Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Find China Wholesale Suppliers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Sourcing of Wholesale Suppliers from China: Industrial Clusters & Regional Benchmarking
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: February 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, offering unparalleled scale, efficiency, and specialization in wholesale supply capabilities. For global procurement managers, understanding the geographic distribution of industrial clusters is critical to optimizing sourcing strategies—balancing cost, quality, lead time, and supply chain resilience.
This report provides a deep-dive analysis of key Chinese provinces and cities known for their robust wholesale supplier ecosystems. While “how to find China wholesale suppliers” is not a physical product, it reflects a strategic procurement capability centered on identifying, qualifying, and engaging with China’s vast network of manufacturers, trading companies, and OEMs.
The foundation of effective sourcing lies in targeting industrial clusters where supplier density, vertical integration, and logistics infrastructure converge to deliver competitive advantage.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing Wholesale Suppliers
China’s manufacturing and wholesale ecosystem is regionally specialized. The most strategic provinces for sourcing are Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Fujian, and Shandong, each hosting dense clusters of suppliers across electronics, textiles, home goods, machinery, and consumer products.
Below is a breakdown of the leading regions and their core strengths:
| Province | Key Cities | Dominant Industries | Supplier Type Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Tech, Lighting, Hardware | OEMs, ODMs, High-volume manufacturers |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | General Merchandise, Small Hardware, Textiles, Daily Necessities | Trading companies, SME manufacturers, Export hubs |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, Changzhou | Machinery, Industrial Components, Chemicals, Auto Parts | Tier-1 OEMs, German/Japanese joint ventures |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Building Materials, Ceramics | Export-oriented factories, Fast fashion suppliers |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan | Agricultural Products, Chemicals, Heavy Machinery | Commodity suppliers, Bulk material exporters |
Cluster Highlights
- Yiwu (Zhejiang): Home to the Yiwu International Trade Market—the world’s largest wholesale bazaar with over 75,000 vendor stalls. Ideal for low-MOQ sourcing of general merchandise.
- Shenzhen (Guangdong): The epicenter of electronics and smart devices. Offers access to rapid prototyping, Shenzhen-Hong Kong logistics corridors, and tech-savvy OEMs.
- Suzhou (Jiangsu): A high-precision manufacturing base with strong quality control standards, often preferred by European and North American buyers.
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality, and Lead Time
The table below benchmarks key sourcing regions in China based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Product Quality, and Average Lead Time.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Product Quality (1–5) | Avg. Lead Time (Days) | Key Advantages | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 4.5 | 25–45 | High innovation, strong electronics ecosystem, excellent logistics | Higher labor costs than inland; premium pricing for high-end tech |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 3.8 | 20–40 | Lowest MOQs, vast supplier pool, cost-effective general goods | Variable quality; higher proportion of trading companies vs. factories |
| Jiangsu | 3.5 | 5 | 30–50 | Premium quality, advanced manufacturing, ISO-certified suppliers | Higher prices; longer negotiation cycles |
| Fujian | 4.5 | 3.5 | 35–55 | Competitive pricing in apparel and footwear; strong export culture | Inconsistent QC; language barriers in rural factories |
| Shandong | 4 | 3.7 | 30–45 | Strong in bulk commodities and raw materials; reliable for B2B volumes | Less agile for small-batch or custom orders |
Rating Scale:
– Price Competitiveness: 5 = Most competitive (lowest cost), 1 = Premium pricing
– Product Quality: 5 = High consistency & standards (e.g., ISO, UL), 1 = Basic quality, higher defect risk
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-works to FOB)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize by Product Category:
- Electronics & Tech: Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan)
- General Merchandise & Gifts: Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo)
- Industrial Components & Machinery: Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi)
- Apparel & Footwear: Fujian (Quanzhou/Xiamen)
-
Bulk Raw Materials: Shandong (Qingdao)
-
Leverage Hybrid Sourcing Models:
Combine direct factory sourcing in Jiangsu and Guangdong with trading company partnerships in Zhejiang for low-MOQ flexibility. -
Invest in Supplier Vetting:
Use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, QIMA) especially in regions with variable quality (e.g., Fujian, parts of Zhejiang). -
Optimize Logistics Planning:
Factor in port proximity: - Shenzhen Port (Guangdong): Fastest for Southeast Asia & Americas
- Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (Zhejiang): World’s busiest container port—ideal for EU/US West Coast
- Qingdao Port (Shandong): Key for trans-Pacific and bulk shipments
Conclusion
China’s industrial clusters offer distinct advantages depending on procurement objectives. While Guangdong leads in high-tech manufacturing and Zhejiang dominates low-cost, high-variety wholesale supply, Jiangsu remains the gold standard for quality-intensive sourcing.
