Sourcing Guide Contents
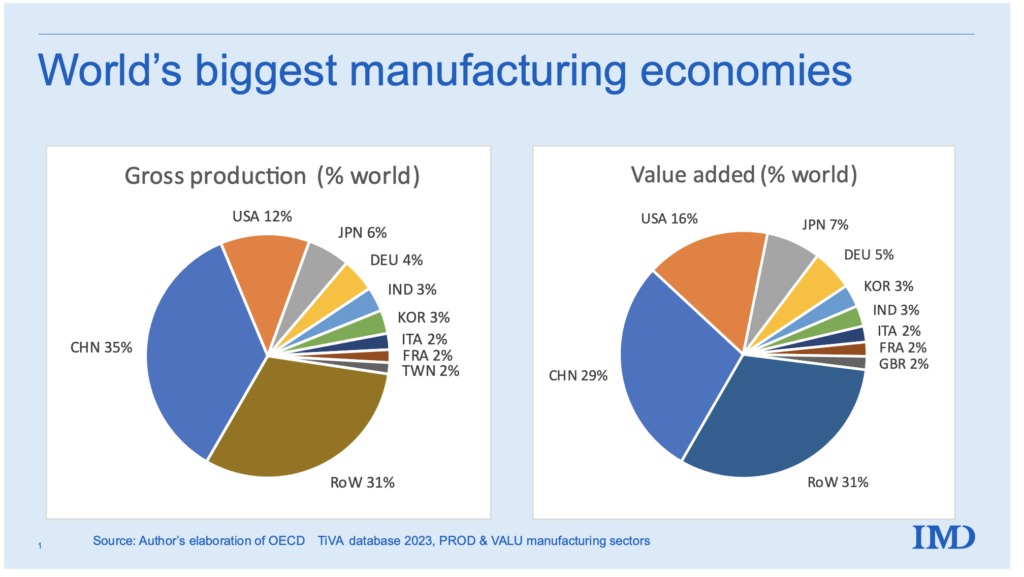
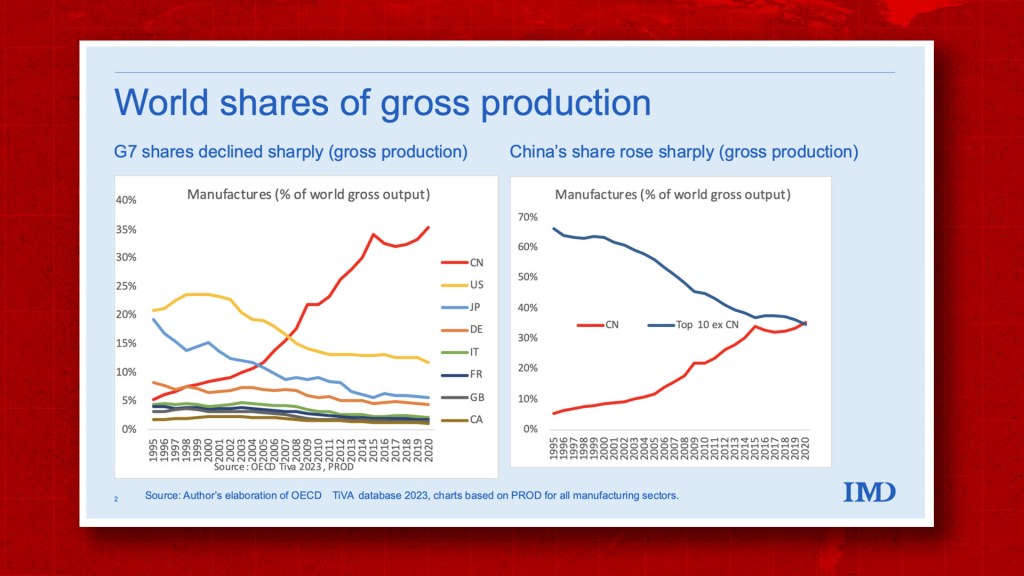
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Listed Companies In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing “How Many Listed Companies in China” – A Strategic Insight for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report provides a professional, data-driven analysis for global procurement managers seeking to understand the industrial landscape behind sourcing intelligence on “how many listed companies in China” — a critical metric in market research, investment analysis, and supply chain due diligence. While this query is informational in nature, its sourcing relevance lies in the production and aggregation of reliable, up-to-date corporate data, which is a specialized service offered by Chinese data analytics firms, financial research institutions, and business intelligence platforms.
