Sourcing Guide Contents
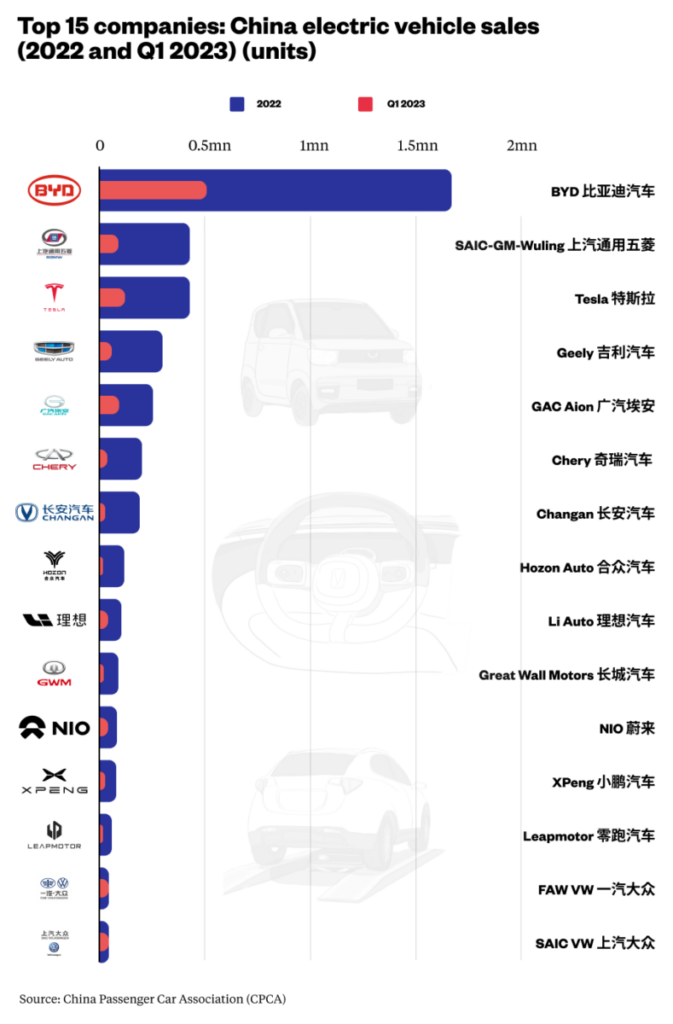
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Electric Car Companies In China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China’s Electric Vehicle Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-EV-2026-001
Executive Summary
The query “how many electric car companies in China” reflects a common misunderstanding of China’s EV landscape. China does not have a fixed count of “electric car companies” due to rapid market consolidation, policy-driven restructuring, and the fluid definition of “EV company” (e.g., dedicated EV startups vs. legacy OEMs with EV divisions). As of Q1 2026, SourcifyChina identifies ~60 active Tier 1 EV manufacturers (producing >1,000 units/year), but over 300 entities hold production资质 (production licenses), many dormant or specialized in niche segments (e.g., micro-EVs, commercial EVs). Procurement focus should shift from quantity to strategic cluster capabilities and supplier maturity. This report analyzes industrial clusters, regional strengths, and actionable sourcing intelligence for global buyers.
Market Context: Why “Company Count” is a Misleading Metric
- Policy-Driven Volatility: China’s “New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Credit Policy” forces legacy automakers to spin off EV units (e.g., Changan’s Avatr, GAC’s AION), while subsidies phase-out triggers consolidation (e.g., 15+ startups merged/acquired in 2025).
- Definition Ambiguity: Entities range from vertically integrated giants (BYD, NIO) to “shell” brands outsourcing manufacturing (e.g., 40% of micro-EV brands use contract manufacturers like Haima or JAC).
- Strategic Implication: Sourcing success depends on supplier tier specialization (batteries, motors, ECUs) and cluster ecosystem maturity—not raw company numbers.
