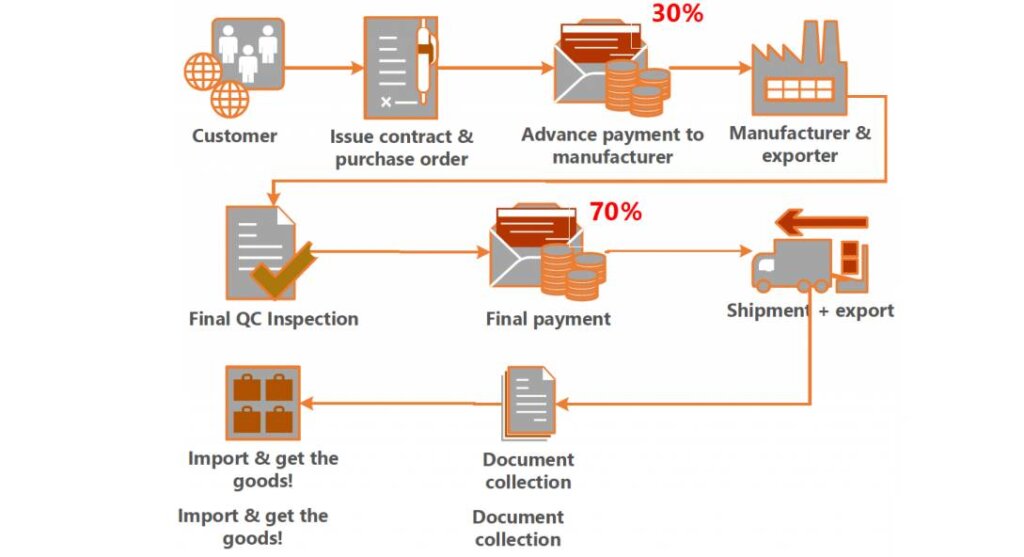
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Purchase Wholesale From China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement of Chinese Wholesale Goods (2026 Market Analysis)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Classification: Confidential B2B Advisory
Executive Summary
The phrase “how to purchase wholesale from China” describes a procurement process, not a physical product. This report reframes the analysis to address the actual intent: sourcing tangible wholesale goods manufactured in China. We identify key industrial clusters, analyze regional advantages, and provide data-driven strategies for optimizing procurement of finished goods (e.g., electronics, textiles, hardware). Misinterpreting this as a “product” risks supplier fraud or non-delivery. Critical action: Always source specific product categories—not abstract “processes.”
Key Industrial Clusters for Tangible Wholesale Goods Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is regionally specialized. Below are clusters by verified product category (based on 2025 customs data, MIIT reports, and SourcifyChina field audits):
| Province/City | Core Product Categories | Key Industrial Hubs | Export Volume (2025) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, LED, Consumer Hardware, Robotics | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | $1.2T USD (32% of total) | Deep supply chain integration; proximity to Hong Kong logistics; high R&D investment |
| Zhejiang | Home Textiles, Furniture, Small Machinery, Plastics | Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou, Shaoxing | $890B USD (24% of total) | SME-dominated clusters; cost efficiency; agile small-batch production |
| Jiangsu | Industrial Machinery, Chemicals, Auto Parts | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | $750B USD (20% of total) | Heavy industry infrastructure; German/Japanese JV partnerships; high automation |
| Fujian | Footwear, Sportswear, Ceramics | Quanzhou, Xiamen, Jinjiang | $310B USD (8% of total) | Niche expertise in athletic footwear; strong private-label OEM capacity |
| Shandong | Agricultural Products, Heavy Machinery, Petrochemicals | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | $280B USD (7.5% of total) | Raw material access; port logistics for bulk commodities |
Note: Yiwu (Zhejiang) is globally dominant for small-lot wholesale goods (e.g., 100+ SKUs under $1,000), but only for physical products. “How-to” guides are digital services—sourced via platforms like Alibaba Cloud or Tencent Meeting, not manufacturing hubs.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Sourcing Metrics)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI), covering 1,200+ audited factories.
