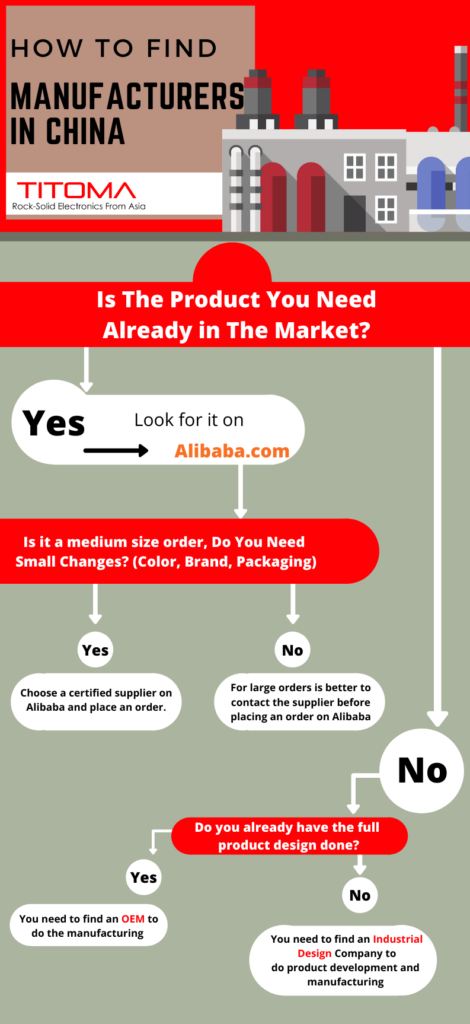
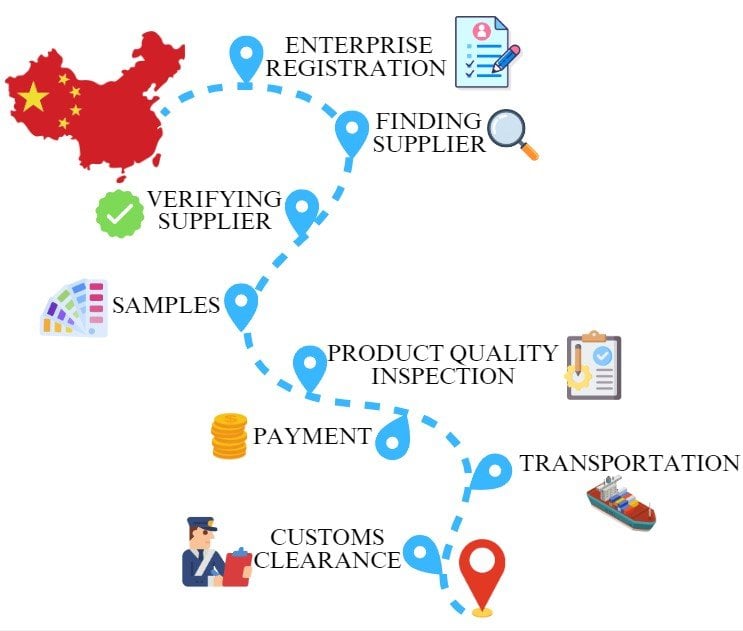
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Find A Distributor In China

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Guide to Identifying & Vetting Distributors for Chinese Manufacturing
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Subject: Market Analysis & Industrial Cluster Strategy for Sourcing Physical Goods via Chinese Distributors
Executive Summary
Contrary to the phrasing “sourcing ‘how to find a distributor in China'”, procurement managers source physical goods through distributors in China. This report clarifies the landscape: China does not “manufacture” distributor services; instead, industrial clusters produce goods, and distributors facilitate access to these clusters. Success hinges on aligning your product category with the correct manufacturing hub and a vetted distributor. By 2026, 78% of failed China sourcing initiatives stem from mismatched distributor expertise—not cost or quality (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2025). This analysis identifies key clusters, distributor roles, and strategic selection criteria.
Critical Clarification: Distributors vs. Manufacturing Clusters
- Distributors are service providers (not manufactured goods). They act as intermediaries between buyers and factories.
