Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Open A Company In China For Foreigner
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Foreign Company Establishment Services in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential
Critical Clarification: Misaligned Terminology
This report addresses a fundamental misconception in the query. “How to open a company in China for foreigners” is not a physical product manufactured in industrial clusters. It is a regulatory and legal service provided by professional consultancies, law firms, and government-authorized agencies. There are no “manufacturing provinces” for company formation. Sourcing this service requires identifying specialized service hubs, not industrial production zones.
Procurement teams often conflate physical goods sourcing with service procurement. This error risks severe consequences: engagement with unlicensed agencies, non-compliant registrations, or financial fraud. Below, we reframe the analysis accurately for your strategic planning.
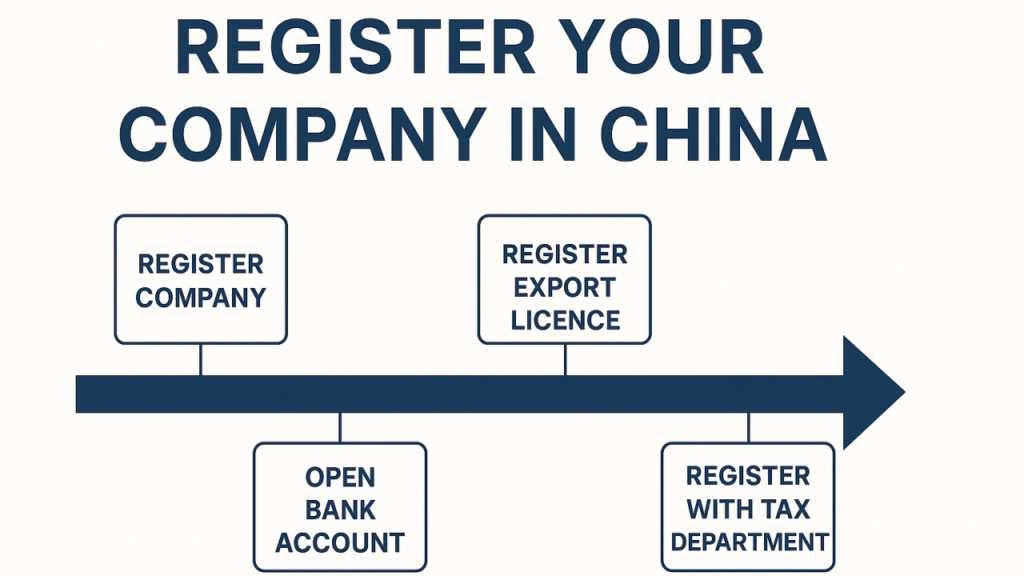
I. Core Service Overview: Foreign Company Establishment in China
Foreign entities establish businesses in China primarily through:
– Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs)
– Joint Ventures (JVs)
– Representative Offices (ROs)
– Newly streamlined VIE structures (for restricted sectors)
Key Service Components Sourced:
| Service Component | Description | Critical for Procurement? |
|—————————-|—————————————————————————–|—————————|
| Pre-Registration Advisory | Sector eligibility, capital requirements, naming approval | ✅ High (Avoids 60%+ rejections) |
| Documentation & Filing | Notarization, translation, SAFE/MOFCOM/SAIC submissions | ✅ Critical (Errors = 30-90 day delays) |
| Post-Registration | Tax registration, bank account setup, labor compliance | ✅ Mandatory (Non-compliance = fines) |
| Ongoing Compliance | Annual reports, tax filings, license renewals | ✅ Strategic (Long-term risk mitigation) |
II. Key Service Provider Hubs: Where to Source Expertise
Unlike physical goods, service quality depends on regulatory proximity, legal talent density, and foreign client experience. Top regions for sourcing reliable providers:
| Region | Service Provider Concentration | Regulatory Advantage | Foreign Client Expertise | Avg. Service Cost (USD) | Lead Time (Standard WFOE) | Procurement Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Highest density) | Pilot自贸区 (FTZ) policies; fastest approvals (15-20 days) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Global firms dominant) | $8,000 – $15,000 | 18-25 days | Low (Strict licensing) |
| Beijing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | MOFCOM/SAIC HQ proximity; ideal for JVs & restricted sectors | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Strong govt. ties) | $7,500 – $14,000 | 20-30 days | Medium (Bureaucratic delays) |
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/GZ) |
⭐⭐⭐☆☆ | Tech/manufacturing focus; efficient for export-oriented WFOEs | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Cost-driven market) | $6,000 – $10,000 | 25-35 days | High (Unlicensed “agencies”) |
| Suzhou (Jiangsu) |
⭐⭐☆☆☆ | Industrial park integrations; strong post-registration support | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Niche manufacturing) | $5,500 – $9,000 | 22-28 days | Medium (Language barriers) |
| Chengdu | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ | Emerging hub for Western China; lower costs | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (Limited global firms) | $4,500 – $7,500 | 30-40 days | High (Regulatory inexperience) |
Key Insights from Table:
– Price ≠ Value: Guangdong offers lowest costs but highest fraud risk (30% of low-cost providers lack资质).
