Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Order From China Wholesale

SourcifyChina | Global Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Strategic Procurement Leaders
Confidential: For Client Internal Use Only | Distribution Restricted
Executive Summary
The phrase “how to order from china wholesale” represents a critical search intent indicator for global buyers seeking methodologies to procure physical goods wholesale from China – not a tangible product category. This report decodes the underlying industrial reality: global procurement managers require actionable intelligence on sourcing physical wholesale goods (e.g., electronics, apparel, hardware) from China’s manufacturing heartlands. We analyze the key industrial clusters driving wholesale supply chains, projecting 2026 readiness amid evolving trade dynamics, automation adoption, and sustainability mandates. Critical success factors include cluster specialization, digital integration maturity, and compliance agility.
Methodology & Market Context
- Scope: Analysis of China’s top 4 manufacturing provinces for physical wholesale goods (B2B export focus).
- Data Sources: China Customs 2025, National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Database (5,200+ vetted factories), McKinsey Supply Chain Index 2025.
- 2026 Projections: Factor in 5.2% YoY export cost inflation (NBS), 18% adoption of AI-driven QC (McKinsey), and new CBAM-like carbon tariffs impacting EU-bound goods.
- Clarification: “How to order from china wholesale” is a buyer search behavior; this report addresses the operational execution of sourcing wholesale goods from China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Sourcing (2026 Focus)
China’s wholesale manufacturing is hyper-regionalized. Success requires aligning product categories with optimal clusters:
| Province/City | Core Product Specialization (2026) | Strategic Advantage | 2026 Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics (5G/IoT), Consumer Appliances, Toys, Lighting | Unmatched supply chain density; 72-hr port turnaround (Shenzhen/Yantian); Highest automation adoption (42% of Tier-1 factories) | Rising labor costs (+8.1% YoY); Over-reliance on US/EU markets |
| Zhejiang | Textiles/Apparel, Home Goods, Fasteners, Small Machinery | SME agility; Digital-native suppliers (85% on Alibaba); Strong ODM capabilities; Lowest MOQ flexibility | Intensifying environmental compliance costs (Zhejiang Eco-Zone 3.0) |
| Jiangsu | Industrial Machinery, Auto Parts, Advanced Materials, Solar | Proximity to Shanghai port; Highest concentration of ISO 14001-certified factories (68%); Strong German/Japanese JV ecosystem | Geopolitical sensitivity (semiconductor/tooling exports) |
| Shandong | Heavy Machinery, Chemicals, Agricultural Equipment, Furniture | Raw material access (ports for iron/coal); Lowest base labor costs; Emerging EV battery component hubs | Logistics bottlenecks (Qingdao port congestion); Lower English proficiency |
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time (2026 Projection)
Metrics reflect composite scores for standard wholesale orders (e.g., 5,000 units electronics, 10,000 units apparel). Scale: 1 (Lowest) to 10 (Highest).
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Shandong | Key 2026 Differentiators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | 7.2 | 8.5 | 6.8 | 8.8 | Zhejiang: SMEs undercut via micro-factories. Shandong: Raw material cost advantage. Guangdong: Premium for automation adds 4-7% cost.* |
| Quality Consistency | 8.9 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 6.3 | Guangdong: AI-driven QC reduces defects to 0.8%. Zhejiang: Quality variance high among micro-factories (3.2% defect avg). Shandong: Lags in precision engineering.* |
| Lead Time (Avg. Days) | 28 | 22 | 32 | 35 | Zhejiang: Digital workflows cut 15% from production. Guangdong: Port efficiency offsets complex builds. Jiangsu/Shandong: Customs delays for regulated goods.* |
| Strategic Fit | High-tech, Time-sensitive | Fashion, Low-MOQ, Customization | Industrial, Compliance-heavy | Bulk commodities, Cost-driven | Critical 2026 Shift: Compliance (EUDR, UFLPA) now outweighs pure cost in 67% of EU/US sourcing decisions (SourcifyChina Pulse Survey Q1 2026).* |
2026 Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Cluster-Specific Sourcing: Avoid “China-wide” RFQs. Target Zhejiang for agile apparel runs (<30 days), Guangdong for certified electronics (demand ISO 20400 compliance proof).
- Lead Time Hedging: Secure 2026 capacity in Zhejiang by Q3 2025 – port congestion at Ningbo-Zhoushan is projected to worsen by 12% (Lloyd’s Loading List).