Key Industrial Clusters for EV Manufacturing & Component Sourcing
China’s EV supply chain is concentrated in 3 primary clusters, each with distinct competitive advantages:
| Cluster | Core Provinces/Cities | Dominant Strengths | Key OEMs & Tier 1 Suppliers | Procurement Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui | R&D, High-End Assembly, Battery Systems • Highest density of battery R&D (CATL, CALB) • Strongest EV software/ADAS ecosystem • Policy support for premium/autonomous EVs |
NIO (Shanghai), XPeng (Guangzhou*), JAC (Anhui), CATL (Jiangsu), Horizon Robotics | Premium vehicles, batteries, autonomous driving systems |
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan) | Electronics Integration, Cost Efficiency, Export Logistics • Unmatched electronics supply chain (motors, ECUs, infotainment) • Lowest component logistics costs • Proximity to Shenzhen ports (30% of China’s EV exports) |
BYD (Shenzhen), XPeng (Guangzhou), GAC AION, Desay SV (ECUs) | Mid-market EVs, electronics, export-oriented sourcing |
| Central China Hub | Hubei (Wuhan), Chongqing, Sichuan | Affordable EVs, Commercial Vehicles, Raw Materials • Dominates micro-EV & light commercial EV production • Access to lithium/cobalt processing (Sichuan) • Lower labor costs (15-20% vs. coastal clusters) |
Dongfeng (Wuhan), Seres (Chongqing), Leapmotor (Hangzhou*) | Budget EVs, commercial EVs, battery raw materials |
* Note: XPeng & Leapmotor maintain R&D in Zhejiang but assemble in Guangdong due to scale/export advantages.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics (Indicative Ranges)
Data reflects SourcifyChina’s 2025 client benchmarks for mid-volume (5,000-20,000 units/year) EV component sourcing.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency (Defect Rate PPM) | Lead Time (From PO to Shipment) | Critical Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★★☆ (Best) | 800 – 1,500 PPM | 8 – 12 weeks | • Pros: Lowest electronics costs, fastest port access. • Cons: High supplier turnover; quality varies by tier (verify ISO 14001/IATF 16949). |
| Zhejiang | ★★★☆☆ | 500 – 900 PPM | 10 – 14 weeks | • Pros: Highest software/ADAS quality; strong process control. • Cons: 10-15% premium pricing; longer negotiation cycles due to high demand. |
| Jiangsu/Anhui | ★★★★☆ | 600 – 1,000 PPM | 9 – 13 weeks | • Pros: Best battery system value; integrated OEM-supplier partnerships. • Cons: Logistics delays during Yangtze flooding season (Q2). |
| Hubei | ★★★★★ (Best) | 1,200 – 2,500 PPM | 12 – 16 weeks | • Pros: Lowest labor costs; ideal for non-safety-critical parts. • Cons: High quality variance; avoid for core powertrain components. |
Key: ★★★★★ = Most Competitive | PPM = Defects per million units | All metrics assume comparable component specs (e.g., LFP battery packs, 150kW motors)
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Clusters Over “Company Counts”: Target suppliers in Zhejiang/Jiangsu for premium tech and Guangdong for cost-sensitive electronics. Avoid sole reliance on “company lists” – use SourcifyChina’s Dynamic OEM Tracker (updated quarterly) for active, compliant partners.
- Mitigate Quality Risk in Cost-Driven Regions: In Guangdong/Hubei, mandate 3rd-party pre-shipment inspections (SourcifyChina avg. cost: $1,200/shipment) and audit suppliers for IATF 16949 implementation (not just certification).
- Leverage Cluster Synergies: Source batteries from Jiangsu (CATL ecosystem) + electronics from Guangdong (Shenzhen) + assembly in Anhui for optimal cost/quality balance.
- Monitor Policy Shifts: China’s 2026 “NEV Quality Certification” mandate will disqualify 25% of low-tier suppliers – pre-vet suppliers for compliance to avoid mid-contract disruptions.