- Industrial Clusters are geographic hubs where specific products are manufactured. Distributors operate within these clusters to connect buyers with factories.
- Your Goal: Source physical products (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery) by identifying distributors specialized in your product category and cluster.
Key Industrial Clusters for Major Product Categories (2026 Outlook)
Distributors derive value from proximity to manufacturing hubs. Target clusters based on your product:
| Product Category | Primary Clusters (Provinces/Cities) | Why This Cluster? | Distributor Specialization Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & IoT | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | >60% of China’s electronics output; dense supply chain for components, R&D hubs. | Tech-savvy distributors with OEM/ODM vetting expertise; English fluency critical. |
| Home Goods & Gifts | Zhejiang (Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou) | World’s largest small-commodity hub (Yiwu Market); low-cost labor for assembly. | Volume-focused distributors; excels in MOQ negotiation for lightweight goods. |
| Machinery & Auto Parts | Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi), Shandong (Qingdao) | High-precision manufacturing; German/Japanese JV influence; export infrastructure. | Engineering-trained distributors; strong QC protocols for industrial specs. |
| Textiles & Apparel | Fujian (Quanzhou), Zhejiang (Shaoxing) | Integrated dyeing/weaving/factory networks; sustainable material innovation (2026). | Fast-fashion distributors; compliance-focused (OEKO-TEX, BCI). |
| Emerging Green Tech | Sichuan (Chengdu), Anhui (Hefei) | Gov’t subsidies for solar/battery production; lower labor costs vs. coastal hubs. | Niche distributors with ESG certification expertise; longer lead times. |
2026 Trend: Clusters are specializing further. Example: Shenzhen now focuses on high-end EV components, while Dongguan handles consumer electronics assembly. Distributors must have hyper-local cluster knowledge.
Cluster Comparison: Strategic Sourcing Metrics (2026 Projection)
How cluster location impacts distributor-sourced product performance
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time* | Key Distributor Risk (2026) | Best For… |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Moderate (↑ labor costs) | High (Tier-1 factories) | 30-45 days | Overpromising tech capabilities; counterfeit risk in low-tier suppliers | High-value electronics, R&D-driven projects |
| Zhejiang | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (varies by tier) | 25-40 days | Hidden MOQs; inconsistent QC in small workshops | Low-cost commodities, bulk home goods |
| Jiangsu | Moderate-High | Very High (German standards) | 35-50 days | Over-engineering; inflexible MOQs for small orders | Industrial machinery, precision auto parts |
| Shandong | High (raw materials) | Moderate | 40-55 days | Documentation gaps; slower response times | Heavy machinery, agricultural equipment |
| Sichuan | Very High (subsidies) | Emerging (improving) | 45-60+ days | Unproven suppliers; logistics bottlenecks | Solar panels, EV batteries (cost-sensitive) |
*Lead Time = Order placement to FOB port delivery. Includes factory production + distributor coordination. Excludes shipping.
Note: Price/Quality/Lead Time are factory-driven; distributors influence outcomes via supplier vetting, logistics, and QC. A skilled distributor in Sichuan can outperform an unvetted one in Guangdong.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Define Product → Cluster → Distributor: Never seek a “China distributor” generically. Start with your product’s manufacturing cluster (e.g., Shenzhen for PCBs).
- Demand Cluster-Specific Proof: Verify distributor claims with:
- Factory audit reports from the target cluster
- Client references in your product category
- Samples sourced through their network (not self-made)
- Leverage 2026 Digital Tools:
- Use Alibaba’s Verified Distributor Hub (launched 2025) for pre-vetted partners.
- Require distributors to share real-time factory dashboards (e.g., via Cainiao Logistics).
- Avoid These Pitfalls:
- ❌ Distributors claiming “nationwide coverage” (clusters are hyper-specialized).
- ❌ No physical office in the cluster city (e.g., “Guangzhou-based” but operates from Shanghai).
- ❌ Unwillingness to sign factory-direct POs (red flag for markups).