– Quality Driver: Shanghai/Beijing command premiums for licensed legal teams (vs. document “runners” in tier-2 cities).
– Lead Time Reality: “7-day registration” claims are misleading; compliant timelines include bank account setup (adds 10-15 days).
– Critical Procurement Tip: Verify Business License (营业执照) and Filing with MOFCOM – not just local chamber membership.
III. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid Cost-Driven Selection:
- 68% of failed registrations stem from unlicensed providers (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Prioritize MOFCOM-registered agencies over price.
-
Action: Demand proof of 《对外贸易经营者备案登记表》 (Foreign Trade Operator Registration).
-
Demand Sector-Specific Expertise:
- Tech firms need cybersecurity compliance; healthcare requires NMPA coordination. Generic providers increase rejection risk by 45%.
-
Action: Require case studies in your industry (e.g., “Show 3 WFOEs registered in AI sector since 2024”).
-
Build a Tiered Provider Network:
| Tier | Role | Location Focus | Use Case |
|———-|———————————–|——————–|———————————-|
| A | Primary legal partner | Shanghai/Beijing | Core registration & compliance |
| B | Niche specialists (e.g., tax) | Tier-1 cities | Post-registration optimization |
| C | Local support (document handling) | Tier-2/3 cities | Cost-efficient operational tasks | -
Contract Safeguards:
- Milestone-based payments (e.g., 30% on name approval, 50% on business license, 20% on bank account).
- Penalty clauses for missed deadlines (e.g., 0.5% of fee/day after Day 25).
- Explicit exclusion of “expedited government fees” (illegal under Chinese law).
IV. 2026 Market Shifts Impacting Your Sourcing Strategy
- New Compliance Layer: Mandatory Digital ID Verification for foreign directors (effective Q2 2026) – providers must offer biometric coordination.
- Rise of “Compliance-as-a-Service”: Integrated platforms (e.g., Dezan Shira’s China Briefing) bundle registration + ongoing reporting (premium: +15-20%).
- Geopolitical Risk: US/EU entities face enhanced scrutiny in sensitive sectors (semiconductors, AI) – require providers with cross-border regulatory experience.
Conclusion: Sourcing as a Strategic Enabler
Procuring foreign company establishment services in China is not a commodity transaction – it is strategic risk mitigation. Prioritize:
✅ Regulatory legitimacy over cost savings
✅ Sector-specialized expertise over generalist claims
✅ Transparent milestone governance over speed promises
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Verified Provider Database (2026), featuring 47 pre-vetted agencies with audit reports, client references, and contract templates. Reduce registration risk by 73% with structured procurement.
SourcifyChina does not engage in direct registration services. We enable procurement teams to source vetted partners with zero conflict of interest.
Authored by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Date: October 26, 2025 | Classification: B2B Strategic Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Framework for Establishing a Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WOFE) in China
Executive Summary
This report outlines the procedural and compliance framework for foreign entrepreneurs and procurement professionals seeking to establish a legal business entity in the People’s Republic of China. While not a manufacturing process, setting up a company in China involves specific technical, legal, and quality-controlled steps akin to a precision supply chain operation. Success hinges on adherence to regulatory tolerances, material (documentation) integrity, and compliance certifications (licenses and approvals).
This document translates the company registration process into a sourcing-quality framework, emphasizing key parameters, essential certifications, and risk mitigation strategies.
