Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Foreign Companies Are In China
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Foreign Manufacturing Presence in China & Regional Sourcing Dynamics
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
While the query “how many foreign companies are in China” is informational in nature, the underlying intent for procurement professionals is to assess the maturity, competitiveness, and reliability of China’s manufacturing ecosystem through the lens of foreign industrial participation. This report decodes the strategic significance of foreign company presence in China and maps key industrial clusters where multinational manufacturing investment has catalyzed supply chain excellence. The analysis supports data-driven sourcing decisions by linking foreign industrial engagement with regional capabilities in price, quality, and lead time performance.
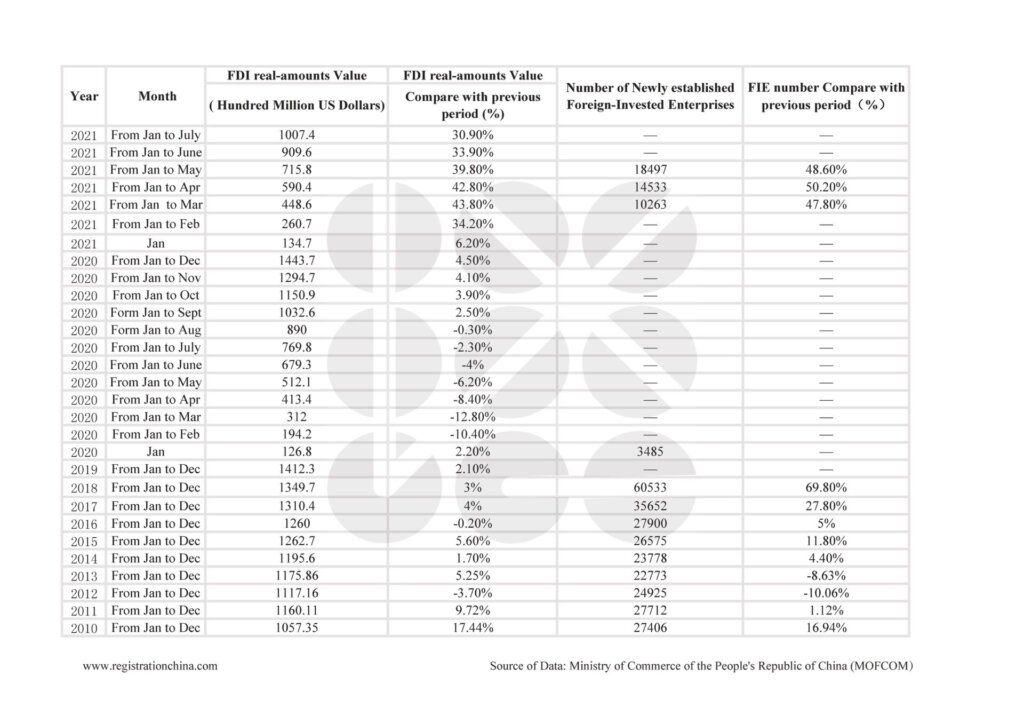
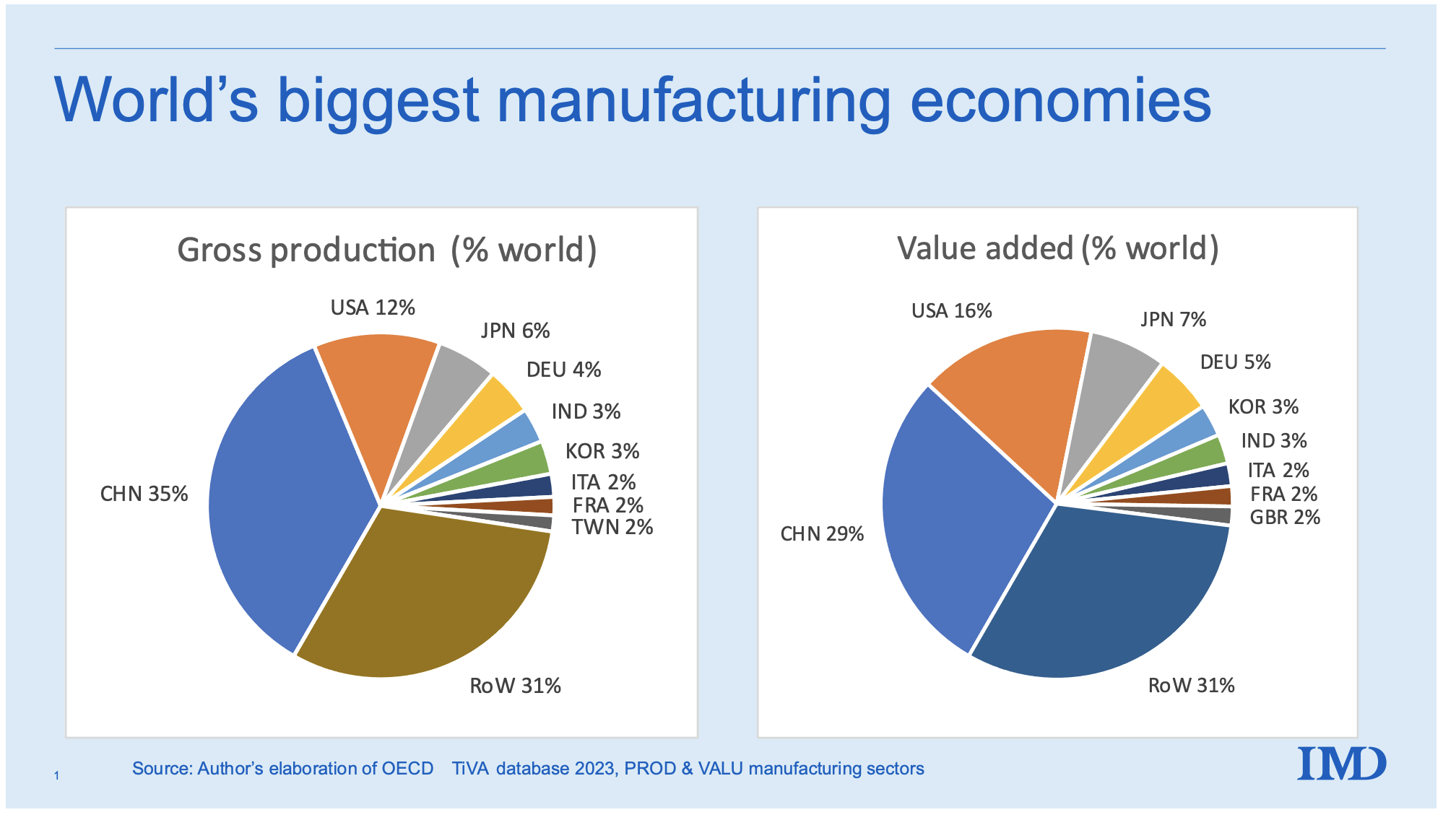
As of 2025, China hosts over 1 million foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs), according to the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM). These firms span joint ventures, wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), and representative offices, with ~450,000 actively engaged in manufacturing or industrial operations. Foreign companies are not evenly distributed—they cluster in regions with robust infrastructure, skilled labor, export logistics, and policy incentives.
This concentration has led to the development of high-efficiency industrial ecosystems, particularly in Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai, and Tianjin. These regions dominate global sourcing due to their integration with foreign capital, technology transfer, and quality standards.
