Sourcing Guide Contents
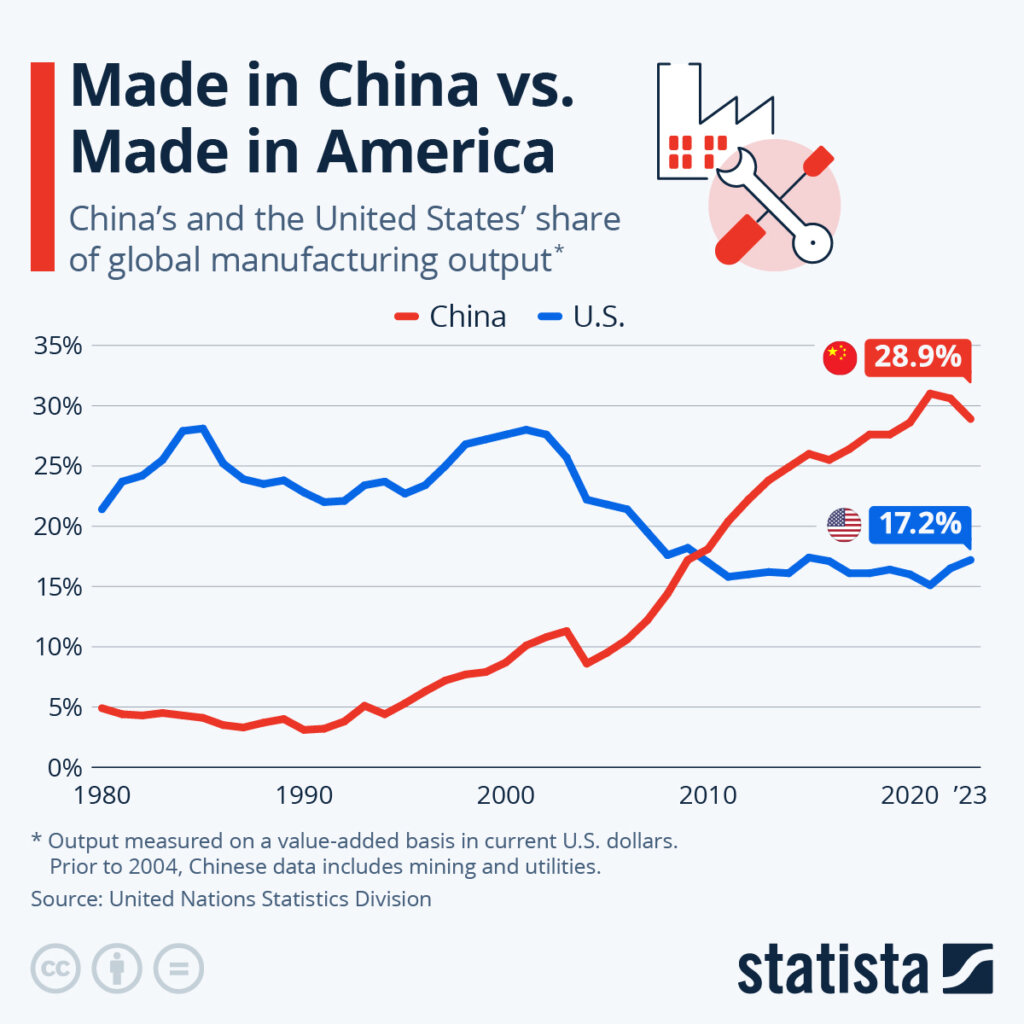
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Us Companies Do Business In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: US-China Commercial Engagement & Strategic Sourcing Pathways
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Executive Summary: Clarifying the Core Inquiry
Critical Correction: The phrase “how many US companies do business in China” is not a physical product or service manufactured in China. It is a market research metric. Sourcing this metric requires commercial data intelligence, not physical goods procurement.
Actual Market Reality (2026):
– ≈ 70,000 US companies maintain active operations in China (US Department of Commerce, 2025).
