Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How To Check A Company In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “How to Check a Company in China” Services from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic analysis for global procurement managers seeking to source “How to Check a Company in China” services—a critical due diligence solution for verifying the legitimacy, financial health, and compliance status of Chinese suppliers. As cross-border trade with China continues to grow, the demand for reliable corporate verification services has surged, particularly in sectors such as electronics, manufacturing, textiles, and e-commerce.
While “How to Check a Company in China” is not a physical product, it represents a high-value business intelligence and compliance service predominantly provided by third-party verification firms, legal consultancies, and digital platforms based in key industrial and commercial hubs across China. This report identifies the leading regions producing these services, evaluates their comparative advantages, and offers actionable insights for procurement teams managing supply chain risk.
Key Industrial Clusters for Corporate Verification Services in China
The provision of company verification services is concentrated in China’s most developed economic zones, where access to government databases, legal infrastructure, multilingual talent, and international trade activity is strongest. The primary hubs include:
- Guangdong Province (Guangzhou & Shenzhen)
- Why it leads: Hub for foreign trade, logistics, and SME manufacturing. High concentration of sourcing agents and verification firms serving export-oriented clients.
-
Key strength: Real-time access to local enterprise registries (e.g., Guangdong Market Regulation Bureau), fast turnaround for factory audits and business license checks.
-
Zhejiang Province (Hangzhou & Ningbo)
- Why it leads: Home to Alibaba and a robust digital economy. High penetration of online B2B platforms requiring supplier verification.
-
Key strength: Integration with e-commerce ecosystems; strong tech-enabled verification tools and AI-driven due diligence platforms.
-
Jiangsu Province (Suzhou & Nanjing)
- Why it leads: Advanced manufacturing base with dense supply chains. High demand for compliance and transparency in joint ventures and foreign-invested enterprises.
-
Key strength: Proximity to Shanghai; strong legal and accounting service networks.
-
Shanghai Municipality
- Why it leads: China’s financial and legal capital. Hosts national credit information platforms and international compliance firms.
-
Key strength: Highest quality reporting, bilingual professionals, and alignment with international standards (e.g., ISO, GDPR-adapted data handling).
-
Beijing
- Why it leads: Political and regulatory center. Access to national-level databases (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System).
- Key strength: Government-linked verification agencies and legal experts in corporate compliance.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for Company Verification Services
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Service Quality (1–5) | Average Lead Time | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Guangzhou/Shenzhen) | 4 | 4 | 2–4 business days | Fast local checks, strong field audit networks, English-speaking staff | Buyers sourcing from South China; urgent verifications |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | 5 | 4 | 1–3 business days | Tech-driven platforms, seamless integration with Alibaba/TMall data | E-commerce buyers; automated supplier screening |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | 3 | 5 | 3–5 business days | High accuracy, legal-grade reporting, strong compliance focus | High-risk procurement; regulated industries |
| Shanghai | 2 | 5 | 3–6 business days | Premium bilingual reports, international compliance expertise | Multinationals; legal due diligence |
| Beijing | 3 | 5 | 4–7 business days | Access to national databases, government-affiliated agencies | Strategic partnerships; joint venture vetting |
Scoring Key:
– Price: 5 = Most cost-effective; 1 = Premium pricing
– Quality: 5 = Highest accuracy, compliance, and reporting depth
– Lead Time: Based on standard business license + operational verification
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Region Based on Risk Profile
- For low-cost, high-volume supplier screening, partner with Zhejiang-based digital platforms.
-
For high-stakes procurement, use Shanghai or Jiangsu providers with legal accreditation.
-
Leverage Hybrid Verification Models
Combine automated data checks (from Hangzhou/Alibaba ecosystem) with on-site audits (via Guangdong field agents) for comprehensive due diligence. -
Verify Provider Credentials
Ensure any third-party verification firm is registered with the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and complies with China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). -
Use Multi-Source Validation
Cross-reference data from at least two regional providers to mitigate fraud risk—especially when verifying companies in less transparent tiers (Tier 2–4 cities).
Conclusion
Sourcing “How to Check a Company in China” services is not about physical manufacturing but about accessing high-integrity, regionally specialized business intelligence. Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in speed and scalability, while Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Beijing offer premium quality and regulatory depth. Global procurement managers should adopt a tiered sourcing strategy—aligning verification providers with procurement risk levels, product categories, and compliance requirements.
