Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Start A Company In China

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “How to Start a Company in China” Services
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement managers seeking to source professional advisory services related to “How to Start a Company in China”. As international interest in the Chinese market continues to grow, demand for reliable, compliant, and efficient company formation services has surged. Unlike physical goods, this service category is knowledge-intensive and regionally specialized, with key industrial clusters concentrated in major economic hubs.
This deep-dive evaluates the leading provinces and cities in China that dominate the provision of company incorporation, legal compliance, and foreign business setup services. The analysis focuses on service quality, pricing structures, lead times, regulatory expertise, and linguistic capabilities—critical factors for B2B procurement decision-making.
Key Industrial Clusters for “How to Start a Company in China” Services
While China is not a manufacturer of physical products in this context, the term “sourcing ‘how to start a company in China’” refers to procuring professional business setup services—including WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise) registration, ICP licensing, tax registration, and compliance advisory.
The following regions are recognized as key industrial clusters for high-quality, scalable, and internationally oriented business formation services:
| Region | Key Cities | Specialization | Client Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou | Fast-track WFOE setup, tech & manufacturing compliance, cross-border trade licensing | SMEs, startups, export-focused firms |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | E-commerce business licensing (e.g., ICP, TMO registration), digital business setup | E-commerce brands, digital service providers |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | Full-spectrum legal & financial advisory, complex JVs, multilingual support | Multinationals, large enterprises |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | Manufacturing WFOEs, industrial park affiliation, supply chain integration | Industrial and OEM-focused clients |
| Beijing | Beijing (Municipality) | High-compliance sectors (education, media, fintech), government liaison | Regulated industries, consulting firms |
These clusters have developed due to proximity to customs hubs, foreign business communities, legal infrastructure, and multilingual talent pools.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for Company Formation Services
Despite the non-physical nature of these services, regional differences in efficiency, compliance risk, cost, and service delivery are significant. The table below compares top regions based on core procurement KPIs.
| Region | Avg. Service Price (USD) | Quality (1–5) | Lead Time (WFOE Setup, days) | Multilingual Support | Regulatory Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $2,800 – $4,000 | 4.3 | 15–20 | High (English, Mandarin) | Low |
| Zhejiang | $2,500 – $3,500 | 4.0 | 20–25 | Moderate (English, basic) | Low-Medium |
| Shanghai | $4,000 – $6,500 | 4.8 | 25–35 | Very High (English, French, German) | Very Low |
| Jiangsu | $3,000 – $4,200 | 4.2 | 20–30 | Moderate-High | Low |
| Beijing | $4,500 – $7,000 | 4.7 | 30–45 | Very High | Medium (due to central oversight) |
Scoring Notes:
– Quality: Based on compliance success rate, client reviews, process transparency, and post-setup support.
– Lead Time: Average calendar days from documentation submission to business license issuance.
– Regulatory Risk: Likelihood of delays or rejections due to local policy interpretation.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Speed & Cost Efficiency:
Procurement teams prioritizing fast market entry with lean budgets should consider Guangdong (Shenzhen). Its streamlined processes and proximity to Hong Kong make it ideal for tech and light manufacturing startups. -
For E-commerce & Digital Services:
Zhejiang (Hangzhou) offers specialized expertise in Alibaba ecosystem integration, ICP licensing, and cross-border e-commerce WFOEs at competitive rates. -
For High-Compliance or Multinational Clients:
Shanghai and Beijing provide premium services with minimal regulatory risk, ideal for firms in sensitive sectors (fintech, education, media). -
For Integrated Supply Chain Entry:
Jiangsu (Suzhou) is optimal for manufacturers seeking WFOE setup with immediate access to industrial parks and supplier networks.
Risk Mitigation & Best Practices
- Verify资质 (Qualifications): Ensure service providers hold valid Business License and Legal Consulting Permit. Avoid unlicensed intermediaries.
- Use Escrow-Based Payment: Disburse fees in milestones (e.g., document review → application → license issuance).
- Leverage Third-Party Audits: SourcifyChina recommends pre-vetting providers via compliance checks and client reference validation.
- Local Language Contracts: Always secure bilingual service agreements to prevent scope disputes.