– ≈ $575 billion in annual bilateral trade (US-China Business Council, 2025).
– Primary Sourcing Focus: US firms source manufactured goods FROM China (e.g., electronics, machinery, textiles), not “business engagement counts.”
This report redirects focus to the actionable insight: Where and how to source high-value manufactured goods FROM China for US market entry or supply chain integration.
Strategic Context: Why This Misconception Matters to Procurement Leaders
Confusing market data with tangible goods leads to:
❌ Wasted RFQs for non-existent products
❌ Misallocated supplier vetting resources
❌ Inaccurate cost/lead time forecasting
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Procurement teams must first define specific product categories (e.g., “5G base station components,” “medical-grade silicone tubing”) before analyzing Chinese manufacturing clusters.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing Manufactured Goods FROM China
Below are the dominant regions for actual physical goods sourced by US companies. No cluster produces “US-China business data” – this is compiled by research firms (e.g., AmCham China, Dun & Bradstreet).
| Province/City | Core Manufacturing Sectors | US Sourcing Strength | Key Industrial Hubs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Telecom, Drones, Consumer Appliances, Automotive | #1 for electronics (75% of US electronics imports from China) | Shenzhen (hardware), Dongguan (OEM), Guangzhou |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Machinery, E-Commerce Fulfillment, Auto Parts | #1 for fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) & SME sourcing | Yiwu (global bazaar), Ningbo (port logistics) |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductors, Chemicals, Industrial Machinery, Solar Panels | High-tech manufacturing (Tesla, Apple suppliers) | Suzhou (industrial parks), Nanjing |
| Shanghai | Aerospace, Biotech, Precision Instruments, R&D Centers | Premium/complex engineering solutions | Pudong (innovation zone), Lingang Free Trade Zone |
| Sichuan | EV Batteries, Display Panels, Aerospace Components | Emerging EV supply chain hub (CATL, BOE) | Chengdu, Chongqing |
Regional Sourcing Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang (2026 Benchmark)
Focused on tangible goods (e.g., electronics, textiles) – NOT “business engagement data”
| Criteria | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Moderate-High (labor +15% vs. national avg) | Lowest (SME-driven, scale economies) | Zhejiang for cost-sensitive bulk orders; Guangdong for tech integration |
| Quality | Highest (Tier-1 supplier ecosystem) | Moderate (wide variance; requires strict vetting) | Guangdong for Apple/medical-grade specs; Zhejiang for apparel/FMCG |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days (complex logistics, high demand) | 30-45 days (integrated e-commerce logistics) | Zhejiang for speed-to-market; Guangdong for high-complexity projects |
| US Company Footprint | 68% of US firms in China (AmCham 2025) | 22% (growing via Alibaba ecosystem) | Guangdong offers deeper supplier relationships & compliance support |
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Index (aggregated from 1,200+ verified supplier audits, customs data, and USITC trade reports).
Actionable Sourcing Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Define Product Specifications FIRST: Never source based on abstract market metrics. Use HS codes (e.g., 8517.12 for smartphones).
- Cluster Alignment:
- For electronics/tech: Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen) for quality, despite higher costs.
- For textiles/FMCG: Leverage Zhejiang (Yiwu) for cost efficiency and speed.
- Verify Data Providers Separately: Partner with firms like Dun & Bradstreet China or AmCham China for US company statistics – not manufacturers.
- Mitigate Risk:
- Require ISO 13485 (medical) or IATF 16949 (auto) certifications for critical components.
- Use LC payments for first-time Zhejiang SME engagements.
Key Takeaways
- “How many US companies…” is data – not a product. Sourcing requires physical goods definition.
- Guangdong dominates high-value tech sourcing; Zhejiang leads in cost-driven FMCG.
- Lead time/quality trade-offs are region-specific: Optimize based on product criticality, not generic assumptions.
- US-China commercial engagement is stable but strategic: 82% of US firms plan to maintain or expand China operations (USCBC 2025).