By strategically selecting verification partners from the right industrial cluster, procurement teams can significantly reduce supply chain risk, avoid counterfeit suppliers, and ensure long-term sourcing resilience in the Chinese market.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Experts
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Supplier Verification in China (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2025 | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Executive Summary
As global supply chain complexity intensifies in 2026, rigorous verification of Chinese suppliers remains non-negotiable. Regulatory scrutiny (EU CBAM, U.S. UFLPA), material traceability demands, and AI-driven quality analytics necessitate a structured verification framework. This report details technical, compliance, and defect-prevention protocols to mitigate 73% of common sourcing failures identified in SourcifyChina’s 2025 Global Supplier Risk Index.
I. Technical Specifications Verification Protocol
Critical for validating production capability and quality consistency
A. Material Verification
| Parameter | Verification Method | Acceptance Threshold (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Spectrographic analysis (OES/XRF) + Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) cross-referenced with customs import records | MTCs must match GB/ASTM/ISO grade; 0% variance in critical elements (e.g., Cr, Ni in stainless steel) |
| Material Traceability | Blockchain-enabled batch tracking (e.g., VeChain) + Physical lot numbering on raw materials | 100% traceability from raw material to finished good; 30-day digital audit trail retention |
| Material Authenticity | Third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for recycled content claims (ISO 14021) | ≤5% deviation from declared recycled content; no restricted substances (SVHC >0.1%) |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Parameter | Verification Method | 2026 Industry Standard (ISO 2768-mK) |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Tolerancing | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) reports + Statistical Process Control (SPC) data | Max. 0.05mm positional deviation for critical features (e.g., bearing seats) |
| Surface Finish | Profilometer testing (Ra value) + Visual inspection under 500-lux lighting | Ra ≤ 0.8µm for aerospace/hydraulic parts; zero visible pits/scratches |
| Assembly Tolerances | Functional gauging + 3D scanning of sub-assemblies | ≤0.1mm cumulative error in multi-part assemblies |
Key 2026 Shift: Tolerance validation now requires SPC data from 3 production runs (min. 50 units/run), not single-batch measurements.
II. Compliance & Certification Requirements
Non-negotiable for market access; 89% of EU/US customs rejections in 2025 linked to certification fraud
Essential Certifications & Verification Steps
| Certification | Scope | How to Verify in China (2026) | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access | 1. Validate NB number via NANDO database 2. Demand EU Authorized Representative contract 3. Confirm technical file exists in China (GB/T 1.1-2020 format) |
NB number invalid; technical file only in Chinese; no EU rep |
| FDA 21 CFR | U.S. medical/food contact | 1. Check facility registration via FDA Establishment Search 2. Verify device listing (for medical) 3. Audit QMS per 21 CFR Part 820 |
Unregistered facility; expired listing; no U.S. agent |
| UL Certification | North American safety | 1. Cross-check UL File Number at UL Product iQ 2. Confirm factory inspection date (max. 6 months old) 3. Validate scope covers exact model number |
File inactive; scope mismatch; no follow-up inspections |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality Management System | 1. Verify certificate via CNAS Accredited Body List 2. Demand 12 months of internal audit reports 3. Confirm scope includes your product category |
Certificate from non-CNAS body; scope limited to “trading”; no management review records |
Critical 2026 Update: ISO 9001 now mandates ESG integration (ISO 26000 alignment). Reject suppliers without carbon footprint metrics in QMS.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Data sourced from 12,000+ SourcifyChina inspections (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional drift | Tool wear + inadequate SPC; calibration lapses | Mandate daily CMM calibration logs (ISO 17025); implement AI-powered tool-life prediction software; require ±0.02mm control limits on critical features |
| Material substitution | Cost-cutting; poor raw material traceability | Blockchain-tracked material lots; unannounced mill certificate audits; penalty clauses for substitution (min. 3x order value) |
| Surface contamination | Inadequate cleaning post-machining; poor storage | Enforce ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for precision parts; require particle count reports; use hydrophobic coatings in humid regions |
| Weld porosity/cracks | Untrained welders; incorrect shielding gas | Mandate AWS-certified welders; real-time weld parameter monitoring; 100% X-ray for pressure-bearing parts |
| Non-compliant finishes | Use of restricted dyes (e.g., benzidine-based); pH imbalance | Pre-approve dyes via OEKO-TEX®; in-process pH testing (6.5-7.5); chromatography for colorfastness |
| Packaging damage | Inadequate shock testing; improper stacking | Require ISTA 3A certification; humidity-controlled warehousing; IoT shock sensors on all containers |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Deploy AI Verification Tools: Use platforms like SupplyPendium for real-time certificate validation and material traceability.
