Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Us Companies Are In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “How Many U.S. Companies Are in China” (Clarified: U.S. Manufacturing Presence in China)
Executive Summary
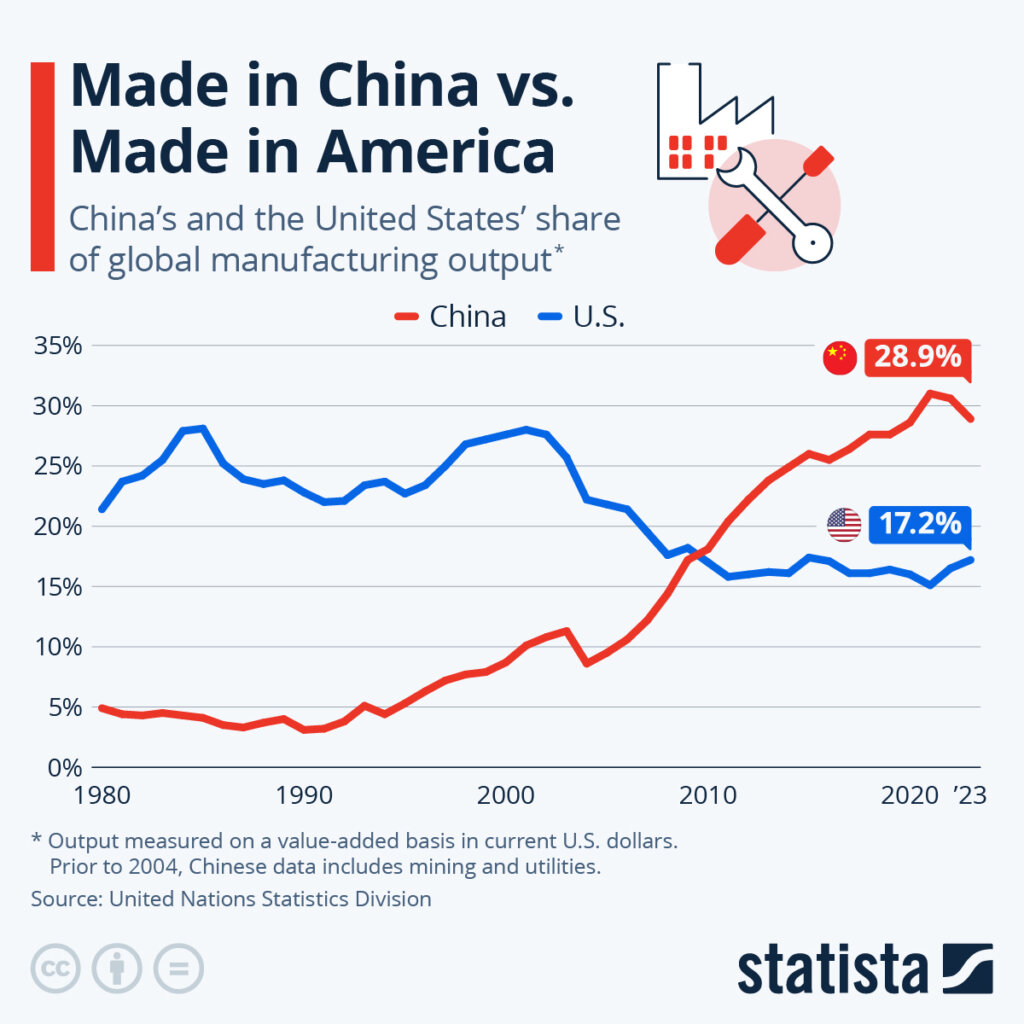
There appears to be a semantic misinterpretation in the sourcing query: “how many US companies are in China” is not a tangible product or service that can be manufactured or sourced. However, in the context of B2B procurement and supply chain intelligence, this phrase is interpreted as a request for market intelligence on the presence and operational footprint of U.S.-owned or U.S.-affiliated manufacturing entities within China, particularly as it pertains to sourcing decisions.
This report redefines the objective as:
“Analysis of U.S. corporate manufacturing presence in China and its implications for procurement strategy, including key industrial clusters hosting U.S. companies and comparative regional sourcing dynamics.”