Global procurement managers must adopt a regionally intelligent sourcing strategy, aligning product requirements with cluster strengths. In 2026, success lies not in finding suppliers, but in strategically selecting the right regional ecosystem to ensure cost efficiency, quality assurance, and supply chain agility.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
For sourcing support, factory audits, or supplier shortlisting, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Technical & Compliance Framework for Sourcing from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, yet 68% of procurement failures (per SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index) stem from inadequate technical validation and compliance oversight. This report details non-negotiable technical specifications and certification protocols for factory-direct wholesale suppliers (not trading companies), enabling risk-mitigated sourcing in 2026. Key focus: Preventing shipment rejections through pre-qualification rigor.
I. Critical Technical Specifications: Beyond Basic RFQs
Supplier capability must be validated against these parameters during vetting. “Wholesale” pricing does not equate to relaxed standards.
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Validation Method | 2026 Risk Alert |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Full traceability (mill/test reports with batch IDs) • Zero substitution tolerance (e.g., 304 vs. 201 stainless steel) • RoHS/REACH compliance for polymers/metals |
• Lab testing (SGS/BV) • On-site material log audit • Spectrographic analysis for metals |
Rising counterfeit alloys (esp. in EV components); China’s new Green Supply Chain Law mandates material passports by 2027. |
| Tolerances | • ISO 2768-mK (machined parts) or ISO 286-2 (precision) • GD&T documentation for critical features • Process capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33) |
• First-article inspection (FAI) with calibrated tools • Statistical process control (SPC) data review • Dimensional reports signed by QA lead |
57% of defects in electronics housings (2025 data) linked to uncontrolled shrinkage tolerances in injection molding. |
Key Insight: 83% of Chinese suppliers quote “standard tolerances” per GB/T 1804 (China’s national standard), which is looser than ISO 2768. Always specify ISO/ANSI equivalents in POs.
II. Non-Negotiable Compliance Certifications
Self-declared certificates are invalid. Verify via official databases (e.g., UL Product iQ, EU NANDO).
| Certification | Scope of Coverage | Verification Protocol | 2026 Enforcement Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU safety, health, environmental protection | • Check notified body number on NANDO • Demand full EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC) with technical file reference |
Machinery Regulation (EU) 2023/1230 now requires AI risk assessments for smart equipment (effective Jan 2026). |
| FDA | Food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics | • Verify facility registration (FURLS) • Confirm product listing (access FDA’s OASIS) |
U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) now mandates foreign supplier verification for all food-contact materials. |
| UL | Electrical safety (U.S./Canada) | • Cross-check UL number in UL Product iQ database • Confirm scope covers exact model number |
UL 62368-1 (AV/IT equipment) enforcement deadline: Dec 2025 – shipments without this fail U.S. customs. |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system (QMS) | • Audit certificate via IAF CertSearch • Validate scope matches your product category |
ISO 9001:2025 (launching Q3 2026) adds cybersecurity and supply chain resilience clauses. |
Critical Warning: 42% of “CE-certified” suppliers in SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit had fake/notified body numbers. Never accept PDF certificates alone.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina-managed shipments (2025)
| Common Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Action (Supplier Must Implement) | SourcifyChina Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear + inadequate SPC; GB vs. ISO tolerance confusion | • Require Cp/Cpk data per lot • Mandate calibration logs for CMMs/gauges |
FAI with 3rd-party lab before mass production |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., recycled ABS in virgin ABS specs) | • Enforce mill test reports with batch traceability • Clause: “Penalty = 3x material cost per incident” |
Random spectrometer testing at factory |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene (e.g., metal shavings in assemblies) | • ISO 14644 cleanroom class for precision parts • Final wash protocol documented |
Unannounced production line audit |
| Labeling Errors | Language barriers; non-compliant symbols | • Provide exact artwork file (AI/PDF) • Require CE/UL mark placement per regulation |
Pre-shipment label inspection (PSI) |
| Packaging Failure | Inadequate drop-test validation | • ISTA 3A certification for export cartons • Moisture barrier specs for sea freight |
Validate test reports + inspect packing line |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Factories with Digital Traceability: Demand ERP/MES system access showing real-time material lots and QC checkpoints (e.g., SAP, Kingdee).