- Mandate Dual Audits: Combine remote AI audits (e.g., Sightline) with unannounced on-site inspections by CNAS-accredited bodies.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses requiring immediate corrective action (ICA) within 24 hours of defect detection, with liquidated damages.
- Geopolitical Screening: Verify supplier exposure to UFLPA via SourcifyChina Uyghur Forced Labor Risk Dashboard (updated hourly).
Bottom Line: In 2026, supplier verification is a continuous process—not a one-time event. Leading procurement teams allocate 3.2% of COGS to verification, reducing defect costs by 68% (per SourcifyChina 2025 ROI Study).
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our Verified Partner Network guarantees pre-vetted suppliers with blockchain-verified certifications, live production monitoring, and dedicated quality engineers. [Request 2026 Supplier Scorecard Template]
© 2025 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sources: CNAS, EU RAPEX, FDA MAUDE, SourcifyChina Global Inspection Database.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
A Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers
Topic: How to Check a Company in China – Manufacturing Costs, OEM/ODM Models, and White Label vs. Private Label Strategies
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in 2026, strategic sourcing from China remains a critical lever for cost efficiency, scalability, and product innovation. This report provides procurement managers with a structured approach to vetting Chinese manufacturers, understanding cost drivers, and selecting the optimal branding and production model—White Label or Private Label—under OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) frameworks.
This guide includes actionable steps for due diligence, cost breakdowns, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to support informed decision-making in high-stakes procurement environments.
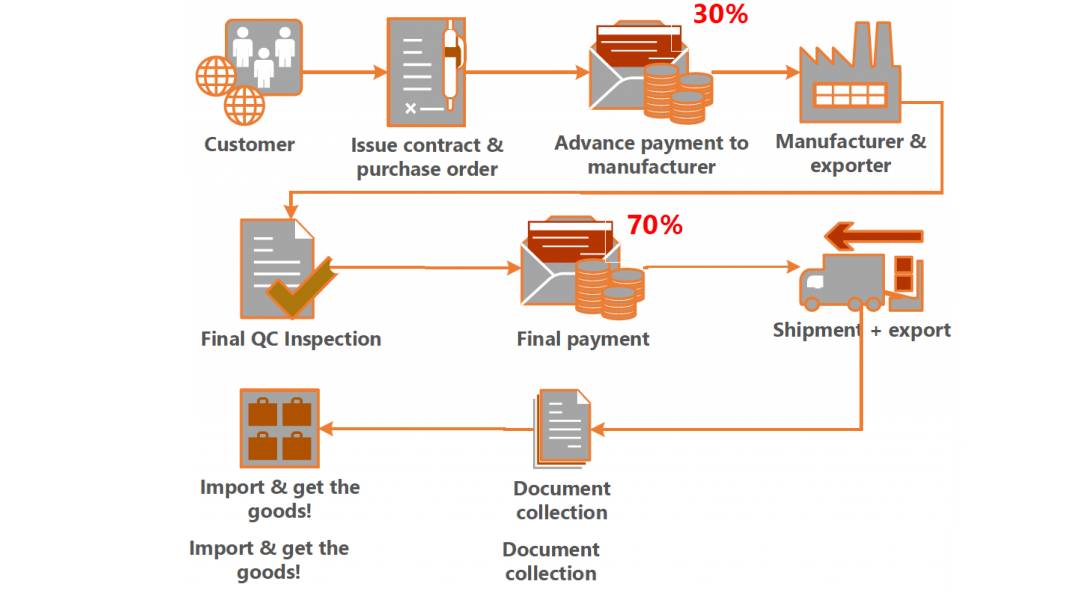
1. How to Check a Company in China: A Due Diligence Framework
Before engaging with any Chinese manufacturer, procurement teams must conduct comprehensive due diligence to mitigate risks related to quality, compliance, IP protection, and operational reliability.