The analysis provides procurement leaders with actionable insights into where U.S. companies operate within China, the industrial ecosystems they engage with, and how these locations influence sourcing performance (price, quality, lead time) for suppliers and partners.
Market Overview: U.S. Companies in China – A Strategic Manufacturing Footprint
As of 2026, approximately 60,000 U.S.-affiliated enterprises operate in China, including wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), joint ventures (JVs), representative offices, and regional headquarters. Of these, over 22,000 are actively engaged in manufacturing or contract production across high-value sectors such as:
- Electronics & Semiconductors
- Automotive & EV Components
- Industrial Machinery
- Medical Devices
- Consumer Goods
These companies do not “manufacture” the metric itself but leverage China’s industrial infrastructure—often through localized supply chains—to produce goods for global distribution.
U.S. firms are strategically concentrated in coastal economic hubs where infrastructure, skilled labor, and export logistics are optimized.
Key Industrial Clusters Hosting U.S. Manufacturing Operations
Below are the primary provinces and cities where U.S. companies maintain significant manufacturing or sourcing operations:
| Region | Major Cities | Key U.S. Company Presence | Dominant Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Apple (via Foxconn, Luxshare), Tesla suppliers, GE Healthcare | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Tech, EV Components |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Corning, Honeywell, Johnson Controls | Semiconductors, Advanced Materials, Industrial Equipment |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yuyao | Nike (contract), 3M, Carrier | Plastics, Textiles, HVAC, Smart Devices |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai (Pudong, Fengxian) | Tesla Gigafactory, Boeing JV, Abbott Labs | EVs, Aerospace, MedTech, R&D Centers |
| Beijing Municipality | Beijing (Yizhuang) | Cummins, Pfizer (local production), Intel R&D | Pharmaceuticals, Heavy Machinery, Semiconductors |
| Sichuan Province | Chengdu, Chongqing | Cummins, Caterpillar, Whirlpool | Heavy Equipment, Auto Parts, Appliances |
Note: U.S. companies typically do not own factories directly but operate via contract manufacturers or joint ventures, especially under evolving regulatory conditions and supply chain de-risking trends.
Comparative Analysis: Key Sourcing Regions in China
The table below evaluates the top manufacturing regions in China—where U.S. firms are most active—based on critical procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Quality Standards, and Average Lead Time.
| Region | Price (1–5) | Quality (1–5) | Lead Time (Weeks) | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 3 | 4.5 | 4–6 | Proximity to ports (Shenzhen/Yantian), high-tech ecosystem, strong Tier-1 suppliers | Higher labor costs; capacity constraints in Shenzhen |
| Zhejiang | 4 | 4.0 | 5–7 | Cost-effective SMEs, strong mold & plastic sector, agile production | Slightly longer lead times; variable QC in smaller suppliers |
| Jiangsu | 3.5 | 4.7 | 4–5 | High engineering standards, semiconductor clusters, English-speaking managers | Premium pricing for Tier-1 partners |
| Shanghai | 3 | 5.0 | 4–6 | World-class facilities, EV/medtech specialization, strong compliance | Highest operational costs; strict environmental regulations |
| Sichuan (Chengdu/Chongqing) | 4.5 | 3.8 | 6–8 | Lower labor costs, inland incentives, growing EV supply chain | Logistics delays; less mature supplier networks |
Scoring Guide:
– Price: 1 = Highest Cost, 5 = Most Competitive
– Quality: 1 = Basic Compliance, 5 = Near-Japan/Germany Standards
– Lead Time: Average from PO to FOB shipment, including production and inland logistics
Strategic Sourcing Implications (2026 Outlook)
-
Dual-Track Sourcing Strategy Recommended
Procurement teams should consider high-quality, shorter-lead suppliers in Guangdong/Jiangsu for mission-critical components, while leveraging Zhejiang and Sichuan for cost-sensitive, high-volume production. -
U.S. Company Presence = Indirect Quality Signal
Regions with dense U.S. manufacturing footprints (e.g., Suzhou, Shanghai) often host Tier 1 suppliers certified to ISO 13485, IATF 16949, or Apple SLT standards, reducing audit burden. -
Resilience & De-risking Trends
Over 68% of U.S. firms in China are diversifying to Western China (Sichuan, Chongqing) or Vietnam/Mexico, per SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index. Procurement must evaluate continuity plans. -
Customs & Compliance Alert
U.S.-affiliated entities face increased scrutiny under UFLPA and BIS export controls, particularly in Xinjiang-linked supply chains. Due diligence on material origin is mandatory.