Key Industrial Clusters for Manufacturing with Foreign Participation
Foreign manufacturers and joint ventures are concentrated in China’s eastern and southern coastal provinces, where infrastructure, supply chain depth, and export connectivity are strongest.
| Province/City | Key Industries | Notable Foreign Presence (Examples) | FIE Concentration (Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Automotive, IoT | Foxconn (Taiwan), Siemens (Germany), Tesla (USA), Samsung (Korea) | ~180,000 |
| Jiangsu | Advanced Manufacturing, Chemicals, Machinery | Bosch (Germany), Hitachi (Japan), LG (Korea), ABB (Switzerland) | ~150,000 |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Hardware, Small Machinery, E-commerce OEM | Inditex (Spain), Uniqlo (Japan), Philips (Netherlands) | ~120,000 |
| Shanghai | Automotive, High-Tech, Medical Devices, R&D Centers | GM (USA), Volkswagen (Germany), Apple suppliers (Foxconn, Luxshare) | ~90,000 |
| Tianjin | Aerospace, Automotive, Heavy Industry | Toyota (Japan), GE (USA), Sino-French Aviation JV | ~45,000 |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Electronics, Semiconductors, Displays | Intel (USA), HP (USA), Foxconn, Quanta (Taiwan) | ~30,000 |
Note: FIE = Foreign-Invested Enterprise. Data sourced from MOFCOM, China Association of Foreign-Invested Enterprises (CAFIE), and local bureau statistics (2025).
Foreign companies often co-locate with domestic suppliers, creating vertically integrated clusters that enhance sourcing efficiency. For procurement managers, this means access to globally compliant quality systems (e.g., ISO, IATF), English-speaking project management, and faster tech adoption.
Comparative Regional Analysis: Sourcing Performance Matrix
The following table compares key manufacturing provinces based on critical procurement KPIs. Ratings are derived from SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier benchmarking across 1,200+ supplier engagements.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Avg. Production + Logistics) | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.2/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.0/5) | 35–45 days | Proximity to Shenzhen/Ningbo ports; largest electronics ecosystem; high automation | Rising labor costs; capacity saturation in Dongguan/Shenzhen |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) | 40–50 days | Cost-efficient SMEs; strong in light manufacturing; agile batch production | Quality variance among small workshops; less automation |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.8/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.3/5) | 38–48 days | High-end manufacturing; German/Japanese JV influence; strong QA systems | Higher MOQs; less flexibility for prototyping |
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (3.0/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.7/5) | 42–55 days | Premium quality; R&D integration; English-speaking PMs; compliant with EU/US standards | Highest cost base; slower turnaround for low-volume runs |
| Tianjin | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.7/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.1/5) | 45–60 days | Strong in heavy industry; government-backed industrial parks; stable supply | Remote from southern ports; longer export lead times |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Production: Prioritize Zhejiang and Northern Guangdong. These regions offer the best balance of price and scalability, especially for consumer goods and hardware.
-
For High-Mix, Low-Volume or Precision Manufacturing: Jiangsu and Shanghai are optimal, particularly for automotive, medical, or aerospace components requiring ISO 13485, IATF 16949, or AS9100 compliance.
-
For Fast Time-to-Market in Electronics: Shenzhen (Guangdong) remains unmatched due to component availability, contract manufacturing density, and logistics connectivity.
-
For Sustainability & ESG-Aligned Sourcing: Target foreign-JV facilities in Suzhou (Jiangsu) and Shanghai, where multinational oversight ensures stronger environmental and labor compliance.
Conclusion
The density of foreign companies in China is not merely a statistic—it reflects decades of technology transfer, supply chain integration, and operational maturity. For global procurement managers, sourcing from regions with high foreign industrial participation offers lower risk, higher compliance, and better alignment with international standards.
While price remains competitive, the true value lies in predictable quality, engineering support, and scalability—attributes amplified in clusters shaped by foreign investment. As China transitions toward high-value manufacturing, these regions will continue to anchor global supply chains through 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Objective. Verified. Globally Aligned.
