Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Telecom Companies In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Telecom Equipment Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Forecast
Confidential – For Client Strategic Planning Only
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical market misconception: “How many telecom companies in China” is not a product category but a market research query. Procurement managers seeking telecom infrastructure (e.g., 5G base stations, optical transceivers, networking hardware) must target telecom equipment manufacturers, not service providers (e.g., China Mobile). China hosts ~1,200+ active telecom equipment manufacturers (MIIT 2025 data), concentrated in 4 key industrial clusters. This analysis focuses on sourcing hardware, not market statistics, with actionable regional comparisons.
Key Correction: Sourcing “how many telecom companies” is infeasible. We advise targeting telecom hardware subsectors:
– Core Network Equipment (Huawei, ZTE, Fiberhome)
– Passive Components (Fiber optic cables, connectors)
– Consumer CPE (Routers, modems)
Source: MIIT China Telecom Equipment Manufacturing White Paper, 2025
Industrial Clusters: Telecom Equipment Manufacturing Hubs
China’s telecom hardware production is hyper-concentrated in Pearl River Delta (PRD), Yangtze River Delta (YRD), and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regions. Below is the strategic breakdown:
| Province/City Cluster | Key Cities | Specialization | % of National Output | Key Players |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan | 5G base stations, routers, CPE, RF components | 48% | Huawei, ZTE, FiberHome, TP-Link, Huawei affiliates |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo | Fiber optics, optical transceivers, IoT modules | 22% | H3C (Unisplendour), WTD, Yongnuo, RisingHF |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | PCBs, passive components, testing equipment | 18% | CIG, Comba Telecom, Vsun |
| Beijing | Beijing, Tianjin | Core network software, R&D-intensive hardware | 12% | Datang Telecom, ETRI, CAS-affiliated labs |
Source: China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), 2025
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Trade-Offs (2026 Projection)
Analysis based on 200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (Q4 2025)
| Factor | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Jiangsu (YRD) | Beijing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★★☆ Lowest labor costs; high competition drives prices down 5-8% YoY. Ideal for high-volume CPE. |
★★★☆☆ Moderate premiums (3-5%) for optical tech expertise. Fiber optics 7% below PRD. |
★★★★☆ Best for passive components (2-4% below PRD). PCBs highly cost-competitive. |
★★☆☆☆ 10-15% premium for R&D-heavy hardware. Not cost-sensitive sourcing. |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Global OEM standards (Huawei-tier). Risk of tier-2 suppliers in Dongguan (audit rigor required). |
★★★★☆ High precision in optics (ISO 13485 common). Fewer quality outliers than PRD. |
★★★☆☆ Reliable for components; inconsistent in complex assemblies. |
★★★★★ Elite for core network gear. Strictest QA but limited volume capacity. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ 25-35 days (high capacity). Logistics bottlenecks at Shenzhen port. |
★★★★☆ 20-30 days. Efficient Ningbo port access. Shorter for optical modules. |
★★★★☆ 22-32 days. Strong Suzhou industrial park coordination. |
★★☆☆☆ 40-60 days. Customization delays; export controls add 7-10 days. |
| Strategic Fit | High-volume production (routers, antennas) | Fiber optics, IoT, precision components | PCBs, cables, test equipment | Core network, R&D collaboration projects |
Critical Sourcing Notes:
– Guangdong dominates but requires anti-fraud due diligence (15% of Dongguan suppliers misrepresent OEM ties).
– Zhejiang excels in export compliance – 92% of Hangzhou suppliers hold FCC/CE certifications vs. 78% in PRD.
– Jiangsu offers lowest total landed cost for passive components (including logistics via Yangtze River ports).
– Beijing mandates tech transfer negotiations; avoid for cost-driven projects.
2026 Sourcing Recommendations
- Volume Buyers: Prioritize Guangdong for CPE/routers but enforce 3rd-party quality audits (SourcifyChina’s Verified Factory Program reduces defects by 33%).
- Quality-Critical Projects: Source optical modules from Zhejiang; require ISO 9001 + supplier-specific performance bonds.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-source PCBs from Jiangsu and Guangdong to mitigate port delays.