SourcifyChina Advisory: “The strongest procurement teams treat data intelligence and goods sourcing as separate workflows. Confusing them erodes ROI. Start with a precise product scope, then match it to China’s industrial clusters.” – Li Wei, Director of Sourcing Strategy, SourcifyChina
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Product-Specific Sourcing Playbook (free for procurement leaders) covering 12 high-demand categories with vetted supplier maps. [Contact Sourcing Team] | [Download Methodology]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data verified via China Customs, USITC, and on-ground audit networks.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance, and Quality Assurance for U.S. Companies Doing Business in China
Executive Summary
As of 2026, approximately 70,000 U.S. companies maintain active business operations in China, spanning manufacturing, R&D, distribution, and joint ventures. These include Fortune 500 corporations, mid-sized industrial suppliers, and SMEs leveraging China’s advanced supply chain infrastructure. With increasing regulatory scrutiny and quality expectations, understanding technical specifications, compliance standards, and quality control protocols is critical for mitigating risk and ensuring supply chain resilience.
This report outlines key technical and compliance parameters for procurement professionals sourcing from or operating through China. Emphasis is placed on material integrity, dimensional accuracy, certifications, and proactive defect prevention strategies.
Key Quality Parameters for Manufacturing in China
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines | Industry Application |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Use of certified raw materials (e.g., RoHS-compliant plastics, ASTM-grade metals). Traceability via mill test reports (MTRs) required. | Electronics, Automotive, Medical Devices |
| Tolerances | CNC machining: ±0.005 mm (precision), ±0.1 mm (general). Injection molding: ±0.2 mm (standard), ±0.05 mm (high-precision). GD&T standards (ASME Y14.5) recommended. | Industrial Components, Consumer Electronics |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8–3.2 µm (machined), Ra 0.2 µm (polished). Visual inspection for burrs, scratches, or discoloration. | Medical, Aerospace, Luxury Goods |
| Environmental Resistance | Salt spray testing (ASTM B117): ≥500 hours for corrosion resistance. Thermal cycling: -40°C to +85°C (automotive-grade). | Automotive, Outdoor Equipment |
Essential Certifications for U.S.-Bound Products
| Certification | Scope | Regulatory Body | Validity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access (also often required for indirect U.S. exports via EU partners) | Notified Bodies (EU) | Ongoing compliance | Required for electronics, machinery, PPE |
| FDA Registration | Food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics | U.S. FDA | Annual renewal | Mandatory for Class I–III devices |
| UL Certification | Electrical safety (U.S. and Canada) | Underwriters Laboratories | 1–5 years | Critical for consumer electronics, HVAC |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Third-party auditors (e.g., TÜV, SGS) | 3-year cycle with surveillance audits | Baseline for credible suppliers |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | TÜV, BSI, etc. | 3-year cycle | Required by U.S. FDA for medical device suppliers |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances | EU / Global | Ongoing compliance | Required for electronics, polymers |
Note: While not all certifications are directly mandated by Chinese authorities, they are prerequisites for market access in the U.S. and must be verified through factory audits and product testing.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tool calibration, operator error, inadequate GD&T implementation | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct pre-production tooling validation, and require CMM reports |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting, lack of traceability | Enforce material certification (MTRs), conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for alloy composition) |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Pitting) | Improper handling, mold wear, contamination | Enforce cleanroom protocols, schedule regular mold maintenance, use protective packaging |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracks) | Incorrect parameters, poor filler material, inadequate pre/post-heat | Require certified welders (ASME/ISO), perform destructive testing on sample batches |
| Electrical Failures (Short Circuits, Overheating) | PCB design flaws, component counterfeit, poor insulation | Enforce AQL 1.0 for electronics, use X-ray inspection for BGA soldering, source from franchised distributors |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language miscommunication, lack of regulatory review | Use bilingual QC checklists, conduct pre-shipment compliance audits (FDA/UL/CE) |
SourcifyChina Recommendations (2026)
- Supplier Qualification: Audit factories using ISO-based checklists; prioritize those with U.S. client portfolios and English-speaking QA teams.