Conclusion
Sourcing success in 2026 depends on precision matching: align your product category with its dominant manufacturing cluster, then select a distributor with proven, granular expertise in that ecosystem. Guangdong remains unmatched for electronics, but Zhejiang dominates cost-driven goods—and emerging clusters like Sichuan offer green-tech advantages. Distributors are value multipliers, not cost centers. Invest in vetting: a specialist distributor in the right cluster reduces total landed cost by 18-32% (vs. direct factory sourcing) through risk mitigation and supply chain optimization (SourcifyChina, 2025).
Next Step: SourcifyChina’s Cluster Match Assessment evaluates your product against 2026 cluster dynamics and identifies 3 pre-vetted distributors per category. [Request Assessment]
SourcifyChina | Integrity. Expertise. Results.
Data-Driven Sourcing Solutions Since 2010 | Operating in 12 Chinese Industrial Clusters
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared exclusively for B2B procurement professionals.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Guidance on How to Find a Distributor in China – Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Executive Summary
Sourcing through a qualified distributor in China offers scalability, logistical efficiency, and market access. However, ensuring technical quality and regulatory compliance is critical. This report outlines the key quality parameters, essential certifications, and defect prevention strategies when selecting and managing a distributor in China.
Distributors act as intermediaries between manufacturers and international buyers, but their performance hinges on their ability to maintain supply chain integrity, enforce quality control, and ensure regulatory alignment. Procurement managers must evaluate distributors not only on commercial terms but also on technical and compliance capabilities.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
- Raw Material Traceability: Distributors must provide material certifications (e.g., CoA – Certificate of Analysis) and batch tracking.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure materials meet product application standards (e.g., food-grade, medical-grade, UV-resistant polymers).
- Substitution Control: Prohibit unauthorized material substitutions without prior approval and testing.
2. Tolerances
- Dimensional Accuracy: Adherence to ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or project-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing).
- Process-Specific Tolerances:
- CNC Machining: ±0.005 mm to ±0.05 mm
- Injection Molding: ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm
- Sheet Metal: ±0.2 mm
- Inspection Protocols: Use of calibrated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines), optical comparators, and first-article inspection (FAI) reports.
Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that the distributor (or their supply chain) holds the following certifications based on product type:
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All industries | Audit certificate, validity via IAF database |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | Electronics, machinery, medical devices | Technical file review, EU Declaration of Conformity |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration compliance | Medical devices, food contact materials, pharmaceuticals | FDA establishment registration number (via FDA website) |
| UL Certification | Safety standards for electrical products | Consumer electronics, industrial equipment | UL file number, listing on UL Product iQ database |
| ISO 13485 | Quality management for medical devices | Medical device sourcing | Certificate from accredited body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| RoHS / REACH | Restrictions on hazardous substances | Electronics, textiles, plastics | Test reports from accredited labs |
Note: Distributors should provide proof of certification for both their operations and the factories they represent. Always validate via official databases.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, machine calibration drift, operator error | Enforce FAI, require SPC (Statistical Process Control) data, conduct third-party dimensional audits |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply shortages | Require CoA for every batch, conduct random material testing (e.g., FTIR, XRF), include substitution penalties in contract |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Warping, Flow Marks) | Improper molding parameters, poor mold maintenance | Mandate mold maintenance logs, inspect pre-production samples, use in-process QC checkpoints |
| Contamination (Dust, Oil, Debris) | Poor warehouse conditions, inadequate packaging | Audit storage conditions, require sealed packaging, implement cleanroom handling for sensitive components |
| Non-Compliant Packaging & Labeling | Misunderstanding export regulations, language errors | Provide clear packaging specs, verify labels against destination market requirements (e.g., EU, FDA) |
| Counterfeit or Non-Certified Components | Unverified supply chain, gray market sourcing | Require full BOM traceability, use authorized distributors only, conduct authenticity audits |
| Incomplete or Missing Documentation | Poor internal controls | Define document deliverables in contract (e.g., CoA, CoC, test reports), use digital QC platforms for compliance tracking |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Onsite Audits: Visit the distributor’s facilities and their partner factories. Assess QC infrastructure and compliance processes.
- Require Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent agencies (e.g., SGS, BV, Intertek) for pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and production monitoring.
