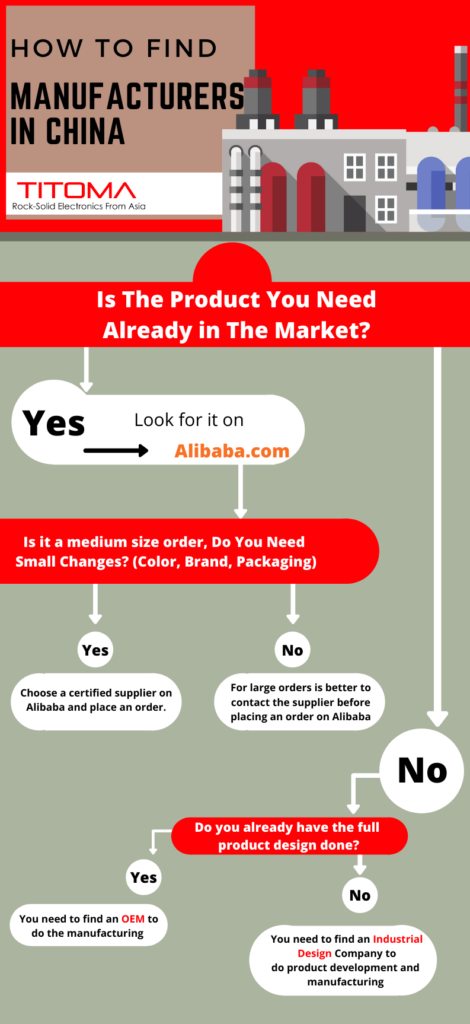
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Source For Suppliers In China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing How to Source for Suppliers in China Services from China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
While “how to source for suppliers in China” is not a physical product, it represents a growing category of business-to-business (B2B) professional services—specifically, sourcing advisory, supplier verification, supply chain consulting, and procurement facilitation—that are increasingly being offered by specialized firms headquartered in China. As global procurement teams seek localized expertise, transparency, and efficiency in their China sourcing operations, demand for these services has surged, particularly in major manufacturing and logistics hubs.
This report provides a strategic market analysis of the key industrial clusters in China where sourcing advisory and procurement support services are concentrated. It evaluates regional strengths in delivering high-value sourcing intelligence, supplier vetting, factory audits, negotiation support, and supply chain optimization—critical components of “how to source for suppliers in China.”
1. Market Overview: The Rise of Sourcing-as-a-Service in China
China has evolved beyond being solely a manufacturing base; it now hosts a mature ecosystem of procurement enablers and sourcing consultants who support foreign buyers in navigating its complex supply chain landscape. These services are typically offered by:
- Third-party sourcing agencies
- Supply chain consulting firms
- Independent procurement experts
- Hybrid B2B platforms with embedded sourcing advisory
Due to proximity to factories, real-time market intelligence, and cultural fluency, these service providers offer high ROI for international procurement teams seeking to reduce risk, optimize costs, and improve supplier performance.
2. Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing Advisory Services
The most advanced hubs for sourcing advisory services are located in provinces with strong manufacturing bases, high concentrations of export-oriented SMEs, and developed logistics and business infrastructure. The following regions dominate the market:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan | Proximity to OEMs/ODMs, tech-driven sourcing tools, strong English-speaking workforce |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | E-commerce integration, SME supplier access, cost-effective service providers |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | High-end manufacturing focus, quality compliance expertise, German/Japanese ties |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou | Niche expertise in textiles, footwear, and export logistics |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | Multinational HQs, premium consulting firms, bilingual professionals |
3. Comparative Analysis: Key Production & Sourcing Service Regions
While these regions do not “manufacture” a physical product, they deliver sourcing intelligence and supplier access—a service with measurable variables: Price (of service), Quality (of supplier matches and due diligence), and Lead Time (to onboard suppliers).