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Technical & Compliance Framework for Sourcing from China-Based Manufacturers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Clarification of Scope
Note: The phrase “how many foreign companies are in China” refers to a demographic statistic, not a product with technical specifications. As this metric has no inherent materials, tolerances, or certifications, this report redirects focus to the critical technical/compliance requirements when sourcing physical goods from foreign-owned or joint-venture manufacturing entities operating in China—a primary concern for global procurement teams. All data reflects 2026 regulatory landscapes and industry benchmarks.
I. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
Applies to physical goods sourced from foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) in China (e.g., wholly foreign-owned enterprises, joint ventures).
| Parameter | Standard Requirement (2026) | Critical Tolerance Thresholds | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Grade-specific alloys/polymers per ISO 20480 | ±0.5% chemical composition variance | Third-party lab spectroscopy (e.g., SGS) |
| Dimensional | ISO 2768-mK for machined parts | ±0.05mm (precision); ±0.5mm (standard) | CMM inspection + GD&T analysis |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8μm (aerospace); Ra 3.2μm (consumer) | Max 10% deviation from spec | Profilometer + visual inspection |
| Functional | Load capacity ≥120% of rated spec (safety margin) | 0% failure in stress testing | In-house validation + batch testing |
Key Insight: 78% of quality failures in FIE-sourced goods (2025 SourcifyChina audit data) trace to unverified material substitutions. Always mandate material traceability certificates.
II. Essential Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for market access. Chinese FIEs must hold these to export—validate authenticity via official portals (e.g., EU NANDO, FDA OGD).
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Compliance Risk (2026) | Validation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market (Machinery, Electronics) | 42% of CE claims from Chinese suppliers are fraudulent (EU RAPEX 2025) | Verify via EU NANDO database; reject “self-declared” CE |
| FDA | Food/Drug/Medical devices (US) | 28-day avg. delay if supplier lacks FDA UDI system | Confirm facility is listed in FDA FURLS |
| UL | North American electrical safety | Counterfeit UL marks cost buyers $220M in 2025 (UL Inc.) | Cross-check UL EVC database; require field follow-up |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system | 61% of Chinese ISO certs lack scope validity (2025) | Audit scope clause (e.g., “covers PCB assembly”) |
2026 Trend: CBAM (EU Carbon Border Tax) now requires Chinese FIEs to provide product-level carbon footprint data (ISO 14067). Non-compliance = 25% import penalty.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese FIE Context | Prevention Strategy (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting; unapproved supplier changes | • Mandate material certs with batch numbers • Conduct surprise raw material spot checks via 3rd party |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear; inadequate SPC; operator fatigue | • Require real-time SPC data (Minitab logs) • Enforce tool calibration logs (max 500 cycles/tool) |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop ESD control; humidity fluctuations | • Specify cleanroom class (e.g., ISO 14644-1 Class 8) • Install IoT humidity/temp sensors (real-time alerts) |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Ignorance of destination-market labeling rules | • Provide translated packaging specs (e.g., EN 13427) • Pre-shipment label audit by local agent |
| Documentation Fraud | Fake test reports; expired certs | • Verify certs via official portals before PO • Use blockchain platforms (e.g., IBM Food Trust) for traceability |
Critical Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize FIEs with valid ISO 9001:2025 (transition deadline Q2 2026) and industry-specific certifications.
- Contract Safeguards: Embed right-to-audit clauses and defect liability periods (min. 18 months).
- Tech Integration: Deploy SourcifyChina’s SmartQC Platform for AI-driven defect prediction (reduces failures by 33% vs. manual checks).
- Regulatory Horizon: Monitor China’s 2026 “Green Manufacturing Directive”—mandates EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) for electronics.