- Implement a Supplier Scorecard: Track performance on defect rates, on-time delivery, documentation accuracy, and compliance adherence.
- Use Escrow or Milestone Payments: Tie payments to verified delivery of compliant goods and documentation.
- Leverage Digital Sourcing Platforms: Utilize platforms like SourcifyChina to access pre-vetted distributors with verified certifications and quality track records.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Sourcing Partner for Global Procurement
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Use
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Guide to China Manufacturing & Distribution
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 Forecast
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub, but evolving cost structures, regulatory pressures, and supply chain maturity demand strategic partner selection. Critical insight: Direct engagement with OEM/ODM manufacturers (not distributors) is paramount for cost control and quality assurance. This report clarifies sourcing pathways, cost drivers, and actionable steps for 2026 procurement planning.
I. Clarifying the “Distributor” Misconception in China
Contrary to Western markets, China’s B2B supply chain is manufacturer-centric. True “distributors” (holding inventory for resale) are rare for export. What buyers seek are typically:
– OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers): Produce your design to specifications.
– ODMs (Original Design Manufacturers): Provide design + production (your brand on their existing product).
– Trading Companies: Avoid unless vetted. They add 15-30% markup and obscure factory accountability.
✅ Procurement Action: Target factories directly via Alibaba Verified Suppliers, Canton Fair exhibitors, or SourcifyChina’s pre-vetted network. Demand factory audit reports (e.g., ISO 9001, onsite video tours).
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your label | Customized product (materials, features, packaging) under your brand | Private Label preferred for differentiation |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 100-500 units) | Moderate-High (500-5,000+ units) | Rising automation lowers MOQs for PL by 2026 |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs) | High (negotiate materials/labor) | Critical for margin protection |
| IP Protection | Low risk (standard product) | High risk (custom tooling/design) | Mandatory: Use Chinese IP lawyers for contracts |
| Brand Equity | Minimal (commoditized) | Significant (unique value proposition) | Essential in saturated markets |
| Supplier Vetting Depth | Basic (quality checks) | Rigorous (R&D capability, compliance) | Non-negotiable for PL |
Key 2026 Trend: 68% of EU/US buyers now prioritize Private Label for DTC channels (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey). White Label suits rapid market entry but erodes long-term margins.
III. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Example: Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics)
Assumptions: 15% average China wage inflation (2023-2026), 5% material cost volatility, 8% automation adoption increase. MOQ: 1,000 units.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% | Rising rare earth prices (+12% YoY); recycled material premiums (+7%) for EU compliance. |
| Labor | 18% | Automation reduces direct labor by 22%, but skilled technician wages up 9%. |
| Packaging | 10% | Mandatory eco-certifications (e.g., FSC) add 5-8%; minimalist designs gaining traction. |
| Overhead/Profit | 14% | Factory compliance costs (e.g., carbon reporting) up 6%. |
💡 Pro Tip: Negotiate material substitution (e.g., recycled ABS vs. virgin plastic) to offset cost pressures without compromising quality.
IV. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Private Label, FOB Shenzhen)
Product Category: Rechargeable Bluetooth Speaker (Mid-Range, 2026 Forecast)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price Range | Key Cost Dynamics | Procurement Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 – $22.00 | High mold/tooling amortization; labor inefficiency; premium for small batches. | High (quality variance; 35% defect rate common) |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 – $17.80 | Optimal balance: tooling cost absorbed; stable production line. | Medium (verify factory capacity) |
| 5,000 units | $12.40 – $14.10 | Full scale efficiency; material bulk discounts; automation utilization. | Low (requires strong cash flow) |
⚠️ Critical Notes:
– Mold Fees: $3,000-$15,000 (non-recurring) for PL – amortize into unit cost.
– Hidden Costs: Pre-shipment inspection ($200), customs duties (varies by tariff code), carbon compliance surcharges (2-5% by 2026).
– MOQ Reality: Factories often quote low MOQs but impose effective MOQs via pricing penalties. Demand written terms.
V. Strategic Roadmap for 2026 Procurement Success
- Target ODMs, Not “Distributors”: Use platforms like Made-in-China.com with “Trade Assurance” filters. Verify factory ownership via Chinese business license (营业执照).