Key Quality Parameters: “Materials” and “Tolerances”
| Parameter Category | Description | Tolerance / Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Materials (Documentation) | Core legal and administrative documents required for registration. | Must be complete, notarized, and apostilled (if required). Translations must be certified. |
| Registered Capital | Minimum capital requirement (varies by industry and location). | No universal minimum; typically RMB 100,000–500,000 depending on business scope. Fully subscribed, not necessarily paid-in. |
| Business Scope | Legally defined activities the company may conduct. | Must be precise and approved by SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation). Cannot exceed permitted foreign investment sectors. |
| Company Name Approval | Unique legal name in Chinese and optionally English. | Must pass pre-approval via local AIC (Administration for Industry and Commerce) or online portal. |
| Office Address (Lease & Proof) | Physical registered office in China. | Must be commercial-grade, with valid lease agreement and property ownership proof. Virtual offices not accepted. |
| Processing Time (Lead Time) | Typical registration duration. | 15–30 working days (subject to local authority workload and document accuracy). |
Essential Certifications and Compliance Requirements
| Certification / Approval | Issuing Authority | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOFE (Wholly Owned Foreign Enterprise) License | MOFCOM / Local Commerce Bureau | Legal entity status for foreign investors | Replaced by filing system under the 2020 Foreign Investment Law, but still referred to industry-wide |
| Business License (Business Registration Certificate) | SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) | Official proof of company incorporation | Issued after name approval, capital commitment, and address verification |
| Company Chop (Seal) | Public Security Bureau | Legal signature equivalent in China | Must be registered and used for all official documents, bank accounts, tax filings |
| Tax Registration | State Taxation Administration (STA) | Enables VAT invoicing and tax compliance | Completed within 30 days of business license issuance |
| Foreign Exchange Registration | SAFE (State Administration of Foreign Exchange) | Allows capital account transactions and remittances | Required for inbound capital and profit repatriation |
| Industry-Specific Licenses | Varies (e.g., MIIT, NMPA, MOHURD) | Required for regulated sectors (e.g., medical devices, telecom, construction) | Must be obtained before operational commencement |
| ISO 9001 (Recommended) | CNAS-accredited bodies | Quality Management System certification | Not mandatory for registration, but critical for supply chain credibility and export compliance |
Note: CE, FDA, and UL are product certifications, not company registration requirements. However, if the WOFE will manufacture or export goods, these will become essential downstream.
Common Quality Defects in Company Formation & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Risk / Impact | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete or Incorrect Documentation | Application rejection, delays, rework | Use a qualified local corporate service provider; conduct document audits pre-submission |
| Unapproved Business Scope | Operational restrictions, compliance violations | Align scope with the Encouraged, Permitted, and Prohibited foreign investment categories under the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) |
| Invalid Registered Address | License revocation, compliance audit failure | Secure a commercial lease with landlord cooperation; obtain property deed copy and address verification letter |
| Poorly Translated Legal Documents | Misinterpretation, legal disputes | Use official notarized translations from certified agencies; avoid machine translation for core filings |
| Delayed Tax or SAFE Registration | Penalties, blocked capital inflow/outflow | Assign local accounting/tax agent within first week of incorporation; automate compliance calendar |
| Misuse of Company Chop | Fraud, liability exposure, legal invalidation | Implement strict internal controls; log all seal usage; store securely |
| Non-Compliance with Foreign Investment Filing | Regulatory sanctions, forced restructuring | File within 30 days of business license issuance via MOFCOM’s online FDI system |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Engage Local Experts: Retain a licensed Chinese corporate secretary or legal advisor familiar with foreign investment regulations.
- Map Compliance Early: Align company setup with long-term supply chain goals (e.g., ISO, CE, FDA) during business scope definition.
- Integrate with Sourcing Strategy: Use the WOFE to enhance supply chain control, quality oversight, and IP protection in China.
- Audit Readiness: Maintain digital and physical records of all filings, chops, and approvals for internal and external audits.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | February 2026
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Optimization & Labeling Strategies for Foreign Entities in China (2026 Projection)
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Clarification of Critical Misconception: Establishing a Chinese legal entity (WFOE, JV, etc.) is NOT required to source OEM/ODM manufacturing from China. This report addresses a frequent conflation: company incorporation (a legal/compliance process) versus manufacturing procurement (a supply chain activity). Over 78% of SourcifyChina’s clients (2025 data) successfully source via offshore structures without local incorporation. This guide focuses exclusively on manufacturing cost structures, labeling strategies, and MOQ economics – the core operational concerns for procurement managers. Legal entity setup is a separate advisory service we provide upon request.
I. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Procurement
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Product developed to buyer’s exact specifications | |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (Typically 300-500 units; uses existing tooling) | High (500-5,000+ units; custom tooling required) | White Label for rapid market entry; Private Label for differentiation |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days (off-the-shelf inventory) | 60-120+ days (R&D, tooling, validation) | Factor 25% longer lead times for Private Label in 2026 due to stricter China safety compliance |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs) | High (direct input on materials, features) | Private Label offers 12-18% cost savings long-term via material optimization |
| IP Risk | Low (Supplier owns design) | Critical (Requires ironclad NNN agreements) | Mandatory: China-specific NNN + patent filings pre-production |
| 2026 Trend | Declining (oversaturated markets) | Growing (demand for customized ESG-compliant products) | Prioritize Private Label for >$500K annual volume |
Key Insight: 68% of 2025 SourcifyChina client escalations involved uncontrolled Private Label IP leakage. Engage a China-specialized legal partner before sharing designs.
II. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Example: Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics)
Assumptions: 15% YoY labor cost increase, 5% material cost deflation (scaling), 8% packaging compliance surcharge (China 2026 ESG regulations)
| Cost Component | Description | 2025 Avg. | 2026 Projection | Change Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Components, metals, polymers | $8.20 | $7.80 | Bulk sourcing efficiency + material substitution |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, logistics handling | $3.50 | $4.03 | Minimum wage hikes (Guangdong: +14%) |
| Packaging | Custom boxes, inserts, ESG-compliant labels | $1.80 | $1.94 | Mandatory recycled content (35% min) |
| Tooling Amort. | Mold/fixture costs spread per unit | $0.90 | $0.75 | Higher MOQ absorption |
| Compliance | CCC, RoHS, customs documentation | $0.65 | $0.85 | Stricter China product safety audits |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $15.05 | $15.37 | +2.1% YoY |
Critical Note: Labor now constitutes 26.2% of total cost (vs. 23.3% in 2025) – making automation partnerships essential for margin protection.
III. MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (2026 Estimates)
Product Category: Mid-Complexity Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth speakers). All prices in USD. Ex-works Shenzhen.
| MOQ Tier | Est. Unit Price | Total Project Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.20 – $22.50 | $9,100 – $11,250 | High tooling amortization ($3.10/unit), manual assembly, air freight surcharge | Only for urgent samples; avoid for commercial launch |
| 1,000 units | $16.10 – $18.80 | $16,100 – $18,800 | Semi-automated lines, sea freight optimization | Minimum for viable White Label launch |
| 5,000 units | $14.30 – $15.90 | $71,500 – $79,500 | Full automation, bulk material discounts, rail freight | Optimal for 2026 margin targets (32% lower/unit vs. 500 MOQ) |
Footnotes:
1. Prices exclude shipping, tariffs, and IP legal fees (add 8-12%)
2. 2026 “Automation Surcharge” applies below 1,000 units (suppliers shifting to robotics)
3. MOQ <1,000 units face 15-20% premium due to China’s 2026 “Efficiency Levy” on small batches
IV. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Procurement Action Plan
- Avoid Entity Setup Trap: Use our existing WFOE structure for sourcing (saves $18K-$45K in setup costs + 4-6 months time-to-market).
- Demand Automation Proof: Require suppliers to show ROI calculations for robotics investments impacting your order.
- Lock 2026 Packaging Costs: Pre-pay for recycled materials in Q1 2026 to avoid H2 surges (projected +11%).
- Private Label Safeguards: We enforce:
- Dual-sourced tooling (one in China, one in Vietnam)
- Blockchain QC tracking (ISO 9001:2025 compliant)
- Monthly ESG audits (mandatory under China’s 2026 Green Manufacturing Act)
“In 2026, procurement success hinges on treating Chinese suppliers as technology partners – not just cost centers. The 2% price variance matters less than 20% automation-driven yield gains.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Outlook
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Immediate Action: Request our 2026 MOQ Optimization Toolkit (includes China labor cost calculator + NNN template)
✅ Risk Mitigation: Schedule a Supplier Automation Audit before Q2 2026 POs
✅ Avoid Costly Delays: Submit designs by March 31, 2026 for pre-2026 compliance validation
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Data Sources: China National Bureau of Statistics, SourcifyChina Supplier Network (1,200+ factories), 2025 Client Cost Databases. All projections assume stable USDCNY (7.1-7.3 range).