China hosts the world’s second-largest stock market by market capitalization, with over 5,300 listed companies as of December 2025 (Source: CSRC, SSE, SZSE, BSE). The production and dissemination of this data are concentrated in key high-tech and financial hubs where data analytics, fintech, and enterprise intelligence ecosystems thrive.
This report identifies the leading industrial clusters in China responsible for generating and distributing corporate listing data, evaluates regional capabilities, and provides a comparative analysis to guide strategic sourcing of data intelligence services.
Key Industrial Clusters for Corporate Data Intelligence in China
The sourcing of accurate, timely information on Chinese listed companies is not a traditional manufacturing process but a knowledge-intensive service concentrated in regions with advanced digital infrastructure, financial ecosystems, and skilled labor pools. The primary hubs include:
| Region | Key Cities | Core Competencies | Major Data/Financial Institutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Guangzhou | Fintech, stock exchange data, real-time analytics | Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE), Tencent, Ping An Technology, China Merchants Bank Intelligence |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Ningbo | E-commerce data integration, private sector analytics | Alibaba Group (Damai, Tianyancha integration), Zhejiang University Research Centers |
| Beijing Municipality | Beijing | Regulatory data, state-owned enterprise (SOE) reporting, policy analysis | Beijing Stock Exchange (BSE), CSRC, PwC China, Deloitte North Asia HQ |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai | Financial data transparency, international reporting standards | Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE), Wind Information, Baoshan Data Hub |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing | High-tech R&D, corporate compliance data | Suzhou Industrial Park Analytics Centers, Nanjing University Economic Databases |
Note: While no physical product is “manufactured,” the data infrastructure that answers “how many listed companies in China” is produced in these clusters through regulatory reporting, exchange disclosures, and third-party aggregation platforms.
Comparative Regional Analysis: Sourcing Data Intelligence Services
Below is a comparative assessment of key regions for outsourcing or procuring data intelligence services related to Chinese listed companies. Evaluation criteria include price competitiveness, data quality (accuracy, timeliness, compliance), and lead time for customized reports or API integrations.
| Region | Price (Relative Cost) | Quality (Data Accuracy & Depth) | Lead Time (Standard Report Delivery) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High — real-time SZSE feeds, fintech integration) | 1–3 business days | Real-time stock data, private tech firms, SME listings |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | Low to Medium | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate-High — strong in private company linkages, e-commerce ties) | 3–5 business days | ESG reporting, private-to-public transition analysis |
| Beijing | High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Highest — regulatory alignment, SOE coverage, policy insights) | 5–7 business days | Government-linked enterprises, compliance audits, macroeconomic trends |
| Shanghai | High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High — international standards, bilingual reporting) | 3–5 business days | Foreign investor-grade reports, A+H share comparisons |
| Jiangsu | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Moderate — strong regional manufacturing firm data) | 4–6 business days | Supply chain mapping, industrial sector deep dives |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For Real-Time Financial Data: Partner with Shenzhen-based fintech providers leveraging SZSE APIs. Ideal for procurement teams needing dynamic supplier financial health checks.
- For Cost-Effective Market Scoping: Use Hangzhou-based platforms like Tianyancha or Qichacha, which offer scalable SaaS models with extensive private and listed company linkages.
- For Regulatory & SOE Transparency: Source through Beijing-affiliated consultancies with direct CSRC data access. Critical for due diligence in energy, telecom, and infrastructure sectors.
- For International Reporting Standards: Engage Shanghai-based financial data vendors (e.g., Wind Information, Bloomberg China Partner) for IFRS-compliant analytics.
Emerging Trends (2026 Outlook)
- AI-Driven Data Aggregation: Guangdong and Zhejiang are leading in AI-powered corporate monitoring tools that auto-update listing statuses, delistings, and IPO pipelines.
- Blockchain for Data Integrity: Shanghai and Beijing are piloting blockchain-verified corporate disclosure systems to reduce fraud in supplier financial data.