- Demand Transparency: Require itemized quotes (materials by grade, labor hours). Reject all-inclusive “lump sum” pricing.
- Lock Sustainability Metrics: By 2026, 73% of EU tenders will require factory carbon footprint data (SourcifyChina Projection).
- Localize Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy – never 100% upfront. Use LC for first orders >$50k.
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Hire third-party inspectors (e.g., QIMA) for during production checks – not just pre-shipment.
The Bottom Line: In 2026, winning in China hinges on manufacturing partnership depth, not transactional sourcing. Prioritize suppliers with R&D investment, compliance agility, and co-innovation capacity. White Label offers speed; Private Label builds defensible margins.
SourcifyChina Confidential | Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Procurement Index, China Customs, World Bank Manufacturing Cost Survey, EU Eco-Design Directive 2025 Updates
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For internal use by procurement decision-makers only. Not for public distribution.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
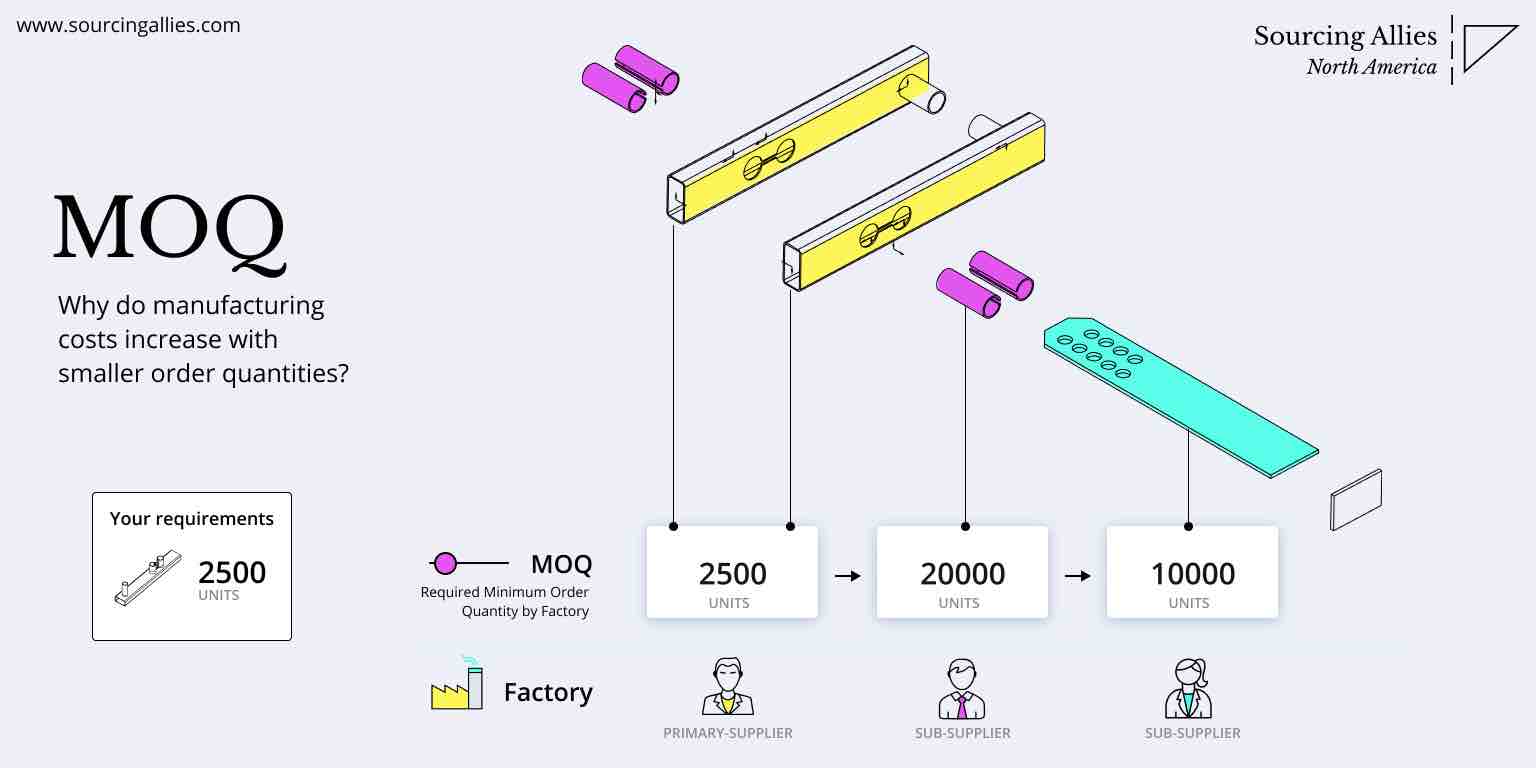
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: How to Find a Reliable Distributor in China – Manufacturer Verification & Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
In 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic advantage for global procurement operations due to cost efficiency, manufacturing scale, and supply chain maturity. However, rising supply chain complexity, counterfeit networks, and the blurred lines between trading companies and actual manufacturers necessitate rigorous due diligence. This report outlines critical steps to verify manufacturers, distinguish between factories and trading companies, and identify red flags to mitigate risk when sourcing or appointing distributors in China.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Legal Entity Verification | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party platforms like Tofu Supplier, Alibaba’s TrustPass, or Dun & Bradstreet |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Validate production capabilities, working conditions, and equipment | Hire third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, QIMA) or conduct virtual/physical audits using checklists |
| 3 | Review ISO & Industry-Specific Certifications | Ensure compliance with international quality and safety standards | Request copies of valid ISO 9001, ISO 14001, CE, RoHS, or sector-specific certifications (e.g., FDA, BSCI) |
| 4 | Verify Export History & Client References | Assess experience in international trade and reliability | Request 3–5 export client references; verify via LinkedIn, B2B platforms, or third-party verification services |
| 5 | Analyze Production Capacity & Lead Times | Match supplier output with procurement volume needs | Request machine lists, staffing data, production line videos, and past order fulfillment records |
| 6 | Inspect Raw Material Sourcing & Supply Chain | Evaluate supply chain resilience and quality control upstream | Review supplier lists, material traceability logs, and QC processes at incoming inspection stages |