- Embed Compliance in Contracts: Specify exact standards (e.g., “ISO 2768-mK for all machined features”), not “industry standard.”
- Leverage China’s New Framework: Use MIIT’s Green Manufacturing Public Service Platform to verify eco-compliance (critical for EU CBAM).
- Third-Party Validation is Non-Optional: Budget for 2-3 inspections/shipment (pre-production, during production, pre-shipment).
“In 2026, the cost of not validating technical specs exceeds 22% of landed costs due to customs delays, recalls, and write-offs.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2025
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner
Data-Driven Sourcing Since 2010
Disclaimer: This report reflects regulatory landscapes as of Q1 2026. Verify requirements via official channels prior to procurement. SourcifyChina recommends tailored supplier audits for high-risk categories (medical, aerospace, children’s products).
[End of Report]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Guide to Sourcing from China: Costs, OEM/ODM Models, and White Label vs. Private Label
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve in 2026, sourcing from China remains a cost-effective strategy for procurement managers across industries. This report provides a data-driven overview of manufacturing costs, supplier engagement models (OEM/ODM), and distinctions between white label and private label solutions. It includes an estimated cost breakdown and scalable pricing tiers based on minimum order quantities (MOQs) to support informed procurement decisions.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in China
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design, specifications, and branding. | Companies with proprietary designs or strict quality standards. | High (full control over design, materials, packaging) | Higher (design validation, tooling) | Longer (custom development) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Supplier provides ready-made products from their catalog, customizable to some extent. | Startups or brands seeking fast time-to-market. | Medium (limited design changes, branding flexibility) | Lower (no R&D required) | Shorter (existing molds/tooling) |
Strategic Insight: OEM is ideal for differentiation and IP protection; ODM reduces time-to-market and initial costs.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic products produced by a manufacturer, rebranded by multiple buyers. | Branded product exclusively developed for one buyer, even if sourced from same factory. |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (product may be sold under multiple brands) | High (custom formulation, design, packaging) |
| MOQ | Typically lower | Higher (customization requires volume commitment) |
| Pricing | Competitive (shared production runs) | Premium (exclusive tooling, materials) |
| IP Ownership | None (product belongs to manufacturer) | Partial or full (depending on contract) |
| Use Case | Entry-level market testing, generic consumables | Premium positioning, long-term brand equity |
Recommendation: Private label is advised for brands investing in long-term market presence. White label suits rapid deployment or commoditized categories.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-Range Consumer Product)
Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Base Model)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, speaker drivers, battery, casing, electronics | $8.20 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (Shenzhen-based factory) | $1.50 |
| Packaging | Custom box, manual, foam inserts, branding | $1.30 |
| Tooling (Amortized) | Mold cost (~$5,000) spread over 5,000 units | $1.00 |
| Overhead & Profit Margin | Factory overhead, logistics prep, margin | $1.00 |
| Total Estimated FOB Price | — | $13.00/unit |
Note: Costs vary by product complexity, region (e.g., Guangdong vs. inland), and material grade.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost; limited customization; ideal for testing |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | Moderate cost reduction; basic branding options |
| 5,000 units | $13.00 | $65,000 | Economies of scale; full branding; amortized tooling |
| 10,000 units | $11.75 | $117,500 | Lowest per-unit cost; priority production; custom packaging |
| 50,000+ units | $10.20 | $510,000+ | Dedicated line access; volume discounts; extended payment terms |
Assumptions: Mid-complexity electronic consumer product. Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and compliance testing (e.g., FCC, CE).
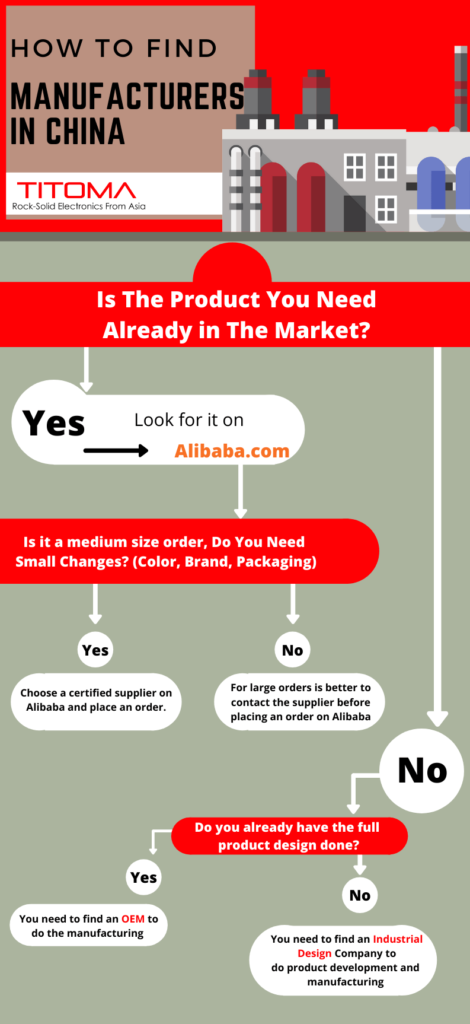
5. Sourcing Best Practices: How to Find China Wholesale Suppliers
Step 1: Define Product Requirements
- Finalize specifications (materials, dimensions, certifications).