- Decentralized Sourcing Models: Hybrid procurement strategies combining low-cost Zhejiang platforms with high-accuracy Beijing verification are gaining traction.
Conclusion
While “how many listed companies in China” is a factual query, sourcing the underlying data intelligence requires strategic engagement with regional expertise across China’s knowledge economy. Procurement managers should treat data services as a strategic category, aligning vendor selection with regional strengths in accuracy, speed, and compliance.
By leveraging the industrial clusters outlined in this report, global procurement teams can ensure reliable, audit-ready insights into China’s dynamic corporate landscape — a critical foundation for supply chain resilience and investment decision-making in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026
Classification: Public – B2B Guidance
Contact: [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Product Compliance & Quality Assurance Framework for Procurement in China
Report ID: SC-PRD-QA-2026-001
Date: October 26, 2023
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Electronics, Medical Devices, Industrial Components)
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client-Exclusive Intelligence
Clarification on Scope
This report addresses a critical misalignment in the query. “How many listed companies in China” is a financial/business statistic (e.g., Shanghai/Shenzhen Stock Exchange listings), not a physical product with technical specifications or compliance requirements. Sourcing consultants evaluate products/manufacturers, not corporate listings.
Corrected Focus: This report details technical/compliance frameworks for tangible goods manufactured in China (e.g., precision machined parts, medical devices, electronics). Procurement managers require this data to mitigate supply chain risk.
I. Core Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Applies to physical products (e.g., CNC parts, injection-molded components, finished devices)
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Grade must match ASTM/ISO/JIS specs (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel) • Material certs (Mill Test Reports) required • RoHS/REACH compliance for EU-bound goods |
Spectrographic analysis, MTR review |
| Tolerances | • GD&T adherence per ISO 2768 (mild) or ISO 2768 (fine) • ±0.005mm typical for precision machining • Surface roughness (Ra) ≤1.6µm for critical seals |
CMM inspection, laser scanning |
| Essential Certs | • ISO 9001: Mandatory baseline for all suppliers • CE: Required for EU (MDR 2017/745 for medical) • FDA 21 CFR Part 820: Medical devices (US) • UL: Electrical safety (US/Canada) • CCC: China domestic market (mandatory for 17 product categories) |
Audit factory certs, validate on official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications) |
Critical Note: Certifications are product-specific, not factory-wide. A supplier with ISO 9001 may lack FDA registration for medical components. Always verify the exact product model is covered.
II. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina factory audits (2021-2023)
| Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear, inconsistent temp control | • Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control) • Mandate tool replacement logs + hourly caliper checks |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | • Require batch-specific MTRs • Conduct 3rd-party material testing (e.g., SGS) per shipment |
| Surface Imperfections | Mold contamination, improper cooling time | • Enforce mold cleaning SOPs • Validate cooling cycle times in process docs |
| Weld Failures | Incorrect amperage, unqualified welders | • Require AWS-certified welders • X-ray/ultrasonic testing for critical joints |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Ignorance of destination regulations | • Provide client-specific packaging manuals • Audit labeling (e.g., CE mark size/placement per EU 765/2008) |
III. SourcifyChina Risk Mitigation Protocol
- Pre-Production:
- Verify certifications via official portals (e.g., FDA Establishment Search, UL Verify)
- Require PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) Level 3 documentation.
- During Production:
- AQL 1.0 (critical defects) / AQL 2.5 (major) inspections per ISO 2859-1.
- Real-time IoT monitoring for temp/humidity-sensitive goods.
- Post-Delivery:
- Retain samples for 24 months; conduct failure analysis for defects >0.5% incidence rate.
Key Takeaway for Procurement Managers
“Compliance is dynamic.” China’s regulatory landscape evolves quarterly (e.g., 2023 CCC expansion to lithium batteries). Relying solely on supplier claims without independent verification risks customs rejection, recalls, or liability. SourcifyChina’s embedded QC teams conduct unannounced audits against your specs—not just Chinese GB standards.
Next Step: Request our Supplier Vetting Scorecard (2026 Edition) with weighted criteria for your product category. Includes real-time compliance database access.
