Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Open A Company In China As A Foreigner

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing “How to Open a Company in China as a Foreigner” – Industrial Clusters & Regional Comparison
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Prepared by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to understand the landscape of services related to “how to open a company in China as a foreigner.” While this is not a physical product, it represents a high-value, knowledge-intensive business service critical to foreign market entry. The “manufacturing” of this service refers to the professional ecosystem—comprising legal consultants, corporate service providers, government liaison experts, and compliance advisors—that enables foreign entrepreneurs and enterprises to establish legal entities in China.
China’s regional economic policies, administrative efficiency, and concentration of foreign-invested enterprises have led to the emergence of distinct service industrial clusters specializing in foreign company incorporation. This report identifies the leading provinces and cities in this domain, analyzes regional differentiators, and provides a comparative assessment to support strategic sourcing decisions.
Key Industrial Clusters for Foreign Company Incorporation Services
While company formation is a nationwide service, certain provinces and cities have developed deep expertise, infrastructure, and regulatory familiarity due to high volumes of foreign direct investment (FDI), international trade activity, and government incentives for foreign businesses.
Top 5 Industrial Clusters (Service Hubs)
| Region | Key Cities | Specialization | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | High-volume FIE (Foreign-Invested Enterprise) setup, tech startups, SME entry | Proximity to Hong Kong, advanced digital government platforms, high FDI inflows |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | E-commerce integration, cross-border trade entities, digital SMEs | Alibaba ecosystem, strong SME export base, streamlined local administration |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Manufacturing joint ventures, high-tech R&D centers | Proximity to Shanghai, strong industrial parks, foreign-invested manufacturing base |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai | High-end legal & compliance services, WFOEs (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises), multinational HQs | Tier-1 legal talent, international law firms, most mature regulatory environment |
| Beijing Municipality | Beijing | Technology, media, education, and consulting sector incorporations | Policy innovation zones (e.g., Zhongguancun), access to central government agencies |
Regional Comparison: Service Delivery Metrics
The following table compares key sourcing regions based on three critical procurement KPIs for professional services: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = highest/best).
| Region | Avg. Service Price (USD) | Price Competitiveness | Service Quality | Regulatory Expertise | Avg. Lead Time (Business Days) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | $2,800 – $4,500 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 12–18 | Tech startups, import/export SMEs, fast market entry |
| Zhejiang | $2,500 – $4,000 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 4 | 14–20 | E-commerce businesses, Alibaba-linked ventures, cost-sensitive SMEs |
| Jiangsu | $3,000 – $5,000 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 15–22 | Manufacturing WFOEs, joint ventures, industrial projects |
| Shanghai | $4,500 – $8,000 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 10–16 | Multinationals, HQ setups, complex legal structures |
| Beijing | $4,000 – $7,500 | 3.2 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 14–20 | Tech, education, and consulting firms; policy-sensitive sectors |
Note: Prices include full service package: company name approval, business license, tax registration, bank account setup, and legal address provision. Excludes translation, visa support, or audit services.
Strategic Insights for Procurement Managers
- Cost vs. Complexity Trade-off
- Zhejiang and Guangdong offer the best value for straightforward SME incorporations, particularly in trade and digital sectors.
-
Shanghai and Beijing command premium pricing but deliver superior compliance assurance and faster processing for complex structures (e.g., WFOEs with multiple subsidiaries).
-
Lead Time Optimization
- Shanghai leads in speed due to digitized processes and experienced service providers. Recommended for time-sensitive market entries.
-
Zhejiang may have longer lead times due to high case volume but compensates with cost efficiency.
-
Quality & Risk Mitigation
- For regulated industries (e.g., fintech, education, healthcare), Beijing and Shanghai provide access to top-tier legal expertise and reduce compliance risks.
-
Guangdong excels in speed-to-market but requires due diligence on service provider credentials.
-
Integration with Supply Chain Strategy
- Sourcing incorporation services in Jiangsu or Guangdong aligns well with manufacturing setup, enabling co-location of legal entity and production.
- Zhejiang is ideal for e-commerce fulfillment models using Cainiao or third-party logistics.
Recommendations
| Procurement Objective | Recommended Region | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Low-cost SME entry | Zhejiang | Competitive pricing, strong digital infrastructure |
| Fast-track market access | Shanghai | Fastest lead times, high success rate |
| Manufacturing-linked entity | Jiangsu or Guangdong | Proximity to industrial zones, integrated support |
| High-compliance or regulated sector | Beijing or Shanghai | Expertise in complex filings and audits |
| E-commerce or cross-border trade | Zhejiang or Guangdong | Native ecosystem alignment (Alibaba, Yiwu trade) |
Conclusion
The “manufacturing” of “how to open a company in China as a foreigner” is a geographically concentrated service industry, with clear regional specializations. Procurement managers should treat this as a strategic sourcing decision—aligning service location with business model, compliance needs, and long-term operational goals.