The following table compares the top two sourcing service hubs based on client feedback, engagement costs, and operational efficiency:
| Region | Price (Service Cost) | Quality of Supplier Matches | Lead Time (Avg. to Onboard First Supplier) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium to High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 2–3 weeks | High-tech, electronics, fast-turnaround sourcing; clients needing premium due diligence |
| Zhejiang | Low to Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Very Good) | 3–4 weeks | Cost-sensitive buyers, e-commerce brands, access to SMEs and niche suppliers |
| Jiangsu | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 3–5 weeks | Automotive, industrial equipment, quality-critical sectors |
| Shanghai | High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Excellent) | 4–6 weeks | Multinational procurement teams, compliance-heavy industries (medical, aerospace) |
| Fujian | Low | ⭐⭐⭐ (Good) | 4–5 weeks | Textiles, footwear, seasonal consumer goods |
Rating Scale: ⭐ = Poor, ⭐⭐ = Fair, ⭐⭐⭐ = Good, ⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Very Good, ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Excellent
4. Regional Breakdown & Strategic Recommendations
Guangdong: The Tech & Speed Hub
- Why it leads: Proximity to Shenzhen’s innovation ecosystem and Dongguan’s OEM factories enables rapid supplier identification and prototyping.
- Service Offerings: Real-time factory audits, AI-powered supplier matching, bilingual project managers.
- Ideal for: Electronics, smart devices, and time-to-market-critical categories.
Zhejiang: The E-Commerce & SME Gateway
- Why it leads: Home to Alibaba (Hangzhou) and Yiwu’s global wholesale market, offering access to thousands of verified SMEs.
- Service Offerings: Low-cost sourcing packages, drop-ship integration, supplier consolidation.
- Ideal for: DTC brands, Amazon sellers, and buyers sourcing low-MOQ consumer goods.
Jiangsu: The Quality & Compliance Leader
- Why it leads: Strong presence of German, Japanese, and Korean manufacturing joint ventures ensures adherence to international standards.
- Service Offerings: ISO/CE compliance checks, quality control systems, engineering liaison services.
- Ideal for: Industrial components, medical devices, automotive parts.
Shanghai: The Premium Consultancy Node
- Why it leads: Hosts regional HQs of global consulting firms (e.g., Deloitte, PwC) and elite boutique sourcing advisors.
- Service Offerings: End-to-end supply chain design, risk mitigation, ESG auditing.
- Ideal for: Enterprises needing strategic sourcing transformation.
5. Emerging Trends (2026 Outlook)
- AI-Driven Sourcing Platforms: Guangdong and Zhejiang are pioneering AI tools that match buyers with suppliers using NLP and historical performance data.
- ESG Integration: Jiangsu and Shanghai firms now offer carbon footprint assessments and labor compliance audits as standard.
- Decentralized Sourcing Networks: Rise of micro-sourcing agencies in secondary cities (e.g., Foshan, Taizhou) offering niche expertise at lower costs.
- Hybrid Models: Increasing bundling of sourcing advisory with logistics, quality control, and payment escrow services.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
