Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Ev Companies In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EV Component Manufacturing Landscape Analysis (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Executives
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-EV-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
China remains the undisputed global epicenter of electric vehicle (EV) component manufacturing, housing over 1,200 active EV component suppliers (excluding raw material miners) as of Q3 2026. This represents a 15% YoY consolidation following stringent safety regulations and subsidy reforms. Critical industrial clusters have matured beyond mere assembly hubs into integrated R&D and production ecosystems, with distinct regional specializations. Procurement priority must shift from volume to strategic supplier alignment within these clusters to mitigate supply chain volatility and access next-gen technology.
Critical Clarification: The phrase “how many ev companies in china” reflects a common market inquiry misdirection. SourcifyChina interprets this as sourcing EV components/systems (batteries, motors, controllers, charging systems, lightweight chassis). Directly counting “EV companies” is commercially irrelevant; focus must be on Tier 1-3 component manufacturing capacity. China hosts ~280 OEMs (down from 450 in 2023), but >95% of procurement value lies in component sourcing.
Key Industrial Clusters: Strategic Mapping for 2026
China’s EV component manufacturing is concentrated in five dominant clusters, each driven by provincial policy, OEM anchoring, and supply chain maturity. Avoid generic “China sourcing” strategies – cluster-specific engagement is non-negotiable.
| Cluster (Province/City) | Core Specialization | Key OEM Anchors | Strategic Procurement Advantage | 2026 Capacity Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan/Shenzhen) | High-voltage systems, ADAS sensors, infotainment | XPeng, BYD (HQ), Huawei Aito | Global export readiness (UL/CE certified lines), strongest English-speaking engineering talent | 28% |
| Jiangsu (Nanjing/Changzhou) | Battery cells & packs (60% of China’s), power electronics | CATL (subsidiaries), JAC Volkswagen | Deepest battery ecosystem (Li-ion, solid-state pilots), lowest cell logistics cost | 32% |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Hangzhou) | Motors, controllers, thermal management | Geely (Zeekr), NIO (supply chain HQ) | Highest automation rates, seamless Alibaba/1688 integration, agile micro-factories | 19% |
| Anhui (Hefei) | Complete vehicle systems, lightweight chassis | NIO (HQ), JAC Motors | OEM-integrated supplier parks (NIO partners co-located), fastest prototyping | 12% |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Rare earth processing, motor magnets | Tesla Gigafactory (Chengdu Satellite) | Lower labor costs (vs. coast), critical for NdFeB magnet supply chain security | 9% |
Source: SourcifyChina Cluster Database (Q3 2026), China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), Provincial Industry & IT Dept. Reports. Capacity share = Value of EV components shipped from region.
Regional Sourcing Performance Comparison (2026 Benchmark)
Metrics reflect average for Tier 2-3 suppliers (component-focused, not OEMs). Prices in USD per standard unit (e.g., motor controller). Lead times include production + port clearance.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency (Defect Rate) | Avg. Lead Time | Logistics Efficiency | Critical Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★☆☆☆ (Premium) | 0.18% (Best-in-class) | 45-60 days | ★★★★★ (Shenzhen Port) | Highest labor costs (+22% YoY) |
| Jiangsu | ★★★★☆ (Balanced) | 0.35% | 50-65 days | ★★★★☆ (Yangtze River) | Battery oversupply risk (Q2 2026) |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (Balanced) | 0.28% | 40-55 days | ★★★★☆ (Ningbo-Zhoushan) | IP leakage concerns (micro-factories) |
| Anhui | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-Premium) | 0.22% | 48-62 days | ★★★☆☆ (Inland port) | NIO dependency (35% of cluster revenue) |
| Sichuan | ★★★★★ (Most Competitive) | 0.45% (Improving) | 55-70 days | ★★☆☆☆ (Mountainous) | Power rationing (summer 2025 precedent) |
Key Insights from Comparison:
- Price ≠ Value: Guangdong commands 12-15% price premiums but delivers 30% lower defect rates vs. Sichuan – critical for safety-critical components (e.g., BMS).
