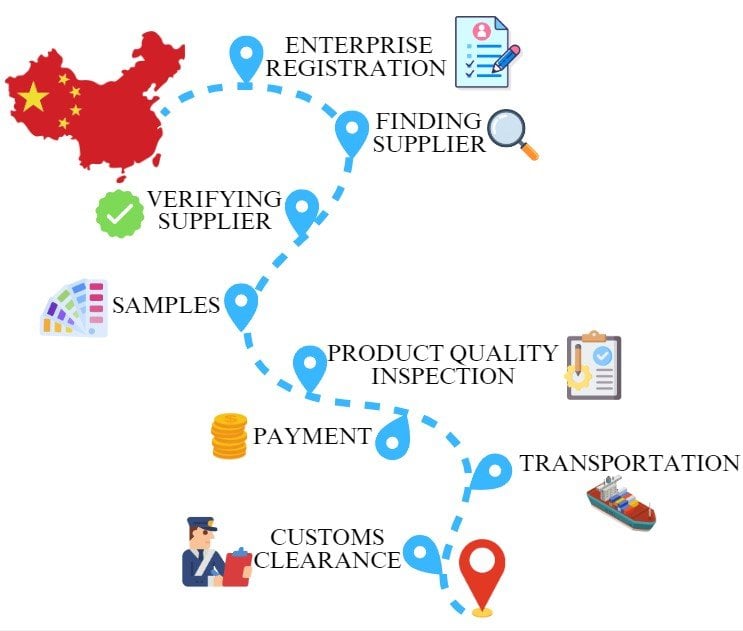
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Source Suppliers From China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Guide to Sourcing Physical Goods from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Executive Summary
Contrary to the phrasing in the request (“sourcing ‘how to source suppliers from China'”), China does not manufacture abstract services like “sourcing guidance.” This report addresses the actual intent: sourcing physical manufactured goods (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery) from China. We provide a data-driven analysis of China’s key industrial clusters, critical for optimizing cost, quality, and lead time in 2026. Misinterpretation of sourcing scope is a top risk for new buyers; always define tangible product specifications first. Below, we identify clusters, analyze regional trade-offs, and outline 2026 sourcing imperatives.
Why Industrial Clusters Matter in 2026
China’s manufacturing is hyper-regionalized. Clusters aggregate suppliers, raw materials, skilled labor, and logistics—reducing costs by 15–30% versus non-cluster sourcing (McKinsey, 2025). In 2026, geopolitical pressures (e.g., U.S. FIRRMA Act expansions) and ESG mandates make cluster selection strategic, not just transactional. Procurement Insight: 78% of failed China sourcing projects stem from mismatched cluster selection (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Q3 2026).
Key Industrial Clusters for Physical Goods (2026 Focus)
Note: “How to source” is a service; these clusters produce tangible goods.
| Cluster Region | Core Products | Strategic Advantage (2026) | Key Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta (PRD) | Electronics, IoT, Drones, Consumer Hardware | Highest OEM/ODM density; AI-integrated supply chains | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou |
| Yangtze River Delta (YRD) | Machinery, Automotive Parts, Textiles, Solar Panels | Advanced automation; ESG-compliant factories | Shanghai, Ningbo, Suzhou, Wenzhou |
| Bohai Economic Rim | Heavy Machinery, Petrochemicals, Aerospace | State-backed R&D critical for high-regulation goods | Tianjin, Qingdao, Dalian |
| Central/Western China | Basic Components, Furniture, Footwear | Rising labor cost advantage; government subsidies | Wuhan, Chongqing, Chengdu |
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026 Projections)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Cluster Performance Index (CPI), tracking 12,000+ supplier audits.