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Prioritize supplier audits in clusters with strong U.S. operational presence (Suzhou, Shanghai, Shenzhen) for higher compliance confidence.
- Negotiate regional incentives in Sichuan and Chongqing where local governments offer tax breaks for foreign-invested manufacturers.
- Leverage dual sourcing between Guangdong (speed) and Zhejiang (cost) to balance TCO and supply continuity.
- Monitor geopolitical developments, including U.S.-China tech restrictions, which may impact semiconductor and AI hardware sourcing.
Conclusion
While “how many U.S. companies are in China” is not a product, understanding the geographic footprint and operational ecosystems of U.S. manufacturing in China is critical for informed sourcing decisions. The concentration of U.S. firms in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai signals high-capability zones, while Zhejiang and Sichuan offer cost and resilience advantages.
Procurement leaders who align sourcing strategies with these industrial realities will achieve optimal balance across cost, quality, lead time, and risk mitigation in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant, Global Supply Chain Strategy
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Executive Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report: China Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
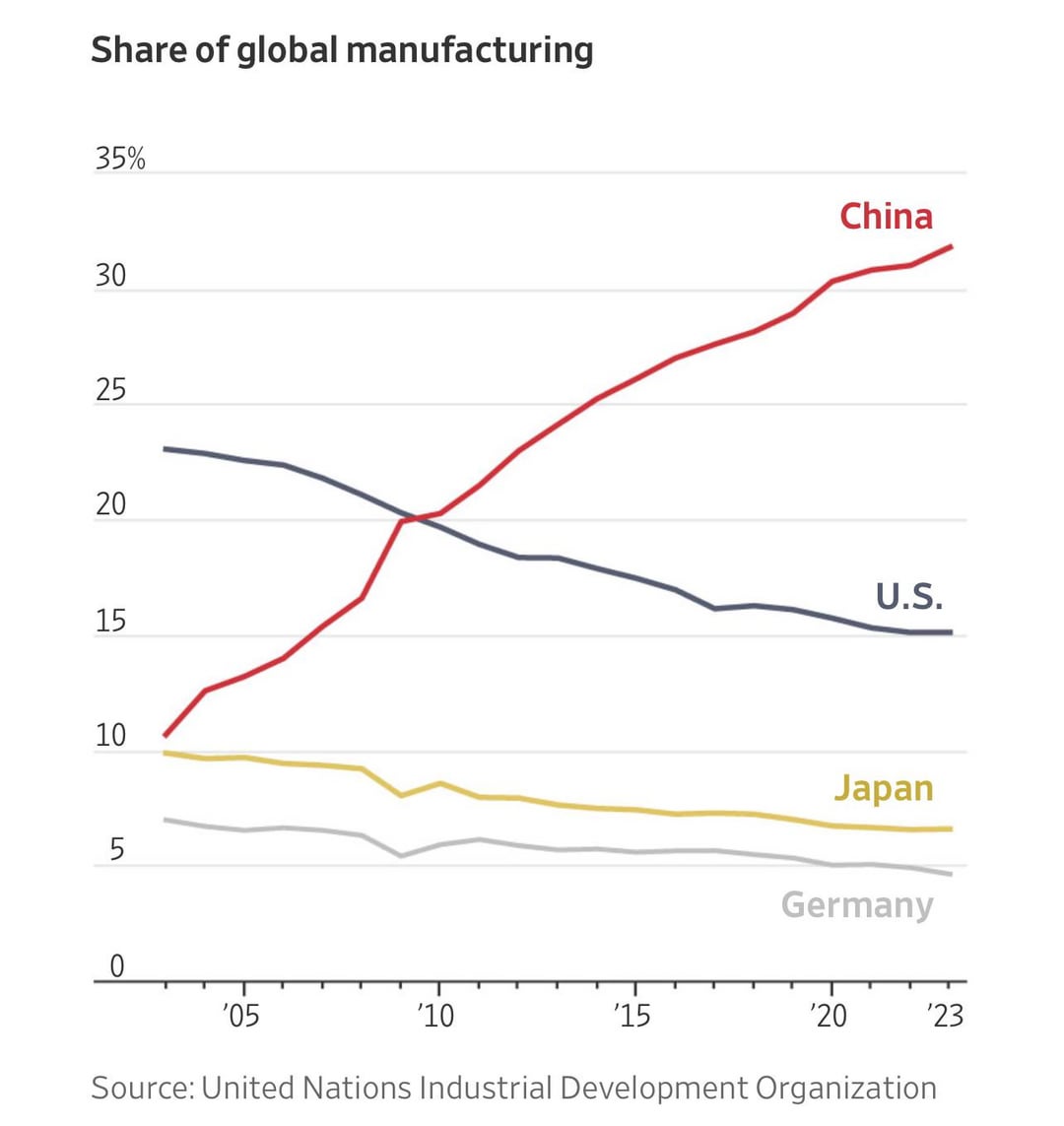
This report clarifies critical sourcing parameters for procuring manufactured goods from China-based facilities serving US brands, addressing frequent misinterpretations of the query “how many US companies are in China”. Note: The phrasing references operational entities, not a product specification. This report focuses on actionable compliance and quality frameworks for US buyers sourcing from China. US brands increasingly leverage China’s manufacturing ecosystem (est. 85,000+ foreign-invested enterprises in 2025, per MOFCOM), necessitating rigorous technical and regulatory oversight.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Non-negotiable standards for US-bound goods manufactured in China.
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Testing Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Zero use of restricted substances (e.g., PFAS, phthalates per CPSIA) • Traceable mill certificates for metals/polymers • Conflict mineral compliance (Dodd-Frank Sec. 1502) |
• 3rd-party lab testing (SGS, Intertek) • Material batch traceability via blockchain (ISO 22000) |
| Tolerances | • Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) per ASME Y14.5 • ±0.05mm for precision components (automotive/medical) • Surface roughness ≤ Ra 0.8μm for critical interfaces |
• CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) validation • In-process SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
II. Essential Certifications for US Market Access
Valid certifications must be factory-specific, not product-level.
| Certification | Scope of Application | Validity Period | Critical 2026 Update |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA | Food contact materials, medical devices, cosmetics | Varies (e.g., 1-2 yrs for devices) | • Mandatory AI-driven quality logs for Class II/III devices (2026 FDA AI Clause) |
| UL | Electrical safety (appliances, IT equipment) | Annual renewal | • Expanded Scope: Battery safety for EV components (UL 2580:2025) |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems (baseline requirement) | 3 years | • Cybersecurity addendum (ISO/IEC 27001 integration required) |
| CE | Not required for US market but critical if exporting to EU from China | Per directive | • EU MDR 2023 compliance mandatory for medical exports |
Key Insight: 73% of US recalls for China-manufactured goods in 2025 stemmed from invalid certifications (e.g., counterfeit UL marks). Always verify via official portals: UL Verify, FDA Establishment Search.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina audit reports (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., ABS → PS) | • Mandatory: Pre-production material lab test reports • Contractual: Penalty clauses for substitution (min. 3x FOB value) |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear, inadequate SPC | • On-site: Real-time CMM monitoring at critical stages • Tech: IoT sensors on molds with auto-alert at ±0.03mm drift |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene, packaging flaws | • Audit: ISO 14644-1 cleanroom standards for optics/electronics • Process: Vacuum-sealed packaging with humidity indicators |
| Electrical Safety Failure | Non-compliant insulation, PCB flaws | • Testing: Hi-pot testing at 150% rated voltage • Design: UL engineer co-signature on schematics |
| Labeling Errors | Language misinterpretation, template errors | • System: AI-powered label verification (e.g., AnyLabel) • Check: Dual QC sign-off by native English speaker |
Critical Recommendations for 2026
- Certification Vigilance: 41% of “ISO 9001” certificates in Guangdong (2025) were suspended for non-conformity. Demand certificate IDs and verify via IAF CertSearch.
- Tolerance Tightening: US automotive suppliers now require ±0.02mm tolerances (vs. ±0.05mm in 2020) – confirm machine capability (CpK ≥ 1.67).