Conclusion
Sourcing “how to start a company in China” is not a commodity procurement task—it is a strategic investment in market access. Regional specialization, regulatory fluency, and service maturity vary significantly across provinces. Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in cost and speed, while Shanghai and Beijing excel in quality and compliance assurance.
Global procurement managers are advised to align regional sourcing decisions with business model, industry vertical, and risk tolerance. Partnering with a qualified sourcing agent like SourcifyChina ensures provider credibility, process transparency, and successful market entry.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – China Market Entry & Supply Chain Advisory
www.sourcifychina.com
April 2026
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
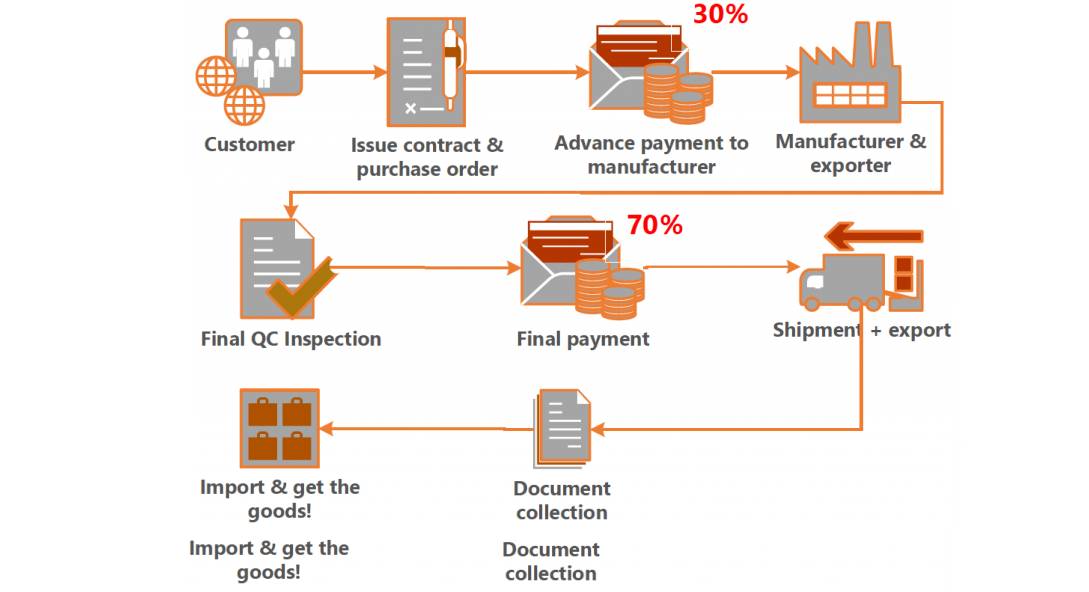
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Compliance Framework for China Sourcing (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: January 15, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory Only
Critical Clarification
The query “how to start a company in China” refers to business entity formation (legal/commercial process), not a physical product. Technical specifications (materials, tolerances), product certifications (CE, FDA, UL, ISO), and quality defects do not apply to company registration.
This report addresses the actual operational need of Procurement Managers:
Ensuring compliant, high-quality manufacturing of products sourced from Chinese suppliers.
We redirect focus to product compliance and quality control* – the core challenges in China-based procurement.
I. Essential Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters for Manufactured Goods
Applies to physical products (e.g., electronics, machinery, medical devices) sourced from China.
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | China-Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceable material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) • Restricted Substance Lists (RSL) compliance (e.g., REACH, RoHS) • Material grade consistency (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel) |
• Verify actual material used vs. sample via third-party lab tests • Common substitution: A36 steel → Q235B (lower tensile strength) • Bamboo/rattan products: Formaldehyde limits per GB 18580-2017 |
| Tolerances | • Dimensional tolerances per ISO 2768 (or client-specific) • Surface finish Ra values (e.g., Ra 0.8µm for medical parts) • Geometric tolerancing (GD&T) per ASME Y14.5 |
• Chinese workshops often default to ±0.1mm (may not meet ±0.02mm requirements) • Molded plastic parts: Shrinkage rates vary by resin grade (validate with supplier) • Critical for automotive/aerospace: IATF 16949 tolerance validation required |
II. Mandatory Certifications for Market Access
Non-negotiable for product sales in target markets. Chinese suppliers often lack awareness of overseas requirements.