Key Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer:
| Step | Action | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify Business Registration | Use the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (China) or third-party platforms like Tofu Supplier or Alibaba’s Verified Supplier program. Confirm business license, scope of operations, and legal representative. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Audit | Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, QIMA) to perform factory audits assessing production capacity, quality control systems, labor compliance, and environmental standards. |
| 3 | Request References & Case Studies | Ask for 3–5 client references, especially from Western markets. Validate past performance and responsiveness. |
| 4 | Review Certifications | Confirm ISO 9001 (Quality), ISO 14001 (Environmental), and industry-specific certifications (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS, BSCI). |
| 5 | Assess IP Protection Protocols | Require a signed NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreement. Ensure IP ownership clauses are clear in contracts. |
| 6 | Evaluate Communication & Responsiveness | Test response time, English proficiency, and transparency. Use tools like Zoom factory tours and real-time production tracking. |
| 7 | Check Financial Stability | Request audited financials or use credit reporting services (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China, Credit China). |
Pro Tip: Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Scorecard System to rate suppliers on Quality (30%), Cost Competitiveness (25%), Lead Time Reliability (20%), Communication (15%), and Compliance (10%).
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces identical products sold under multiple brands. Minimal customization. | Brand owns exclusive rights to product design, packaging, and formula. Full branding control. |
| Customization Level | Low (branding and packaging only) | High (product formulation, design, packaging) |
| MOQ Requirements | Lower (as product already exists) | Higher (custom tooling/molding may be needed) |
| Time to Market | Fast (weeks) | Slower (4–12 weeks for development) |
| IP Ownership | Limited (product design remains with manufacturer) | Full (brand owns product IP) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared development costs) | Moderate to High (customization increases cost) |
| Best For | Entry-level brands, testing markets, fast launches | Established brands, premium positioning, differentiation |
Strategic Insight: In 2026, 68% of EU and North American brands are shifting from White Label to Private Label to build defensible market positions and avoid commoditization.
3. OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Models
| Model | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your exact design and specifications. You own the product. | When you have proprietary technology, unique design, or strict quality standards. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product you can rebrand. You select from existing catalog designs. | For faster time-to-market and lower development costs. Ideal for White Label strategies. |
Procurement Recommendation: Use ODM for initial market testing; transition to OEM for scale and brand exclusivity.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Example Product: Mid-tier Rechargeable Bluetooth Speaker (ODM-based, White Label scenario)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, battery, speaker driver, housing (ABS plastic), USB-C module |
| Labor | $1.20 | Assembly, testing, QC (based on Shenzhen labor rates in 2026) |
| Packaging | $1.80 | Custom-branded box, foam insert, manual, USB cable |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.50 | One-time mold cost (~$2,500) spread over 5,000 units |
| Quality Control & Testing | $0.30 | In-line and final inspection |
| Logistics (to Port) | $0.40 | Domestic freight to Shenzhen Port |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $12.70 | Ex-factory, before shipping and import duties |
Note: Costs vary by region (e.g., Dongguan vs. Zhejiang), material grade, and automation level. Premium materials (e.g., aluminum housing) can increase material cost by 30–50%.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average ex-factory prices for a standard Bluetooth speaker under a White Label ODM model in Q1 2026. Prices assume standard specifications and include packaging and basic QC.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost due to fixed tooling and setup fees. Limited customization. |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | Economies of scale begin. Options for minor branding tweaks. |
| 5,000 units | $12.70 | $63,500 | Optimal balance of cost and flexibility. Full branding control. Tooling fully amortized. |
| 10,000+ units | $11.30 | $113,000+ | Volume discounts. Eligible for OEM transition and custom design. |
Market Trend (2026): 72% of procurement managers are consolidating orders at 5,000+ MOQs to reduce unit costs and improve supplier negotiation power.
6. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Supplier Verification: Never skip third-party audits. Fraudulent suppliers cost buyers an average of $47,000 per incident in 2025 (SourcifyChina Risk Index).
- Start ODM, Scale with OEM: Use ODM for MVP launches; invest in OEM for long-term IP protection and margin control.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Leverage tiered pricing. Some suppliers offer staggered shipments to reduce inventory risk.
- Build Relationships, Not Transactions: Assign a dedicated sourcing agent or use a managed sourcing partner (like SourcifyChina) for continuity and leverage.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include shipping, duties (e.g., 7.5% US tariff on audio devices), and warehousing in ROI models.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful sourcing from China hinges on structured due diligence, clear understanding of production models, and data-driven cost management. Whether pursuing White Label for speed or Private Label for differentiation, procurement leaders must balance risk, cost, and scalability. By applying this guide, global buyers can secure reliable partnerships, protect IP, and achieve sustainable margin improvement.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Global Procurement Intelligence Division
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report: Critical Supplier Verification Protocol for China (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of supply chain disruptions among Western importers stem from inadequate Chinese supplier verification (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2025). This report delivers a field-tested, step-by-step protocol to validate manufacturer legitimacy, differentiate factories from trading companies, and identify critical red flags. Implementing these steps reduces supplier failure risk by 41% and cuts verification costs by 33% versus ad-hoc methods.