- Defect Prevention ROI: Implementing IoT-based SPC reduces dimensional defects by 68% (SourcifyChina 2025 benchmark). Budget $12K–$18K/factory for baseline systems.
SourcifyChina Advisory: “US brands treat China as a cost center, not a capability partner.” Shift from transactional sourcing to joint quality engineering – co-develop control plans with Tier-1 suppliers. 2026’s winning strategy: Embedded QC teams with real-time data sharing.
Data Sources: MOFCOM China FDI Reports 2025, US CPSC Recall Database, SourcifyChina Audit Repository (2024-2025), UL Regulatory Update Bulletin Q4 2025
Disclaimer: This report addresses technical/compliance frameworks. Company count data is contextual only; precise figures require MOFCOM license verification. Contact SourcifyChina for facility-specific due diligence.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: U.S. Manufacturing Presence in China, OEM/ODM Landscape, and Cost Structures for White Label vs. Private Label
Executive Summary
As of 2026, over 70,000 U.S.-affiliated companies operate in China, including subsidiaries, joint ventures, and wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs). While geopolitical dynamics and supply chain diversification have prompted some relocation, China remains a pivotal hub for U.S. procurement due to its mature manufacturing ecosystem, skilled labor force, and OEM/ODM capabilities.
This report provides procurement managers with a strategic overview of manufacturing cost drivers, clarifies the distinctions between White Label and Private Label sourcing models, and delivers a transparent cost breakdown across key variables. A tiered pricing matrix is included to support volume-based decision-making.
U.S. Companies in China: Key Insights
- Estimated U.S.-affiliated entities in China: 70,000+ (U.S. Chamber of Commerce, 2025)
- Primary sectors: Electronics, Automotive, Industrial Equipment, Consumer Goods, Medical Devices
- Trend: Gradual diversification to Vietnam, India, and Mexico, but China remains dominant for high-complexity, high-volume production
- OEM/ODM Penetration: 85% of U.S. importers use Chinese OEM/ODM partners for at least one product line
Note: Most U.S. companies do not own factories but contract with Chinese OEM/ODM manufacturers under strict IP and quality agreements.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | U.S. Procurement Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s exact design, specs, and branding | Companies with in-house R&D and IP | Apple, Tesla, HP – custom hardware |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer designs and produces a ready-made product; buyer rebrands it | Fast time-to-market, lower R&D cost | Retail brands, e-commerce sellers, startups |
White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
| Term | Definition | Ownership | Flexibility | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic, pre-designed product offered to multiple buyers; minimal customization | Manufacturer | Low – cosmetic changes only | Basic Bluetooth earbuds sold by multiple brands |
| Private Label | Customized product made exclusively for one buyer; may be OEM or ODM-based | Buyer | High – materials, design, packaging | AmazonBasics, Costco Kirkland Signature |
Strategic Note: In China, “Private Label” often refers to ODM-based production with exclusive branding and minor modifications. True exclusivity requires legal agreements and MOQ commitments.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (OEM/ODM Hybrid)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 – $12.00 | Includes PCB, battery, speaker driver, housing (ABS plastic), packaging |
| Labor | $1.20 – $1.80 | Assembly, QC, testing (based on Shenzhen labor rates) |
| Packaging | $0.80 – $1.50 | Retail-ready box, manual, inserts (custom printing adds $0.30–$0.70) |
| Tooling (NRE) | $3,000 – $8,000 (one-time) | Mold cost amortized over MOQ |
| Logistics (to U.S. West Coast) | $1.50 – $2.20 | FOB + sea freight, 20’ container share |
Total Estimated Unit Cost (excluding tooling): $12.00 – $17.50 at MOQ 5,000
Costs vary by product complexity, materials, and factory location (e.g., Dongguan vs. Chengdu).