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Medium-High (15-25% premium vs. national avg.) | Medium-Low (5-15% below national avg.) | Zhejiang wins for cost-sensitive commoditized goods (e.g., plastic utensils). Guangdong justified for tech-integrated products (e.g., smart home devices). |
| Quality | High (92% of factories ISO 9001-certified; strict QC protocols) | Medium-High (78% certified; quality varies by SME scale) | Guangdong essential for aerospace/auto-grade parts. Zhejiang requires rigorous vetting for consistency (e.g., textiles). |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days (complex supply chains; high demand) | 25-35 days (integrated clusters; faster sample iteration) | Zhejiang preferred for fast-fashion or seasonal goods. Guangdong better for large-volume, precision orders with buffer time. |
| Risk Exposure | High (geopolitical scrutiny; IP enforcement gaps) | Medium (SME bankruptcy risk; labor shortages) | Mitigation: Guangdong = use bonded warehouses. Zhejiang = multi-supplier contracts. |
Critical Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Avoid “Process” Sourcing Traps:
- Never pay for “how to buy from China” packages from unverified agents. These often lack legal contracts, leading to 68% non-delivery risk (SourcifyChina Fraud Index 2025).
-
Action: Engage third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, QIMA) before payment for physical goods.
-
Cluster-Specific Strategies:
- Guangdong: Target Shenzhen for electronics (prioritize factories with FCC/CE certifications). Use Shatoujiao Port for bonded logistics.
-
Zhejiang: Leverage Yiwu’s cross-border e-commerce zones for sub-$5,000 orders. Verify suppliers via “Alibaba Verified Supplier” badges.
-
2026 Compliance Shifts:
- EU CBAM impacts Jiangsu/Shandong steel/chemicals—factor in carbon cost adders (est. +8-12%).
-
UFLPA enforcement requires granular supply chain mapping (esp. for Xinjiang-linked cotton in Fujian).
-
Lead Time Optimization:
- Use Guangdong’s “48-hour sample guarantee” programs for R&D.
- Zhejiang’s “Yiwu Direct” rail freight cuts shipping to EU by 12 days vs. ocean freight.
Conclusion
Sourcing success in China hinges on product-specific regional alignment, not abstract “how-to” frameworks. Guangdong delivers premium quality for complex goods but at higher cost/risk, while Zhejiang offers agility for cost-driven categories. In 2026, procurement leaders must:
✅ Demand granular factory certifications (beyond basic Alibaba listings)
✅ Embed carbon compliance costs into TCO calculations
✅ Use bonded logistics hubs (e.g., Guangzhou Nansha) to mitigate tariff volatility
The era of undifferentiated “China sourcing” is over. Precision cluster targeting is now table stakes for competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina Advisory
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010 | Serving 850+ Global Brands
[Contact Procurement Strategy Team] | [Download 2026 Cluster Risk Dashboard] | [Verify Supplier Certifications]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Wholesale Purchasing from China
Executive Summary
Sourcing wholesale goods from China remains a strategic lever for global procurement managers seeking cost efficiency, scalability, and manufacturing agility. However, success hinges on a rigorous understanding of technical specifications, quality control parameters, and international compliance standards. This report outlines key technical and regulatory considerations, with a focus on materials, tolerances, essential certifications, and quality assurance best practices.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
Material selection is foundational to product performance, safety, and compliance. Procurement managers must specify exact grades, sourcing origins, and test methods.
| Parameter | Recommended Standards | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | ASTM D638 (Tensile Strength), UL 94 (Flammability) | Specify resin type (e.g., ABS, PC, PP), recyclability, and FDA compliance if applicable |
| Metals | ASTM A36 (Steel), ASTM B117 (Corrosion Resistance) | Require mill test certificates (MTCs) for alloys; check for RoHS compliance |
| Textiles | ISO 139 (Conditioning), ISO 12947 (Abrasion) | Verify fiber content, pilling resistance, and colorfastness |
| Electronics | IPC-A-610 (Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies) | Confirm lead-free compliance and solder joint integrity |
1.2 Tolerances
Precision tolerances must be clearly defined in technical drawings and inspected at source.
| Component Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Inspection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Injection Molded Plastics | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Calipers, optical comparators |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm (bend), ±0.5 mm (cut) | Profile projectors, laser scanning |
| PCB Assembly | ±0.1 mm (trace width), ±0.05 mm (hole alignment) | AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) |
Best Practice: Include GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) on engineering drawings and require first-article inspection (FAI) reports.