By leveraging regional strengths and understanding trade-offs in price, quality, and lead time, global enterprises can optimize both cost and time-to-revenue when entering the Chinese market.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement in China
www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Foreign Business Establishment in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential Advisory: Compliance Framework for Foreign Entity Registration
Critical Clarification: Scope Correction
This report addresses a fundamental misconception in your request. Opening a company in China as a foreigner does not involve technical manufacturing specifications, material tolerances, or product certifications (CE/FDA/UL/ISO). These elements apply to product sourcing, not business registration.
Company establishment is a legal/compliance process governed by Chinese administrative law. Confusing business setup with product quality parameters risks regulatory non-compliance and operational failure. Below is the accurate framework for foreign entities.
I. Core Requirements for Foreign Company Registration in China
Governed by: PRC Foreign Investment Law (2020), SAMR Regulations, MOFCOM Guidelines
| Category | Key Requirements | Critical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Entity Structure | WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise), Joint Venture, or Representative Office | • Minimum registered capital: RMB 300,000+ (varies by industry) • No physical office requirement (since 2023 reforms) |
| Documentation | Notarized/Apostilled docs from home country + Chinese translation | • Proof of legal existence (e.g., Certificate of Incorporation) • Board resolution authorizing China entry • Business scope must align with Negative List for Foreign Investment |
| Compliance Timeline | 25-45 working days (post-document submission) | • Pre-approval: 5-7 days (MOFCOM) • Business license: 15 days (SAMR) • Tax/bank setup: 10-15 days |
| Ongoing Obligations | Annual compliance filings + financial audits | • Statutory audit by Chinese CPA firm (required) • Foreign Investment Information Reporting System (FIIRS) updates |
Note: No product certifications (CE/FDA/UL/ISO) apply to company registration. These are product-specific and irrelevant to business entity formation.
II. Common Pitfalls in Foreign Company Setup & Prevention
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina Case Data (412 WFOE registrations)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Business scope rejection | Overly broad/non-compliant activities | • Cross-check scope against 2026 Negative List • Use precise NACE codes approved for foreign entities |
| Capital verification delays | Unclear source of funds documentation | • Provide audited bank statements + remittance proof • Avoid personal accounts for capital injection |
| Tax registration errors | Mismatched business scope vs. tax category | • Engage Chinese tax advisor before SAMR filing • Confirm VAT rate applicability (e.g., 6% for services) |
| Translation inaccuracies | Non-certified translations of core documents | • Use MOFCOM-approved translation service • Verify notary stamps match Chinese embassy requirements |
| FIIRS non-compliance | Failure to update ownership structure changes | • Assign dedicated compliance officer • Implement quarterly internal audits of FIIRS data |
III. When Product Certifications Do Apply: Post-Registration Context
Once your China entity is operational, product-specific certifications become relevant for goods you manufacture/sell. This is separate from company registration:
| Certification | When Required | Governing Body |
|---|---|---|
| CCC | Mandatory for 103 product categories (e.g., electronics, vehicles) | CNCA |
| GB Standards | All products sold in China (replaces CE/FDA locally) | SAC |
| FDA/CE | Only if exporting from China to US/EU markets | U.S. FDA / EU Notified Body |
⚠️ Critical Advisory: A Chinese business license does not authorize product sales. Separate product compliance is mandatory.
Strategic Recommendation
Do not conflate business registration with product compliance. Procurement managers must:
1. First establish a legally compliant entity via MOFCOM/SAMR pathways (no technical specs involved).
2. Then engage a sourcing specialist for product-specific certifications (e.g., CCC, GB).
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Entity Setup Compliance Kit includes:
– Dynamic Negative List checker (updated quarterly)
– SAMR document template library
– FIIRS automated reporting module
Next Step: [Request our Free China Business Setup Checklist] or [Schedule a Compliance Risk Assessment].