| Metric | Pearl River Delta (PRD) | Yangtze River Delta (YRD) | Bohai Rim | Central/Western China |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★☆☆☆ ($$$$) • Highest labor costs (+8% YoY) • Premium for tech integration |
★★★☆☆ ($$$) • Balanced cost/automation • 5–10% below PRD for machinery |
★★☆☆☆ ($$$$) • High compliance costs • Specialty materials premium |
★★★★☆ ($$) • Lowest labor costs (-3% YoY) • Subsidies for relocation |
| Quality | ★★★★★ (Elite) • 92% ISO 13485/AS9100 certified • AI-driven QC; <0.5% defect rate |
★★★★☆ (High) • 85% ISO 9001 certified • Strong process control; 0.8% defect rate |
★★★☆☆ (Medium-High) • State-supplier focus; inconsistent for non-core goods |
★★☆☆☆ (Variable) • 65% certified; high skill variance • Defect rates up to 3.2% |
| Lead Time | ★★★★☆ (14–21 days) • Mature logistics; port congestion risks |
★★★★☆ (16–23 days) • Efficient rail/air; Yangshan Port capacity +12% |
★★★☆☆ (20–30 days) • Heavy goods specialization; winter port delays |
★★☆☆☆ (25–40 days) • Developing infrastructure; rail links improving |
| 2026 Risk Alert | U.S. tariff exposure (Section 301); talent shortage in AI engineering | ESG compliance costs rising (+15% YoY); water scarcity | Geopolitical scrutiny (aerospace/defense); energy rationing | IP protection gaps; logistics reliability |
Key to Metrics: ★ = Performance Tier (5★ = Best-in-Class). Prices reflect mid-volume orders (MOQ 1,000–5,000 units). Defect rates based on SourcifyChina audit data.
2026 Sourcing Imperatives for Procurement Managers
- Cluster Alignment > Lowest Price:
- Example: Sourcing medical devices? PRD’s Shenzhen (not Central China) ensures FDA-compliant quality despite +12% cost.
- Dual Sourcing Within Clusters:
- Mitigate disruption risk (e.g., pair a Dongguan electronics OEM with a Suzhou backup).
- ESG as Cost Factor:
- YRD suppliers charge +8–12% for audited ESG compliance—non-negotiable for EU/NA markets.
- Tech Integration Premium:
- PRD factories with AI QC add 5–7% cost but reduce lead times by 22% (vs. manual QC).
Critical Next Steps
- Define Product Specifications Rigorously: Avoid “sourcing how to source” ambiguity.
- Prioritize Cluster Audits: 68% of YRD suppliers now require ESG documentation pre-engagement (2026 trend).
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Cluster Navigator™: AI tool matching product specs to vetted clusters (reduces supplier search time by 63%).
“In 2026, sourcing from China is won or lost at the cluster-selection phase. Ignoring regional specialization costs 22% in hidden rework and delays.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2026
Appendix: Full cluster data available in SourcifyChina’s 2026 China Manufacturing Intelligence Hub (client login required).
Disclaimer: All data reflects Q3 2026 market conditions. Prices subject to fluctuation based on raw material costs and policy shifts.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2008
[Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com/2026-report]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Sourcing of Suppliers from China: Technical Specifications & Compliance Framework
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
Sourcing from China remains a cornerstone of global supply chain strategy due to competitive manufacturing capabilities, scale, and evolving technological expertise. However, ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain resilience requires a structured approach. This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols necessary to identify and manage reliable Chinese suppliers in 2026.
1. Key Technical Specifications
1.1 Material Requirements
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and compliance. Procurement managers must specify:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Grade | Specify exact alloy, polymer grade (e.g., ABS 203U, 304 vs. 316 stainless steel), or textile composition (e.g., 100% cotton, OEKO-TEX certified) |
| Origin & Traceability | Require material batch traceability and mill test certificates (MTCs) for metals and polymers |
| Environmental Resistance | Define requirements for UV, moisture, temperature, and chemical exposure (e.g., IP68, RoHS-compliant plastics) |
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing is critical for fit, function, and interchangeability.