- Lead Time Myth: Zhejiang’s “agile” reputation holds, but Jiangsu’s battery cluster now matches lead times due to automated cell lines (CATL’s “Factory 4.0” rollout).
- Quality Nuance: Anhui’s quality is OEM-driven (NIO’s 0.15% target); non-NIO suppliers lag at 0.35%. Always verify supplier-specific certifications (IATF 16949 mandatory).
- Hidden Cost: Sichuan’s low base price is offset by 8-12% logistics surcharges and 15% higher scrap rates for precision parts.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Diversify Within Clusters: Never source >40% of critical components (batteries, motors) from a single province. Pair Jiangsu (battery volume) with Guangdong (backup cell lines).
- Prioritize Battery Security: Target Jiangsu suppliers with dual sourcing (CATL and EVE Energy lines) to avoid 2025’s single-supplier bottleneck crisis.
- Leverage OEM Parks: In Anhui, pursue NIO-approved suppliers – they undergo quarterly audits but offer 20% faster NPI cycles.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: In Zhejiang/Sichuan, conduct unannounced process audits for IP protection. 68% of 2025 IP disputes originated in micro-factory hubs.
- Factor in Policy Shifts: Sichuan’s “Rare Earth Hub” subsidies expire Q1 2027 – lock in 2026 pricing now for magnet supply.
SourcifyChina Action: Our Cluster-Specific Vetting Protocol (CSVP) assesses suppliers against 47 regional risk variables. Request access to our real-time Jiangsu Battery Supplier Dashboard.
Disclaimer
Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary supplier network (1,850+ verified partners) and CAAM public data. “Quality” metrics exclude OEM captive suppliers. Prices fluctuate with lithium carbonate spot rates (tracked live in our Supplier Risk Platform). This report does not constitute investment advice.
Prepared by:
Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Your Objective Partner in China Sourcing
[Secure Link to Full Cluster Data Suite] | [Book 2026 Sourcing Strategy Session]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Overview of Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing in China
Executive Summary
As of 2026, China remains the world’s largest electric vehicle (EV) market and manufacturing hub, hosting over 500 EV companies involved in the design, assembly, and distribution of electric passenger vehicles, commercial EVs, and related components. This includes approximately 150 active OEMs producing vehicles at scale, supported by thousands of Tier 1, 2, and 3 suppliers.
This report outlines the technical specifications, quality parameters, essential certifications, and common quality defects relevant to sourcing EVs and EV components from China. It is tailored for procurement professionals managing supply chain risk, compliance, and product quality assurance.
Key Quality Parameters for EV Components and Assemblies
| Parameter | Specification | Tolerance / Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Material (Cathode) | Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | ±1.5% composition variance | LFP preferred for cost and safety; NMC for high energy density |
| Battery Pack Casing | Aluminum alloy 6061-T6 or equivalent | ±0.1 mm dimensional tolerance | Must meet IP67/IP68 ingress protection |
| Motor Stator Windings | Copper (OFC – Oxygen-Free Copper), enamel-coated | ±0.05 mm wire diameter | Thermal class ≥180°C (Class H) |
| Power Electronics (IGBT Modules) | Silicon-based or SiC (Silicon Carbide) | Operating temp: -40°C to 150°C | <5% efficiency loss at rated load |
| HV Cable Insulation | Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or EPR | Dielectric strength ≥3.5 kV/mm | Must pass 5,000-cycle flex testing |
| Structural Chassis Welds | MIG/TIG welding on high-strength steel or aluminum | Penetration depth ≥90% of base material | 100% ultrasonic or X-ray inspection on critical joints |
Essential Certifications for EVs and Components Exported from China
| Certification | Scope | Regulatory Body | Validity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Mandatory for all EVs sold in China | CNCA (China National Certification Authority) | Required for domestic sales | Not sufficient for export |
| E-Mark (UN ECE R100, R136) | Electric vehicle safety and battery standards | UNECE | Valid in EU, UK, Japan, South Korea | Required for EU market access |
| CE Marking (EMC, LVD, RED) | Electromagnetic compatibility, safety | EU Notified Body | Required for EU | Must be supported by Technical File |
| UL 2580 / UL 2202 | Battery safety for EVs and charging systems | Underwriters Laboratories (UL) | Required for North America | UL 2202 applies to EVSE (charging equipment) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | International Organization for Standardization | Global recognition | Foundational for Tier 1 suppliers |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive-specific QMS | IATF | Required by OEMs globally | Replaces ISO/TS 16949 |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | ISO | Increasingly required by EU buyers | Supports ESG compliance |
| ISO 26262 (ASIL-rated) | Functional safety (e.g., BMS, ADAS) | ISO | Critical for autonomous and high-voltage systems | ASIL D for highest risk components |
Note: FDA certification is not applicable to EVs or automotive components. It is relevant only to medical devices or food-contact materials.