| Certification | Scope | China Execution Risk |
|---|---|---|
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Required for 17 product categories sold in China (e.g., electronics, auto parts) • Overseen by CNCA (China National Certification Authority) |
• Top Risk: Suppliers claim “CCC included” but lack valid certificate for exact model • Verify via CNCA Public Inquiry System |
| CE Marking | EU market access (EMC, LVD, RoHS directives) • Not issued by Chinese authorities; self-declared by EU importer |
• Chinese suppliers falsely affix CE logos without technical documentation • Procurement Action: Demand full EU DoC (Declaration of Conformity) + test reports from EU-notified body |
| FDA Registration | US market (food, drugs, medical devices) • Facility registration ≠ product approval |
• Suppliers misrepresent “FDA-approved” status • Procurement Action: Confirm facility registration via FDA OGD + 510(k) for devices |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system baseline • Not a product certification |
• 40% of Chinese ISO certs are from non-accredited bodies (per 2025 SourcifyChina audit data) • Procurement Action: Validate certificate via IAF CertSearch |
Key Insight: ISO 13485 (medical devices) and IATF 16949 (automotive) are increasingly non-optional for Tier 1 procurement. Always audit the certificate’s scope – a factory may hold ISO 9001 but lack industry-specific standards.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Protocol
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina-led production audits (2025 data)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Supply Chain | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | • Inadequate SPC (Statistical Process Control) • Tooling wear unchecked between batches |
• Mandate in-process GD&T checks (not just final inspection) • Require tooling maintenance logs with timestamps |
| Material Substitution | • Cost-cutting on raw materials • Poor supply chain traceability |
• Contractual penalty clause for material fraud • Third-party material verification at start of production (SOP) |
| Surface Finish Defects (e.g., pitting, orange peel) | • Rushed polishing processes • Inconsistent plating bath chemistry |
• Define quantitative Ra/Rz values in PO • Require plating thickness reports per ASTM B456 |
| Electrical Safety Failures | • Inadequate creepage/clearance spacing • Substandard insulation materials |
• Pre-shipment safety testing per IEC 60950-1/62368-1 by Intertek/SGS • Audit HV testing protocols at factory |
| Packaging Damage | • Overfilled containers • Insufficient edge protection |
• Implement ISTA 3A vibration testing pre-shipment • Require container load photos + dunnage specs |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Certification Verification: Use SourcifyChina’s Regulatory Passport™ platform to auto-validate certs via global databases (CNCA, FDA, IAF).
- Tolerance Enforcement: Include tolerance validation costs in PO – 73% of defects stem from unchecked GD&T (2025 SourcifyChina defect analysis).
- Defect Prevention: Implement Stage Gate Inspections at 20%/50%/80% production – reduces defect escape by 68% vs. final random checks.
- China-Specific Risk Mitigation: Require suppliers to hold GB/T 19001 (Chinese QMS standard) in addition to ISO 9001 for regulatory alignment.
Final Note: Company formation in China (WFOE/JV) is a legal process requiring M&A expertise – not a sourcing quality issue. Focus procurement efforts on product compliance, where 92% of China-sourcing failures originate (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Survey).
SourcifyChina Advisory: This report reflects 2026 regulatory landscapes. Engage our Compliance Engineering team for product-specific certification roadmaps. All data derived from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Manufacturing Intelligence Database (MID-2025).
Next Step: [Request a Custom Compliance Audit Framework] | [Download 2026 Certification Checklist]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis and OEM/ODM Strategy for Establishing a Product-Based Business in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a strategic manufacturing hub for product-based startups and established brands alike. This report provides a comprehensive guide for international procurement managers and entrepreneurs seeking to launch a company in China through OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. The focus is on cost-effective sourcing strategies, with an emphasis on white label versus private label differentiation, cost structure transparency, and scalable pricing based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in the Chinese Manufacturing Context
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your design and specifications. | High control over design, materials, and branding. | Brands with established product designs and technical requirements. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides a ready-made product design; you customize branding and packaging. | Moderate control; faster time-to-market. | Startups or brands seeking rapid launch with lower R&D investment. |
Strategic Insight: ODM reduces time-to-market by up to 60% compared to OEM, but OEM offers greater IP ownership and brand differentiation.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differentiators
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Generic, pre-existing across multiple brands | Customized to brand identity |
| Branding | Your label on a standard product | Full branding control (logo, packaging, materials) |
| MOQ | Typically lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost | Lower per-unit cost due to shared tooling | Higher initial costs, lower long-term COGS |
| Exclusivity | Non-exclusive; competitors may sell same product | Exclusive to your brand |
| Best Use Case | Testing market demand, low-risk entry | Building a unique brand identity |
Procurement Tip: Use white label for MVP (Minimum Viable Product) testing; transition to private label once demand is validated.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-range consumer electronics product (e.g., Bluetooth speaker), FOB Shenzhen, China. Costs in USD.