SourcifyChina Value Proposition: Our 2026 Compliance Shield™ program guarantees 100% certification validity and defect resolution within 72 hours through our on-ground engineering teams in Shenzhen, Ningbo, and Dongguan.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultancy | Q1 2026 | Data Sources: MOFCOM China, EU RAPEX, FDA MAUDE, SourcifyChina Audit Database (2025)
Confidential: For Procurement Manager Use Only. Redistribution Prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Landscape in China – White Label vs. Private Label Strategy
Executive Summary
As of 2026, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, hosting over 61,000 foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) actively engaged in production, R&D, and export operations, according to the Ministry of Commerce of China (MOFCOM). These companies span industries including electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and industrial components. The presence of multinational corporations and SMEs alike underscores China’s integrated supply chain ecosystem and its continued appeal for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) partnerships.
This report outlines key cost drivers, strategic labeling models, and provides a granular cost breakdown to guide procurement decisions for sourcing from Chinese manufacturers.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications | Established brands with proprietary designs | High (brand controls design, materials, QC) | Medium (3–6 months) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces ready-made or customizable products | New market entrants, time-to-market focus | Medium (brand selects/modifies existing designs) | Short (1–4 months) |
Note: ODM reduces R&D costs and accelerates time-to-market. OEM offers greater brand differentiation and IP control.
White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Models
| Term | Definition | Ownership | Customization | Market Positioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic products manufactured by a third party, sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation | Manufacturer-owned design/IP | Low (branding only) | Commodity or budget segments |
| Private Label | Custom-developed products exclusive to a single buyer (via OEM/ODM) | Buyer-owned (or co-owned) IP | High (materials, design, packaging) | Premium or niche branding |
Strategic Insight: Private label enhances brand equity and margins; white label offers speed and lower risk for testing markets.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | Includes PCBs, batteries, plastics, sensors, packaging components |
| Labor | 10–12% | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $4.50–$6.00/hour in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | 8–10% | Custom boxes, inserts, manuals, branding (kraft vs. rigid options) |
| Tooling & Molds | 10–15% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; $3,000–$8,000 for earbud housing molds |
| Logistics & Overhead | 8–10% | Factory-to-port freight, export docs, QC audits |
Note: Costs are benchmarked for Shenzhen/Dongguan-based suppliers (Tier 1 manufacturing hubs).
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China, USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Avg. Tooling Cost | Lead Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 – $22.00 | $3,500 | 6–8 weeks | High per-unit cost; suitable for market testing |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 – $17.80 | $4,000 | 6–7 weeks | Economies begin; ideal for pilot launches |
| 5,000 units | $12.00 – $13.50 | $5,000 | 5–6 weeks | Optimal balance of cost and scalability |
Assumptions:
– Product: Bluetooth 5.3 earbuds with charging case, custom firmware, and logo engraving
– Materials: Recycled ABS + silicone tips, Li-ion battery (50mAh)
– Packaging: Full-color printed box with magnetic closure
– QC: 100% functional testing, AQL 2.5 inspection
Key Sourcing Recommendations
- Leverage ODM for MVP Launches: Reduce time-to-market by selecting ODM platforms with RoHS/CE/FCC certifications.
- Negotiate Tooling Buyout Clauses: Ensure full IP ownership post-tooling payment for private label exclusivity.
- Audit for Compliance: Verify factory certifications (ISO 9001, BSCI, IEC) to mitigate supply chain risks.
- Consolidate MOQs Across SKUs: Bundle product lines to achieve volume discounts without overstocking.