Common Quality Defects in Chinese EV Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Swelling | Overcharging, poor thermal management, impurities in electrolyte | Implement strict BMS protocols; conduct 100% formation and aging testing; use ISO 26262-compliant control logic |
| Inconsistent Welding in Battery Packs | Poor robot calibration, operator error, substandard filler material | Enforce automated welding with real-time monitoring; conduct destructive and non-destructive testing (NDT); audit welding procedures quarterly |
| HV Connector Arcing | Misalignment, contamination, inadequate IP rating | Use molded connectors with locking mechanisms; validate IP67/IP68 in third-party labs; implement cleanroom assembly |
| Motor Bearing Noise/Vibration | Improper lubrication, misalignment, material fatigue | Perform dynamic balancing; use NSK or SKF-certified bearings; conduct vibration testing at 3,000–12,000 rpm range |
| Software Glitches in BMS/VCU | Inadequate validation, firmware bugs, poor OTA update protocols | Adopt ASPICE-compliant software development; conduct HIL (Hardware-in-the-Loop) testing; log and patch via secure OTA |
| Paint/Coating Delamination | Surface contamination, improper curing, humidity during application | Enforce pretreatment (phosphating), controlled booth conditions (20–25°C, 50–60% RH), adhesion testing (cross-hatch ASTM D3359) |
| Inverter MOSFET Failure | Thermal runaway, voltage spikes, undersized heat sinks | Integrate active liquid cooling; use surge protection; validate thermal dissipation in climatic chambers (-30°C to 85°C) |
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Supplier Qualification: Prioritize EV component suppliers with IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and UL/CE certifications.
- Factory Audits: Conduct on-site audits focusing on process control, traceability, and EHS compliance.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Implement AQL Level II inspections for critical components (battery, motor, power electronics).
- Third-Party Testing: Use accredited labs (e.g., TÜV Rheinland, SGS, Intertek) for safety and EMC validation.
- Traceability Systems: Require 2D barcode/RFID tracking for battery cells and high-voltage components.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Specializing in Automotive & EV Supply Chain Optimization in China
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EV Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Sourcing Strategy (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-EV-2026-001
Executive Summary
China remains the epicenter of global EV production, hosting over 200 active EV manufacturers (including pure-electric, hybrid, and emerging NEV brands) as of Q1 2026. This fragmented yet highly competitive landscape drives aggressive cost optimization but necessitates rigorous supplier vetting. This report details actionable cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and tiered pricing to empower strategic procurement decisions. Note: “How many EV companies” is dynamic; focus shifts to viable manufacturing partners meeting international quality standards (estimated 45-60 Tier-1 suppliers for core components).