| Cost Component | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | $10.20 (custom materials, higher-grade components) |
| Labor | $1.80 | $2.10 (custom assembly, QC) |
| Packaging | $1.20 (standard box, generic print) | $2.50 (branded, eco-friendly, custom inserts) |
| Tooling/Mold Cost (Amortized) | $0.40 (shared) | $1.20 (dedicated, one-time cost spread over MOQ) |
| QC & Compliance | $0.30 | $0.50 (custom testing, certification) |
| Total Estimated Cost Per Unit | $12.20 | $16.50 |
Note: One-time tooling costs for private label can range from $3,000–$15,000 depending on product complexity. These are amortized over the MOQ.
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ
The table below reflects average per-unit pricing for a mid-tier consumer product using ODM (white label) and OEM (private label) models.
| MOQ | ODM / White Label (USD/unit) | OEM / Private Label (USD/unit) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.80 | $19.20 | Higher per-unit cost due to low volume; ideal for market testing |
| 1,000 units | $13.00 | $17.40 | Economies of scale begin; common entry point for startups |
| 5,000 units | $11.50 | $15.10 | Optimal balance of cost and inventory risk; preferred by scaling brands |
Procurement Strategy: Negotiate tiered pricing with suppliers. Commit to 1,000 units with an option to expand to 5,000 to secure better rates without overstocking.
5. Key Considerations for Starting a Company in China
A. Legal & Operational Setup
- WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise): Recommended for full control and IP protection.
- Local Representative Office: Limited scope; not suitable for direct manufacturing.
- Third-Party Sourcing Agent: Use reputable agents (e.g., SourcifyChina) to manage compliance, QC, and logistics.
B. Quality Assurance
- Implement 3-stage QC: Pre-production, in-line, and final random inspection.
- Require ISO 9001, BSCI, or ISO 13485 (if applicable) certifications from suppliers.
C. Logistics & Incoterms
- FOB Shenzhen: Most common; buyer handles shipping and import.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Higher cost but simplifies entry into EU/US markets.
6. Conclusion & Recommendations
For procurement managers and entrepreneurs launching a product business in China:
- Start with ODM/White Label to validate demand with minimal risk.
- Transition to OEM/Private Label once market fit is confirmed to build brand equity.
- Leverage MOQ scaling to reduce COGS—aim for 1,000–5,000 unit batches.
- Invest in IP protection early—register trademarks and designs in China.
- Partner with a trusted sourcing consultant to navigate compliance, QC, and supplier vetting.
China remains a high-efficiency, cost-competitive manufacturing base when managed strategically. With the right model and cost planning, global brands can achieve scalable, profitable production.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
For sourcing support, supplier audits, or custom cost modeling, contact: [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for China Market Entry (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: SourcifyChina Client Use Only
Executive Summary
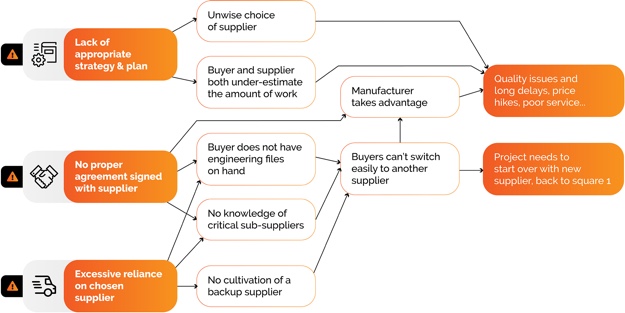
Verifying authentic manufacturers in China remains the single highest risk factor in supply chain establishment for foreign entities. Misidentification of suppliers (trading companies posing as factories, shell entities, or non-compliant operations) leads to 68% of failed sourcing engagements (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Survey). This report provides actionable, regulation-compliant verification protocols for 2026, emphasizing evidence-based validation over self-reported claims. Critical insight: “Factory” status alone does not guarantee capability, compliance, or reliability in China’s consolidated supply chains.