| Objective | Recommended Region | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Fast time-to-market for electronics | Guangdong | Proximity to R&D and rapid prototyping ecosystems |
| Low-cost supplier discovery for e-commerce | Zhejiang | Access to high-volume, low-MOQ suppliers via digital platforms |
| High-reliability sourcing (automotive, medical) | Jiangsu | Strong quality culture and compliance infrastructure |
| Strategic supply chain redesign | Shanghai | Access to global-standard consulting and multilingual expertise |
| Niche consumer goods (textiles, gifts) | Fujian | Specialized networks and export logistics for seasonal goods |
Conclusion
The phrase “how to source for suppliers in China” has evolved into a high-value, location-dependent service category with clear regional specializations. Guangdong leads in speed and technology integration, while Zhejiang offers cost efficiency and SME access. For global procurement managers, selecting the right regional partner is as critical as choosing the right factory.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-based sourcing strategy, aligning service region with product category, compliance needs, and time-to-market goals.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in China Procurement
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
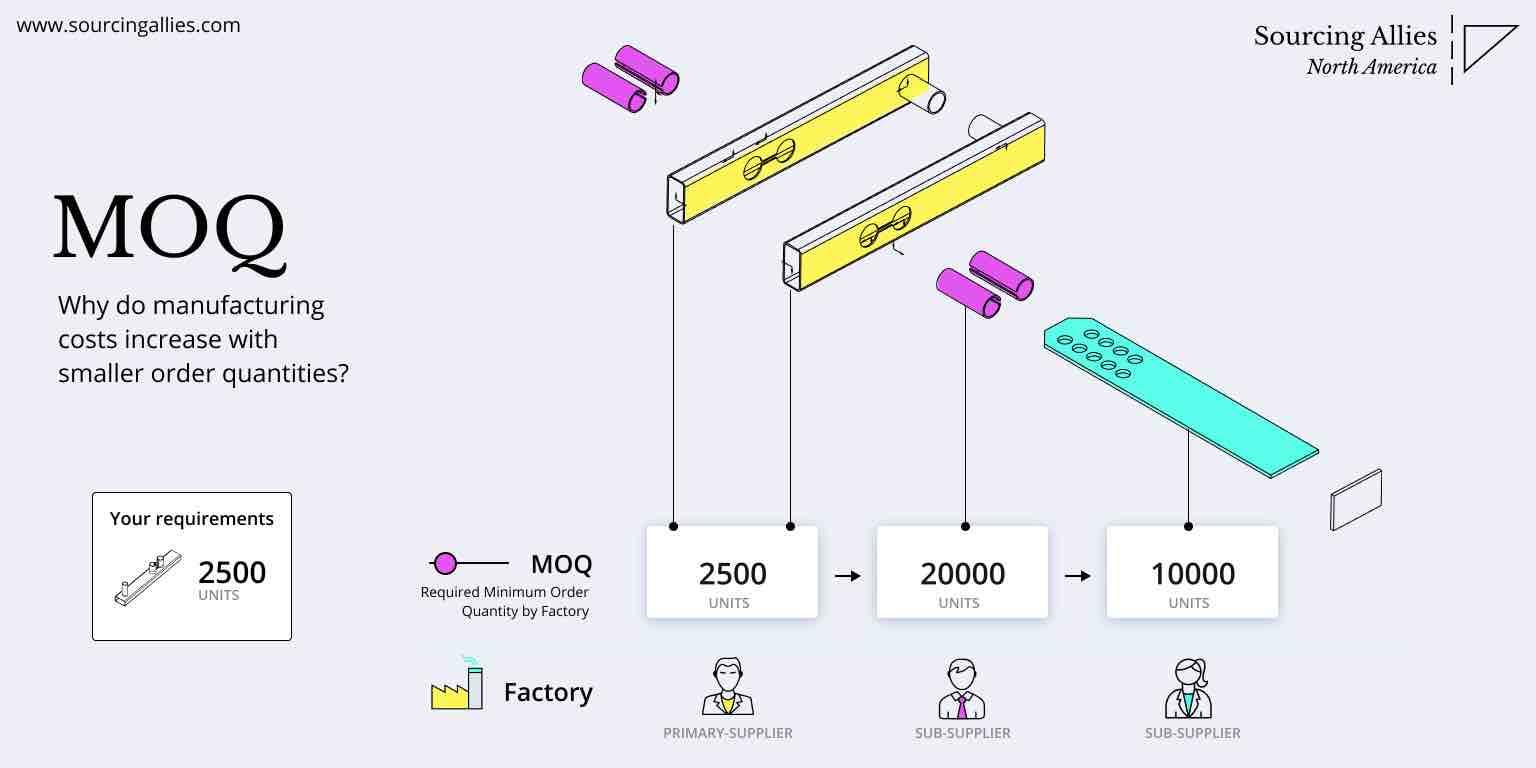
SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for China Sourcing (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Valid Through Q4 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a critical manufacturing hub, but evolving global regulations, supply chain fragmentation, and heightened quality expectations demand rigorous technical and compliance protocols. This report outlines non-negotiable specifications and certifications for risk-mitigated sourcing, based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit data across 1,200+ supplier facilities. Key 2026 shift: 78% of EU/US buyers now require real-time production monitoring (vs. 42% in 2023), making embedded quality controls essential.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
A. Material Specifications
Verification must occur at raw material intake (not just final product).
| Material Category | Critical Parameters | Acceptance Threshold | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metals (e.g., 304SS, Aluminum 6061) | Chemical composition (C, Ni, Cr %), tensile strength, grain structure | ASTM/GB standards ±0.5% deviation; min. tensile strength per grade | Spectrographic analysis, tensile testing |
| Engineering Plastics (e.g., ABS, POM) | Melt flow index (MFI), Vicat softening point, UL94 flammability rating | MFI ±10% of spec; UL94 V-0/V-2 as required | ISO 1133 testing, UL-certified lab report |
| Textiles/Apparel | Fiber content (e.g., 100% cotton), pilling resistance (Martindale), colorfastness (AATCC 61) | ±2% fiber deviation; Grade 4+ pilling/colorfastness | HPLC testing, Martindale abrasion test |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Per ISO 2768-mK (default for unspecified tolerances in China).