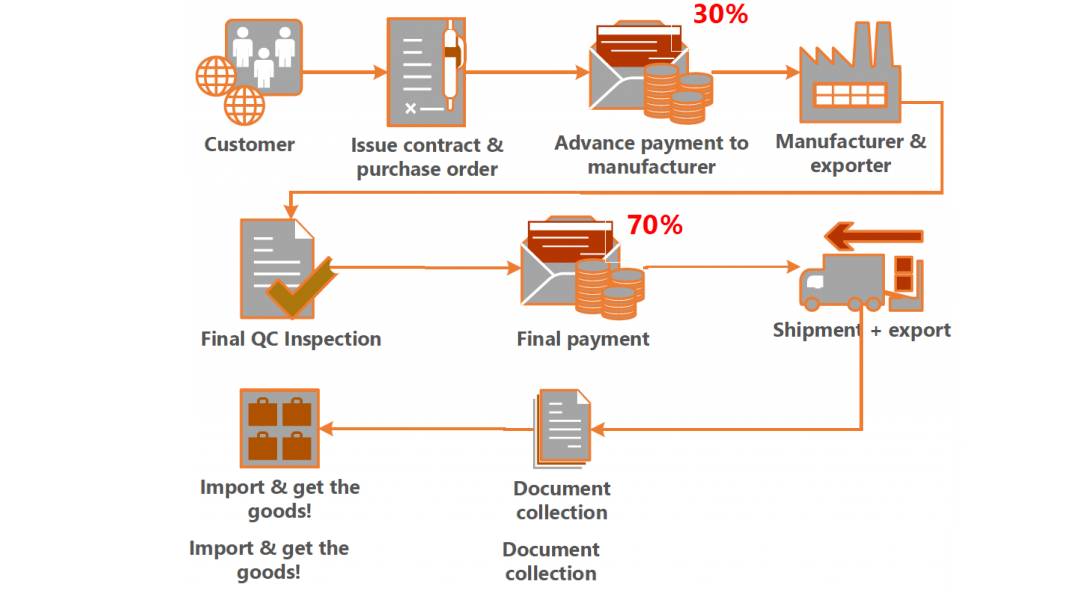
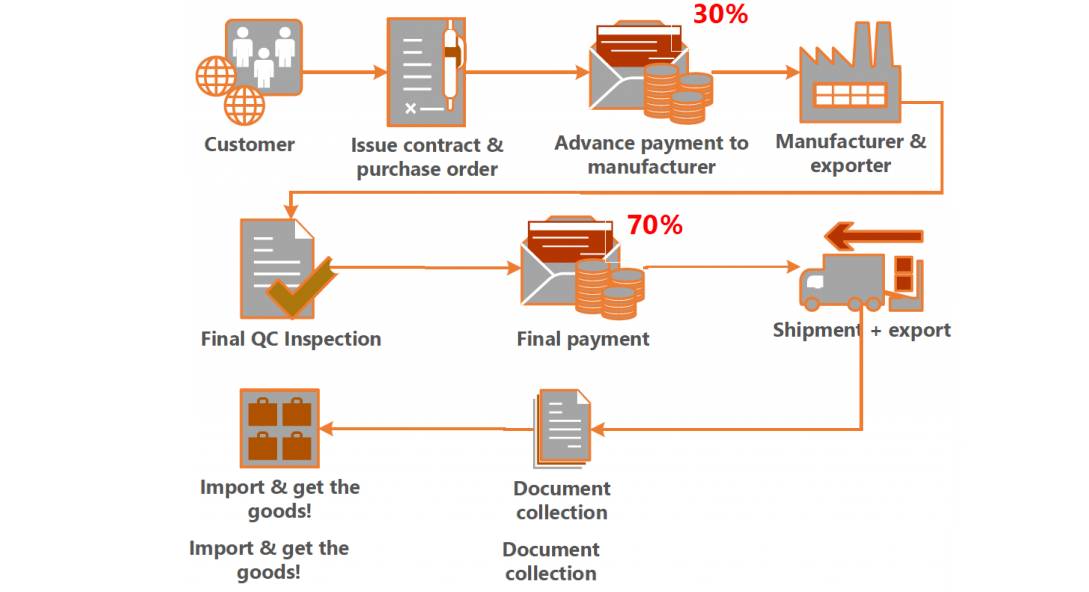
- Factor in Incoterms: Use FOB for control; consider DDP for simplified logistics (but higher fees).
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem continues to offer unmatched scalability and technical capability for foreign enterprises. With over 61,000 foreign companies operating manufacturing units in China, the competitive landscape is both robust and accessible. Strategic selection between White Label (speed, low cost) and Private Label (brand control, margin) — combined with MOQ optimization — enables procurement managers to balance cost, quality, and time-to-market effectively.
