, Salmonella) and spoilage organisms
– Sensory evaluation for taste, odor, and appearance
Testing frequency and methods must align with regulatory requirements and internal quality standards.
Regulatory Compliance and Audits
Facilities using HTST pasteurisation must comply with applicable regulations, including:
– FDA Pasteurized Milk Ordinance (PMO) in the United States
– EU Hygiene Regulations (EC) No 852/2004 and (EC) No 853/2004
– Codex Alimentarius standards
Regular internal audits and third-party inspections (e.g., by state milk control agencies) must be conducted to verify compliance. Non-conformances must be documented and corrected promptly.
Emergency Procedures and Recalls
A documented emergency response plan must include:
– Immediate shutdown procedures for temperature or flow deviations
– Protocols for diverting under-processed product
– Product hold and recall procedures in case of failure
Recall simulations must be performed at least annually to ensure effectiveness.
Conclusion
HTST pasteurisation is a critical control point in food processing that requires rigorous logistics management and adherence to compliance standards. By maintaining proper equipment, monitoring procedures, personnel training, and documentation, processors can ensure the safety, quality, and legality of their products in domestic and international markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing HTST Pasteurization Equipment:
Sourcing HTST (High-Temperature Short-Time) pasteurization systems is a critical step for dairy and liquid food processing operations aiming to ensure product safety, extend shelf life, and meet regulatory standards. After evaluating key suppliers, technology offerings, cost considerations, and after-sales support, it is evident that selecting the right HTST system requires a balance between efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Investing in a well-designed, easily maintainable HTST unit from a reputable manufacturer not only enhances product quality and consistency but also supports long-term operational efficiency. Additionally, compliance with food safety standards such as FDA, EHEDG, or 3-A Sanitary Standards is essential to ensure hygienic processing. Ultimately, the decision to source HTST pasteurization equipment should align with the facility’s production capacity, product range, and future growth plans, ensuring a robust foundation for safe and high-quality food production.