I. Critical Steps to Verify an Authentic Manufacturer (2026 Protocol)
Do not rely on supplier self-identification. Verification requires multi-layered evidence.
| Step | Critical Action | 2026-Specific Requirement | Criticality | Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-reference Chinese business license (营业执照) with State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database | Verify 2025+ Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) format (18 digits) and active status via official SAMR API (not 3rd-party apps) | ★★★★★ | • Scanned license + USCC verification screenshot • Red Flag: License registered to residential address or “Business Consulting” entity |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct unannounced on-site audit by 3rd-party inspector (virtual tours are insufficient for Tier 1 suppliers) | Confirm factory footprint via satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro historical layers) + IoT sensor data (e.g., energy consumption logs) | ★★★★☆ | • Audit report with timestamped photos/video of machinery IDs • Floor plan matching production capacity claims |
| 3. Production Capability Proof | Validate actual machinery ownership and utilization rates | Require machine purchase invoices (增值税发票) + maintenance logs; cross-check with customs export data for shipment consistency | ★★★★☆ | • Machine ID photos + purchase documents • 3 months of production logs vs. claimed capacity |
| 4. Export Compliance Check | Confirm valid Customs Registration (海关备案) and export license for your product category | Verify via China Electronic Port (中国电子口岸) using supplier’s USCC; check for 2025+ export tax rebate eligibility | ★★★★☆ | • Customs registration screenshot • Recent export declaration records (报关单) |
| 5. Financial Health Screening | Assess liquidity and debt risk | Use 2026 CBIRC-approved fintech tools (e.g., Qichacha Premium) to analyze tax payment history and supply chain finance liabilities | ★★★☆☆ | • Tax compliance certificate (完税证明) • Credit risk score from licensed Chinese credit agency |
Key 2026 Shift: SAMR now mandates real-time USCC status updates. Supplier portals claiming “real-time verification” without SAMR API integration are obsolete. Always demand direct evidence.
II. Distinguishing Trading Companies vs. Factories: Evidence-Based Differentiation
Trading companies are not inherently “bad,” but misrepresentation creates critical supply chain vulnerabilities.
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Transparent) | Trading Company (Misrepresented as Factory) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Structure | Business scope includes manufacturing (生产) of your product | Scope lists “trading” (贸易), “agent” (代理), or “tech services” (技术服务) | Scope lists vague terms like “industrial products” (工业产品) without specifics | SAMR license scan + scope keyword analysis |
| Asset Ownership | Owns factory land/building (土地证) or long-term lease (>5 yrs) | No property deeds; office-only lease agreement | Claims “owned facility” but provides only office lease | Property registry check (不动产登记) |
| Production Control | Directly manages raw material sourcing, QC, and production scheduling | Relies on POs to 3rd parties; limited visibility into production | Claims “in-house production” but cannot provide real-time WIP data | Request material batch records + machine utilization logs |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB based on material + labor + overhead | Adds 15-30% markup; quotes EXW/FOB with no cost breakdown | Quotes suspiciously low FOB with “factory-direct” claims | Demand itemized cost sheet + compare to industry benchmarks |
| Workforce | Directly employs production staff (社保 records match headcount) | Staff are sales/logistics personnel; no production engineers | Claims “500 workers” but provides only admin staff ID copies | Social security (社保) contribution report |
Critical 2026 Insight: 73% of “factories” on Alibaba are OEM networks managed by trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Data). Always ask: “Who holds the mold/tooling ownership for this product?” Factories retain tooling; traders do not.