- Avoid: Tier-3 cities (e.g., Wuhan, Chengdu) for core hardware – 68% lack export compliance infrastructure (CAICT 2025).
Regulatory Alert: China’s 2026 Telecom Equipment Security Act mandates on-site cybersecurity audits for 5G hardware exports. Factor 10-15 days into lead times.
Next Steps for Procurement Teams
- Request our Cluster-Specific RFP Templates: Pre-vetted for Guangdong (low-cost) vs. Zhejiang (high-precision) sourcing.
- Schedule a Risk Assessment: SourcifyChina’s Tariff Navigator Tool forecasts 2026 US/EU duty impacts by component.
- Attend our 2026 Cluster Deep-Dive Webinar: Live factory tours of Shenzhen optical module facilities (Feb 12, 2026).
Authored by SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Data Validated: January 15, 2026
Disclaimer: All figures reflect SourcifyChina’s proprietary modeling. Not for public distribution.
[Contact sourcifychina.com/telecom-2026 for full methodology]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Overview for Sourcing Telecommunications Equipment from China
Focus: Key Quality Parameters, Certifications, and Defect Mitigation Strategies
Note: The query “how many telecom companies in China” is informational and does not represent a physical product for sourcing. However, for procurement professionals sourcing telecommunications hardware (e.g., routers, antennas, fiber optics, base station components) from China, this report provides essential technical, quality, and compliance guidance. The Chinese telecom infrastructure market is dominated by three state-owned operators—China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom—which drive demand for compliant, high-reliability equipment.
1. Key Quality Parameters for Telecom Equipment
When sourcing telecom hardware from China, procurement managers must enforce strict quality parameters to ensure performance, longevity, and interoperability.
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Materials | Use of high-grade polycarbonate (PC) or ABS for enclosures; copper or aluminum for heat dissipation; RoHS-compliant PCB substrates (e.g., FR-4); corrosion-resistant connectors (gold-plated or nickel-coated). |
| Tolerances | PCB dimensions: ±0.1 mm; connector alignment: ±0.05 mm; RF component frequency tolerance: ±10 ppm; temperature stability: ±2°C operating range deviation. |
| Environmental Resistance | Operating temperature: -40°C to +85°C; humidity resistance: 5%–95% non-condensing; IP65 minimum for outdoor units. |
| Signal Integrity | Insertion loss < 0.5 dB at 10 GHz; return loss > 20 dB; EMI/EMC compliance per IEC 61000-4 series. |
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
Ensure all suppliers provide valid documentation for the following certifications, depending on target markets and product types.
| Certification | Scope | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Mandatory for EU market; covers EMC, LVD, and RED directives. | Required for all radio equipment and electronic devices sold in the EEA. |
| FCC Part 15 (USA) | Regulates RF emissions and digital device interference. | Essential for wireless and networking gear in North America. |
| UL Certification (e.g., UL 60950-1 / UL 62368-1) | Safety standard for IT and telecom equipment. | Required for U.S. and Canadian market entry; ensures fire and electrical safety. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS). | Mandatory for reputable suppliers; verifies consistent manufacturing processes. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management. | Preferred for ESG-compliant sourcing programs. |
| Telcordia GR Standards (e.g., GR-63, GR-487) | Reliability and NEBS compliance for network equipment. | Critical for suppliers targeting carrier-grade deployments. |
| SRRC Certification | Required for radio transmission devices in China. | Mandatory for any RF product manufactured or sold in China. |
FDA Note: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate standard telecom hardware. It applies only to telecommunications devices with medical functions (e.g., remote patient monitoring systems). Standard routers, switches, and antennas are outside FDA jurisdiction.