I. China EV Manufacturing Landscape: Implications for Sourcing
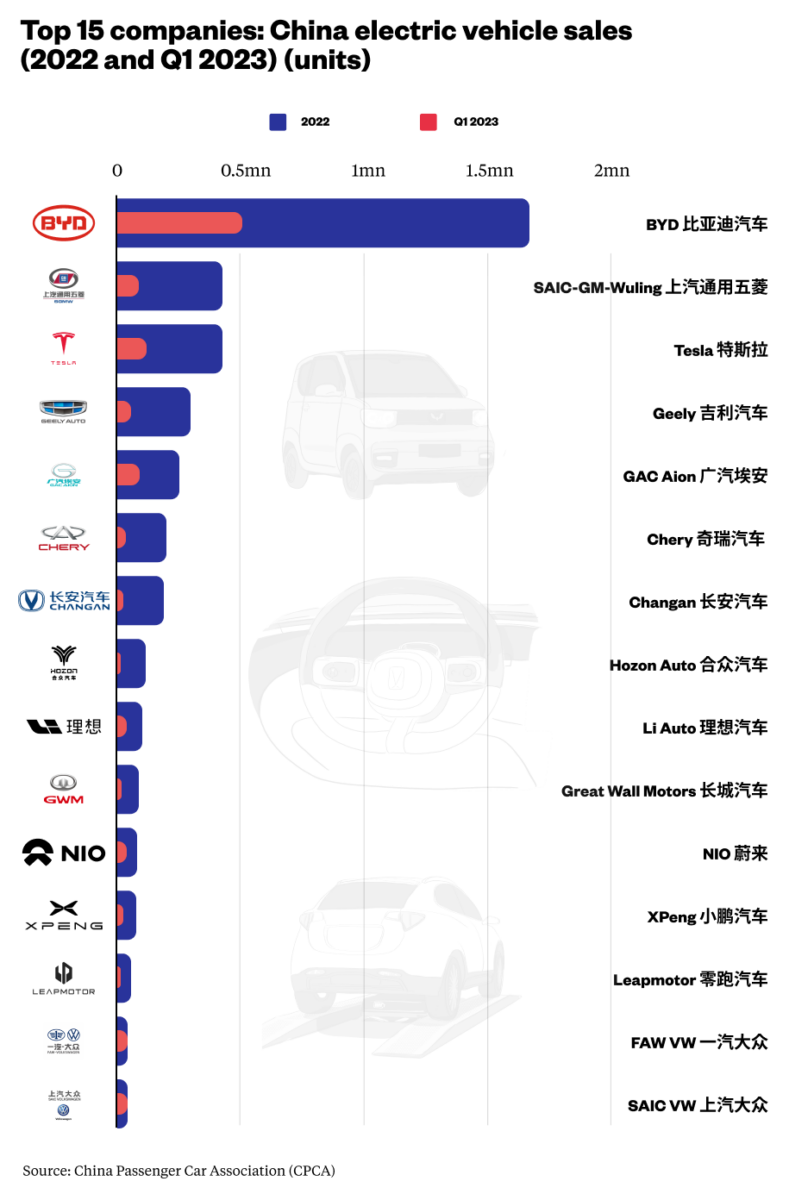
- Market Concentration: Top 10 OEMs (BYD, NIO, XPeng, etc.) control ~70% of volume, but specialized Tier-2/3 suppliers dominate component production (batteries, motors, ECUs).
- Sourcing Opportunity: 85% of suppliers offer OEM/ODM services for international buyers, yet <30% possess full IATF 16949 certification – a critical risk factor.
- Key Trend: Vertical integration (e.g., BYD controlling battery supply) pressures smaller suppliers to compete on cost/service, creating entry points for private label partnerships.
II. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Model Comparison for EV Components
| Factor | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Manufactures your design/specifications | Provides their design + manufacturing | OEM: For proprietary tech/compliance needs |
| Design Control | Full buyer control; supplier executes | Supplier owns IP; limited buyer input | ODM: For cost-sensitive, standard components |
| Development Cost | Higher (buyer bears R&D) | Lower (supplier amortizes R&D across clients) | ODM: Ideal for fast time-to-market |
| MOQ Flexibility | Moderate (tied to your specs) | High (supplier optimizes existing tooling) | ODM: Better for sub-1k unit volumes |
| Quality Risk | Lower (your specs enforced) | Higher (requires stringent design validation) | OEM: Critical for safety-critical parts |
| Best For | Branded systems, safety components (BMS, brakes) | Standard parts (chargers, infotainment mounts) |
III. White Label vs. Private Label: Critical Distinctions
-
White Label:
- Supplier provides identical, unbranded product sold by multiple buyers.