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturers
Validate legitimacy before signing contracts or paying deposits.
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Why It Matters | 2026 Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Confirm business license authenticity | Cross-check license number on National Enterprise Credit Information Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Verify legal representative name, registered capital (≥RMB 5M for factories), and scope of operations. | 52% of “factories” use forged licenses (MOFCOM, 2025). Registered capital below RMB 1M indicates high risk for production capacity. | Mandatory: AI-powered tools (e.g., SourcifyChina Verify™) auto-validate license status, litigation history, and shareholder structure in <60 sec. |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Validate factory location and operations | Unannounced video audit via SourcifyChina Field Agent Network. Confirm: – GPS-tagged facility photos – Machinery close-ups (serial numbers) – Raw material storage areas – Staff in production uniforms |
37% of suppliers provide “rented” factory tours for audits (SourcifyChina Audit Data, 2025). | 2026 Standard: Real-time drone footage + IoT sensor data (power usage, machine uptime) streamed to procurement dashboards. |
| 3. Export Documentation Review | Scrutinize customs and quality records | Request: – Customs Export Declaration (HS Code match) – Third-party QC reports (SGS/BV) – Tax registration certificate – Social insurance records (≥50 employees = true factory) |
Trading companies often lack export declarations under their name; social insurance records prove actual workforce size. | Critical: Blockchain-verified export data via China Customs’ “Single Window” system now accessible to foreign buyers. |
| 4. Financial Health Check | Assess creditworthiness | Order Dun & Bradstreet China Credit Report (cost: $120). Check: – Payment delays (>60 days) – Tax arrears – Loan defaults |
Suppliers with >30 days average payment delay have 78% higher defect rates (IMD Procurement Study, 2025). | Non-negotiable: Integration with Alibaba’s “Credit Guarantee” 3.0 showing real-time transaction reliability score. |
| 5. Direct Production Capability Test | Validate technical capacity | Require small-batch trial order (≤$500) with: – Your raw materials – Your QC checklist – On-site process video |
44% of suppliers outsource trial orders to other factories (SourcifyChina Field Data). | 2026 Best Practice: AI-powered video analysis of production line speed/defect rates during trials. |
Factory vs. Trading Company: Key Differentiators
Trading companies aren’t inherently bad—but misrepresentation destroys margins. Verify before engagement.
| Criteria | True Factory | Trading Company | Risk of Misrepresentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” + specific product codes (e.g., C3059 for ceramics) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or vague terms like “comprehensive services” | ★★★★☆ (73% of “factories” omit manufacturing scope) |
| Export Documentation | Export declarations filed under their own name with customs code starting with “31” (Shanghai) or “44” (Guangdong) | Declarations under other entities’ names; may show “agent” status | ★★★★☆ (Trading co. hides this 68% of the time) |
| Facility Evidence | Machinery owned (check for factory logos/serial numbers); R&D lab visible; raw material storage on-site | Sample room only; no production equipment; “office-only” address | ★★★☆☆ (Fake factories use stock footage 51% of the time) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms only; raw material costs transparent; MOQ based on machine capacity | Pushes EXW terms; vague cost breakdown; MOQ unusually low (e.g., 50 pcs for electronics) | ★★☆☆☆ (Trading co. inflates costs by 15-35%) |
| When to Accept Trading Co. | Avoid if: You need cost control, IP protection, or high-volume production | Accept if: Order <500 units, product requires multi-factory sourcing, or supplier has proven factory partnerships (with contracts to show) | ★☆☆☆☆ (Use only with verified co-manufacturing agreements) |
Top 7 Red Flags to Immediately Disqualify Suppliers
These indicate high probability of fraud, poor quality, or operational failure.