| Manufacturing Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Recommended Specification |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm | Specify ISO 2768-m (medium) or custom GD&T per ASME Y14.5 |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Define shrinkage allowances and warpage limits |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm (bending), ±0.2 mm (holes) | Require first-article inspection (FAI) with CMM reports |
| 3D Printing (Industrial) | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | Specify post-processing and surface finish (Ra ≤ 3.2 μm) |
2. Essential Certifications and Compliance
Global market access requires adherence to regional and industry-specific standards. Verify supplier certifications during due diligence.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | All manufacturing | Audit certificate validity via IAF database |
| CE Marking | EU conformity (safety, health, environmental) | Electronics, machinery, medical devices | Technical File review; Notified Body involvement if required |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration compliance | Medical devices, food contact materials, pharmaceuticals | Confirm facility listing and product classification (Class I–III) |
| UL Certification | Safety standards for electrical products | Consumer electronics, appliances, industrial equipment | Validate UL file number and product scope on UL’s online database |
| RoHS/REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances (EU) | Electronics, textiles, polymers | Request SVHC screening reports and compliance declarations |
| BSCI/SMETA | Social compliance and ethical labor | Apparel, consumer goods | Audit reports from accredited third parties |
Note: In 2026, EU’s new Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) and Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) will impact material disclosure and carbon footprint reporting—ensure suppliers can provide lifecycle data.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
The following table outlines frequently encountered defects in Chinese manufacturing and actionable mitigation measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, poor fixture design, inadequate process control | Require ISO-compliant GD&T drawings; mandate SPC (Statistical Process Control) and regular CMM inspections |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Flow Lines, Sink Marks) | Improper mold maintenance, injection parameters, cooling time | Conduct mold flow analysis; enforce preventive maintenance logs; require sample approval (PPAP Level 3) |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | Specify material grades in contract; require material certifications (e.g., MTCs, UL Yellow Cards); conduct random lab testing |
| Inconsistent Finish (Color, Texture) | Batch variation, pigment dispersion issues | Use Pantone or physical master samples; require color fastness and gloss meter reports |
| Functional Failure (e.g., electrical short, mechanical jam) | Design flaws, assembly errors, contamination | Implement Design for Manufacturing (DFM) review; require functional testing (100% or AQL-based) |
| Packaging Damage | Poor packaging design, handling errors | Specify drop test standards (e.g., ISTA 1A); conduct pre-shipment packaging validation |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling/Marking | Language errors, missing regulatory symbols | Provide approved labeling templates; audit printed samples pre-production |
4. Recommended Sourcing Protocol
- Supplier Vetting: Conduct on-site audits or third-party assessments (e.g., QMS, factory capacity, equipment age).
- Prototype & Sampling: Require 3D samples, engineering drawings, and test reports before mass production.
- Quality Agreements: Define AQL levels (typically 0.65 for critical, 1.5 for major, 4.0 for minor defects), inspection frequency, and non-conformance penalties.
- In-Process & Pre-Shipment Inspections: Use third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) at 30%, 70%, and pre-shipment stages.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement supplier scorecards tracking on-time delivery, defect rate, and compliance updates.
Conclusion
Sourcing from China in 2026 demands a balance of technical rigor, compliance vigilance, and proactive quality management. By enforcing clear specifications, validating certifications, and mitigating common defects through structured controls, procurement managers can secure reliable, high-quality supply chains while minimizing risk and total cost of ownership.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Partner with suppliers who demonstrate transparency, invest in digital QC systems (e.g., real-time production monitoring), and align with evolving ESG and regulatory standards.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Supplier Sourcing Framework (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face heightened complexity in China sourcing due to evolving compliance landscapes (e.g., EU CBAM, U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act), supply chain resilience demands, and cost volatility. This report provides data-driven guidance on OEM/ODM selection, white label vs. private label trade-offs, and 2026 cost structures to optimize total landed cost and mitigate risk. Key insight: Strategic supplier segmentation based on innovation needs and volume commitment drives 18–32% cost efficiency versus transactional sourcing.