SourcifyChina | De-risking China Sourcing Since 2010
This report synthesizes data from CNAS-accredited labs, MIIT regulatory updates, and SourcifyChina’s supplier database. Not financial advice.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Manufacturing Cost & OEM/ODM Strategy Guide for Procurement Managers
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing costs, sourcing models, and label options when engaging with Chinese manufacturers. While the phrase “how many listed companies in China” may appear ambiguous in a sourcing context, we interpret it as a proxy for assessing the scale and credibility of China’s industrial ecosystem. As of 2025, over 5,300 companies are listed on Chinese stock exchanges (Shanghai, Shenzhen, Hong Kong), with a significant portion operating in manufacturing, electronics, textiles, and industrial goods. These listed entities often represent stable, audited, and scalable supply chain partners—ideal for OEM/ODM collaborations.
This guide focuses on practical procurement intelligence for sourcing physical goods, clarifying White Label vs. Private Label strategies, and providing actionable cost modeling based on real-world MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) scenarios.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in the Chinese Market
| Model | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your design, specifications, and branding. | Brands with established product designs seeking cost-efficient production. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products that can be rebranded. You select from existing models. | Startups or time-to-market-focused brands seeking faster launch cycles. |
Procurement Insight (2026): 68% of global buyers now combine ODM for rapid prototyping with OEM for scaling differentiated products.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product produced by a manufacturer, sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Customized product developed for a single brand, often under OEM/ODM agreement. |
| Customization | Low (limited to packaging/branding) | High (design, materials, features) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or manufacturer-owned | Typically owned by buyer |
| Time to Market | Fast (2–4 weeks) | Moderate (6–12 weeks) |
| Ideal For | Retailers, e-commerce resellers | Brands building long-term equity |
Strategic Note: Private Label is increasingly preferred by DTC (Direct-to-Consumer) brands seeking margin control and product differentiation.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumptions: Mid-tier consumer electronics accessory (e.g., wireless earbuds, smart home device), Guangdong-based factory, standard quality (RoHS compliant), sea freight included.
| Cost Component | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | Includes PCBs, batteries, plastics, sensors |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Skilled labor in Shenzhen/Dongguan clusters |
| Packaging | 10–12% | Retail-ready box, inserts, manuals |
| Tooling & Setup | 5–10% (one-time) | Molds, firmware programming, QA setup |
| QA & Compliance | 5% | Pre-shipment inspection, safety certifications |
Tooling Cost Estimate: $3,000–$8,000 one-time (reusable across batches).
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | Low risk entry; ideal for White Label or test batches |
| 1,000 units | $14.75 | $14,750 | 20% savings vs. 500; suitable for Private Label launch |
| 5,000 units | $10.20 | $51,000 | 31% savings vs. 1K; economies of scale, better margin control |
Notes:
– Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and VAT.
– Unit cost reduction beyond 5K units averages 3–5% per additional 5K increment.
– Private Label at 500 MOQ may incur +$2–$3/unit due to setup allocation.
5. Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage Listed Manufacturers for Stability
Prioritize suppliers with public financials (e.g., Shenzhen-listed SMEs) for transparency and scalability. -
Start ODM, Scale with OEM
Use ODM for MVP validation; transition to OEM for brand differentiation. -
Negotiate Tooling Buyback Clauses
Ensure ownership or full reimbursement of tooling costs after 3–5 production runs. -
Factor in Compliance Early
Budget for CE, FCC, or UKCA certifications during design phase to avoid delays. -
Use Third-Party QC Inspections
Allocate 1–2% of budget for pre-shipment audits (e.g., SGS, QIMA).
Conclusion
China’s deep manufacturing ecosystem—supported by over 5,300 listed industrial and tech firms—offers unmatched scalability for global procurement teams. By strategically selecting between White Label and Private Label models and optimizing MOQs, procurement managers can achieve cost efficiency without sacrificing brand control. The 2026 landscape favors agile sourcing partnerships with transparent, audit-ready suppliers.