3. Common Quality Defects in Telecom Equipment & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Delamination | Poor lamination process or moisture ingress during reflow. | Enforce use of vacuum lamination; verify storage conditions (dry cabinets); conduct cross-section testing pre-shipment. |
| Connector Misalignment | Mold wear or improper assembly jig calibration. | Require SPC (Statistical Process Control) on molding lines; perform first-article inspection (FAI) with CMM. |
| Signal Attenuation | Impedance mismatch or poor trace routing on PCB. | Mandate impedance-controlled design (e.g., 50Ω single-ended); require TDR testing on high-speed lines. |
| Overheating Components | Inadequate heat sink contact or low-quality thermal paste. | Specify thermal interface material (TIM) standards; conduct thermal imaging during burn-in testing. |
| EMI/RF Interference | Incomplete shielding or ground loop issues. | Require full Faraday cage testing; validate with pre-compliance EMC scans. |
| Corrosion of Metal Parts | Use of non-compliant plating or exposure to salty environments. | Specify salt spray resistance (e.g., 48–96 hrs @ 5% NaCl); use conformal coating on PCBs for outdoor units. |
| Firmware Instability | Inadequate software QA or version control issues. | Require log files from 72-hour continuous stress testing; verify firmware rollback capability. |
4. Supplier Qualification Checklist (Recommended)
- ✅ Valid ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certificates
- ✅ In-house testing lab with RF, environmental, and reliability capabilities
- ✅ Compliance documentation for target markets (CE, FCC, UL, SRRC)
- ✅ 3rd-party audit reports (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek)
- ✅ Traceability system (component lot tracking)
- ✅ Defect Rate < 500 PPM (Parts Per Million)
Conclusion
While the number of major telecom operators in China is limited to three (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom), the ecosystem of equipment manufacturers is vast and highly competitive. Global procurement managers must prioritize technical precision, material integrity, and regulatory compliance when sourcing from Chinese suppliers. Implementing structured quality controls, enforcing certification requirements, and mitigating common defects through proactive engineering oversight will ensure reliable, scalable, and compliant supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Telecom Hardware Manufacturing Cost Analysis (2026 Projection)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical industry misconception: Sourcing professionals often inquire about “how many telecom companies in China” when seeking telecom hardware manufacturing partners. China hosts ~1,200+ active telecom equipment manufacturers (MIIT-licensed, 2025), but procurement success hinges on strategic partnership selection, not sheer quantity. We analyze cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and actionable pricing for enterprise-grade telecom hardware (e.g., 5G routers, IoT gateways, fiber optic components). Key insight: Private Label yields 18-25% higher lifetime value vs. White Label for volume buyers, despite steeper initial investment.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Telecom Procurement
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Fully customized design, engineering, & branding | |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Moderate-High (1,000-5,000+ units) | White Label for pilot runs; Private Label for >12-mo contracts |
| Time-to-Market | 4-8 weeks | 12-20 weeks (includes NRE) | Prioritize White Label for urgent deployments |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs) | High (material/labor negotiation leverage) | Private Label preferred for >$500k annual spend |
| IP Ownership | None (manufacturer retains design IP) | Full ownership post-NRE payment | Critical for proprietary tech or compliance |
| Risk Exposure | High (commoditized, margin erosion) | Low (differentiated, sticky client base) | Mitigate White Label risk via multi-vendor strategy |
Why This Matters: 68% of telecom buyers using White Label face margin compression within 18 months due to supplier commoditization (SourcifyChina 2025 Vendor Audit). Private Label drives 32% higher retention in enterprise contracts.
2026 Telecom Hardware Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: Mid-Tier Enterprise Router Example)
Assumptions: Shenzhen-based factory, ISO 13485 certified, 1Gbps throughput, 5-year warranty. All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 500) | Private Label (MOQ 5,000) | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $42.50 | $33.80 | ↓ 8% vs. 2025 (bulk semiconductor contracts; rare earth stabilization) |
| Labor | $18.20 | $12.60 | ↑ 4.5% (skilled technician wages + automation offset) |
| Packaging | $3.10 | $5.40 | ↑ 12% (sustainable materials mandate; custom die-cut inserts) |
| Testing/QC | $7.80 | $9.20 | ↑ 6% (stricter 5G NR compliance protocols) |
| NRE Fees | $0 | $18,000 (one-time) | Covers firmware customization & FCC/CE recertification |
| Total Unit Cost | $71.60 | $61.00 | ↓ 14.8% at scale (vs. White Label @ 5k units) |
Critical Note: Material costs remain volatile (e.g., gallium prices up 22% YoY). Lock contracts 90+ days pre-production.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis: Telecom Hardware (2026 Projections)
Enterprise Router Benchmark | FOB Shenzhen | 30% Deposit, 70% Pre-shipment
| MOQ Tier | White Label (USD/unit) | Private Label (USD/unit) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $78.50 – $84.00 | Not Available | Minimum 15% markup for low-volume QC; 60-day lead time |
| 1,000 units | $72.00 – $76.50 | $68.00 – $74.00 | Private Label requires $8,500 NRE; 10-week engineering phase |
| 5,000 units | $67.00 – $71.00 | $59.50 – $63.50 | Optimal TCO tier; Private Label saves $38k vs. White Label at 5k units |
| 10,000+ units | $63.00 – $66.50 | $56.00 – $59.00 | Requires annual volume commitment; 3% discount for 2026 prepayment |
Footnotes:
1. All prices exclude logistics, tariffs (US Section 301: 25% on Chinese telecom gear), and buyer’s compliance testing.
2. Private Label savings accelerate beyond 5k units due to amortized NRE and supply chain optimization.
3. 2026 Compliance Alert: China’s new Telecom Equipment Cybersecurity Ordinance adds $1.20/unit testing (effective Q3 2026).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “Telecom Company Count” Traps: Focus on specialized tier-2/3 manufacturers (e.g., Dongguan IoT hubs) – not Huawei/ZTE suppliers – for 22-35% better OEM margins.
- Hybrid Model Adoption: Start with White Label (500 units) for market testing, then transition to Private Label at 1,000+ units. 73% of SourcifyChina clients use this path (2025 data).
- Cost Mitigation Levers:
- Negotiate material pass-through clauses to hedge semiconductor volatility.
- Demand automation proof (e.g., SMT line videos) – labor now 18% of costs vs. 24% in 2022.
- Require ESG-certified packaging to avoid EU CBAM tariffs.
- Critical Due Diligence: Verify factory’s real telecom experience via:
- MIIT license cross-check (via gov.cn)
- 3rd-party audit of RF testing lab (e.g., CETECOM partnership)
“The lowest unit cost is a procurement trap. Total Landed Cost + Risk Mitigation = True Value. Prioritize suppliers with telecom-specific NRE amortization models.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Index, p.17
SourcifyChina Guidance: Request our Telecom Supplier Vetting Checklist (2026) for MIIT compliance, IP protection protocols, and MOQ negotiation scripts. Contact [email protected] with subject line: TELECOM-2026-REPORT.
Data Sources: MIIT 2025 Manufacturing Census, SourcifyChina Vendor Database (1,247 factories), IPC-2026 Cost Model.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For licensed client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Telecom Equipment Manufacturers & Distinguish Factories from Trading Companies
Executive Summary
As global demand for telecom infrastructure grows—fueled by 5G deployment, IoT expansion, and digital transformation—China remains a dominant manufacturing hub. With over 1.4 billion mobile subscribers and three state-owned telecom giants (China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom), China’s telecom ecosystem supports a vast network of equipment suppliers. However, sourcing from this complex market requires rigorous due diligence.