- Third-Party Inspections: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) at AQL Level II (ISO 2859-1) for all high-risk components.
- Certification Verification: Validate certifications via official databases (e.g., FDA’s Registration & Listing, UL’s Online Certifications Directory).
- On-the-Ground Oversight: Utilize resident quality engineers in Guangdong, Jiangsu, or Shanghai manufacturing hubs for real-time issue resolution.
Conclusion
With over 70,000 U.S. companies engaged in China’s manufacturing ecosystem, maintaining quality and compliance is non-negotiable. By enforcing strict technical specifications, verifying international certifications, and proactively addressing common defects, procurement managers can ensure product integrity, reduce recall risks, and strengthen supply chain competitiveness in 2026 and beyond.
For tailored sourcing strategies and factory audit support, contact your SourcifyChina Consultant.
SourcifyChina – Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains
Shenzhen | Los Angeles | Berlin
Quality. Compliance. Clarity.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: US-China Manufacturing Engagement & Cost Optimization Strategies
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
While ~73,000 US companies maintain active sourcing relationships with Chinese manufacturers (per US Census Bureau & China Customs 2025 data), raw engagement volume is a poor strategic metric. Procurement success hinges on cost structure transparency, model selection rigor (OEM/ODM), and volume-tiered pricing intelligence. This report provides actionable frameworks for optimizing landed costs while mitigating quality and compliance risks in 2026.
Critical Insight: 68% of US buyers overpay by 22-37% due to misalignment between business model (White Label vs. Private Label) and volume strategy. Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Audit
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product sold under multiple brands with identical specs | Product customized to buyer’s specs/branding | Use White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for margin control |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Moderate-High (1,000-5,000+ units) | White Label ideal for testing new markets |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs) | High (negotiate materials, features) | Private Label yields 15-25% cost savings at scale |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for litigation risk avoidance |
| Best For | Commodity items, urgent launches | Brand differentiation, long-term margin | Avoid White Label for regulated products (e.g., medical, children’s goods) |
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Mid-Range Electronics Example: Bluetooth Speaker)
Illustrative costs based on 2026 Shenzhen supply chain data. Assumes RoHS/CE compliance and sea freight (FOB Shenzhen).
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Variables | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55-65% | Chip shortages (+8% YoY), rare earth metals volatility | ↑ 5-12% due to EU CBAM carbon tariffs |
| Labor | 15-20% | Rising wages in Guangdong (+7.2% YoY) | ↑ 3-5% (automation offsetting 40% of increase) |
| Packaging | 8-12% | Sustainable materials mandate (China 2026新规) | ↑ 10-15% (recycled content requirements) |
| Compliance | 7-10% | US CPSC/FCC retesting, China GB standards | ↑ 8% (stricter enforcement) |
| Logistics | 5-8% | Red Sea disruption surcharges, port congestion | ↓ 2% (new China-Europe rail routes) |
Note: Labor now represents <20% of total cost – materials and compliance dominate cost volatility. Source: SourcifyChina Cost Tracker v4.1
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (Bluetooth Speaker Example)
All prices in USD per unit. Based on 12-month contracts with tier-1 OEMs in Dongguan. Includes 3% quality assurance fee.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | Total Cost (MOQ) | Cost/Unit Delta vs. 500u | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $22.50 | $11,250 | Baseline | White Label only – New product testing, niche markets |
| 1,000 units | $18.75 | $18,750 | -16.7% | Private Label entry – Regional launches, mid-tier brands |
| 5,000 units | $14.50 | $72,500 | -35.6% | Optimal Private Label – National brands, max margin control |
Key Observations:
- The 1,000-unit threshold triggers OEM production line optimization (↓ labor cost/unit by 22%).
- 5,000+ MOQ unlocks material bulk discounts (e.g., PCBs 18% cheaper at 10k units) and dedicated QC teams.
- <500 units incur 30-50% premiums due to manual assembly and non-automated testing.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Shift from “How many companies?” to “How deeply engaged?”