Next Step: Request a free Supplier Vetting Checklist and Cost Simulation Tool from SourcifyChina to model your specific product category.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Shenzhen & Shanghai | sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework for China Procurement (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Authored by Senior Sourcing Consultants | SourcifyChina | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese manufacturing partners remains the #1 risk factor in supply chain integrity for 78% of global procurement teams (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Risk Index). This report provides a field-tested, step-by-step protocol to eliminate misrepresentation risks—specifically addressing the critical confusion between trading companies and authentic factories. Note: “Listed companies” in China typically refers to publicly traded entities (e.g., Shanghai/Shenzhen Stock Exchange). This report focuses on verifying all legitimate manufacturers, whether listed or private.
Critical 5-Phase Verification Protocol
Follow this sequence to validate 100% of supplier claims before engagement
Phase 1: Legal Entity Authentication (Non-Negotiable First Step)
| Verification Step | Method | Red Flag Indicator | Validation Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Check | Cross-reference Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) against official databases | USCC invalid or mismatched with supplier name | National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (NECIP) |
| Scope of Operations | Confirm manufacturing-specific language (e.g., “production,” “processing”) | Vague terms like “trading,” “import/export,” “agency” | Physical license copy + NECIP verification |
| Registered Capital | Analyze adequacy for scale (e.g., <¥5M RMB = likely trader for industrial goods) | Discrepancy between capital and claimed production capacity | NECIP + Industrial benchmark analysis |
Phase 2: Physical Facility Verification (Remote & On-Site)
| Verification Method | Key Actions | Authentic Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite Imagery | Use Google Earth/Mapbox to verify厂区 (factory area) size, loading docks, equipment | Visible production lines, raw material storage, QC labs | Office buildings only; no industrial infrastructure |
| Video Audit | Request real-time walkthrough during operating hours (not pre-recorded) | Live machinery in operation, worker uniforms, batch logs | Studio-set “production” footage; no raw materials |
| Utility Verification | Request 3-month electricity/gas bills (industrial rates) | High consumption matching claimed capacity | Bills show commercial/office rates only |
Phase 3: Production Capability Stress Test
Demand evidence beyond marketing materials:
– Raw Material Traceability: Require batch numbers linking to supplier invoices (e.g., steel mill certificates)
– Mold/Tooling Ownership: Insist on photos of your product molds with factory logo stamped on base
– OEE Metrics: Request Overall Equipment Effectiveness data (factories track this; traders cannot provide)
Phase 4: Financial Health Screening
| Metric | Factory Threshold | Trading Company Pattern | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Export License | Directly held (Customs Code) | Not held (uses 3rd-party license) | Cross-check with China Customs |
| VAT Rebate Rate | 9-13% (manufacturing sector) | 0% (trading = 0% rebate) | Tax bureau records |
| R&D Expenditure | ≥4% of revenue (gov’t verified) | Near 0% | Financial audit + tax filings |
Phase 5: Contractual Safeguards
- Clause Requirement: “Supplier warrants it is the legal owner of all production equipment listed in Appendix A”
- Penalty Clause: 200% of deposit refund if proven to be a trading company misrepresenting as factory
- Right-to-Audit: Unannounced onsite verification rights for full production lifecycle
Factory vs. Trading Company: Critical Differentiators
Use this table during supplier interviews (traders often fail these questions)
| Verification Point | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Time Explanation | “Mold setup: 30 days + 15-day production cycle” | “Typically 45-60 days after deposit” | Factories control timelines; traders add buffer |
| Pricing Structure | Breaks down material/labor/OH costs | Single FOB price with no cost components | Transparency = production control |
| Minimum Order Quantity | Based on machine changeover costs (e.g., 500 units/mold) | Fixed container-based MOQ (e.g., 1x20ft) | Factories optimize runs; traders optimize shipments |
| Engineering Questions | On-site engineer joins call; shares CAD files | “Our QC team will check” – no technical depth | Direct process ownership |
| Sample Production | Made on actual production line (shows batch tag) | Sourced from multiple suppliers; inconsistent finishes | Quality system maturity |
Top 5 Red Flags Requiring Immediate Disqualification
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina audit data (92% of flagged suppliers failed within 6 months)
-
“We Own Multiple Factories” Claim
→ Reality: 98% of such suppliers are trading conglomerates. Verify each facility’s USCC separately.