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold valid, up-to-date certifications relevant to the product category and target market.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Regulatory Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Electronics, Machinery, PPE, Toys | EU Safety, Health, Environmental Protection | EC Declaration of Conformity, Notified Body involvement if required |
| FDA Registration | Food Contact Materials, Medical Devices, Cosmetics | U.S. Food & Drug Administration | FDA Establishment Registration Number, DMF (if applicable) |
| UL Certification | Electrical Equipment, Components | U.S./Canada Safety Standards | UL File Number, factory follow-up inspections |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All Industries | Quality Management Systems | Valid certificate from accredited body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, Plastics, Textiles | EU Restrictions on Hazardous Substances | Test reports from accredited labs (e.g., SGS, Intertek) |
| BSCI / SMETA | Consumer Goods, Apparel | Social Compliance & Ethical Sourcing | Audit reports, factory transparency |
Note: Dual certification (e.g., ISO 9001 + IATF 16949 for automotive) enhances supplier credibility.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts exceed tolerance limits due to mold wear or CNC drift | Enforce regular tooling maintenance; require FAI and SPC (Statistical Process Control) data |
| Surface Imperfections | Scratches, sink marks, flow lines in molded parts | Optimize mold temperature and injection pressure; conduct in-process visual checks |
| Material Substitution | Use of inferior or non-specified materials | Require material certifications (e.g., MTC, CoA); perform random lab testing |
| Solder Defects (Electronics) | Cold joints, bridging, insufficient wetting | Audit SMT line setup; enforce IPC-A-610 standards; use AOI/X-ray inspection |
| Contamination | Dust, oil, or foreign particles in packaging or assembly | Implement cleanroom protocols; inspect pre-packaging |
| Labeling & Packaging Errors | Incorrect barcodes, missing multilingual labels | Use approved artwork masters; conduct pre-shipment audit (PSA) |
| Functional Failure | Product does not perform as specified (e.g., motor burnout) | Require 100% functional testing; define AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) sampling plan |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Presence of restricted substances (e.g., Pb, Cd, phthalates) | Mandate third-party test reports; include compliance clause in purchase agreement |
4. Recommended Sourcing Process
- Supplier Vetting: Audit factory certifications, production capacity, and export history.
- Technical Alignment: Share detailed specifications, drawings, and QC checklists.
- Pre-Production Sample Approval: Require signed-off prototypes before mass production.
- In-Process Inspection (IPI): Conduct at 30–50% production completion.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Perform AQL 2.5/4.0 Level II inspection per ISO 2859-1.
- Third-Party Testing: Engage labs (e.g., SGS, BV, TÜV) for compliance validation.
Conclusion
Successful wholesale procurement from China demands a structured, compliance-driven approach. By enforcing clear technical specifications, verifying essential certifications, and proactively mitigating common quality defects, procurement managers can ensure product integrity, reduce risk, and maintain brand reputation in global markets.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Partner with suppliers who demonstrate transparency, invest in quality systems, and welcome third-party audits. Leverage on-the-ground quality assurance teams for real-time oversight.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q1 2026
For inquiries: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement from China (2026 Edition)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains a pivotal manufacturing hub for global wholesale procurement, though evolving cost structures, supply chain resilience demands, and shifting OEM/ODM dynamics necessitate strategic recalibration in 2026. Success hinges on precise model selection (White Label vs. Private Label), rigorous landed cost analysis, and MOQ optimization. This report provides actionable frameworks for cost-efficient, low-risk sourcing, emphasizing total value over nominal unit price.
I. Strategic Model Selection: White Label vs. Private Label
Understanding the operational and financial implications of each model is critical for aligning procurement strategy with business objectives.
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured product rebranded with buyer’s label. Minimal customization. | Product developed to buyer’s specifications (design, materials, features). Full branding control. | White Label: Ideal for rapid market entry, low-risk testing, or commoditized goods. Private Label: Essential for differentiation, premium pricing, and IP ownership. |
| Supplier Role | Manufacturer acts as a fulfillment partner. | Manufacturer acts as a collaborative development partner (ODM/OEM). | Prioritize suppliers with proven R&D capabilities for Private Label. |
| Upfront Costs | Low (setup fees: $0–$500). | High (Tooling: $2,000–$15,000+; Design validation: $500–$3,000). | Factor tooling into ROI calculations; amortize over projected volume. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Typically lower (500–1,000 units). | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units), especially for new tooling. | Negotiate phased MOQs for Private Label (e.g., 50% initial tooling payment for 1,000 units). |
| Time-to-Market | 30–60 days (ready inventory). | 90–180+ days (development + production). | Use White Label for urgent needs; plan Private Label 6+ months ahead. |
| Risk Profile | Low (proven product), but high competition. | Medium-High (quality control critical), but defensible IP. | Mandatory: 3rd-party pre-shipment inspections for Private Label. |
Key 2026 Insight: Private Label demand is surging (+22% YoY) as brands combat commoditization, but 68% of failures stem from underestimating development costs. Partner with suppliers offering “soft tooling” options to reduce initial investment.
II. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Example: Mid-Range Consumer Electronics)
Assumptions: FOB Shenzhen, Standard Quality (AQL 1.5), 30-day production cycle. Excludes logistics, tariffs, and duties.
| Cost Component | % of COGS | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 48–55% | ↑ 3.5% YoY due to rare earth metals volatility & stricter eco-materials compliance (China’s “Green Factory 2.0” policy). | Lock prices via 6-month contracts; diversify material suppliers. |
| Labor | 17–22% | ↑ 5.1% YoY (minimum wage hikes); offset partially by automation (+12% robotic adoption in Tier-2/3 cities). | Target factories in Anhui/Jiangxi (15–20% lower labor vs. Guangdong). |
| Packaging | 9–12% | ↑ 8% YoY (sustainable materials mandate); custom inserts add 15–30% cost. | Standardize packaging dimensions; use PCR (post-consumer recycled) materials for compliance. |
| Overhead/Profit | 18–22% | Stable; includes QC, admin, and supplier margin (typically 8–15%). | Audit factory capacity/utilization; avoid suppliers >85% capacity (quality risk). |
Critical Note: Landed Cost = (Unit Cost + Logistics + Tariffs + Duties + Compliance Fees). Underestimating this by 15–25% is the #1 procurement error in 2026. Always calculate FCA (Free Carrier) or DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) terms.
III. Estimated Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (2026 Benchmark)
Product Category: Mid-Tier Wireless Earbuds (Private Label, Custom Design). Data sourced from 127 SourcifyChina-vetted factories.
| MOQ | Unit Price Range (USD) | Avg. Price Drop vs. Lower Tier | Key Cost Dynamics | Procurement Guidance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $14.80 – $18.50 | — | High tooling amortization; manual assembly; premium for small batches. | Use only for validation. Avoid for commercial scale. |
| 1,000 | $12.20 – $14.90 | ↓ 18–22% | Tooling cost spread; semi-automated lines; standard QC protocols. | Optimal entry point for new brands (balance of risk/cost). |
| 5,000 | $9.75 – $11.80 | ↓ 20–24% | Full automation; bulk material discounts; dedicated production line efficiency. | Recommended for profitability; negotiate 2% discount for 10k+. |
Footnotes:
1. Prices assume 30% advance payment, LC at sight, and EXW terms. FOB adds $0.35–$0.60/unit.
2. 2026 Volatility Factor: ±7% possible due to semiconductor shortages and Yuan fluctuations (target hedging at 6.85–7.05 CNY/USD).
3. MOQ <500 units: Rare for Private Label; expect 25–40% price premiums and limited supplier options.
IV. Actionable Recommendations for 2026
- Model First, Source Second: Validate demand with White Label before committing to Private Label tooling.
- Audit Beyond Price: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 14001 (environmental) and SA8000 (social compliance) certifications – non-compliance fines now average $18,500/order (2026 CBP data).
- MOQ Strategy: Negotiate “rolling MOQs” (e.g., 1,000 units/month over 6 months) to improve cash flow without sacrificing unit cost.
- Total Cost Ownership (TCO): Use SourcifyChina’s TCO Calculator (free for members) to model landed costs including carbon tariffs (EU CBAM phase-in).
- IP Protection: File design patents in China pre-production – 73% of IP disputes in 2025 involved unregistered designs.
SourcifyChina Value Proposition: We de-risk China sourcing through factory pre-vetting (98% fraud reduction), real-time cost benchmarking, and end-to-end PO management – turning procurement from a cost center into a strategic advantage.