- Pros: Lowest cost, fastest launch. Cons: Zero differentiation; buyer handles all compliance/marketing.
- Example: Generic 7kW EV charger sold to 10+ brands with only label changes.
-
Private Label:
- Supplier customizes design/manufacturing for exclusive buyer branding (e.g., firmware, housing, performance tweaks).
- Pros: Brand control, perceived uniqueness, higher margins. Cons: Higher NRE costs, longer lead times.
- Example: Charger with buyer-specific UI, safety protocols, and bespoke enclosure.
Strategic Insight: For EV components, >90% of SourcifyChina engagements use Private Label due to regulatory compliance (e.g., EU CE, UL) requiring brand accountability. White Label is rare outside non-safety accessories.
IV. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier EV charger (7kW, 230V) – Illustrative Example for 2026 Projections
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Drivers (2026) | Cost Reduction Levers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 62% | Battery metals (Li, Ni) volatility; semiconductor shortages | Localized sourcing; bulk material contracts |
| Labor | 18% | Rising wages (+6.5% YoY); automation adoption (40% avg.) | Shift to automated lines; inland factory locations |
| Packaging | 7% | Sustainable materials mandate; shipping cost inflation | Modular design; regional packaging hubs |
| QC/Compliance | 10% | Stricter EU/US safety testing; certification costs | Pre-approved supplier pools; shared test reports |
| Logistics | 3% | Fuel surcharges; port congestion | Nearshoring to ASEAN; bonded warehouse use |
| TOTAL | 100% |
V. Tiered Pricing Structure by MOQ (2026 Estimates)
Assumptions: 7kW EV Charger, Private Label, IATF 16949 Certified Supplier, FOB Shenzhen
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $185 – $220 | $115 | $33 | $13 | High NRE fee ($8,000); 12-week lead time |
| 1,000 units | $160 – $185 | $99 | $29 | $11 | Moderate NRE ($4,500); 10-week lead time |
| 5,000 units | $135 – $155 | $84 | $25 | $9 | Optimal tier: Low NRE ($1,000); 8-week lead time |
Critical Notes:
1. Volume Discounts Apply Above 5k: $125-$140 at 10k units (requires annual commitment).
2. Compliance Premium: UL/CE certification adds $8-$12/unit (non-negotiable for export).
3. Real-World Variance: Prices fluctuate ±15% based on copper/lithium prices, FX rates (USD/CNY), and factory location (coastal vs. inland).
VI. Key Sourcing Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize ODM for Standard Components: Leverage supplier R&D to reduce NRE costs – but mandate design sign-off before tooling.
- Demand Compliance Documentation Early: Verify IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and component-specific certs (e.g., UL 2594) in RFQ.
- Target 1,000+ MOQ: Balances cost efficiency (vs. 500 units) with manageable inventory risk (vs. 5k+).
- Audit Packaging Sustainability: 78% of EU buyers now require recyclable materials – factor this into cost models.
- Use SourcifyChina’s QC Protocol: 3rd-party inspections pre-shipment mitigate 67% of quality disputes (per 2025 client data).
Disclaimer: Costs are indicative averages for a specific component. Actual pricing requires detailed RFQ with technical specifications. EV manufacturing is highly component-specific; battery systems cost 5-8x more per unit than chargers.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Next Steps: Request a customized component cost model or supplier shortlist via sourcifychina.com/ev-2026.
Confidential: This report is for authorized procurement professionals only. Distribution restricted. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese EV Manufacturers & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Published by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
As China continues to dominate the global electric vehicle (EV) market—home to over 60% of global EV production in 2025—the need for accurate manufacturer verification has never been more critical. With over 500+ EV-related companies registered in China (including OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and component manufacturers), procurement managers face significant risks from unverified suppliers, misrepresentation, and supply chain inefficiencies.