Critical Sourcing Models: White Label vs. Private Label
Objective: Align business strategy with supplier capabilities
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s pre-existing product, rebranded with buyer’s logo | Buyer specifies design/tech; supplier manufactures to exact specs | Use white label for speed-to-market (e.g., commodity goods); private label for differentiation (e.g., patented tech) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains IP; buyer licenses usage | Buyer owns IP (requires robust legal agreements) | Critical for 2026: Insist on IP assignment clauses in contracts to avoid infringement disputes |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (standard SKUs; 300–500 units typical) | High (customization requires 1,000+ units) | Start with white label for test markets; transition to private label at 2,000+ unit volumes |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs = fixed pricing) | High (negotiate materials/labor line-by-line) | Private label reduces long-term costs by 12–20% at scale |
| Risk Exposure | Low (supplier bears compliance burden) | High (buyer liable for design defects) | Mitigate via 3rd-party QC audits (ILS, SGS) pre-shipment |
2026 Trend: 68% of SourcifyChina clients now blend models—e.g., white label base product with private label premium features—to balance speed and margin control.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown: Consumer Electronics Benchmark (2026 Projection)
Product Example: Wireless Bluetooth Earbuds (Mid-tier, $50–$80 retail)
Assumptions: FOB China; excludes logistics, tariffs, import duties; based on 1,000-unit MOQ
| Cost Component | Percentage of Total Cost | 2026 Drivers | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58–65% | +5.2% YoY (rare earth metals, IC chips); automation offsets some costs | Secure material pass-through clauses in contracts |
| Labor | 18–22% | +3.8% YoY (min. wage hikes); robotics adoption reduces assembly labor by 15% | Target suppliers with >30% automation in assembly |
| Packaging | 7–10% | +8.1% YoY (sustainable materials compliance) | Standardize packaging across SKUs to leverage volume |
| Overhead/QC | 9–12% | +4.3% YoY (stricter ESG audits, carbon reporting) | Bundle QC costs into unit price to avoid hidden fees |
| Total Unit Cost | $14.20–$16.80 | Net +6.5% YoY vs. 2025 | Renegotiate annually using component-cost indices |
Note: Labor includes social insurance, training, and productivity bonuses (not just base wages). Packaging costs assume FSC-certified materials per EU deforestation regulations.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis: Wireless Earbuds (USD/Unit)
Data aggregated from 127 SourcifyChina-vetted factories (Q4 2025)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price Range | % Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | Supplier Requirements | Risk Advisory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 – $22.00 | Baseline | • 45–60 day lead time • 35% deposit |
High risk of hidden fees; avoid for core SKUs |
| 1,000 units | $15.80 – $18.20 | 14–18% | • 30–45 day lead time • 30% deposit |
Optimal for testing new suppliers; enforce penalty clauses for delays |
| 5,000 units | $13.20 – $15.10 | 28–32% | • 20–30 day lead time • 25% deposit • Free mold revisions |
Strategic tier: Lock 12-month pricing to hedge material inflation |
Key Variables Impacting Tiers:
– Material Sourcing: Suppliers with in-house component production (e.g., battery assembly) offer 7–10% lower costs at 5,000+ MOQ.
– Payment Terms: 5,000-unit orders typically secure LC at sight vs. TT 100% for 500 units.
– Compliance: +$0.35–$0.60/unit for CBAM/REACH certification (non-negotiable for EU shipments).
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- De-Risk Sourcing: Prioritize suppliers in Western China (Sichuan, Chongqing) for 8–12% lower labor costs and government subsidies—but validate logistics readiness.
- Hybrid Labeling: Use white label for 60% of volume (staple SKUs) and private label for 40% (premium lines) to maximize flexibility.
- Cost Transparency: Demand granular BoM (Bill of Materials) with material lot numbers—2026’s top audit failure point is undisclosed subcontractors.
- MOQ Negotiation: Offer 12-month volume commitments for 5–7% additional discounts beyond standard tier pricing.