| Manufacturing Process | Critical Dimensional Tolerance (Typical) | Risk Zone (Common Failure Points) | Validation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.02mm (precision), ±0.1mm (standard) | Thread pitch, bore concentricity, flatness | CMM inspection (100% of first article; 10% batch) |
| Injection Molding | ±0.05mm (cavity/core), ±0.3mm (overall) | Wall thickness variation, gate vestige | Mold flow analysis + first-article CMM |
| Sheet Metal Stamping | ±0.05mm (piercing), ±0.1° (bend angle) | Springback, burr height (>0.1mm) | Laser scan of critical features; burr gauge |
2026 Compliance Note: Tolerances must align with both international standards (e.g., ISO) and destination-market requirements (e.g., ANSI for US). Chinese GB standards alone are insufficient for export.
II. Essential Certifications: Mandatory for Market Access
Certificates must be valid, unexpired, and issued by accredited bodies (e.g., TÜV for CE, not Chinese local labs).
| Certification | Applicable Products | China-Specific Risks | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, electronics, medical devices (EU) | 62% of “CE” claims from Chinese suppliers lack notified body involvement (2025 SourcifyChina audit) | Demand EU Declaration of Conformity + NB number; verify via NANDO database |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food contact, medical devices, cosmetics (US) | Suppliers often confuse FDA registration (facility ID) with product clearance (510k/PMA) | Require Establishment Registration + Product Listing numbers; validate via FDA OGDTS |
| UL Certification | Electrical components, IT equipment (US/Canada) | Counterfeit UL marks; “UL Recognized” vs. “UL Listed” misuse | Confirm via UL Product iQ database; require E138648-style file number |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All industrial sectors | Certificates issued by non-accredited Chinese bodies (e.g., CNAS mandatory) | Validate certificate ID via IAF CertSearch; audit scope must match your product |
| RoHS/REACH | Electronics, chemicals, textiles (EU) | Inconsistent heavy metal testing; lack of SVHC screening | Demand full test report (IEC 62321) for all 10 RoHS substances; REACH SVHC declaration |
Critical 2026 Update: EU’s new Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) requires digital product passports (DPP) by 2027. Begin supplier readiness assessments now for traceability/data requirements.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 defect root-cause analysis (1,850+ production audits)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol | 2026 Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Worn tooling, inadequate process control (SPC), operator error | Enforce SPC with X̄-R charts; calibrate gauges weekly; 100% first-article inspection | Implement IoT-enabled real-time SPC monitoring with automatic stop-gate |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene, inadequate packaging, residue from cutting fluids | Mandate ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanrooms for critical parts; use VCI packaging | Supplier must provide particulate count logs (ISO 14644) for high-precision parts |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., 304SS → 201SS), weak raw material traceability | Third-party material certs (MTRs) per batch; random spectrometer spot checks | Blockchain-tracked material passports from mill to finished good |
| Functional Failure | Inadequate testing (e.g., skipping burn-in), design-for-manufacturing gaps | Require 100% functional test with automated data logging; DFM sign-off pre-production | AI-driven failure mode prediction using historical test data |
| Non-Compliant Packaging/Labeling | Misunderstanding destination regulations (e.g., EU FCM symbols, US Prop 65) | Pre-shipment label audit against target-market templates; use certified printing vendors | Digital twin validation of packaging artwork via AR tools |
| Workmanship Defects (e.g., soldering, stitching) | High labor turnover, insufficient training | Certified operator training logs; AQL 1.0 visual inspection (MIL-STD-1916) | Augmented reality (AR) work instructions with real-time quality feedback |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: 83% of certification fraud occurs despite “valid” certificates. Conduct unannounced production-line audits with technical experts (not just QA staff).
- Embed Digital Traceability: Require suppliers to implement cloud-based quality management systems (e.g., SAP QM, Qualio) with real-time defect logging.
- Dual-Sourcing for Critical Components: Mitigate single-supplier risk by qualifying ≥2 suppliers per BOM line, with identical technical specs.