Action: Demand separate business licenses for each “factory” location. -
Alibaba “Verified Supplier” Badge Without NECIP Match
→ Reality: Alibaba verification only checks business registration (not production capability).
Action: NECIP must confirm manufacturing scope before trusting platform badges. -
Refusal to Provide Factory Layout Map
→ Reality: Factories have standardized floor plans for efficiency; traders cannot produce them.
Action: Require CAD layout showing your product’s workflow path. -
Samples Shipped from Different City Than Factory
→ Reality: Traders source samples from multiple suppliers to “match” specs.
Action: Track sample shipment origin via logistics provider API. -
Payment Demanding 100% TT Before Production
→ Reality: Factories with real capacity accept LC or 30% deposit; traders demand full prepayment.
Action: Insist on 70% balance against B/L copy – no exceptions.
Strategic Recommendation
“In 2026, China’s manufacturing sector faces unprecedented consolidation (NBSC 2025 data shows 12,400+ factory closures). Verification must shift from document-checking to operational proof. Demand real-time production data streams via IoT sensors on machinery – a non-negotiable standard for SourcifyChina’s Tier-1 partners. Trading companies cannot replicate this transparency.”
— Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
1. Implement this 5-phase protocol for all new Chinese supplier onboarding
2. Retest 20% of existing suppliers annually using Phase 2-3 methods
3. Integrate NECIP checks into your ERP procurement module (API available)
Need verification support? SourcifyChina provides:
✓ NECIP/Customs Code automated screening ($299/supplier)
✓ Unannounced factory audits (from $850/site)
✓ IoT production monitoring integration
[Contact SourcifyChina Verification Team] | [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary verification methodologies. Data sources: National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), General Administration of Customs PRC, SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database (n=1,842 suppliers). © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Not for redistribution.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Accelerate Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Intelligence
In today’s hyper-competitive global supply chain landscape, accuracy, speed, and due diligence are non-negotiable. For procurement professionals targeting China—a market of over 5,000 listed companies and 50+ million enterprises—identifying reliable, scalable, and compliant suppliers remains a persistent challenge.
Conventional search methods yield fragmented, outdated, or unverified data, leading to increased risk, extended lead times, and costly procurement errors.
SourcifyChina delivers a strategic advantage through our Pro List™—a rigorously vetted database of verified Chinese manufacturers and listed enterprises, engineered specifically for high-performance procurement teams.
Why the Pro List™ Eliminates Sourcing Delays
| Challenge | Traditional Research | SourcifyChina Pro List™ |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Public databases often include defunct, shell, or misrepresented companies | All suppliers undergo 7-point verification: business license, production capacity, export history, quality certifications, financial standing, site validation, and compliance checks |
| Time to Shortlist | 4–8 weeks of manual vetting, cold outreach, and qualification | Immediate access to pre-qualified suppliers; reduce shortlisting time by 70%+ |
| Risk Exposure | High risk of fraud, misrepresentation, or non-compliance | Each Pro List supplier is audited and monitored quarterly |
| Scalability | Limited to known networks or third-party platforms with opaque vetting | Curated access to tier-1 suppliers across electronics, machinery, textiles, automotive, and new energy sectors |
Key Insight: “How Many Listed Companies in China?” — Beyond the Number
While over 5,300 companies are publicly listed on mainland exchanges (Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing), only a fraction meet international procurement standards for export readiness, quality control, and scalability.
Our Pro List™ isolates the top 12% of compliant, export-capable enterprises, including subsidiaries and suppliers to listed firms—giving you access not just to public companies, but to their vetted supply ecosystems.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Roadmap Today
Stop wasting valuable procurement cycles on unreliable leads and unverified claims. SourcifyChina’s Pro List™ is the trusted sourcing intelligence tool used by Fortune 500 procurement teams, EU importers, and North American distributors to:
- Reduce supplier qualification time from weeks to days
- Mitigate supply chain risk with real-time compliance data
- Scale sourcing initiatives with confidence in supplier legitimacy
👉 Take the next step toward faster, smarter China sourcing.
Contact our Sourcing Support Team today:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available in English, Mandarin, and German to support your global procurement strategy.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Pro List™ is a trademark of SourcifyChina. Data as of Q1 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.