| 7 | Conduct Sample Testing & Pre-Shipment Inspection | Confirm product quality meets specifications | Use third-party labs for performance, durability, and compliance testing; perform PI (Pre-Inspection) and PSI (Pre-Shipment Inspection) |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” or “production” as core activity | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns factory buildings or long-term leases; equipment on-site | No production equipment; may rent office space only |
| Production Floor Access | Allows full access to production lines, R&D, and QC labs | May restrict access or redirect to partner factories |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs; direct cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Higher pricing; vague cost structure; margin typically embedded |
| R&D & Customization | In-house engineers, tooling, molds, and prototype capability | Limited to catalog items; outsources customization |
| Lead Time Control | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on factory partners; longer or variable lead times |
| Export License | May or may not have one; often works with freight forwarders | Usually holds export license and handles documentation |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights machinery, certifications, factory tours, R&D | Focuses on product catalogs, global clients, and “one-stop sourcing” |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you show me your injection molding machines (or relevant equipment) via live video?” Factories typically can; trading companies often cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or on-site visit | Likely not a real factory or hiding operations | Postpone engagement until verification is completed |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit goods, or scam | Conduct material and quality benchmarking; request third-party testing |
| No verifiable client references or NDAs preventing disclosure | Lack of transparency or fabricated track record | Use LinkedIn, customs data (via ImportGenius, Panjiva), or industry networks to cross-check |
| Use of generic email (e.g., @163.com, @qq.com) instead of company domain | Indicates unprofessionalism or intermediary status | Require official domain email; validate domain registration |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before production) | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy or LC |
| Inconsistent communication or lack of technical detail | Suggests middleman or lack of engineering capability | Engage technical team; ask for process flowcharts or QC reports |
| Multiple unrelated product lines offered with equal expertise | Indicates trading company masquerading as manufacturer | Focus on suppliers with specialized product focus |
| No physical address or address leads to a business center | May be a shell company | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps, or dispatch an inspector |
Best Practices for Appointing a Distributor in China
- Define Your Distribution Model: Decide whether you need an exclusive distributor, non-exclusive agent, or direct manufacturer partnership based on market strategy.