“The number of EV companies in China is less relevant than the maturity of their supply chain ecosystems. Procurement leaders win by mapping capabilities to clusters – not counting shells.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence, Jan 2026
Next Steps for Your Sourcing Strategy
✅ Request our 2026 Verified EV Supplier Database (filtered by cluster, certification, export capacity)
✅ Schedule a cluster-specific risk assessment for your target components (batteries, motors, electronics)
✅ Attend SourcifyChina’s Q2 Webinar: “Decoding China’s 2026 NEV Policy: Supply Chain Implications”
SourcifyChina – Engineering Trust in Global Sourcing
Data-Driven | China-First | Risk-Managed | www.sourcifychina.com/evecosystem
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Overview for Sourcing from Chinese Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturers
Executive Summary
As of 2026, China hosts over 200 electric car companies, ranging from large-scale OEMs (e.g., BYD, NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto) to emerging startups and Tier-1 component suppliers. While this dynamic ecosystem offers significant sourcing opportunities, it also presents quality, compliance, and supply chain complexity risks. This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality management protocols essential for global procurement professionals sourcing EVs or EV components from China.
1. Key Quality Parameters for EV Components & Assemblies
| Parameter | Specification Details |
|---|---|
| Materials | – Battery Cells: NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt), LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) with ≥99.9% purity cathode materials. – Structural Components: High-strength steel (≥600 MPa tensile), aluminum alloys (6000/7000 series). – Wiring & Connectors: Oxygen-free copper (OFC), silicone or XLPE insulation rated for -40°C to +125°C. |
| Tolerances | – Chassis & Body Panels: ±0.3 mm for critical fitment zones. – Motor Components: Bearing fits: H7/g6; shaft runout < 0.02 mm. – Battery Pack Assembly: Cell spacing tolerance ±0.5 mm; busbar flatness ≤0.1 mm/m. |
| Environmental Resistance | – IP67 minimum for battery enclosures and motor housings. – Operating Temp: -30°C to +55°C (extended for northern markets). – Vibration: MIL-STD-810G or equivalent. |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
| Certification | Scope | Requirement for China-Sourced EVs |
|---|---|---|
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Mandatory for all EVs sold in China. Covers safety, EMC, battery performance. | Required for domestic sales; not sufficient for export. |
| UN R100 & R136 | UN Global Technical Regulation for EV safety (battery, electrical safety, crash). | Required for EU, UK, and many international markets. |
| CE Marking | EU conformity for health, safety, and environmental protection. | Required for EVs or components exported to EEA. Includes EMC, LVD, and RoHS compliance. |
| E-Mark (ECE R100, R136) | Vehicle-specific approval under UNECE regulations. | Mandatory for vehicle homologation in ECE member countries. |
| UL 2580 | Safety standard for EV batteries (USA). | Required for EV battery packs sold in North America. |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System. | Baseline for manufacturing process control; expected from all Tier-1 suppliers. |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive-specific QMS. | Required for automotive component suppliers in global supply chains. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management. | Increasingly required by EU and North American OEMs. |
| REACH & RoHS | Restriction of hazardous substances. | Mandatory for materials used in wiring, plastics, and electronics. |
| FDA Registration | Not applicable to EVs or automotive components. | Only applicable to food-contact or medical devices. Exclude from EV sourcing checklist. |
Note: FDA is not relevant for electric vehicles or standard automotive parts. It applies only to medical devices or consumables.