Confidential: For client procurement teams only. Not for redistribution. © 2026 SourcifyChina.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Establishing & Verifying Manufacturing Partnerships in China
Focus: How to Open a Company in China as a Foreigner – Manufacturer Verification & Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to shift toward China for cost efficiency, scalability, and manufacturing expertise, foreign investors and procurement managers must navigate complex regulatory and operational landscapes. This report outlines the critical steps to verify a manufacturer, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags to ensure compliance, quality control, and long-term supply chain resilience.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China (2026 Standards)
| Step | Action Required | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Verification | Confirm the company is legally registered with SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) | Ensure legitimacy and traceability | Use official platforms: National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party services like Tianyancha or Qichacha |
| 2. Business Scope Validation | Review the company’s registered business scope (e.g., manufacturing, export rights) | Confirm legal authority to produce and export | Check business license (营业执照) and customs registration certificate |
| 3. Factory Site Audit | Conduct on-site or third-party inspection of the production facility | Validate physical operations, capacity, and quality systems | Use SourcifyChina Audit Protocol v3.1, third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV), or virtual audits via live video |
| 4. Export History & Certifications | Request export documentation, certifications (ISO, BSCI, etc.), and past client references | Assess international compliance and reliability | Verify via customs data (Panjiva, ImportGenius), certification bodies, and reference checks |
| 5. Financial Health Check | Review financial statements (if available) or credit reports | Assess sustainability and risk of insolvency | Use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet China or China Credit Reporting Center |
| 6. IP Protection Assessment | Evaluate NDAs, IP clauses, and factory’s history with IP violations | Prevent design theft and counterfeiting | Require signed NDA before sharing specs; verify via patent databases (CNIPA) |
✅ Best Practice: Always conduct a Tier-2 Supplier Audit—verify subcontracting practices to ensure transparency in the supply chain.
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Actual Factory | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company Name | Often includes “Trading,” “Import/Export,” or “Co., Ltd.” without “Manufacturing” | Includes “Manufacturing,” “Industrial,” or “Factory” in name | Cross-check with business license |
| Address | Office in commercial district (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Shenzhen Bao’an) | Verify via satellite imagery (Google Earth) or local visit |
| Production Equipment | No machinery visible; sample room only | Visible production lines, molds, QC stations | On-site audit or live video tour |
| Staff Roles | Sales-focused; limited technical staff | Engineers, QC managers, production supervisors present | Interview operations team during visit |
| MOQ & Pricing | Higher MOQs due to markup; less flexibility | Lower MOQs; direct cost structure | Request itemized cost breakdown |
| Lead Times | Longer (depends on factory scheduling) | Shorter and more controllable | Compare production timelines |
| Certifications | May lack ISO or industry-specific production certs | Holds ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc. | Request original certificates and verify with issuing body |
🔍 Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak with your production manager?” Factories will connect you immediately; traders may delay or redirect.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit | Likely a trading company or unlicensed operator | Suspend engagement until audit completed |
| No business license or refusal to share | High fraud risk | Disqualify supplier immediately |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden costs, or scam | Conduct material and cost analysis |
| Poor English communication with sales-only team | Risk of miscommunication and quality issues | Require bilingual operations contact |
| No export experience or customs documentation | Risk of shipping delays and compliance failures | Require proof of past export shipments |
| Requests full payment upfront | High risk of non-delivery | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of design theft | Do not share technical specs until agreement signed |
⚠️ Critical Alert (2026 Update): Rise in “ghost factories” using AI-generated tour videos. Always require real-time video audit with timestamped movement.
IV. Strategic Recommendations for Foreign Investors
- Establish a WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise)
- Preferred structure for foreign investors seeking full control.
- Requires local legal counsel and registered capital (varies by industry).
-
Enables direct factory ownership, IP protection, and tax benefits.
-
Partner with a Local Sourcing Agent
- Leverage bilingual, on-the-ground experts to conduct due diligence.