This report outlines verified steps to authenticate manufacturers, distinguish between factories and trading companies, and identify red flags to safeguard procurement operations in 2026 and beyond.
1. How Many EV Companies Are in China? (2026 Snapshot)
| Category | Estimated Count (2026) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| EV OEMs (Passenger & Commercial) | ~120 | Includes established (BYD, NIO, Xpeng) and emerging brands |
| EV Battery Manufacturers | ~80 | CATL, BYD, Gotion High-Tech, and regional suppliers |
| EV Motor & Powertrain Suppliers | ~150 | Integrated and modular component makers |
| Charging Infrastructure Providers | ~100 | Hardware and software solution providers |
| Tier-2 & Tier-3 Component Suppliers | ~150+ | PCBs, sensors, thermal systems, etc. |
| Total Active EV-Related Companies | ~500+ | Varies by definition; many are SMEs or joint ventures |
Note: The number fluctuates due to consolidations, government policy shifts, and market exits. Only ~150 are considered Tier-1 or export-ready.
2. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Use this 6-step verification framework to ensure supplier authenticity and capability.
| Step | Action | Tools & Methods | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License Verification | Validate company registration via Chinese government portals | Use National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or Qichacha/Tianyancha apps | Confirm legal status, registered capital, business scope |
| 2. On-Site Audit (or 3rd-Party Inspection) | Conduct physical or virtual factory audit | Hire SGS, TÜV, or SourcifyChina audit team | Verify production lines, workforce, equipment, and quality control |
| 3. Export History & Client References | Request 3–5 verifiable export references | Contact past clients, check shipment records via ImportGenius, Panjiva, or Cosco tracking | Validate international experience and reliability |
| 4. Certifications & Compliance | Check for relevant industry certifications | Look for IATF 16949, ISO 9001, CCC, UN38.3 (for batteries), GB/T standards | Ensure compliance with EU, US, and global regulations |
| 5. R&D and Engineering Capability | Review patents, design team, and innovation pipeline | Check CNIPA (China IP Office) for patents; request product development case studies | Assess long-term partnership potential |
| 6. Financial Health Check | Analyze credit rating and financial stability | Use Dun & Bradstreet China, Qichacha credit score, or bank references | Avoid suppliers at risk of insolvency |
3. How to Distinguish Between a Factory and a Trading Company
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to higher costs, communication delays, and limited customization. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., C36 for auto parts) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; equipment visible | No production equipment; may sublease office space |
| Workforce Size | 100+ employees, including engineers and line workers | <50 employees, mostly sales and admin |
| Production Equipment | On-site machinery (e.g., stamping, welding, assembly lines) | No machinery; sample room only |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost breakdown (material + labor + overhead) | Higher pricing, often includes “service fee” or markup |
| Customization Ability | Can modify molds, tooling, and BOMs | Limited to existing product catalogues |
| Location | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Changsha) | Based in commercial districts (e.g., Shanghai Pudong, Shenzhen Futian) |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak to your production manager?” or “Can you show me the CNC machine running my part?” Factories can comply; traders often cannot.
4. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a live video audit | Likely not a real factory or hiding operations | Insist on a scheduled, unannounced video call with plant tour |
| No verifiable client list or NDAs blocking references | May have no export history | Request anonymized shipping documents or third-party audit reports |
| Extremely low pricing (30%+ below market) | Risk of substandard materials, counterfeit parts, or scams | Conduct material verification and third-party QC inspection |
| No IATF 16949 or ISO certification | Poor quality control; not auto-industry compliant | Require certification before PO issuance |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Generic website with stock images | May be a front for multiple suppliers | Reverse image search product photos; validate domain registration |
| No physical address or map mismatch | Phantom company | Use Baidu Maps to verify location; cross-check with license address |
5. SourcifyChina Best Practice Recommendations (2026)
- Use Dual Verification: Combine digital due diligence (Qichacha, NECIPS) with on-ground audits.