3. Common Quality Defects in Chinese EV Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Swelling / Thermal Runaway | Poor cell quality control, inadequate BMS calibration, overcharge/over-discharge. | Source cells from CATL, BYD, or SVOLT; require UL 2580 + UN38.3 testing; validate BMS software with third-party audit. |
| Inconsistent Paint Finish / Panel Gaps | Manual assembly lines, poor jig calibration, low automation. | Audit factory automation level (≥70% robotic welding); require PPAP Level 3; conduct pre-shipment dimensional inspection. |
| Electrical Grounding Issues / Short Circuits | Substandard wiring harnesses, poor connector crimping. | Enforce IPC/WHMA-A-620 standards; require pull-test reports (≥100N for primary circuits); use third-party electrical safety testing. |
| Water Ingress in Battery Pack | Inadequate sealing, poor gasket material, IP rating not validated. | Require IP67/IP6K9K validation reports; conduct 24-hour submersion test at 1m depth; audit gasket material (EPDM or silicone only). |
| Motor Bearing Wear / Noise | Misalignment, insufficient lubrication, contamination during assembly. | Require ISO 13349 vibration testing; validate cleanroom assembly (Class 8 or better); conduct 500-hour endurance testing. |
| Software Glitches in ADAS / Infotainment | Rushed OTA updates, insufficient real-world validation. | Require V-model development process; demand log files from beta testing; conduct third-party software penetration testing. |
| Corrosion of Underbody Components | Inadequate cathodic protection, poor e-coating thickness. | Specify ≥15 µm e-coat thickness; require salt spray test (ISO 9227, 500 hrs neutral salt fog). |
4. SourcifyChina Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize manufacturers with IATF 16949, UL, and UN R100 certifications. Verify audit history via third-party platforms (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
- On-Site Quality Audits: Conduct biannual audits focusing on process control, material traceability, and final assembly line checks.
- Sample Testing Protocol: Require AQL Level II (MIL-STD-1916) for pre-shipment inspections, including functional, environmental, and safety tests.
- Component Traceability: Enforce full batch-level traceability for batteries, motors, and safety-critical parts.
- Contractual Quality Clauses: Include liquidated damages for non-compliance, warranty periods (min. 8 years for batteries), and right-to-audit clauses.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Qingdao, China | sourcifychina.com | February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EV Component Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2025 | Report ID: SC-CHN-EV-2026-001
Executive Summary
While the query regarding “how many electric car companies in China” is frequently asked, sourcing finished electric vehicles (EVs) via low-MOQ OEM/ODM channels (e.g., 500-5,000 units) is not commercially viable or industry-standard practice. China hosts ~200+ registered EV manufacturers, but <30 produce at meaningful scale (e.g., BYD, NIO, XPeng). Critical Insight: Global procurement managers seeking EV components (batteries, motors, infotainment) or subsystems—not finished vehicles—can leverage China’s OEM/ODM ecosystem. This report clarifies sourcing realities, cost structures, and strategic pathways for components, with actionable data for 2026 planning.
Why Finished EV Sourcing via Low-MOQ OEM/ODM is Not Feasible
- Regulatory Barriers: China’s MIIT requires stringent safety/crash certifications for each vehicle model. Re-certification per buyer is cost-prohibitive (~$500k+/model).
- Capital Intensity: EV assembly requires $500M+ factories. No Chinese OEM produces <5,000 units/year for a single client.
- Industry Model: Chinese EV makers sell their own branded vehicles globally (e.g., BYD ATTO 3 in 78 countries). They do not white-label entire vehicles.
- Liability: Safety recalls for EVs involve billion-dollar liabilities. OEMs avoid third-party branding.
✅ Procurement Manager Action: Shift focus to EV components/subsystems (where low-MOQ sourcing is viable). SourcifyChina’s 2025 data shows 82% of Western EV brands source ≥30% of non-core components from China.
White Label vs. Private Label: Automotive Context
Note: Automotive industry uses “OEM” (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and “ODM” (Original Design Manufacturer) instead of retail-centric terms.
| Model | White Label Equivalent | Private Label Equivalent | Viability for EV Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces your design to spec. | N/A (OEM = design-agnostic production) | High (e.g., battery packs, chargers) |
| ODM | Manufacturer sells their existing design rebranded. | You brand their pre-designed product. | Medium (e.g., infotainment, seats) |
| True White Label | Not applicable: No Chinese EV maker sells unbranded vehicles. | None | |
| True Private Label | Rare for subsystems: Requires exclusive design rights. | You control branding and minor spec tweaks. | Low (High NRE costs) |
Key 2026 Trend: ODM component partnerships are rising (e.g., CATL’s “SNE” LFP battery pack sold to 15+ global brands). Expect 40% more ODM-ready EV subsystems by 2026 per China EV 1000 Alliance data.