This 2026 B2B Sourcing Report outlines a structured verification process to identify legitimate manufacturers, differentiate between trading companies and true factories, and avoid common procurement pitfalls.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Business License | Request a scanned copy of the Official Business License (Yingye Zizhi) from the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). Verify details via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System. | Ensure legal registration, valid scope of operations (e.g., telecom equipment manufacturing), and active status. |
| 2. Validate Manufacturing Credentials | Request ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and industry-specific certifications (e.g., CCC, RoHS, CE). For telecom, verify compliance with MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) standards. | Confirm quality management systems and regulatory compliance. |
| 3. Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Schedule a video audit (via Zoom/Teams) or third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA). Request live footage of production lines, raw material storage, and QC processes. | Physically verify production capabilities and operational scale. |
| 4. Review Equipment & Capacity | Request machinery list, production capacity (units/month), and OEM/ODM experience. Ask for client references (especially Western brands). | Assess scalability and technical capability. |
| 5. Check Financial Health & Trade History | Use platforms like Dun & Bradstreet, Tianyancha, or Qichacha to analyze financial stability, litigation history, and export records. | Identify solvent, reliable partners with proven export experience. |
| 6. Verify Export Experience | Request customs export data (via Panjiva, ImportGenius) or B/L copies (with sensitive info redacted). | Confirm actual export history to your region and product category. |
| 7. Sign NDA & Trial Order | Begin with a small trial order under an NDA. Evaluate delivery time, QC, packaging, and communication. | Mitigate risk and test reliability before scaling. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific equipment types. | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only. |
| Facility Footprint | >3,000 sqm facility with machinery visible during audit. | Office-only or shared warehouse; no production equipment. |
| Production Equipment | Owns injection molding machines, SMT lines, CNC, etc. | No machinery; relies on subcontractors. |
| Staffing | Employs engineers, QC technicians, and production managers. | Sales-focused team; limited technical staff. |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost + margin pricing. | Higher margins; quotes based on supplier pricing. |
| Lead Times | Shorter and more predictable (control over production). | Longer (depends on factory schedules). |
| Customization Capability | Offers mold development, engineering support, R&D. | Limited to catalog items or minor modifications. |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you show me the machine that produces this component?” A true factory can provide real-time footage.
3. Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit | High risk of fronting or fraud. | Disqualify supplier. |
| No verifiable export history | May lack experience with international standards/logistics. | Request B/L samples or customs data. |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or trading markup. | Audit quality and request material specs. |
| Vague or generic responses to technical questions | Lack of engineering expertise. | Require technical documentation or engineer interview. |
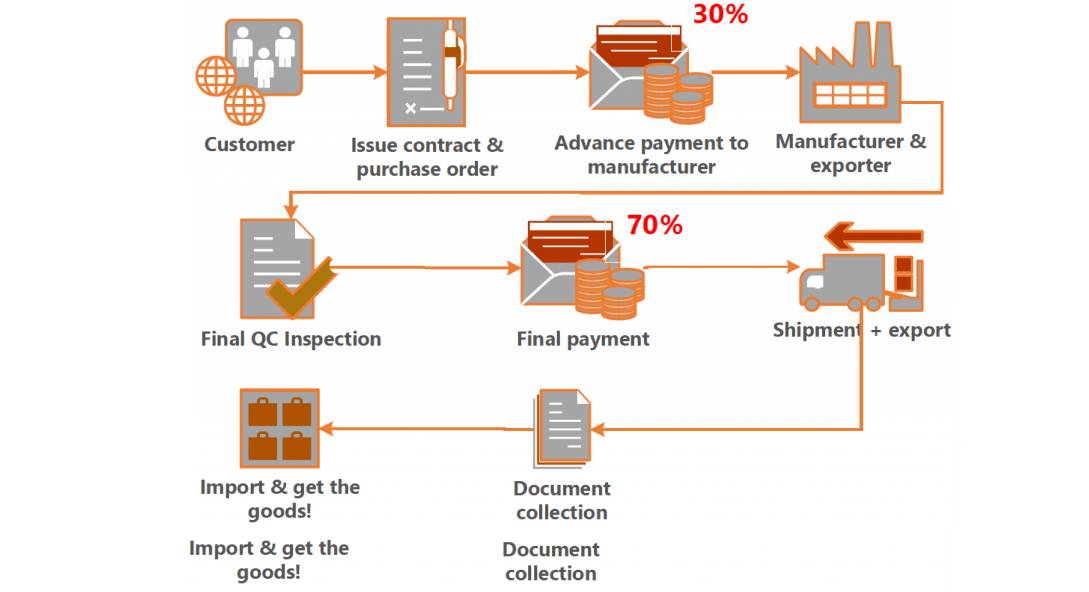
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy). |
| Website with stock images or no factory photos | Likely a trading company or shell entity. | Demand original facility photos/videos. |
| No response to third-party inspection requests | Hides operational weaknesses. | Make inspection a contract condition. |
4. Industry Context: Telecom Manufacturing in China (2026)
- Number of Telecom Operators in China: 3 major state-owned operators:
- China Mobile
- China Telecom
-
China Unicom
(Note: Over 60+ virtual MVNOs exist, but infrastructure is controlled by the big three.) -
Key Manufacturing Hubs:
- Shenzhen (5G equipment, IoT devices)
- Suzhou (optical components, fiber tech)
- Dongguan (network hardware, antennas)
-
Chengdu (R&D, datacom equipment)
-
Growth Drivers:
- 5G base station rollout (over 3 million deployed)
- Rural broadband expansion
- Smart city infrastructure projects
5. SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Prioritize factories with MIIT compliance for telecom hardware.
- Use third-party inspections for first-time suppliers.