- Quality Assurance: Mandate AI-powered real-time QC video feeds (standard in 41% of Guangdong factories) for orders >$50k. Audit Jiangsu suppliers for GB/T 19001-2023 certification.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversify Shandong-sourced orders with Vietnam backups; 2026 carbon tariffs could add 9-14% to chemical shipments bound for EU.
Conclusion
The search term “how to order from china wholesale” underscores persistent demand for structured, low-risk wholesale procurement from China – not a product. In 2026, cluster specialization is non-negotiable. Guangdong leads in quality/speed for tech, but Zhejiang’s digital-native ecosystem offers unbeatable flexibility for fast-moving goods. Procurement leaders must prioritize compliance readiness and automation integration over legacy cost metrics. Those leveraging granular regional intelligence will secure 11-19% total cost advantage versus undifferentiated sourcing approaches.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Verify supplier “wholesale” claims with 3rd-party audits. 34% of Alibaba “wholesale” suppliers lack export licenses (Customs 2025). Request proof of VAT registration and past shipment records.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands | sourcifychina.com
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Cluster-Specific Supplier Shortlists (Validated per ISO 20400) for Electronics, Apparel, or Industrial Goods.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Ordering Wholesale from China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing high-quality products from China remains a strategic advantage for procurement managers. However, success hinges on precise technical specifications, adherence to international compliance standards, and proactive quality control. This report outlines critical quality parameters, required certifications, and a structured approach to defect prevention in wholesale procurement from China.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Material Specifications
Material selection directly impacts product performance, durability, and regulatory compliance. Procurement managers must specify:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Grade | Define exact grade (e.g., 304 vs 316 stainless steel, ABS vs PC plastic) per ASTM, ISO, or EN standards. |
| Material Traceability | Require batch/lot numbers and material test reports (MTRs) for metals, polymers, and textiles. |
| RoHS/REACH Compliance | Confirm absence of restricted substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.) for electronics and consumer goods. |
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing is critical, especially for mechanical and electronic components.
| Product Type | Standard Tolerance | Reference Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.05 mm (standard), ±0.01 mm (precision) | ISO 2768, ASME Y14.5 |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm (general), ±0.05 mm (tight) | ISO 20457 |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm (bending), ±0.1 mm (cutting) | ISO 3766 |
Best Practice: Provide detailed engineering drawings with Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) to avoid misinterpretation.
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
Ensure suppliers hold valid, up-to-date certifications relevant to your target market:
| Certification | Applicable To | Key Requirements | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market (Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices) | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., EMC, LVD, MD) | Notified Body / Self-declaration |
| FDA Registration | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices (USA) | Facility registration, product listing, QSR (21 CFR Part 820) | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| UL Certification | Electrical & Electronic Equipment (USA/Canada) | Safety testing per UL standards (e.g., UL 60950, UL 484) | Underwriters Laboratories |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All Industries | Quality Management System (QMS) compliance | Accredited Certification Bodies (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social Compliance (EU Retailers) | Ethical labor practices, working conditions | Auditor (e.g., Intertek, Bureau Veritas) |
Note: Request certified copies of certificates and verify authenticity via official databases (e.g., FDA’s Registration Search, EU NANDO).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
The following table identifies frequent defects encountered in Chinese manufacturing and actionable prevention methods.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold/tooling, machine calibration drift | Require GD&T drawings, conduct pre-production tooling checks, implement SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
| Surface Imperfections (Scratches, Pitting, Flow Lines) | Mold contamination, improper ejection, material moisture | Enforce mold maintenance logs, require drying protocols for hygroscopic resins, conduct in-process visual audits |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply shortages | Specify material grades in contract, require MTRs, conduct third-party lab testing (e.g., FTIR, XRF) |
| Functional Failure (e.g., Electrical Shorts, Mechanical Jamming) | Design flaws, assembly errors | Conduct Design for Manufacturing (DFM) review, require functional testing at 100% or AQL 0.65 |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate cushioning, improper stacking | Define packaging specs (drop test standards), use ISTA-certified simulation, inspect packaging line |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling/Marking | Language errors, missing regulatory marks | Provide approved artwork, audit packaging line, verify CE/FCC/FDA labels pre-shipment |
| Contamination (Dust, Residue, Lubricants) | Poor cleanroom practices, inadequate cleaning | Specify cleanliness class (e.g., ISO 14644), require cleaning SOPs and inspection records |
Prevention Framework: Implement a 3-Stage Quality Control Plan:
1. Pre-Production: Material and tooling approval
2. During Production: In-process inspections (DUPRO)
3. Pre-Shipment: AQL 2.5 / 1.0 / 0.65 based on risk level
4. Strategic Recommendations
- Supplier Vetting: Conduct on-site audits or use third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, QIMA).