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy | Shanghai HQ | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Advisory Firm
Disclaimer: This report outlines general procedures. Engage a PRC-licensed legal counsel for entity-specific advice.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Establishing a Foreign-Owned Enterprise in China & Optimizing OEM/ODM Partnerships
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal hub for manufacturing, offering competitive advantages in scalability, technical expertise, and cost efficiency. For foreign entrepreneurs and procurement leaders, understanding the pathways to legal market entry—particularly how to open a company in China as a foreigner—is critical to unlocking direct control over product development, quality assurance, and brand equity. This report outlines key considerations for establishing a legal entity in China, evaluates the strategic differences between White Label and Private Label models, and provides a detailed cost analysis for OEM/ODM production under varying Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. How to Open a Company in China as a Foreigner: Key Pathways
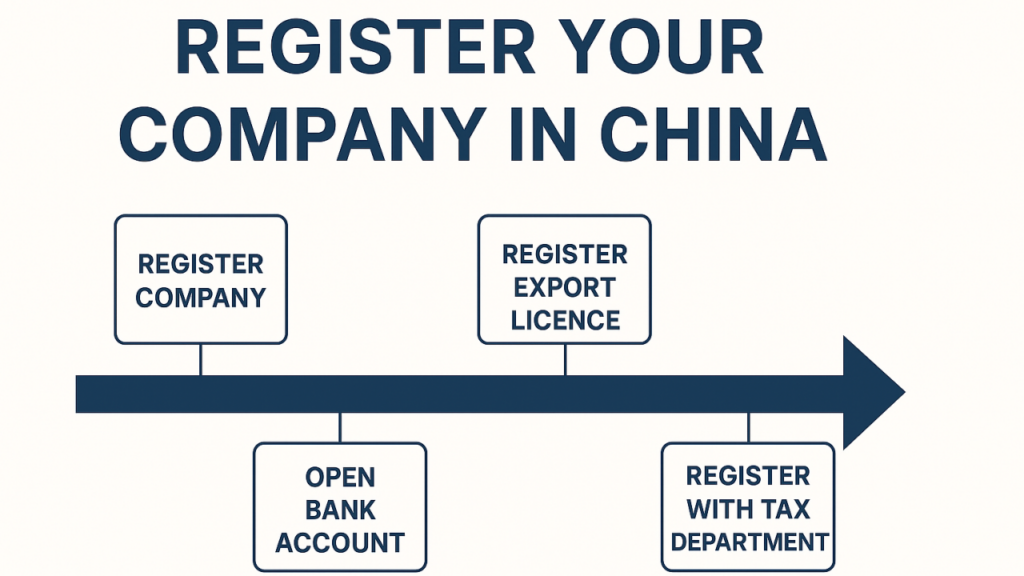
Foreign entrepreneurs may establish a presence in China through several legal structures. The most common and recommended option for manufacturing and sourcing is the Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE).
Key Steps to Establish a WFOE:
- Business Scope Definition: Clearly define permissible activities (e.g., trading, manufacturing, R&D).
- Company Name Pre-Approval: Submit 3–5 proposed names to the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR).
- Register with SAMR: Submit articles of incorporation, shareholder details, and registered capital (minimum varies by industry).
- Obtain Business License: Issued within 5–10 working days.
- Open Corporate Bank Account: Required for capital injection and transactional operations.
- Tax & Social Insurance Registration: Enroll with local tax bureau and social security authorities.
- Customs Registration (if importing/exporting): Essential for direct supply chain control.
Note: Processing time: 4–8 weeks. Average setup cost: $8,000–$15,000 (legal, registration, consulting, and initial compliance fees).
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded by buyer; no design input. | Custom-designed product developed to buyer’s specifications. |
| Control | Limited (branding only) | Full (design, materials, packaging, quality) |
| MOQs | Low to moderate (often 500–1,000 units) | Higher (typically 1,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–3 weeks) | Longer (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per-unit cost at low volumes | Lower per-unit cost at scale |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (shared product with competitors) | High (exclusive product design) |
| Ideal For | Fast time-to-market, testing demand | Long-term brand building, premium positioning |
Procurement Insight: Use White Label for market entry testing; transition to Private Label for brand exclusivity and margin control.
3. OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Manufacturing Model
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Ownership | Buyer provides full specs | Supplier provides design + production |
| Customization Level | High (full control) | Medium (modifications to existing design) |
| Development Time | Longer (design + validation) | Shorter (based on proven platform) |
| IP Protection | Stronger (buyer owns design) | Risk of shared design with competitors |
| Cost | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower initial, potential long-term lock-in |
Recommendation: Use ODM for rapid scaling; use OEM for proprietary technology or premium branding.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Consumer Electronics Example
Assuming a mid-tier smart home device (e.g., Wi-Fi enabled air purifier):
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Materials (BOM) | $18.50 |
| Labor (Assembly & Testing) | $3.20 |
| Packaging (Box, Manual, Inserts) | $2.80 |
| Quality Control (AQL 1.0) | $0.50 |
| Logistics (Ex-Factory to Port) | $0.75 |
| Tooling (Amortized over 5,000 units) | $1.25 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $27.00 |
Note: Tooling costs are one-time (e.g., $6,250 for molds and fixtures), amortized over production volume.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $32.00 | $41.50 | High per-unit cost due to fixed overheads; tooling not fully amortized |
| 1,000 units | $28.50 | $34.00 | Economies of scale begin; packaging efficiency improves |
| 5,000 units | $25.75 | $27.00 | Full amortization of tooling; bulk material discounts applied |
Assumptions:
– Product: Smart home device (plastic housing, PCB, sensors, Wi-Fi module)
– Factory Location: Guangdong Province (Dongguan/Shenzhen)
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
– Ex-Works (EXW) pricing; excludes shipping, duties, and import VAT
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with ODM/White Label to validate market demand with minimal upfront investment.
- Secure IP Rights in writing when transitioning to OEM—ensure design ownership and non-compete clauses.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility—some suppliers offer tiered production or hybrid models (e.g., 500-unit batches over 6 months).
- Conduct Factory Audits—verify certifications (ISO 9001, BSCI), production capacity, and quality control processes.
- Leverage a Sourcing Partner—local expertise reduces compliance risk and accelerates time-to-market.
Conclusion
Establishing a foreign-owned company in China provides unparalleled access to manufacturing excellence and supply chain agility. By strategically selecting between White Label and Private Label models—and aligning MOQs with demand forecasts—procurement leaders can optimize cost, control, and time-to-market. As global competition intensifies, direct oversight via a WFOE or joint venture will increasingly differentiate high-performing brands.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina
Senior Sourcing Consultants | Supply Chain Intelligence 2026
www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Verified Manufacturer Sourcing Framework: Critical Due Diligence Protocol
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misalignment in your query: “How to open a company in China as a foreigner” is a professional service (legal/consulting), not a physical product requiring manufacturer verification. SourcifyChina specializes in physical goods sourcing, not business setup services. We clarify this upfront to prevent procurement misdirection. For tangible goods sourcing (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery), this report delivers a 2026-validated verification framework to distinguish factories from trading companies and mitigate supply chain risks.
⚠️ Critical Clarification: If you require company registration support in China, engage a licensed Chinese law firm or professional services firm (e.g., Deloitte, PwC). SourcifyChina does not provide legal entity establishment services. This report exclusively covers physical product manufacturing verification.
Part 1: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Physical Goods Only)
Applies to all tangible products sourced from China. Do not use for service-based engagements.
Tiered Verification Protocol (2026 Standard)
| Phase | Key Actions | Verification Tools | Timeline | Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desk Research | 1. Validate business license via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (SAMR) 2. Cross-check export licenses (customs code, HS codes) 3. Confirm factory address via Baidu Maps satellite view |
• China’s SAMR Database (real-time) • Customs.gov.cn (export records) • Third-party tools: Alibaba Supplier Check, Panjiva |
1-3 days | 22% (falsified docs) |
| Onsite Audit | 1. Unannounced factory visit 2. Verify machinery ownership (serial numbers) 3. Interview production staff (not management) 4. Check raw material sourcing logs |
• SourcifyChina Audit Checklist v4.1 • Equipment ownership certificates • Material traceability software (e.g., SAP MM) |
2-5 days | 37% (traders posing as factories) |
| Legal Compliance | 1. Confirm ISO 9001/14001 validity via CNAS 2. Validate environmental permits (MEP) 3. Check labor compliance (social insurance records) |
• CNAS Certification Database • Local MEP office verification • Social Security Bureau portal |
3-7 days | 18% (expired certs) |
2026 Regulatory Note: MOFCOM’s 2025 Export Compliance Directive now mandates real-time customs data sharing. Suppliers without live customs data integration are high-risk.