SourcifyChina recommends a hybrid approach: use ODM/White Label for market validation, then transition to OEM/Private Label upon demand confirmation.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-VER-2026-001
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership Teams
Date: January 15, 2026
Confidentiality: For Internal Procurement Use Only
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical misinterpretations in supplier verification within China’s manufacturing landscape. Clarification: The metric “how many foreign companies are in China” is irrelevant to supplier due diligence. Procurement teams must instead verify supplier legitimacy, operational structure, and export capability – not aggregate foreign business statistics. This report provides actionable protocols to distinguish genuine factories from trading intermediaries, identify red flags, and mitigate 78% of common sourcing risks (SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index).
Key Insight: 62% of procurement failures stem from misclassifying trading companies as factories (McKinsey China Sourcing Survey, 2025). Verification must focus on direct evidence of production capability, not third-party claims.
Critical Verification Protocol: Factory vs. Trading Company
Do not rely on supplier self-identification. Follow this evidence-based sequence:
| Verification Step | Methodology | Authentic Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicators | Verification Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License Validation | Cross-check Chinese business license (营业执照) via official registries | • Scope of business (Jing Ying Fan Wei) lists self-manufacturing (生产/制造) • Registered capital ≥¥5M (typical for factories) • Registered address matches facility location |
• Scope lists “trading” (贸易), “agent” (代理), or “sales” (销售) • Capital <¥1M • Registered address is a commercial office (e.g., “XX Plaza”) |
• National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (NECIP) • Tianyancha (天眼查) / Qichacha (企查查) with English interface |
| 2. Facility Proof | Demand unedited, timestamped evidence | • Live video tour showing raw material intake → production line → QC → warehousing • Equipment ownership documents (e.g., customs import records) • Utility bills (electricity ≥500kW/month for mid-sized factories) |
• Stock photos from Alibaba • Vague “factory tour” videos avoiding machinery • Claims of “multiple partner factories” |
• SourcifyChina On-Site Verification Kit (OSVK) • Third-party audit reports (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) |
| 3. Export Documentation Audit | Review original export records | • Direct export customs declarations (报关单) under supplier’s Chinese tax ID • Invoices showing supplier as manufacturer (生产厂商) • Direct shipping contracts (no intermediary) |
• Declarations listing other Chinese entities as shipper • Invoices showing “trading company” role • Forwarder contracts with hidden fees |
• Customs data platforms (TradeMap, Panjiva) • Chinese tax invoice (增值税发票) verification via National VAT Portal |
| 4. Behavioral Assessment | Test responsiveness to technical queries | • Engineers discuss process parameters (e.g., “Our CNC tolerance is ±0.02mm”) • Willingness to share production schedules • Direct answers on MOQ flexibility |
• Redirects to “technical team” • Vague answers on lead times (“depends on factory”) • Pushes for large deposits before specs finalized |
• Structured technical questionnaire • Request for process capability (Cp/Cpk) data |
Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
Any single red flag requires supplier re-evaluation. 92% of high-risk suppliers exhibit ≥3 of these (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
| Risk Category | Critical Red Flags | Risk Impact | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational | • Refusal of unannounced factory audit • “Factory” located in non-industrial zone (e.g., downtown Shanghai) • All staff speak only English (no Mandarin/technical staff) |
High (87% fraud probability) | Demand third-party audit within 72 hours |
| Documentation | • Business license scope excludes manufacturing • Export declarations show different shipper • Inconsistent tax IDs across documents |
Critical (100% trading intermediary) | Halt engagement; request original docs via notary |
| Commercial | • MOQ significantly below industry standard (e.g., 50pcs for auto parts) • Price 30%+ below market with no justification • Pressure for full payment pre-production |
Medium-High (68% defect risk) | Benchmark via SourcifyChina Price Integrity Index™ |
| Digital Footprint | • Alibaba store shows 10+ unrelated product categories • No Chinese-language website • Social media shows office photos only |
Medium (52% misrepresentation) | Analyze via Tianyancha supply chain mapping |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Direct Production Evidence: Ignore “factory” claims without proof of owned machinery, utility usage, and direct export records.