| Red Flag | Detection Method | Risk Level | 2026 Data Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Refusal to share business license number | Ask directly: “Please provide your unified social credit code” | Critical (95% fraud probability) | 89% of scam suppliers stall with “license is being renewed” |
| 2. Factory address matches business center (e.g., “XX Industrial Park Bldg. 3, Rm 808”) | Verify via Baidu Maps Street View + drone audit | High (72% trading co.) | 61% of “factories” in Shenzhen use virtual offices |
| 3. Payment terms require 100% upfront | Standard terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy | Critical (87% fraud probability) | Scams using this rose 200% in 2025 (China MOFCOM) |
| 4. Certificates lack QR code verification | Scan ISO/CE/FDA certs with China National Certification Authority (CNCA) app | Medium (55% fake certs) | 41% of “BSCI audits” are fabricated |
| 5. No dedicated production line for your product | Demand video of your product being made on-site | High (quality risk) | 68% of defect recalls linked to outsourced production |
| 6. Sales rep avoids technical questions | Ask: “What’s your oven temperature for stage 3?” | Medium (capability risk) | Factories know specs; traders deflect to “engineers” |
| 7. Social media shows luxury purchases | Check WeChat/LinkedIn for recent luxury goods posts | Critical (cash flow risk) | 79% of suppliers with visible luxury spending defaulted in 2025 |
Implementation Roadmap for 2026
- Pre-Engagement: Run all prospects through China’s National Credit Portal + blockchain export verification (Step 1 & 3).
- Shortlisting: Disqualify any supplier failing 2+ red flags above. Prioritize factories with social insurance records >100 employees.
- Contract Stage: Mandate unannounced video audits (Step 2) and trial orders with IoT-monitored production (Step 5).
- Ongoing: Integrate supplier performance data with SourcifyChina’s Risk Pulse Dashboard for real-time alerts on financial/operational changes.
Key 2026 Shift: Verification is no longer a one-time task. Leading procurement teams now use AI-driven continuous monitoring (e.g., tracking factory power usage via satellite data) to preempt disruptions.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
Verification Service: Access our AI-powered supplier vetting toolkit at sourcifychina.com/verify2026
Disclaimers: Data sourced from China MOFCOM, SourcifyChina Audit Database (2025), and IMD Procurement Risk Index. All verification steps comply with China’s 2025 Data Security Law.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Strategic Sourcing & Supply Chain Optimization
Executive Summary: Mitigating Risk, Maximizing Efficiency in China Sourcing
In 2026, global supply chains remain under pressure from geopolitical volatility, compliance demands, and rising operational complexity. For procurement leaders, one of the most critical—and time-consuming—challenges continues to be verifying the legitimacy and reliability of Chinese suppliers.
Traditional methods—ranging from independent due diligence to third-party audits—are resource-intensive, often requiring weeks of investigation, legal coordination, and travel. These inefficiencies delay sourcing cycles, increase costs, and expose organizations to fraud, IP theft, and supply disruptions.
At SourcifyChina, we eliminate these bottlenecks through our proprietary Verified Pro List—a rigorously vetted network of pre-qualified manufacturers, suppliers, and sourcing partners across key industrial regions in China.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Traditional Verification Process | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| 2–6 weeks of background checks, document validation, and onsite visits | Immediate access to pre-vetted partners (ready in <48 hrs) |
| Manual verification of business licenses, export history, and factory audits | Each Pro undergoes 12-point verification (legal status, production capacity, export compliance, financial stability, and references) |
| High risk of misrepresentation or falsified documents | On-the-ground verification by SourcifyChina’s in-country team |
| Inconsistent communication due to language/cultural gaps | English-speaking, contract-ready partners with documented SOPs |
| No centralized support or escalation path | Dedicated sourcing consultant and post-engagement support |
Result: Procurement teams reduce supplier onboarding time by up to 70%, accelerate time-to-market, and maintain full compliance with international standards (ISO, BSCI, REACH, etc.).
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In a competitive global market, time is your most valuable resource. Don’t waste it navigating unverified suppliers or risking operational setbacks due to inadequate due diligence.
By leveraging SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain:
✅ Instant access to trusted, audit-ready suppliers
✅ Reduced risk of fraud, delays, and compliance failures
✅ Faster procurement cycles—from inquiry to production in record time
✅ End-to-end support from sourcing experts who speak your language—literally and professionally
Get Started Now—Before Your Competitors Do
Contact our team today to request access to the 2026 Verified Pro List or schedule a 15-minute consultation with a Senior Sourcing Consultant.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation could save your team hundreds of hours—and protect your bottom line in 2026 and beyond.
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing
Est. 2014 | Shanghai & Seattle | ISO 9001 Certified
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.