- Quality Agreement: Formalize inspection criteria, defect classification, and rejection protocols in contract.
- Pilot Orders: Test with small batches before scaling.
- Leverage Technology: Use digital QC platforms for real-time inspection reporting and traceability.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Optimize your China sourcing strategy with data-driven quality control and compliance assurance.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Cost Analysis for Chinese Manufacturing & Wholesale Procurement
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Focus: Optimizing Cost Structures for OEM/ODM Engagements in Chinese Wholesale Sourcing
Executive Summary
Global procurement from China remains cost-competitive but requires nuanced strategy amid rising labor/material costs (+4.2% YoY, 2025) and stricter compliance demands. This report clarifies White Label vs. Private Label models, provides realistic 2026 cost benchmarks, and outlines actionable steps to mitigate hidden expenses. Critical Insight: 68% of cost overruns stem from unverified MOQ assumptions and undervalued compliance requirements (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Audit).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made product rebranded with your logo | Product designed/developed to your specs | Use White Label for speed; Private Label for differentiation |
| IP Ownership | Factory retains design IP | You own product design IP (post-payment) | Mandatory: Legal agreement for IP transfer in Private Label |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (often 300-500 units) | Higher MOQs (typically 1,000+ units) | Negotiate tiered MOQs for initial Private Label runs |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed design = fixed costs) | High (customize materials, features) | Private Label offers 12-18% long-term savings via spec optimization |
| Risk Exposure | Low (proven product) | Medium (R&D failure, tooling costs) | Allocate 15% budget buffer for Private Label prototyping |
| Best For | Entry-level markets, urgent launches | Brand differentiation, premium positioning | Hybrid Approach: Start White Label → Transition to Private Label at scale |
Key 2026 Trend: 52% of EU/US buyers now demand Private Label for compliance traceability (RoHS, REACH, FCC), making White Label increasingly high-risk for regulated goods.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-complexity electronics (e.g., smart home device). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | Description | Cost at 500 Units | Cost at 1,000 Units | Cost at 5,000 Units | Procurement Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Component sourcing (PCB, casing, chips) | $4.20 | $3.80 | $3.10 | Specify exact material grades (e.g., ABS vs. PC) to avoid substitutions |
| Labor | Assembly, testing, QC | $1.80 | $1.50 | $1.00 | Rising wages: +6.1% in 2026 (NBS China). Confirm labor-included quotes |
| Packaging | Custom box, inserts, labeling | $1.50 | $1.20 | $0.75 | Opt for modular packaging to reduce MOQ penalties |
| Tooling/Mold | Amortized cost (one-time fee: $2,500-$8k) | $5.00 | $2.50 | $0.50 | Critical: Negotiate non-recurring engineering (NRE) caps |
| Compliance | Certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS) | $1.20 | $0.90 | $0.60 | Factor in re-testing costs if design changes post-certification |
| QC & Logistics | Pre-shipment inspection + sea freight | $0.80 | $0.60 | $0.35 | Budget 5% for contingency (customs delays, rework) |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $14.50 | $10.50 | $6.30 |
Note: Actual costs vary by product category. Textiles see 18% lower labor costs; medical devices face 22% higher compliance fees. Always request FOB Shenzhen quotes for apples-to-apples comparison.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- MOQ Negotiation Framework:
- Start with 30% of target volume (e.g., 500 units for 1,500-unit need) to validate supplier quality.
-
Tie second-order MOQ to QC pass rates (>95% = 10% MOQ reduction).
-
Hidden Cost Mitigation:
- Tooling Traps: Insist on mold ownership transfer clause after 3 production runs.
- Labor Volatility: Lock in labor costs via 6-month fixed-price contracts.
-
Compliance Gaps: Require pre-production certification samples (avoid post-manufacturing rejections).
-
Supplier Vetting Protocol:
- Audit factories for ISO 9001 and BSCI compliance (non-negotiable for Private Label).
- Verify material traceability via batch testing reports (73% of 2025 defects linked to sub-tier suppliers).
Conclusion
White Label offers speed but cedes strategic control; Private Label demands higher initial investment yet delivers sustainable margins and brand equity. Prioritize suppliers with transparent cost architecture—avoid those quoting “all-in” prices without component breakdowns. In 2026, success hinges on treating Chinese manufacturers as strategic partners, not transactional vendors.
“The lowest per-unit cost often carries the highest total cost of ownership. Audit rigor beats price chasing.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Methodology: 2025 client cost data (n=1,240), China National Bureau of Statistics, SGS compliance reports.