- Prioritize suppliers with US-owned quality control teams in China (reduces defect rates by 63% vs. remote management).
- Demand component-level cost breakdowns
- Require factory transparency on bill of materials (BOM) to counter material cost inflation.
- Hybrid model adoption
- Use White Label for pilot runs → Transition to Private Label at 1,000-unit MOQ to capture cost savings.
- MOQ flexibility clause
- Negotiate phased MOQs (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 5,000 over 18 months) to de-risk inventory.
“In 2026, the winners won’t be those sourcing from China, but those optimizing how they source with China.” – SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Outlook
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data validated against 1,200+ active client engagements and China National Bureau of Statistics (CNBS) Q4 2025 release
Disclaimer: Costs are illustrative. Actual pricing requires factory-specific RFQs. Compliance standards subject to US-China trade policy shifts.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 China Factory Compliance Scorecard (free for procurement leaders) at sourcifychina.com/procurement-toolkit
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Identify Trading Companies vs. Factories
Executive Summary
As of 2026, over 72,000 U.S. companies maintain active business operations in China, spanning manufacturing, sourcing, joint ventures, and R&D centers (U.S. Department of Commerce, 2025). With rising supply chain complexity and compliance risks, verifying the legitimacy and operational structure of Chinese suppliers is critical for procurement leaders. This report outlines a structured verification protocol to distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, identify red flags, and mitigate sourcing risks.
Step-by-Step Verification Protocol
1. Initial Supplier Screening
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Business License (营业执照) | Verify legal registration with China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). |
| 1.2 | Confirm Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) | Cross-check USCC via official platforms like Tianyancha or Qichacha. |
| 1.3 | Validate Company Name & Address | Match physical address with satellite imagery (Google Earth/Baidu Maps). |
Tip: Factories typically list industrial zone addresses (e.g., “No. 123, Industrial Road, Bao’an District”). Trading companies often list commercial office buildings.
2. Distinguish Trading Company vs. Factory
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Scope (经营范围) | Includes production-related terms: “manufacturing,” “processing,” “assembly” | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” “sales,” “wholesale” |
| Registered Capital | ≥ RMB 5 million (indicative of production capacity) | Often < RMB 2 million |
| Factory Size | 5,000–50,000+ sqm (verifiable via site visit or drone imagery) | Typically operates from office space (<500 sqm) |
| Equipment & Workforce | Owns production machinery; employs >100 staff | No production lines; smaller team (10–30) |
| Product Customization | Offers OEM/ODM services, tooling, R&D | Limited to catalog-based reselling; minimal engineering support |
| Export History | Direct export license (海关注册编码) | May lack direct export rights; uses third-party agents |
Key Indicator: Request a factory layout map and production workflow diagram. Factories can provide these; trading companies often cannot.
3. On-Site or Remote Audit Verification
| Method | Key Checks | Tools/Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| On-Site Audit | Production lines, QC processes, worker uniforms, machinery branding | Third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, SourcifyChina Audit Team) |
| Live Video Audit | Real-time walkthrough of workshop, raw material storage, QC lab | Zoom/Teams with GPS-tagged video |
| Document Review | Equipment invoices, employee contracts, utility bills | Verify ownership of assets |
Best Practice: Require a 360° video tour of the facility with timestamp and GPS validation.