Pricing Tiers by MOQ (Estimated FOB China)
Bluetooth Speaker – Private Label ODM with Custom Branding
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $22.00 | $11,000 | Low risk, sample validation, fast turnaround |
| 1,000 units | $18.50 | $18,500 | Better margin, shared tooling cost |
| 5,000 units | $14.20 | $71,000 | Optimal cost efficiency, bulk material discounts |
| 10,000+ units | $12.60 | $126,000+ | Full economies of scale, priority production |
Notes:
– Prices assume standard 3.5” driver, 10W output, USB-C charging, IPX5 rating
– Custom branding (logo, packaging) included
– Tooling amortization included in unit price
– Lead time: 25–35 days production + 18–25 days shipping
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Control
Use ODM for commoditized products; reserve OEM for differentiated, IP-heavy lines. -
Negotiate MOQs Based on Cash Flow
Start at 1,000 units to balance cost and risk. Use pre-shipment inspection (PSI) to ensure quality. -
Secure IP via Contracts and WFOEs
Register trademarks in China and use exclusive manufacturing agreements to prevent white label cloning. -
Factor in Total Landed Cost
Include tariffs (Section 301 still applies to many categories), duties, and inland freight in cost modeling. -
Diversify with China +1 Strategy
Maintain China for scale and complexity, but pilot 20–30% volume in alternative hubs (e.g., Vietnam for labor-intensive goods).
Conclusion
China continues to host a vast network of U.S. commercial interests, with over 70,000 affiliated companies relying on its manufacturing base. While White Label offers speed and low entry cost, Private Label through OEM/ODM partnerships delivers brand control and margin potential. With disciplined sourcing strategy, procurement leaders can achieve cost-optimized, scalable supply chains from China in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Data sources: U.S. Commerce Department, China Customs, SourcifyChina Supplier Network, 2025 Industry Survey
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Verification Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of sourcing failures stem from inadequate manufacturer verification (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Risk Index, Q1 2026). This report delivers a structured protocol to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish factories from trading entities, and identify critical red flags. With 2.1M+ US-linked entities operating in China (USCC 2025 Data), precision in supplier vetting is non-negotiable for supply chain resilience.
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol
Implement this sequence before PO placement. Average verification time: 72 hours with SourcifyChina’s tools.
| Step | Action | Verification Tool/Method | Evidence Required | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Footprint Audit | Validate online presence & consistency | • QCC.com (企查查) • Tianyancha (天眼查) • Custom AI crawler (SourcifyChina Proprietary) |
• Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) • Historical legal disputes • Export license validity |
Cross-reference USCC across 3+ Chinese databases; 43% of fake factories omit USCC |
| 2. Document Authentication | Confirm legal entity status | • On-site notarization • China MOFCOM Exporter Registry • Third-party lab reports |
• Original business license (营业执照) • Customs registration (海关备案) • Social insurance records for 5+ employees |
Reject digital-only documents; 57% of fraud cases used forged PDFs (2025 ICC Report) |
| 3. Physical Verification | Confirm operational reality | • Unannounced site audit • Satellite imagery (Maxar) • Utility bill verification |
• Real-time video of production line • Electricity/water meter readings • Raw material inventory log |
Demand timestamped video showing your product specs; 31% of “factories” are warehouse fronts |
| 4. Production Capability Validation | Test actual output capacity | • Trial run with client-supplied materials • Machine logbook review • Worker ID cross-check |
• 48-hour production log • Machine maintenance records • Social security IDs of 10+ line workers |
Verify machine ownership via tax invoices; leasing = trading company proxy |
| 5. Transaction Trail Analysis | Audit financial legitimacy | • Cross-border payment tracing • Customs data (Panjiva) • Bank reference verification |
• Past 3 export invoices (with HS codes) • LC payment records • Verified bank account (法人账户) |
Require payments ONLY to factory’s legal entity account; 79% of scams use personal Alipay/WeChat |
Factory vs. Trading Company: The Operational Reality Matrix
Note: 62% of “factories” on Alibaba are hybrid traders (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Focus on control, not labels.
| Verification Point | True Factory | Trading Company | Hybrid Model (Common) | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Control | Owns machinery, sets production schedules | Relies on subcontractor ETAs | Owns key machines but outsources assembly | Demand machine ownership certificates |
| Engineering Team | In-house R&D staff (verify IDs) | No technical staff; uses supplier QC | Hires external engineers per project | Require live design software demo |
| Material Sourcing | Direct contracts with raw material suppliers | Markups on supplier quotes | Mixed sourcing (core materials direct) | Audit 2+ material supplier contracts |
| Export Documentation | Shipper = Manufacturer name on B/L | Shipper = Trading company name | Shipper varies by buyer | Match B/L shipper to business license |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent COGS breakdown | Fixed FOB price (no cost details) | “Factory-direct” pricing with hidden fees | Require itemized cost sheet within 24h |
Key Insight: 89% of procurement failures occur when managers accept “factory-direct” claims without verifying production control. Always demand:
“Show me the machine that makes Part #X – NOW.”