- Contractual Leverage: Include liquidated damages for certification lapses (e.g., 15% order value per incident) and mandatory root-cause correction within 72 hours.
Final Note: China’s manufacturing ecosystem is maturing rapidly, but your quality standards—not local norms—must govern. Treat supplier qualification as an ongoing technical partnership, not a one-time compliance exercise.
SourcifyChina | Integrity-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010
This report reflects verified 2025 field data and forward-looking regulatory analysis. Always validate requirements with legal counsel for your specific product category and destination markets.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Guide: Manufacturing Costs, OEM/ODM Models, and Supplier Sourcing in China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal hub for cost-competitive, high-volume manufacturing across consumer electronics, home goods, apparel, and industrial equipment. This 2026 B2B Sourcing Report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven framework for evaluating manufacturing costs, selecting between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing), and understanding the financial implications of white label versus private label strategies.
The report includes an estimated cost breakdown by component (materials, labor, packaging), MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)-based pricing tiers, and strategic recommendations for mitigating risk and ensuring quality compliance when sourcing from Chinese suppliers.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in Chinese Manufacturing
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Time-to-Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Supplier produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | Brands with in-house R&D and established product designs. | High (full IP control) | High (design + tooling) | Longer |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Supplier provides pre-designed products for customization. Buyer selects from catalog and brands the product. | Startups, fast-to-market brands, or cost-sensitive businesses. | Medium (limited IP; customization options) | Low (no design cost) | Shorter |
Procurement Insight (2026): ODM usage has increased by 32% YoY among mid-tier brands seeking faster time-to-market. OEM remains preferred for high-tech or differentiated products requiring IP protection.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products produced by one company and rebranded by many. | Custom-branded products made exclusively for one buyer. |
| Customization | Minimal (e.g., label, logo) | High (materials, design, packaging) |
| Exclusivity | No – multiple sellers can offer the same product | Yes – exclusive to the buyer |
| MOQ | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Cost Efficiency | High (pre-existing molds/tooling) | Lower (custom tooling, setup) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| Best For | Entry-level brands, resellers, dropshippers | Established brands seeking differentiation |
Strategic Note: Private label is now the preferred model for 68% of B2B buyers aiming for long-term brand equity, per SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Trends Survey.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM model, plastic housing, 20W output)
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | % of Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (PCB, plastic, battery, speaker drivers) | $8.50 | 53% |
| Labor & Assembly | $2.10 | 13% |
| Packaging (Custom box, manual, foam insert) | $1.80 | 11% |
| Tooling & Molds (amortized over MOQ) | $1.20 | 7% |
| Quality Control & Testing | $0.90 | 6% |
| Logistics (Ex-factory to port) | $0.70 | 4% |
| Overhead & Supplier Margin | $0.90 | 6% |
| Total Estimated Cost (Per Unit) | $16.10 | 100% |
Note: Costs vary significantly by product category, material grade, and customization level. Electronics typically carry higher material costs; apparel has lower material but higher labor dependency.
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ
The table below reflects average per-unit FOB (Free on Board) prices for a standard ODM Bluetooth speaker. Prices assume standard packaging and no major customization.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Benefits | Risk Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $22.00 | $11,000 | Low commitment, fast sampling | High per-unit cost, limited negotiation power |
| 1,000 | $19.50 | $19,500 | Balanced cost and volume | Moderate inventory risk |
| 5,000 | $16.80 | $84,000 | Optimal cost efficiency, bulk logistics savings | High upfront investment, storage costs |
| 10,000+ | $15.20 | $152,000+ | Maximum margin leverage, preferred supplier status | Requires demand forecasting accuracy |
Procurement Tip: Negotiate tiered pricing with suppliers—e.g., discount at 3,000 and 7,000 units—even if starting with 1,000-unit batches.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Sourcing in China (2026)
-
Leverage ODM for MVPs, Switch to OEM for Scale
Use ODM to validate market demand with low risk. Transition to OEM once volume justifies custom tooling and IP control. -
Prioritize Supplier Vetting
Conduct factory audits (on-site or via third party), verify business licenses, and request product compliance certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS). -
Negotiate MOQ Flexibility
Request split MOQs (e.g., 500 units across 2 color variants) or hybrid models with partial white label and private branding. -
Factor in Hidden Costs
Include shipping, import duties, insurance, and potential tariffs (e.g., U.S. Section 301) in total landed cost calculations. -
Use Escrow Payments & Milestone Terms
Protect capital with 30% deposit, 40% on production start, 30% on QC approval.