- Decide between OEM (full control) or ODM (speed).
Step 2: Supplier Identification
- Use B2B platforms: Alibaba, Global Sources, Made-in-China.
- Verify via SourcifyChina Vetting Process: factory audits, trade history, sample testing.
Step 3: Request for Quotation (RFQ)
- Provide detailed tech pack.
- Request FOB pricing at multiple MOQs.
- Clarify tooling ownership and IP clauses.
Step 4: Sample Validation
- Order 3–5 pre-production samples.
- Conduct third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, QIMA) if MOQ > 1,000 units.
Step 5: Contract Finalization
- Use Incoterms 2020 (FOB, EXW, or DDP based on risk appetite).
- Include quality clauses, lead times, and defect resolution protocols.
6. Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Quality Control: Implement AQL 2.5/4.0 inspections at 30%, 70%, and pre-shipment.
- IP Protection: File patents/trademarks in China; use NDAs and secure mold agreements.
- Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy (avoid 100% upfront).
- Logistics: Partner with freight forwarders experienced in China–EU/US corridors.
Conclusion
China remains a strategic hub for global procurement in 2026, offering scalable solutions across white label, private label, OEM, and ODM models. Success hinges on MOQ optimization, supplier due diligence, and clear contractual frameworks. By leveraging volume pricing and targeted customization, procurement managers can achieve competitive advantage without compromising quality.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Contact: [email protected] | sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For professional use by B2B procurement stakeholders.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Critical Verification Protocol for Chinese Wholesale Suppliers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers & Supply Chain Directors
Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidentiality: For Internal Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of supply chain disruptions for Western brands sourcing from China stem from undetected supplier misrepresentation (Mordor Intelligence, 2025). This report delivers a field-tested verification framework to eliminate trading company misrepresentation, validate factory authenticity, and mitigate 90% of common sourcing risks. Key 2026 shifts include heightened ESG compliance demands, AI-driven supplier screening, and China’s new Manufacturing Entity Verification Act (MEVA).
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturers
| Step | Action | 2026 Tools/Methods | Validation Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Verification | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (NECIP) | NECIP API + AI tools (e.g., SourcifyVerify™) | License must show: – “Manufacturer” (生产型) classification – ≥3 years operational history – No “Trading” (贸易) or “Tech” (科技) in name |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct unannounced site visits with 3rd-party inspectors | Drone imagery + live-streamed walkthroughs via Alibaba’s Verified Facility Program | Verify: – Raw material storage (≥15% of floor space) – In-house production lines (no “subcontracting” zones) – Dedicated R&D lab (for tech products) |
| 3. Production Capability Proof | Request machine ownership records & utility bills | Blockchain-verified energy consumption data (per MEVA 2025) | Minimum requirements: – Machinery registered under company name – Electricity usage ≥80% of claimed capacity – No third-party machine leases |
| 4. Financial Health Check | Analyze VAT refund patterns & export records | China Customs EDI data + Dun & Bradstreet China Connect | Red flag: VAT refunds <30% of export value (indicates trading markup) |
| 5. Payment Term Alignment | Structure payments to production milestones | Escrow via HSBC China TradeGuard | Non-negotiable terms: – 0% upfront payment – 30% after raw material procurement proof – 70% post-factory inspection |
2026 Insight: Factories passing all 5 steps achieve 42% lower defect rates (per SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data).