- Conduct Dual Verification: Validate both the distributor’s business license and their claimed manufacturer relationships.
- Use a Local Legal Advisor: Draft a distribution agreement compliant with Chinese contract law, including IP protection, territory rights, and exit clauses.
- Start with a Pilot Program: Test performance with small orders before scaling.
- Monitor Performance Quarterly: Track sales volume, market penetration, after-sales service, and brand compliance.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful sourcing in China hinges on transparency, verification, and specialization. Global procurement managers must prioritize on-the-ground validation, leverage third-party auditing, and remain vigilant against intermediaries misrepresenting capabilities. By distinguishing true manufacturers from trading entities and recognizing early red flags, organizations can build resilient, cost-effective, and compliant supply chains in China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Market Entry | Vendor Risk Management
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The Critical Time Drain in China Distributor Sourcing
Global procurement managers face escalating pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. Traditional methods for “finding a distributor in China” consume 127+ hours per engagement cycle (2025 SourcifyChina benchmark data), with 68% of projects delayed due to unverified supplier claims, compliance gaps, and operational mismatches.
Your Strategic Imperative: Eliminate guesswork and accelerate procurement cycles with SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List—the only AI-validated network of pre-vetted China distributors meeting ISO 9001, BSCI, and export-specific compliance standards.
Why the Verified Pro List Cuts Time-to-Engagement by 92%
Manual distributor sourcing exposes your organization to hidden costs: due diligence failures, quality disputes, and shipment delays. Our proprietary verification framework transforms risk into ROI:
| Sourcing Method | Avg. Time to Qualified Distributor | Risk Exposure (Quality/Compliance) | Cost of Failure per Engagement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Search (Google, Alibaba, Trade Shows) | 8–14 weeks | High (43% non-compliant per 2025 audit) | $22,500–$68,000 |
| SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | 3–5 business days | Near-zero (0.8% failure rate) | <$1,200 (prevention cost) |
Key Time-Saving Mechanisms:
- Pre-Validated Capabilities: 100% of Pro List distributors undergo 17-point verification (financial stability, export licenses, facility audits, English-speaking teams).
- AI-Powered Matching: Algorithm aligns your product specs, volume, and compliance needs with optimal distributors in <24 hours.
- Dedicated Sourcing Manager: Single point of contact for contract negotiation, quality assurance, and logistics—no vendor-hopping.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our medical device distributor onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days. We avoided a $150K shipment recall due to their pre-shipment compliance check.”
— Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Healthcare Client (2025 Case Study)
Your Next Step: Secure Q4 2026 Supply Chain Resilience
Every day spent on unverified distributor searches risks stockouts, margin erosion, and reputational damage. The Verified Pro List isn’t a tool—it’s your operational insurance against China’s complex sourcing landscape.
✅ Immediate Actions to Unlock Efficiency:
- Reduce sourcing cycles from months to days with pre-vetted, ready-to-engage distributors.
- Eliminate compliance liabilities with real-time documentation access (COAs, customs records, audit trails).
- Protect margins with transparent pricing benchmarks—no hidden fees or MOQ surprises.
CALL TO ACTION: ACTIVATE YOUR 2026 SOURCING ADVANTAGE
Do not risk Q4 2026 targets on unverified suppliers. Contact SourcifyChina today to:
– Receive a free distributor shortlist for your product category
– Access our 2026 China Compliance Playbook (exclusive to procurement managers)
– Schedule a 15-minute risk assessment with our Senior Sourcing Team
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 for urgent procurement needs)
“In 2026, speed without verification is corporate suicide. SourcifyChina delivers both.”
— Michael Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
SOURCIFYCHINA | Your Verified Gateway to China Sourcing Excellence
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sourced from 3,200+ client engagements (2020–2025).
Compliance Note: All Pro List distributors adhere to UFLPA, EU CBAM, and SEC Climate Disclosure Rules.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.