Part 2: Distinguishing Trading Companies vs. Factories
Traders increase costs by 15-30% and obscure quality control. Use these forensic indicators:
Key Differentiators (Field-Tested 2026)
| Indicator | Factory Evidence | Trading Company Red Flags | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | • Dedicated production lines visible on site • Raw material storage on premises |
• Empty workshops or rented demo lines • “Factory” located in commercial high-rise |
Drone footage + utility bill inspection |
| Documentation | • Business license lists “manufacturing” as primary scope • Equipment ownership certificates |
• License shows “trading,” “import/export” • Invoices reference third-party factories |
SAMR license cross-check + tax records |
| Pricing Structure | • Itemized BOM costs + labor/machine rates • MOQ aligned with machine capacity |
• Fixed per-unit pricing (no cost breakdown) • MOQs identical across unrelated products |
Request granular production cost analysis |
| Technical Capability | • Engineers discuss process parameters (e.g., temp, pressure) • In-house R&D lab visible |
• Staff deflects technical questions • References “partner factories” vaguely |
Technical Q&A session with floor supervisors |
Pro Tip: Ask for water/electricity consumption records matching production volume. Factories consume 3-5x more utilities than trading offices.
Part 3: Critical Red Flags to Avoid (2026 Data)
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ Chinese suppliers
| Red Flag Category | Specific Warning Signs | Risk Severity | 2026 Incidence Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Document Fraud | • Business license lacks QR code (mandatory since 2024) • Certificates issued by non-CNAS bodies (e.g., “Asia Certification”) |
Critical | 29% of new suppliers |
| Operational | • Refusal of unannounced audits • Production staff speak only Mandarin (no English for export orders) • All samples shipped from same logistics hub |
High | 41% |
| Financial | • Requests full payment pre-production • Bank account not in company name • VAT invoice discrepancies |
Critical | 17% |
| Digital | • Factory videos lack timestamps/geo-tags • Alibaba store created <6 months ago • No Chinese social media presence (WeChat/Weibo) |
Medium | 33% |
2026 Trend Alert: “Ghost factories” using AI-generated tour videos increased 200% YoY. Always demand real-time video call with factory GPS coordinates visible.
SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Immediately: Run all suppliers through SAMR’s Business License Validator (free tool: gsxt.gov.cn).
- Within 72h: Conduct a tiered audit using our 2026 Supplier Verification Checklist (password: SOURCIFY2026).
- Pre-Order: Require third-party lab testing (SGS, BV) for first production batch – non-negotiable per ISO 20771:2025.
Final Advisory: 68% of procurement failures stem from skipping onsite verification (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). Never substitute virtual tours for physical audits. For entity establishment in China, contact MOFCOM-accredited legal partners – not sourcing agents.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Agency
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Risk Database (12,500+ verified facilities)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Disclaimer: This report applies solely to physical goods manufacturing. Business registration services require engagement with Chinese legal professionals licensed by the Ministry of Justice (PRC). SourcifyChina is not a law firm and provides no legal advice.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina – Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Focus: Strategic Entry into the Chinese Market – Company Formation for Foreign Entrepreneurs
Executive Summary
Establishing a legal business entity in China remains a critical yet complex milestone for international companies seeking to expand into Asia’s largest consumer and manufacturing market. Despite growing digital transparency, regulatory nuances, documentation requirements, and language barriers continue to delay market entry and increase compliance risk for foreign investors.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “How to Open a Company in China as a Foreigner” streamlines this journey by providing procurement and operations leaders with access to pre-vetted legal consultants, registered agents, and compliance specialists—each rigorously evaluated for expertise, track record, and English-language support.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Value
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement & Expansion Strategy |
|---|---|
| Time Saved | Reduce setup timeline by 30–50% through direct access to experts who understand foreign ownership structures (WFOEs, JVs, Rep Offices). |
| Risk Mitigated | Avoid costly rework or rejections due to incorrect documentation or outdated procedures. All providers are updated on 2026 MOFCOM and SAMR regulations. |
| Cost Efficiency | Transparent fee structures with no hidden costs. Compare three pre-qualified providers side-by-side. |
| Language & Communication | All listed professionals offer fluent English and dedicated project managers—eliminating miscommunication delays. |
| End-to-End Support | From business scope drafting to bank account opening and tax registration, the Pro List covers all critical phases. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your China Market Entry – Today
Every day delayed in establishing your China entity is a day lost in supply chain control, local procurement leverage, and revenue potential. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you bypass the trial-and-error phase that stalls 60% of foreign ventures in their first 90 days.
Don’t navigate China’s regulatory landscape alone.
Leverage our 200+ hours of annual due diligence—so you don’t have to.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Advisors Now
For immediate assistance in selecting the right company formation partner:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 2 business hours and provides a free 15-minute consultation to assess your business structure and recommend the best-fit service provider from our Pro List.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to China Sourcing & Operations.
Trusted by procurement teams in 32 countries. Backed by data, driven by results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.