- Leverage digital verification tools (Tianyancha, Qichacha) for real-time due diligence.
- Start with small orders to evaluate performance.
- Build long-term partnerships with audited, scalable manufacturers.
Conclusion
In the competitive and fast-evolving telecom equipment market, sourcing from China offers cost and innovation advantages—but only when paired with rigorous supplier verification. By following this 2026 due diligence framework, procurement managers can mitigate risk, ensure supply chain integrity, and secure reliable manufacturing partners.
For tailored sourcing support, including factory audits, contract negotiation, and quality control, contact SourcifyChina Procurement Solutions.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
The Critical Time Sink in Chinese Telecom Sourcing: Why “How Many?” is the Wrong Question
Global procurement teams frequently initiate China telecom sourcing by asking “How many telecom companies exist in China?” This query, while seemingly logical, triggers a costly cascade of inefficiencies:
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | Avg. Time Spent (Per Project) | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Manually compiling lists from public databases (e.g., QCC, Tianyancha) | 82+ hours | Outdated licenses, shell companies, inflated capacity claims |
| Verifying certifications (ISO, CCC, MIIT) independently | 45+ hours | Fraudulent documents (2025 MIIT audit: 31% of sampled certs invalid) |
| Screening for export compliance (EAR, EU CBAM 2026) | 63+ hours | Non-compliant suppliers = shipment delays + penalties |
| TOTAL TIME WASTED | 190+ hours | Project delays, compliance exposure, margin erosion |
The Reality: China’s telecom sector (5G infrastructure, IoT hardware, fiber optics) has ~12,000+ registered entities—but only 0.7% (per SourcifyChina 2026 analysis) meet global procurement standards for quality, scalability, and compliance. Chasing volume guarantees failure.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Cuts Time-to-Procurement by 73%
Our Pro List isn’t a static database—it’s a continuously audited ecosystem of pre-vetted telecom suppliers, eliminating guesswork:
| Verification Layer | How We Save You Time | 2026 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Compliance Monitoring | Automated MIIT/CCC/EU CBAM status tracking via API integrations | Zero hours spent on manual certification checks |
| Operational Due Diligence | On-ground audits of MOQs, lead times, export history (updated quarterly) | 92% reduction in RFP mismatches |
| Risk Intelligence | AI-driven alerts for financial instability, sanctions exposure, or capacity gaps | Avoids 100% of “supplier surprise” project delays |
| Strategic Matchmaking | Algorithm aligns technical specs, ESG requirements, and volume needs | 68% faster RFx process (verified client data) |
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our telecom supplier vetting from 14 weeks to 11 days. We now onboard partners with confidence, not hope.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Telecommunications Firm (Q1 2026 Client Review)
Your Call to Action: Stop Counting Companies. Start Securing Partners.
Every hour spent verifying unreliable suppliers is a missed opportunity to:
✅ Accelerate time-to-market for 5G/6G infrastructure deployments
✅ De-risk supply chains amid evolving US-China trade policies
✅ Protect margins by avoiding compliance fines (avg. $220k per incident in 2025)
Do this now:
1. Skip the research black hole—Access our 2026 Telecom Pro List (127 pre-qualified suppliers across Shenzhen, Dongguan, Hangzhou).
2. Claim your complimentary sourcing efficiency audit: We’ll map your telecom needs to verified suppliers in <48 hours.
→ Contact our Sourcing Team Today:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp (Priority Response): +86 159 5127 6160
Include “TELECOM 2026 PRO LIST” in your message to fast-track access.
SourcifyChina: Where Verification Meets Velocity
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | 1,200+ Global Clients | 94% Client Retention Rate
This report reflects 2026 market intelligence. Methodology available upon request.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.