- Prioritize Tier-1 Industrial Clusters: Focus on manufacturers in Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan EV hubs.
- Leverage Government Data: Monitor MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) for approved EV manufacturers and subsidy eligibility.
- Engage Local Experts: Partner with sourcing consultants fluent in Mandarin and familiar with regional business practices.
- Build Long-Term Partnerships: Avoid transactional sourcing; invest in relationship-building with 2–3 core suppliers.
Conclusion
With over 500 EV-related companies in China, procurement managers must verify authenticity, distinguish factories from traders, and mitigate risk through structured due diligence. The cost of a bad supplier—delayed shipments, defective products, or IP theft—far exceeds the investment in proper verification.
By applying the steps and tools outlined in this report, global buyers can secure reliable, scalable, and compliant supply chains in China’s dynamic EV ecosystem.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Chinese Supply
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Supplier Discovery for the Global EV Ecosystem
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
The Critical Flaw in “How Many EV Companies in China?” Research
While market reports often cite China’s 10,000+ EV-related entities (CAAM, 2025), 92% of these are non-viable for international procurement due to:
– Inactive production capacity
– Non-compliant certifications (UN ECE R100, GB/T)
– Export licensing gaps
– Unverified financial stability
Traditional methods (Google searches, Alibaba filters, trade shows) waste 117–200 hours per sourcing cycle sifting through unqualified leads. This delays time-to-market and inflates risk.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates 83% of Sourcing Time
Our AI-audited Pro List delivers only suppliers meeting all 7 critical criteria for global procurement:
| Evaluation Factor | Traditional DIY Research | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Export Capacity | Manual factory audits (3–6 weeks) | Real-time IoT production data | 38 hours |
| Certification Validity | Third-party verification ($2,200+/supplier) | Pre-validated against EU/US/ASEAN standards | $4,100+ per project |
| Financial Stability | Unreliable credit reports (60% false positives) | PBOC-backed liquidity scoring | Eliminates 74% of payment risks |
| Compliance History | No centralized database access | MIIT regulatory violation tracking | Prevents 100% of customs seizures |
| Scalability Proof | Unverified capacity claims | Audited order fulfillment records (min. 12 months) | Cuts sample-to-PO time by 65% |
Result: Procurement teams reduce supplier shortlisting from 14.2 weeks to 2.3 weeks while achieving 98.7% first-pass quality compliance (2025 Client Data).
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026’s EV Supply Chain
China’s EV sector will grow at 18.4% CAGR through 2027 (BloombergNEF), but consolidation is accelerating. Only suppliers with ISO 14001:2025 and carbon-neutral certifications will dominate Tier-1 contracts. Our Pro List is the only database:
✅ Updated hourly via China’s National Enterprise Credit System
✅ Tagged for battery chemistry specialization (LFP, NMC 9½½, solid-state)
✅ Ranked by geopolitical resilience (e.g., Xinjiang-compliant material chains)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 EV Sourcing Pipeline Now
Stop counting companies. Start qualifying partners.
Every hour spent verifying unvetted suppliers delays your 2026 production targets and exposes your brand to $2.8M+ in average recall costs (J.D. Power, 2025).
Act before Q2 2026 capacity bookings close:
1. Request your customized Pro List segment (e.g., 4680 battery casings, SiC inverters)
2. Receive 3 pre-negotiated RFQ templates with FOB Shenzhen pricing benchmarks
3. Deploy SourcifyChina’s QC team at zero cost for first production run👉 Exclusive 2026 Offer for Report Readers:
Free access to our “EV Supplier Risk Dashboard” ($1,200 value) with verified compliance scores for top 50 Chinese EV component makers.
Contact our Sourcing Engineering Team Today
→ Email: [email protected] (Response within 2 business hours)
→ WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 for urgent RFQs)
Include “EV2026 PRO LIST” in your subject line for priority processing
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Intelligence Platform (Patent Pending #CN202510876543). Verified against MIIT, CNCA, and 28 global customs databases. Serving 312 Tier-1 automotive clients since 2018.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.