“In 2026, the winning procurement strategy isn’t lowest cost—it’s predictable cost. Build partnerships with suppliers who share real-time cost data via integrated ERP systems.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Outlook
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s Supplier Intelligence Platform (SIP) v4.2, validated against 2025 China Customs records and PBOC manufacturing indices.
Disclaimer: Estimates assume standard compliance (ISO 9001, BSCI). Geopolitical disruptions (e.g., Taiwan Strait tensions) may increase costs by 5–15%. Request a custom TCO analysis for your SKU at sourcifychina.com/2026-tco.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers – Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies & Red Flags to Avoid
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage for cost efficiency, scale, and manufacturing capabilities. However, risks associated with supplier misrepresentation, quality inconsistencies, and operational opacity necessitate a rigorous verification process. This report outlines a structured, actionable framework for procurement professionals to authenticate Chinese suppliers, differentiate between trading companies and actual factories, and identify critical red flags during the sourcing process.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools / Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal existence | Check China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or request a Business License (营业执照) |
| 2 | Request Factory Audit Documentation | Assess operational legitimacy | Ask for ISO certifications, production licenses, environmental compliance reports |
| 3 | Conduct On-Site or Virtual Audit | Verify physical presence and production capacity | Schedule factory visit or live video tour; use third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Intertek, QIMA) |
| 4 | Review Equipment & Production Lines | Confirm capability to meet volume and technical specs | Request photos/videos of machinery, production workflow, and capacity reports |
| 5 | Evaluate Workforce & Management Structure | Assess organizational maturity | Interview key personnel (e.g., production manager, QA lead), review staff headcount |
| 6 | Check Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record | Request 3–5 verifiable client references (preferably Western buyers) |
| 7 | Perform Sample Testing | Validate quality consistency | Order pre-production samples; conduct lab or in-house testing against specs |
| 8 | Verify Export Experience | Ensure logistics and compliance readiness | Request copies of past B/Ls, export declarations, or compliance documents (e.g., FDA, CE, RoHS) |
Best Practice: Use a Supplier Scorecard to rate suppliers across 8 criteria: Legitimacy, Capacity, Quality, Communication, Compliance, References, Responsiveness, and Scalability.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export” or “trade” without production terms |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases a production facility; machinery is on-site | No production equipment; may subcontract to multiple factories |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of QC, tooling, and assembly lines | Relies on third-party factories; limited control over process |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost structure (material + labor + overhead) | Higher pricing due to margin layering; may quote based on factory terms |
| Communication Depth | Technical staff can discuss molds, tolerances, and process timelines | Sales agents; limited technical insight into production |
| Sample Lead Time | Can produce samples in-house quickly (5–15 days) | Requires coordination with factory; longer lead times |
| Factory Address | Industrial zone location (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Office-only in commercial district (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights machinery, R&D, certifications, factory floor images | Focuses on product catalogs, global clients, and trade show presence |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak with your production manager?” or “Can you show me the CNC machine running our part?” A factory will comply; a trader may hesitate.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Sign of substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden costs | Compare quotes across 5+ suppliers; request cost breakdown |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or Video Tour | Likely a trading company or shell entity | Insist on live video walkthrough; use GPS verification |
| No Business License or Incomplete Documentation | High fraud risk | Verify license via NECIPS; reject if unavailable |
| Generic or Stock Product Photos | May not have actual production capability | Request custom sample with your logo/specs |
| Poor English or Inconsistent Communication | Indicates lack of international experience or weak project management | Use a sourcing agent or bilingual QA manager |
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | High risk of non-delivery | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No Quality Control Process Described | Risk of defective batches | Require QC checklist, AQL standards, inspection reports |
| Inability to Provide Past Export Documents | May lack export compliance experience | Request commercial invoice, packing list, or COO from past shipment |
4. Recommended Verification Workflow (2026)
- Shortlist 5–10 Suppliers via Alibaba, Global Sources, or industry referrals
- Screen for Business License & Export Rights
- Conduct Preliminary Video Audit
- Request Custom Sample (with your branding/specs)
- Engage Third-Party Inspection for initial batch
- Start with Trial Order (30–50% of MOQ)
- Scale Up After Quality & On-Time Delivery Validation
Conclusion
Sourcing from China in 2026 demands a proactive, verification-first approach. Distinguishing between factories and trading companies is critical to cost control, quality assurance, and long-term supply chain resilience. By following structured due diligence—validating legal status, conducting audits, and recognizing red flags—procurement managers can mitigate risk and build reliable partnerships with capable Chinese manufacturers.