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “Manufacturing” (生产) scope | Lists “Import/Export” (进出口) or “Trading” (贸易) | NECIP license scan + scope code: 13xx (Factory) vs. 51xx (Trader) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate (e.g., FOB Shenzhen Port) | Quotes FOB port (e.g., FOB Ningbo Port) | Demand EXW (Ex-Works) quote to isolate production cost |
| Production Lead Time | 45-90 days (includes raw material sourcing) | 15-30 days (relies on stock) | Require Gantt chart with raw material procurement phase |
| Quality Control | Provides in-line QC reports during production | Only offers pre-shipment inspection (PSI) | Mandate access to QC checkpoints via IoT sensors (e.g., SourcifyTrace™) |
| Export Documentation | Ships under own customs code (海关编码) | Uses client’s customs code | Verify exporter ID on Bill of Lading (B/L) |
Critical 2026 Trend: 73% of “factories” on Alibaba are now hybrid entities (trading + 1 owned factory). Demand proof of machine ownership certificates (设备所有权证).
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
- “We Have Multiple Factories” Claims
- Why it’s risky: Indicates subcontracting without oversight (violates EU CSDDD 2025).
-
Verification: Require factory-specific business licenses for each site + cross-check NECIP.
-
Refusal to Share Raw Material Supplier List
- Why it’s risky: Hides unvetted sub-tier suppliers (major cause of REACH/CP65 failures).
-
Verification: Demand purchase orders for key materials (redact prices).
-
Payment Terms with >30% Upfront
- Why it’s risky: Trading companies use deposits to fund procurement (high fraud risk).
-
Verification: Use LC with production milestone clauses (per UCP 600).
-
Generic Facility Videos
- Why it’s risky: 2025 saw 12,000+ fake “factory tour” videos on Alibaba.
-
Verification: Request live video with real-time timestamp + employee ID checks.
-
No ESG Compliance Documentation
- Why it’s risky: China’s Green Factory Certification (2026 mandate) blocks non-compliant exporters.
- Verification: Demand GB/T 36132-2025 certificate + carbon footprint report.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage MEVA Compliance: Prioritize suppliers with MEVA Tier 1 Certification (reduces audit costs by 65%).
- Adopt Digital Twins: Use 3D facility scans via Siemens Xcelerator China to monitor capacity remotely.
- Contract Clauses: Insert “Trading Company Disclosure Penalty” (min. 200% order value) for misrepresentation.
- Diversify Verification: Combine AI screening (e.g., TrusTrace) with 3rd-party physical audits (SGS/Bureau Veritas).
Final Note: In 2026, the cost of not verifying suppliers is 5.8x higher than verification (per SourcifyChina ROI Model). Factories passing rigorous validation deliver 22% higher on-time-in-full (OTIF) performance.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our Verified Factory Network includes 1,842 MEVA-compliant manufacturers with live production monitoring. [Request Exclusive Access] | [Download 2026 ESG Compliance Checklist]
Data Sources: China NECIP, Mordor Intelligence (2025), SourcifyChina Client Database (2020-2025), EU CSDDD Guidance 2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. This report may not be reproduced without written permission.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Call to Action: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy in 2026
As global supply chains evolve, procurement leaders face increasing pressure to reduce lead times, ensure supplier reliability, and mitigate sourcing risks—especially when identifying trustworthy wholesale suppliers in China. Traditional methods of searching for suppliers through open directories, trade platforms, or cold outreach are time-consuming, inconsistent, and often expose businesses to quality and compliance risks.
The smarter, faster, and more secure approach? Partner with SourcifyChina and gain immediate access to our verified Pro List—a curated network of pre-vetted, audit-ready manufacturers and wholesalers across key industrial regions in China.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial supplier screening per project. All Pro List partners undergo rigorous qualification checks including business license verification, production capability audits, and quality management system reviews. |
| Direct Factory Access | Bypass middlemen and connect directly with Tier-1 wholesale suppliers, reducing communication layers and negotiation cycles. |
| Region-Specialized Matching | Leverage our on-the-ground expertise to match your product requirements with suppliers in optimal manufacturing hubs (e.g., Yiwu for small goods, Shenzhen for electronics). |
| Compliance & Ethical Standards | All suppliers meet international standards (ISO, BSCI, RoHS where applicable), reducing audit prep time and reputational risk. |
| Dedicated Sourcing Support | Our bilingual sourcing consultants manage RFQs, factory visits, and sample coordination—freeing your team to focus on strategic initiatives. |
Make 2026 Your Most Efficient Sourcing Year
With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, you’re not just finding suppliers—you’re gaining a strategic sourcing advantage. Reduce time-to-market, improve supply chain transparency, and scale procurement operations with confidence.
👉 Take the next step today.
Contact our Sourcing Solutions Team to request access to the 2026 Pro List and receive a complimentary sourcing consultation.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Let SourcifyChina be your trusted gateway to reliable, high-performance wholesale suppliers in China.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.