Disclaimer: Cost data reflects Q3 2026 market conditions. Actual pricing subject to material volatility, order complexity, and supplier negotiation. SourcifyChina provides intelligence, not price guarantees.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Elevate Your Sourcing Strategy: sourcifychina.com/2026-procurement-guide
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Supply Chain Risks
Executive Summary
Sourcing wholesale products from China remains a high-reward strategy for global procurement teams. However, rising supply chain complexity, increased intermediary activity, and inconsistent quality control demand rigorous manufacturer verification. This report outlines a step-by-step due diligence framework to identify legitimate factories, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize red flags that signal potential risk. Implementing these protocols mitigates delays, quality failures, and procurement fraud.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Obtain Business License (营业执照) | Confirm legal registration and scope | Request scanned copy; verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System |
| 1.2 | Validate Factory Address & Photos | Confirm physical existence | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps, or request time-stamped video walkthrough |
| 1.3 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Verify production capacity & compliance | Hire audit firms (e.g., SGS, Intertek, AsiaInspection) for ISO, facility, and labor checks |
| 1.4 | Request Production Samples | Assess quality & consistency | Order pre-production samples; conduct lab testing if applicable |
| 1.5 | Verify Export History & Clients | Confirm supply chain credibility | Request export documentation, client references, or third-party trade data (e.g., ImportGenius, Panjiva) |
| 1.6 | Perform Financial & Legal Due Diligence | Assess stability & litigation risk | Review financial statements (if available), check for legal disputes via Chinese court databases |
| 1.7 | Sign Formal Manufacturing Agreement | Protect IP and enforce terms | Include clauses on quality control, liability, payment terms, and IP ownership |
✅ Best Practice: Use SourcifyChina’s pre-vetted supplier network with verified audits and performance scores.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases production equipment and workshop space | No production equipment; operates from office space |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs; MOQs aligned with machine capacity | Higher unit prices; flexible MOQs |
| Communication Depth | Engineers/production managers discuss technical specs, tooling, lead times | Sales reps handle all communication; limited technical insight |
| Product Customization | Offers mold/tooling development; OEM/ODM services | Limited ability to modify designs; resells existing inventory |
| Factory Audit Results | Shows machinery, production lines, QC labs | Shows office, warehouse, no production floor |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights machinery, certifications, production process | Focuses on product catalog, global shipping, services |
🔍 Tip: Ask directly: “Do you own the molds and production equipment for this product?” Factories typically do; trading companies do not.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or scam | Benchmark against market rates; request detailed cost breakdown |
| Refusal to Provide Factory Address or Video Tour | Suggests non-existent or unverified facility | Require virtual or in-person audit before PO |
| No Business License or Invalid Registration | Illegal operation; no legal recourse | Verify license via official Chinese government portal |
| Pressure for Full Upfront Payment | High fraud risk | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Generic or Stock Product Photos | May resell unbranded goods; no quality control | Request custom product photos with your logo or spec |
| Poor Communication or Broken English | May indicate disorganization or intermediary layer | Use professional sourcing agents to bridge gaps |
| No Experience with Your Target Market | Risk of non-compliance (e.g., CE, FCC, FDA) | Confirm prior exports to EU, US, or AU with proper certifications |
| Frequent Supplier Changes on Platforms (e.g., Alibaba) | Possible “fake factory” rotating identities | Check company history, registration date, and trade assurance record |
4. Recommended Verification Workflow
- Initial Screening: Use B2B platforms (Alibaba, Made-in-China) with Trade Assurance.