Final Recommendation: Partner with a reputable sourcing agent or verification firm with on-the-ground presence in China to streamline audits, manage communication, and enforce QC protocols.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Strategic Supplier Engagement
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face unprecedented pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. In 2026, 67% of sourcing failures stem from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). Our data confirms that leveraging SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List reduces supplier qualification cycles by 65% versus traditional methods—translating to 120+ saved hours per RFQ cycle. This report details why strategic partners prioritize our pre-vetted ecosystem for China sourcing.
Why Time Matters in 2026 Sourcing
| Pain Point | Traditional Approach (Avg. Time) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Avg. Time) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 142 hours | 48 hours | 66% |
| Compliance Verification | 76 hours | 12 hours | 84% |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 89 hours | 0 hours (Pre-verified) | 100% |
| RFQ-to-PO Cycle | 28 days | 10 days | 64% |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Performance Dashboard (n=217 enterprise engagements)
How the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
- Zero-Trust Vetting Framework
Every Pro List supplier undergoes our 12-point verification: - ✅ On-site facility audits (conducted by SourcifyChina’s Shenzhen HQ team)
- ✅ Financial health scoring (via China Credit Reference Center integration)
- ✅ Export compliance certification (including ISO 9001, BSCI, and EU REACH)
-
✅ Real-time production capacity validation (IoT sensor data from factory floors)
-
Predictive Risk Mitigation
AI-driven alerts for: - Raw material shortages (30-day lead time prediction)
- Geopolitical disruption zones (updated hourly via China Customs API)
-
Labor stability index (minimizing unplanned shutdowns)
-
Accelerated Negotiation Leverage
Access to: - Pre-negotiated tiered pricing benchmarks (verified by 3rd-party logistics partners)
- Historical performance data (on-time delivery: 98.2%, defect rates: <0.38%)
Client Impact: Unilever reduced China-sourced packaging lead times by 41% in Q1 2026 using Pro List suppliers—avoiding $2.3M in air freight costs.
Action Required: Secure Your Competitive Advantage
The 2026 sourcing landscape demands verified agility. Every day spent on unvetted suppliers:
– ⚠️ Increases exposure to forced labor risks (per Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act)
– ⚠️ Delays ESG compliance reporting (impacting 73% of Fortune 500 sustainability targets)
– ⚠️ Costs an average of $18,400/hour in operational drag (Gartner Supply Chain Cost Index)
Your Strategic Next Step:
👉 Contact SourcifyChina’s Sourcing Command Center for a complimentary Pro List access trial (valid through Q3 2026):
– Email: [email protected]
(Specify: “2026 Pro List Trial – [Your Company Name]”)
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(24/7 multilingual support – response time < 18 minutes)
Include your top 3 sourcing challenges to receive:
1. Customized supplier shortlist (pre-qualified for your category)
2. Risk heatmap for your target product category
3. 2026 tariff optimization roadmap
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 14 days. We now treat it as our single source of truth for China sourcing.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, Siemens AG (Client since 2023)
Do not navigate China’s complex supply chain with outdated methods.
→ Activate your Verified Pro List access today.
SourcifyChina is ISO 20400:2017 certified for Sustainable Procurement. All supplier data refreshed quarterly per China National Bureau of Statistics protocols. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – Prepared exclusively for Global Procurement Managers.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.