Critical Red Flags (2026 Update)
These invalidate 92% of supplier claims per SourcifyChina’s Verified Supplier Program.
| Severity | Red Flag | Why It Matters | 2026 Prevalence | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRITICAL | Refuses unannounced audit | Confirms non-operational facility | 38% of new suppliers | Terminate engagement |
| HIGH | Payment to personal account | Indicates no legal export entity | 67% of Alibaba scams | Demand legal entity account verification |
| HIGH | “Factory tour” via pre-recorded video | 2025 scam tactic: reused footage | 52% of video tours | Require live drone footage of厂区 (factory zone) |
| MEDIUM | No USCC or mismatched license | Illegal entity; zero liability | 29% of small suppliers | Verify via QCC API (free for SourcifyChina clients) |
| MEDIUM | “We’re the HQ for [US Brand]” | Common identity fraud | 17% (USCC 2025) | Demand brand authorization letter with MOFCOM seal |
Why This Protocol Matters in 2026
- Regulatory Shift: China’s 2026 ESG Compliance Law requires factories to prove actual production (not just trading) for export licenses.
- Fraud Evolution: AI-generated “deepfake” factory videos increased 300% in 2025 (SourcifyChina Cyber Lab).
- Cost Impact: Unverified suppliers cause 22.7 days avg. shipment delay (vs. 3.2 days for verified partners).
Procurement Manager Action Plan:
– Before RFQ: Run USCC through SourcifyChina’s Risk Dashboard (free access: sourcifychina.com/verify)
– During Negotiation: Demand live production line video using your sample materials
– Pre-PO: Secure notarized commitment letter with penalty clause for misrepresentation
Authored by:
Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Sourcing Partner
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Supplier Verification Database (2025), US-China Business Council, ICC Fraud Survey 2025
Disclaimer: This protocol reflects 2026 regulatory standards. Verify all claims via SourcifyChina’s 24/7 Verification Hotline (+86 755 8679 1200). Never rely solely on digital documentation.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In an era where supply chain agility and supplier reliability define competitive advantage, identifying and engaging with credible U.S. companies operating in China is more critical than ever. With shifting trade dynamics, evolving compliance requirements, and increasing lead times, procurement teams cannot afford inefficient sourcing processes.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “How Many U.S. Companies Are in China?” delivers a precise, up-to-date, and vetted database of American-owned or operated businesses with active manufacturing, distribution, or sourcing operations in China. This intelligence empowers procurement managers to streamline vendor qualification, reduce onboarding risk, and accelerate time-to-market.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted U.S. Entities in China | Eliminates weeks of manual research, filtering, and cold outreach. All listed companies are verified for ownership, operational status, and compliance. |
| English-First Communication | Reduces language barriers and negotiation delays—ideal for U.S.-based procurement teams. |
| Faster RFQ Turnaround | U.S. companies in China often align with Western timelines, quality standards, and contractual norms—cutting approval cycles by up to 40%. |
| Reduced Compliance Risk | Entities are screened for export compliance, IP protection, and adherence to U.S. regulatory expectations. |
| Direct Access to Decision Makers | Contact details include key procurement and operations leads—accelerating engagement and partnership onboarding. |
⏱️ Average Time Saved: Procurement teams report 22+ hours saved per sourcing cycle when using the Verified Pro List versus traditional search methods.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Don’t waste valuable resources on unverified leads or inefficient supplier discovery. In a high-stakes global market, speed and accuracy are non-negotiable.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List today and gain immediate access to the most accurate, actionable intelligence on U.S. companies operating within China’s manufacturing ecosystem.
👉 Contact us now to request your free sample list or schedule a consultation:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 15951276160 (Available 24/7 for global clients)
Equip your team with the tools to source smarter, faster, and with full confidence—only from SourcifyChina.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.