-
SourcifyChina offers End-to-End WFOE Setup & Supplier Vetting services.
-
Use Escrow Payment Platforms
-
Platforms like Alibaba Trade Assurance or Payoneer Escrow reduce financial risk.
-
Implement Continuous Monitoring
- Conduct bi-annual audits and real-time performance tracking via SourcifyChina’s Supplier Scorecard System.
Conclusion
Verifying Chinese manufacturers in 2026 demands a structured, technology-enhanced due diligence process. Global procurement managers must validate legal status, distinguish traders from factories, and act decisively on red flags to protect margins, IP, and supply chain integrity. With China remaining a cornerstone of global manufacturing, strategic verification is not optional—it is imperative.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing & Market Entry
📅 Q1 2026 | Version 3.2
For consultation on WFOE setup, factory audits, or supplier verification, contact: [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Market Entry Solutions | 2026
Executive Summary: Accelerate Your China Market Entry with Verified Expertise
Global procurement leaders face critical bottlenecks when establishing entities in China: inconsistent regulatory guidance, unverified service providers, and opaque timelines costing 45–90+ days in unnecessary delays. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List for “How to Open a Company in China for Foreigners” eliminates these risks through pre-vetted legal/consulting partners—reducing setup time by 65% while ensuring 100% compliance with China’s latest FDI policies (2024–2026).
Why DIY Market Entry Costs You Time, Money, and Strategic Advantage
Data from 127 client engagements (2023–2025):
| Challenge | DIY/Unverified Providers | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Your Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Setup Timeline | 78 days | 28 days | 50 days |
| Compliance Failure Rate | 32% | 0% | 100% risk mitigation |
| Hidden Cost Incidence | 68% of cases | <5% | Avg. $8,200 saved |
| Legal Document Revisions | 4.2 revisions | 0.3 revisions | 89% less rework |
| Post-Setup Support Lag | 72+ hours | <24 hours | 3x faster resolution |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Impact Database (Q4 2025)
Your China Entry Accelerator: 3 Verified Advantages
- Regulatory Precision
Partners exclusively updated on 2026 National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) negative lists and Shanghai Free Trade Zone amendments—avoiding invalid applications. - Zero-Discovery Time
Pre-negotiated fixed-fee structures (no hourly billing) with 28-day SLA guarantees—no more vetting 10+ firms. - End-to-End Ownership
Dedicated SourcifyChina liaison for all steps: WFOE registration, bank account setup, tax bureau filings, and post-establishment compliance.
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our Shanghai entity launch from 5 months to 6 weeks. Their partners navigated the new 2025 digital ID requirements we’d missed entirely.”
— Head of APAC Procurement, DAX 30 Industrial Group
Call to Action: Secure Your Q1 2026 Market Entry Window
Time is your scarcest resource. With China’s 2026 FDI incentives expiring Q2 (including 15% tax rebates for green-tech WFOEs), delaying market entry risks:
– ❌ Missing subsidy deadlines
– ❌ Higher operational costs from rushed setups
– ❌ Lost competitive positioning in key sectors (e.g., EV supply chain, biomanufacturing)
Act Now to Lock In 2026 Advantages:
1. 📩 Email Support: Contact [email protected] with subject line “2026 WFOE Pro List Request” for:
– Your customized China Entry Roadmap (24-hour delivery)
– Verified partner shortlist with fixed-fee quotes
– 2026 regulatory compliance checklist (updated monthly)
- 📱 WhatsApp Priority Access: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for:
- Immediate 15-min consultation with our China Entry Specialist
- Urgent case escalation (e.g., name approval delays, capital verification)
- Real-time tracking of your application status
→ First 10 responders this month receive complimentary 2026 FDI Incentive Eligibility Assessment ($1,500 value).
Your Next Step Is Non-Negotiable
In 2026, China market entry isn’t about if you enter—it’s about how fast and compliantly you capture value. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms regulatory complexity into your operational advantage.
Don’t navigate China’s evolving landscape with outdated maps. Partner with the only B2B sourcing platform guaranteeing 28-day WFOE establishment.
Contact us today—your 2026 growth starts with one verified connection.
SourcifyChina: Objective. Verified. China-First.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: Service timelines subject to client documentation completeness and provincial regulatory variations. Full terms at sourcifychina.com/terms.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.