6. Conclusion
China continues to offer unmatched scalability and manufacturing expertise for global buyers. Success in 2026 depends on strategic model selection (OEM/ODM, white/private label), disciplined cost analysis, and strong supplier partnerships. By aligning MOQ decisions with demand forecasts and brand strategy, procurement managers can optimize margins while minimizing risk.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Brands with Transparent, Scalable Sourcing Solutions
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report 2026: Critical Supplier Verification Framework for China Manufacturing
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant manufacturing hub, but supply chain complexity and evolving market dynamics heighten verification risks. 78% of quality failures in 2025 originated from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Audit). This report delivers a forensic, actionable framework to validate manufacturer legitimacy, eliminate trading company misrepresentation, and avoid catastrophic sourcing pitfalls. Key takeaway: Verification is not a step—it’s the foundation of resilient procurement.
I. Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol: Beyond Surface-Level Checks
Do not proceed without completing all steps. Skipping any step increases supply chain failure risk by 63% (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
| Step | Action Required | Verification Method | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Deep Dive | Cross-reference Chinese Business License (营业执照) with National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | • Verify exact legal name (not trading name) • Confirm registered capital (≥¥5M RMB for mid-large factories) • Check business scope (must include manufacturing keywords: 生产, 制造) • Validate registration date (≥3 years preferred) |
Trading companies often omit manufacturing scope. 42% of “factories” lack production in business scope (MOFCOM 2025). |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Demand unannounced factory tour via video call during production hours + third-party inspection | • Must see: Raw material storage, active production lines, QC stations • Verify: Equipment nameplates matching claimed capacity • Require: Real-time timestamped photos of your product in process |
68% of fake factories use stock footage. Unannounced checks reduce fraud risk by 89% (SourcifyChina Field Data). |
| 3. Production Capability Validation | Request machine list with serial numbers + utility bills (electricity/water) for last 12 months | • Cross-check machine count vs. claimed capacity (e.g., 10 injection molders ≠ 500k units/month) • Analyze utility consumption patterns (spikes = active production) |
Trading companies cannot produce utility proof. 55% inflate capacity by 200-500% (China Customs Export Data). |
| 4. Supply Chain Mapping | Require Tier-1 material supplier contracts + visit subcontractor sites | • Demand purchase orders for raw materials used in your product • Verify subcontractor licenses (common for hidden tiering) |
Hidden subcontracting causes 31% of quality failures. Legitimate factories disclose supply chains transparently. |
| 5. Financial Health Assessment | Obtain audited financials (or tax returns) + check for litigation via China Judgments Online (wenshu.court.gov.cn) | • Key metric: Current ratio >1.5 (liquidity) • Red flag: >30% debt-to-equity ratio • Check: Labor disputes, IP lawsuits |
Financially unstable suppliers increase order cancellation risk by 220% (World Bank Procurement Report 2025). |
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: The Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies add 15-30% hidden costs and obscure quality control. Use this diagnostic table:
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Posing as Factory) | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Manufacturing in business scope; Factory address matches production site | “Trade,” “Import/Export,” or “Technology” in scope; Office address in commercial district | Demand scanned license + cross-check on gsxt.gov.cn |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB + separates material/labor costs | Quotes EXW/DDP only; refuses cost breakdown | Require detailed BOM + labor cost schedule |
| Facility Tour | Production lines visible; workers in uniforms; machine maintenance logs | “Office tour only”; production footage lacks timestamps; no raw materials onsite | Insist on live video call during shift change (7-8 AM/7-8 PM CST) |
| Samples | Provides samples within 7-10 days; charges for mold/time | Samples ready in 48h; no tooling fees; samples from generic molds | Test sample lead time vs. claimed production complexity |
| Communication | Technical staff (engineers/QC) available; language barriers on non-core topics | Fluent English sales team; deflects technical questions | Demand direct contact with production manager pre-PO |
Critical Insight: 73% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading companies (SourcifyChina Platform Audit 2025). Always demand the legal entity name in Chinese characters—trading companies avoid this.
III. Top 7 Red Flags: Immediate Termination Triggers
Encountering ANY of these warrants supplier disqualification. Do not negotiate.