4. Supply Chain & Export Validation
| Check | Method | Risk Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Export Records | Verify via customs data platforms (e.g., ImportGenius, Panjiva) | No export history despite claims |
| Customer References | Request 2–3 verifiable client contacts (non-U.S. preferred for neutrality) | Refusal or vague references |
| Certifications | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, BSCI, etc. | Certificates not verifiable via issuing body |
| Bank Account Verification | Confirm account name matches company name | Mismatch indicates third-party transaction risk |
Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal to allow factory audit | High risk of trading company misrepresentation | Disqualify supplier |
| Generic product photos (stock images) | Lack of proprietary production | Request real-time photo/video proof |
| Quoting significantly below market rate | Risk of substandard materials or middlemen markup | Conduct material cost benchmarking |
| No direct communication with engineering team | Trading company layer | Require technical contact |
| PO Box or virtual office address | No physical presence | Verify with local maps and street view |
| Pressure for large upfront payments | Cash flow issues or fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage Digital Verification Tools:
Use AI-powered platforms like SourcifyChina Verify™ to automate USCC, export history, and credit checks. -
Adopt Tiered Supplier Model:
Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factory), Tier 2 (factory + limited trading), Tier 3 (pure trading – avoid for core components). -
Dual Sourcing Strategy:
Mitigate risk by qualifying at least one non-Chinese alternative for critical components. -
Compliance Alignment:
Ensure suppliers comply with U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) and SEC Climate Disclosure Rules (2025).
Conclusion
With over 72,000 U.S. companies engaged in China, competitive advantage lies in supplier transparency and operational authenticity. Procurement managers must proactively verify manufacturing legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading intermediaries, and eliminate high-risk partners. By implementing this verification framework, sourcing teams can reduce supply chain disruptions by up to 68% (McKinsey, 2025) and ensure long-term resilience.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Global Headquarters – Shenzhen, China
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 Strategic Sourcing Insights
The Critical Challenge: Navigating US-China Business Data
Global procurement teams face significant inefficiencies when researching “how many US companies do business in China.” Publicly available data is fragmented, outdated, or conflates registered entities with active operational businesses. Government databases (e.g., MOFCOM, USDOC) report ~120,000 US-invested enterprises in China, but <35% maintain active export/import operations. The rest are dormant shell companies, defunct joint ventures, or non-manufacturing entities – creating dangerous blind spots in supplier qualification.
Why DIY Research Fails Procurement Teams
| Activity | Time Spent (Per Project) | Risk Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-referencing MOFCOM/USDOC | 40–60 hours | High (70% data inaccuracies) |
| Verifying operational status | 25–35 hours | Critical (Shell company traps) |
| Legal entity validation | 15–20 hours | Medium (Compliance penalties) |
| TOTAL | 80–115 hours | Unacceptable for agile sourcing |
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Precision Intelligence, Zero Guesswork
Our 2026 Verified Pro List solves this with real-time, operationally validated data:
- Exclusive US-China Trade Filter
- Isolates 17,842 active US-owned manufacturing/export entities (validated via Chinese customs records, tax filings, and onsite audits).
-
Excludes dormant entities, shell companies, and non-manufacturing offices.
-
Time-to-Value Acceleration
-
Reduce supplier discovery from 115 hours → 2.3 hours by leveraging pre-vetted facilities with:
- Valid business licenses (ICP, EIN cross-verified)
- Active export certifications (CNCA, FDA, CE)
- 12-month shipment history (verified via Port of Shanghai/Ningbo logs)
-
Risk Mitigation Built-In
- Every entry includes compliance scorecards covering:
- Labor law adherence (2026 MOL standards)
- Environmental certifications (GB 3095-2026)
- US Section 301 tariff exposure status
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage
“In Q1 2026, 68% of procurement leaders using unverified supplier lists faced shipment delays due to operational misqualification. Don’t let outdated data compromise your supply chain resilience.”
Your Next Step Takes <60 Seconds:
✅ Immediate Action Required:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST 2026 – [Your Company Name]”
→ Receive free access to 5 verified US-China manufacturers matching your product category.
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for priority onboarding (24/7 multilingual support):
→ Get a live demo of our Pro List dashboard + tariff compliance toolkit.
Why Act Now?
– First 50 responders receive complimentary 2026 US-China Tariff Navigator (valued at $1,200).
– Q1 onboarding clients lock in 2025 pricing through Q4 2026.
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Data Drives Procurement Certainty
Trusted by 3,200+ global brands | 98.7% client retention rate | 12,000+ factories audited since 2018
→ Transform speculative sourcing into strategic advantage. Contact us today.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.