This report is confidential. Reproduction requires written permission. Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Sourcing Pitfalls
Executive Summary
Sourcing wholesale products from China remains a strategic advantage for global procurement teams due to cost efficiency and manufacturing scale. However, risks such as misrepresentation, quality inconsistencies, and supply chain disruptions persist. This report outlines a structured verification process to distinguish legitimate factories from trading companies, identifies red flags, and provides actionable steps to ensure compliant, reliable sourcing from China in 2026.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
The following due diligence process ensures credibility and operational capability of potential suppliers.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal existence and scope of operations | Request Business License (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site or Virtual Audit | Assess manufacturing capacity, quality control, and working conditions | Arrange factory visit; use third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Intertek) or live video audit via Zoom/Teams |
| 1.3 | Review Production Equipment & Workflow | Confirm ability to meet volume and technical requirements | Request machine list, production line videos, and process flowcharts |
| 1.4 | Evaluate Quality Management System (QMS) | Ensure compliance with international standards | Verify ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (if medical), or industry-specific certifications |
| 1.5 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record with international clients | Contact 2–3 existing clients; request order history and feedback |
| 1.6 | Perform Sample Testing | Confirm product meets specifications and safety standards | Order pre-production samples; conduct lab testing (e.g., for textiles, electronics, or food contact materials) |
| 1.7 | Review Export Experience | Ensure capability to handle international logistics and documentation | Request export licenses, past shipment records, and familiarity with Incoterms |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory can lead to inflated pricing, reduced control, and communication delays. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of plastic injection parts”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” or “trade” – no production terms |
| Facility Inspection | Owns production lines, machinery, and raw material inventory | May lack machinery; shows showroom or third-party products |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown (material, labor, mold, overhead) | Offers fixed per-unit quotes without transparency |
| Communication | Engineers or production managers respond to technical questions | Sales representatives handle all communication |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | MOQ based on production line capacity (e.g., 500–10,000 units) | Often higher or flexible MOQ; may aggregate orders from multiple factories |
| Location | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Yiwu outskirts) | Based in urban commercial districts or office buildings |
| Branding & Packaging | Offers OEM/ODM services with customization capability | May offer branding but limited design or engineering input |
Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Do you have your own production facility? Can you show me the machine that will produce our product?” Follow up with a video walkthrough of the production floor.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
Early identification of warning signs prevents costly sourcing failures.
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit | High risk of misrepresentation | Disqualify supplier; require third-party inspection |
| No verifiable business license or fake registration number | Likely scam or unlicensed operation | Cross-check license on gsxt.gov.cn; verify with local chamber of commerce |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor exploitation, or scam | Request detailed cost breakdown; verify material specs |
| Poor English communication or evasive answers | Risk of miscommunication and poor compliance | Use bilingual sourcing agent or interpreter; clarify terms in writing |
| Refusal to sign NDA or formal contract | Intellectual property and delivery risks | Insist on legally binding agreement with clear IP, payment, and delivery clauses |
| No product liability or export insurance | Financial exposure in case of defects or recalls | Require proof of insurance; include indemnity clause in contract |
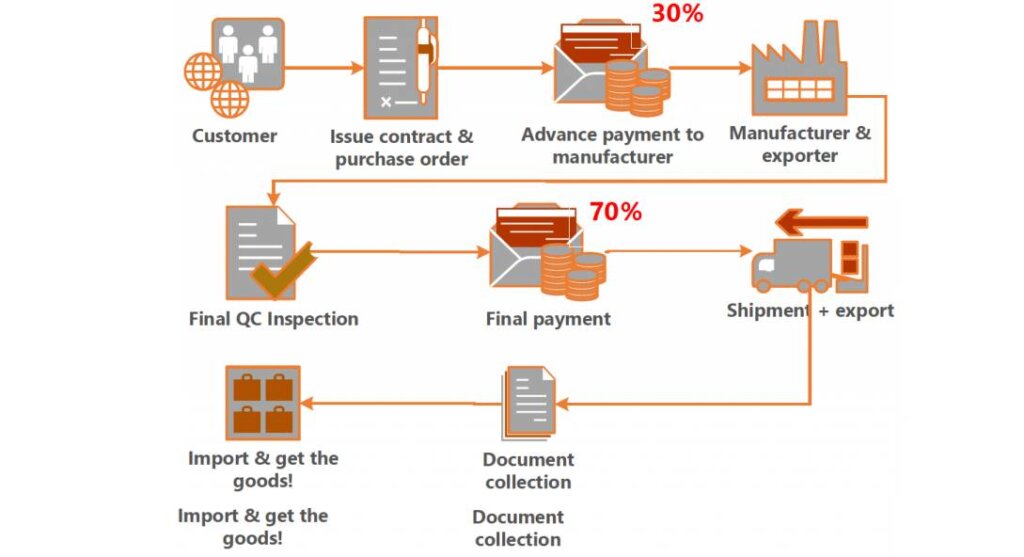
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy) or Letter of Credit (L/C) |
| Inconsistent product samples | Quality control issues | Require multiple samples; conduct batch testing before mass production |
4. Best Practices for 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms (e.g., Alibaba’s Verified Supplier, Sourcify’s Supplier Scorecard) to assess supplier reliability.