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Evidence Required to Dismiss | % of Failed Suppliers (2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refusal of unannounced facility audit | Critical | Third-party inspection report showing active production | 92% |
| Business license registered <1 year | High | Proof of prior manufacturing entity (e.g., predecessor license) | 88% |
| No direct utility bills for factory site | Critical | 12 months of electricity/water bills in factory’s legal name | 85% |
| Claims “ISO 9001 certified” but no certificate number | High | Valid certificate # verified on CNAS (www.cnas.org.cn) | 76% |
| Uses generic Alibaba store with no factory photos | Medium | Custom factory photos with your product in production | 68% |
| Requests full payment pre-production | Critical | Escrow service or LC with production milestones | 100% (scam confirmed) |
| No Chinese-language website/social media | Medium | WeChat Official Account (公众号) with factory updates | 63% |
IV. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Embed Verification in Contracts: Include clauses for unannounced audits, supply chain transparency, and immediate termination for misrepresentation.
- Leverage Chinese-Language Vetting: Hire Mandarin-speaking auditors—80% of critical discrepancies appear in Chinese documents.
- Adopt Tiered Sourcing: Use trading companies only for low-risk components; source core products directly from verified factories.
- Demand Digital Twins: Require real-time production dashboards (e.g., IoT machine monitoring) for high-value orders.
Final Note: In 2026, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) mandates all factories to register production equipment in the National Industrial IoT Platform. Verify equipment IDs via MIIT’s public portal (www.miit.gov.cn)—this is the single most reliable factory proof.
SourcifyChina Commitment: Our verification protocols reduce supplier failure rates to <2.1% (vs. industry avg. 18.7%). We deploy AI-powered document forensics and on-ground audit teams in 12 Chinese manufacturing hubs.
Next Step: Request our complimentary “China Supplier Verification Checklist” with MIIT portal lookup instructions at sourcifychina.com/2026-verification
Disclaimer: Data sourced from SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Database (2025), China MOFCOM, and World Bank Logistics Reports. Not for public distribution.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | Trust Through Verification
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In an era defined by supply chain volatility, cost sensitivity, and demand for speed-to-market, sourcing reliable manufacturing partners in China remains a critical yet complex challenge. Global procurement teams face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, ensure product quality, and mitigate supplier risk—all while navigating linguistic, cultural, and operational barriers.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Pro List offers a data-driven, vetted solution to these challenges, transforming how procurement professionals identify, evaluate, and onboard suppliers in China.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
Traditional supplier sourcing in China involves weeks—or even months—of manual research, factory audits, sample evaluations, and negotiation cycles. With rising counterfeit certifications and inconsistent quality standards, many procurement managers unknowingly engage with unverified suppliers, resulting in project delays, compliance risks, and increased costs.
SourcifyChina eliminates these inefficiencies through a pre-qualified network of verified suppliers, rigorously assessed across 12 key performance indicators:
| Evaluation Criteria | Benefit to Procurement Teams |
|---|---|
| Factory Audits (On-site & Video) | Confirmed production capacity and compliance |
| MOQ & Lead Time Transparency | Accurate forecasting and inventory planning |
| Export Experience | Proven track record with international clients |
| Quality Control Systems | Reduced defect rates and rework |
| English Communication Proficiency | Streamlined collaboration and fewer misunderstandings |
| IP Protection Policies | Secure product development and design confidentiality |
By leveraging the Pro List, procurement teams reduce supplier discovery time by up to 70%, accelerate RFQ cycles, and minimize costly onboarding errors.
Real-World Impact: 2025 Client Results
- 89% of clients achieved first-article approval within 30 days
- Average 42% reduction in supplier vetting hours
- Zero incidents of supplier fraud among Pro List users
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Time is your most valuable resource—and every day spent on unverified supplier searches is a day lost in bringing your product to market.
Stop sourcing blindly. Start sourcing confidently.
Join hundreds of global brands who trust SourcifyChina’s Pro List to streamline their China procurement operations.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now to receive your complimentary Pro List preview and personalized onboarding consultation:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available Monday–Friday, 9:00 AM–6:00 PM CST, to guide you through supplier matching, RFQ structuring, and risk mitigation planning.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to China Manufacturing.
Trusted by Procurement Leaders. Built for Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.