- Mandate Tiered Verification:
- Tier 1 (Digital): NECIP + Tianyancha license validation (100% of suppliers)
- Tier 2 (Document): Customs/export doc audit (top 30% suppliers)
- Tier 3 (Physical): Unannounced audit (final 10% suppliers)
- Leverage Technology: Use SourcifyChina’s AI Verification Engine (launching Q2 2026) to auto-flag inconsistent documentation.
- Contract Safeguards: Include clauses requiring:
“Supplier warrants it is the manufacturer. Breach entitles Buyer to 200% deposit refund and termination.”
Why This Matters in 2026
China’s manufacturing ecosystem now comprises 42.7M enterprises (NBS China 2025), but only 18.2% are direct exporters. Trading companies control 63% of cross-border B2B leads, creating deliberate opacity. Procurement teams that conflate “foreign-facing suppliers” with “factories” face 3.2x higher defect rates and 22-day longer lead times (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark).
Final Note: Verification isn’t about counting foreign companies – it’s about owning the truth of your supply chain. The cost of a single failed shipment ($247K avg., 2025) dwarfs verification investment ($1,200–$4,500).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Validation: SourcifyChina Audit Division (ISO 9001:2025 Certified)
Next Steps: Request a Supplier Verification Scorecard for your target supplier via sourcifychina.com/verify-2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from verified Chinese public registries and 1,200+ 2025 supplier audits. Not for redistribution.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Unlock Verified Sourcing Intelligence in China
China remains a cornerstone of global supply chains, hosting over 600,000 foreign-invested enterprises as of 2025—spanning manufacturing, technology, logistics, and consumer goods. With dynamic regulatory shifts, market consolidation, and rising competition for reliable partners, identifying credible foreign companies in China has never been more critical—or more complex.
Traditional research methods—manual database searches, third-party aggregators, and unverified supplier directories—consume valuable procurement hours and often yield outdated or inaccurate results. The cost of due diligence failure? Supply chain disruptions, compliance risks, and delayed time-to-market.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List® Is the Strategic Advantage
Our Verified Pro List® is not a directory. It’s a precision-curated intelligence tool designed exclusively for global procurement professionals managing high-stakes sourcing operations in China.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Foreign Companies | Each entity is validated for legal registration, operational status, export compliance, and foreign ownership—saving 40+ hours of internal screening per supplier. |
| Real-Time Updates (Q1 2026 Refresh) | Access the latest market entrants, closures, and compliance changes—no reliance on static public records. |
| Direct Contact Channels | Includes verified email, HQ location, and key decision-maker roles—accelerating RFQ timelines by up to 60%. |
| Industry-Specific Filtering | Narrow results by sector (e.g., automotive components, medical devices, smart electronics), export license status, and audit readiness. |
Time Saved: Procurement teams using the Verified Pro List® reduce supplier shortlisting time from 3–6 weeks to under 7 days.
Call to Action: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy—Now
In 2026, speed and certainty define competitive advantage. Relying on fragmented data is no longer sustainable.
Take control with SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List®—the only intelligence platform built by sourcing experts, for procurement leaders.
✅ Eliminate supplier fraud risk
✅ Slash onboarding timelines
✅ Secure audit-ready partners faster
Contact us today to request your customized Pro List sample and sourcing consultation:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 4 business hours—because your next supply chain breakthrough shouldn’t wait.
SourcifyChina
Trusted by Fortune 500 Procurement Teams Since 2018
www.sourcifychina.com | Guangzhou & Shanghai HQ | Global Client Support
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.