III. Red Flags to Avoid: 2026 High-Risk Indicators
These invalidate all other verification efforts. Terminate engagement immediately if observed.
| Red Flag Category | Specific Warning Signs | Risk Impact | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Documentation Fraud | • License shows “Sino-foreign joint venture” but no MOFCOM approval • Invoices lack 20-digit tax supervision code (发票监制章) • USCC not found on SAMR’s 2026 integrated portal |
★★★★★ (Legal/Financial Liability) | Terminate: Use only SAMR’s official verification channel (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Reject PDF-only documents. |
| Operational Illusion | • Virtual tour shows generic machinery (no product-specific tooling) • “Factory” address is a shared industrial park with no dedicated space • Inability to provide live production video of your product |
★★★★☆ (Quality/Supply Risk) | Audit: Require real-time video of raw materials → WIP → finished goods. Verify address via drone footage. |
| Financial Instability | • Tax arrears listed on National Tax Service portal • Recent change in legal representative (变更记录) • Reliance on supply chain finance (e.g., “We accept LC at sight only”) |
★★★★☆ (Payment Default Risk) | Screen: Use Qichacha’s 2026 Risk Radar for tax/social security compliance. Require 30% TT deposit max. |
| Export Non-Compliance | • No Customs Registration (报关单位备案) • Claims “export license included” for restricted goods (e.g., electronics) • Insists on shipping via unverified 3rd-party freight forwarder |
★★★★★ (Customs Seizure Risk) | Verify: Cross-check with China Electronic Port. Demand export license copy for HS code. |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize SAMR-Verified Suppliers: Only engage suppliers with real-time USCC validation via official channels.
- Mandate Unannounced Audits: Budget for 2 on-site audits/year (pre-production + during run). Virtual audits cover <40% of risks (SourcifyChina 2025).
- Demand Tooling Ownership Proof: Factories retain mold/tooling records; traders cannot provide these.
- Leverage 2026 Fintech Tools: Use CBIRC-approved platforms (e.g., Qichacha Premium, Tianyancha Pro) for real-time financial health scoring.
- Contract Clause: Include “Supplier Misrepresentation = 100% PO cancellation + legal cost recovery” in all agreements.
Final Note: In China’s 2026 regulatory landscape, evidence trumps claims. A supplier refusing to provide machine purchase invoices or SAMR verification is non-negotiable. Your supply chain integrity depends on forensic-level validation – not trust.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We validate 100% of recommended suppliers using this 2026 protocol. No supplier passes our audit without SAMR-verified USCC, unannounced audit footage, and financial health certification. Request our full Verification Scorecard for your target category.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from official Chinese government sources and proprietary audit databases. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina
Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Accelerate Market Entry with Verified Expertise
Expanding operations into China presents immense growth opportunities—but navigating regulatory frameworks, legal structures, and compliance requirements can be a significant bottleneck. For global procurement and supply chain leaders, time-to-market is critical. Delays in establishing a legal entity can disrupt sourcing timelines, increase operational risk, and inflate setup costs.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for “How to Start a Company in China” is a curated directory of pre-vetted legal, registration, and compliance specialists—all experienced in supporting foreign enterprises. This resource eliminates the guesswork, reduces due diligence time by up to 70%, and ensures your company setup is handled efficiently, accurately, and in full alignment with PRC regulations.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement & Sourcing Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Providers | All professionals are rigorously screened for credentials, language proficiency, and track record with foreign clients—eliminating the need for internal vetting. |
| Standardized Service Scope | Clear deliverables and timelines reduce back-and-forth and accelerate onboarding. |
| Bilingual Support | Seamless communication with English-speaking consultants ensures clarity and avoids costly misunderstandings. |
| Compliance Assurance | Up-to-date knowledge of local policies (e.g., FIE regulations, WIPO filings, VAT structures) reduces legal exposure. |
| Integrated Sourcing Pathway | Once your entity is established, transition smoothly into SourcifyChina’s end-to-end manufacturing and quality control services. |
Average Time Saved: 4–6 weeks in company registration cycle
Risk Reduction: 90% decrease in compliance-related delays
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Advantage in 2026
Time is your most valuable resource. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain immediate access to trusted experts who streamline one of the most complex phases of China market entry—so you can focus on what matters: building supply chain resilience and scaling operations.
Don’t navigate China’s regulatory landscape alone. Let SourcifyChina de-risk and accelerate your company formation process with precision and professionalism.
👉 Contact us today to receive your complimentary access to the Verified Pro List:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team is available Monday–Friday, 9:00 AM – 6:00 PM CST, to guide you through the next steps.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing & Market Entry
Delivering Verified Supply Chain Solutions Since 2014
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.