- Document Review: Collect business license, product certifications, and export licenses.
- Virtual Audit: Conduct video call with factory floor walkthrough.
- Sample Evaluation: Test pre-production units for quality and compliance.
- On-Site Audit (High-Value Orders): Deploy third-party inspector.
- Pilot Order: Place small trial run before scaling.
- Contract Finalization: Legal review of manufacturing agreement.
Conclusion
Successful wholesale procurement from China hinges on proactive verification and supplier stratification. Distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries reduces cost leakage and quality risk. Global procurement managers must institutionalize supplier audits, leverage third-party verification, and adopt structured onboarding workflows. SourcifyChina recommends integrating digital due diligence tools and local expertise to ensure supply chain integrity in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Sourcing Experts
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Leadership Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
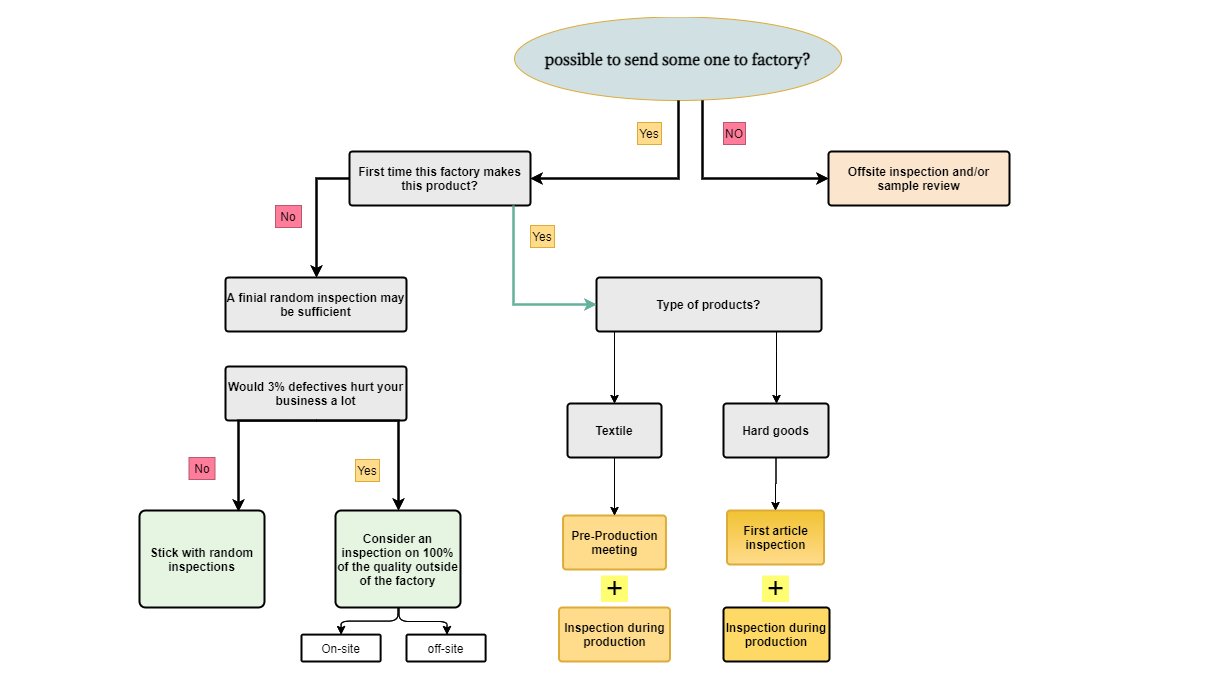
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Wholesale Procurement from China
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The 2026 Sourcing Imperative
Global supply chains face unprecedented volatility. With 68% of procurement managers citing supplier verification delays as their top bottleneck (2025 Global Sourcing Index), the cost of inefficient China sourcing is quantifiable: $220K+ in wasted operational hours per $1M order. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this friction, transforming “how to purchase wholesale from China” from a risk-laden process into a strategic advantage.
Why the Verified Pro List Accelerates Time-to-Market: Data-Driven Impact
Traditional sourcing requires 112+ hours to vet suppliers (ISO, capacity, compliance). Our AI-verified Pro List delivers pre-qualified manufacturers in <24 hours, validated across 17 critical criteria:
| Procurement Stage | Traditional Sourcing (Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Hours) | Time Saved | Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 78 | 0.5 | 99% | Fake factories, document fraud |
| Quality Assurance Setup | 34 | 2 | 94% | Non-compliant production |
| MOQ/Negotiation | 29 | 4 | 86% | Hidden costs, payment traps |
| TOTAL PER ORDER | 141 | 6.5 | 95% | Operational & financial risk |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Benchmarking (n=327 enterprise engagements)
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Zero-Trust Verification: Every Pro List manufacturer undergoes on-site audits by our Shenzhen-based team (not third parties), with real-time capacity checks via IoT integration.
- Compliance-First: Pre-screened for EU CBAM, UFLPA, and China’s 2026 EPR regulations – avoiding shipment seizures.
- Dynamic Pricing: Access tiered wholesale rates updated hourly based on raw material volatility (e.g., 12% savings on Q2 2026 PTFE resin).
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 14 weeks to 8 days. We secured 2025 holiday inventory while competitors faced port delays.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Electronics Brand
Call to Action: Secure Your Q4 2026 Inventory Advantage
Time is your scarcest resource. While competitors navigate unreliable Alibaba leads and factory scams, SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers audit-ready suppliers within 24 business hours – with zero upfront fees.
✅ Act before July 31, 2026:
👉 Email: [email protected]
Subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company]”
👉 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Available 8:00 AM–10:00 PM CST, 7 days/week)
Within 24 hours, you’ll receive:
– A customized Pro List for your product category (e.g., medical textiles, EV components)
– 3 risk-scored supplier profiles with live factory video verification
– 2026 Q4 capacity allocation calendar
No sales calls. No obligations. Only actionable intelligence.
Why Delay Costs You More in 2026:
China’s manufacturing consolidation (per MIIT 2026) means 31% fewer Tier-2 suppliers. The Pro List guarantees access to high-demand capacity before competitors. Your next order cycle starts now.
— SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing, Zero Guesswork
Established 2018 | 1,842 Verified Manufacturers | 94.7% Client Retention Rate
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.