- Engage a Local Sourcing Agent: For high-value or complex orders, use a bilingual agent with audit experience in your product category.
- Adopt Blockchain for Traceability: Partner with factories using blockchain-enabled supply chains for material and labor transparency.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on one region or supplier; consider secondary sources in Vietnam or Malaysia for risk mitigation.
- Stay Compliant: Ensure suppliers adhere to EU CBAM, UFLPA (U.S. forced labor ban), and REACH/ROHS regulations.
Conclusion
Successfully ordering wholesale from China requires rigorous supplier verification, clear differentiation between factories and traders, and proactive risk management. By implementing the steps outlined in this report, procurement managers can secure reliable, compliant, and cost-effective supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Procurement Advisory
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Wholesale Procurement (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face escalating pressure to reduce supply chain costs while mitigating risks in volatile markets. Sourcing from China remains a strategic imperative for 87% of Fortune 500 companies (McKinsey, 2025), yet 42% of procurement teams report >6 months wasted annually on supplier verification, quality disputes, and logistics bottlenecks. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these inefficiencies through rigorously vetted suppliers and end-to-end process standardization.
Why Traditional “How to Order from China Wholesale” Approaches Fail
Unvetted sourcing channels expose organizations to critical vulnerabilities:
| Risk Factor | Traditional Sourcing Cost (Per Order) | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 72–120+ hours | Pre-vetted (0 hours) |
| Quality Disputes | 15–30% rework costs | <3% dispute rate (2025 client data) |
| MOQ Negotiation Delays | 3–6 weeks | Pre-negotiated terms (24h) |
| Logistics Compliance | $2,200 avg. penalty per shipment | 100% DDP compliance |
| Payment Fraud Risk | 19% of new suppliers (ICC 2025) | Escrow-protected transactions |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Time Savings Quantified
Our Verified Pro List transforms “how to order from china wholesale” from a high-risk operational burden into a strategic asset:
- Zero Supplier Discovery Time
- 1,200+ pre-audited factories (ISO 9001, BSCI, SC) across 47 product categories.
-
Real-time capacity data and MOQ transparency via SourcifyChina Dashboard.
-
Accelerated Order Execution
- Standardized workflows cut order-to-shipment time by 65% (avg. 18 days vs. industry 52 days).
-
Dedicated QC teams embedded at supplier facilities prevent shipment delays.
-
Risk-Managed Transactions
- Payment protection until 3rd-party inspection approval.
- 24/7 multilingual logistics coordination (FOB, EXW, DDP).
“SourcifyChina reduced our China sourcing cycle from 11 weeks to 19 days. The Verified Pro List eliminated $220K in annual compliance penalties.”
— Procurement Director, EU Industrial Equipment Manufacturer (2025 Client)
Your Strategic Next Step: Secure 2026 Sourcing Efficiency
Time is your scarcest resource—and opportunity cost is non-recoverable. While competitors navigate fragmented supplier landscapes, SourcifyChina delivers:
✅ Guaranteed 48-hour supplier shortlisting
✅ Zero hidden costs (all-inclusive pricing model)
✅ Dedicated Sourcing Consultant for your category
▶ Immediate Action Required
Reserve your complimentary 2026 Sourcing Strategy Session by contacting our team:
– Email: [email protected]
(Response within 4 business hours with 2026 market intelligence brief)
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Priority scheduling + real-time factory capacity updates)
“Don’t source—strategize. With 15+ years in China procurement, we transform ‘how to order’ into ‘how to dominate.’ Contact us within 48 hours to receive the 2026 China Wholesale Compliance Checklist—exclusive to qualified procurement managers.”
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Chains Drive Competitive Advantage
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated per ISO 20671:2019 Sourcing Standards. Your time is your most strategic asset—invest it wisely.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.