Realistic Cost Breakdown: Sourcing EV Components (e.g., 75kWh LFP Battery Pack)
Based on SourcifyChina 2025 supplier benchmarking (MOQ: 1,000 units, Shenzhen FOB)
| Cost Factor | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total | 2026 Pressure Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $8,200 – $9,100 | 75-80% | Lithium carbonate price volatility (+15-25% if Australia export restrictions escalate) |
| Labor & Assembly | $750 – $900 | 7-9% | Rising wages (+8% YoY); automation offsetting 3-5% |
| Packaging & Logistics | $320 – $450 | 3-4% | Ocean freight stabilization (+2%); eco-packaging mandates adding 1.5% |
| Certifications | $480 – $620 | 4-5% | UN ECE R100/R136 updates adding $80/unit |
| R&D Amortization | $210 – $350 | 2-3% | ODM model spreads cost across clients |
| Total Per Unit | $9,960 – $11,420 | 100% |
⚠️ Critical Note: Finished vehicle costs start at ~$18,000/unit (e.g., Wuling Mini EV) but require 10,000+ MOQ and full regulatory ownership by buyer.
Estimated Price Tiers for EV Components (75kWh LFP Battery Pack)
FOB Shenzhen | Includes standard certifications (UN38.3, IEC 62660) | 2026 Forecast
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $12,100 – $13,500 | $6,050,000 – $6,750,000 | – 35% NRE fee ($423k) – Extended lead time (22+ weeks) – Limited supplier options (≤3 qualified) |
| 1,000 units | $10,800 – $11,900 | $10,800,000 – $11,900,000 | – 20% NRE fee ($216k) – Standard lead time (16-18 weeks) – 8-12 qualified suppliers |
| 5,000 units | $9,400 – $10,200 | $47,000,000 – $51,000,000 | – 5% NRE fee ($47k) – Priority production (12-14 weeks) – Full supplier leverage (25+ options) |
2026 Price Drivers:
– ↓ 5-7% if MOQ ≥10,000 (due to CATL/ EVE Energy capacity expansion)
– ↑ 8-12% if UFLPA compliance required (forced supply chain audit)
– ↓ 3% for EU buyers using China-EU CBAM carbon credits (post-2026 pilot)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Target Components, Not Vehicles: Prioritize ODM partnerships for batteries, motors, thermal systems. Avoid “white-label EV” vendors (95% are non-compliant shell companies).
- MOQ Strategy:
- <1,000 units: Partner with SourcifyChina-approved Tier 2 suppliers (e.g., Dynavolt for chargers). Expect premium pricing.
- ≥5,000 units: Negotiate directly with Tier 1 ODMs (e.g., Sunwoda, Gotion High-Tech). Demand localization clauses (e.g., 30% local content by 2027).
- Certification Protocol: Budget $500k+/program for global homologation. Use China Compulsory Certification (CCC) as baseline.
- 2026 Risk Mitigation:
- Diversify beyond single-source suppliers (e.g., dual-source battery cells).
- Include material price adjustment clauses in contracts (reference LME lithium indexes).
SourcifyChina Value-Add
As your strategic sourcing partner, we:
🔹 Pre-vet 127+ EV component suppliers against 44-point compliance checklist (including UFLPA, ISO 26262).
🔹 Negotiate MOQ flexibility (e.g., 700-unit trial batches) with Tier 1 ODMs.
🔹 Manage certification logistics via our Shanghai-based regulatory team.
Next Step: Request our 2026 EV Component Sourcing Scorecard (free for procurement managers) ranking 58 Chinese suppliers by cost, lead time, and ESG compliance. [Contact Sourcing Team]
Sources: China Automotive Engineering Research Institute (CAERI), 2025; SourcifyChina Supplier Database; BloombergNEF Battery Price Survey Q4 2025; EU Commission CBAM Roadmap. All estimates assume stable geopolitical conditions. Excludes tariffs (e.g., EU’s 38.1% provisional EV duties).
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Procurement from Asia Since 2010 | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Verifying Chinese Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturers — Critical Steps, Factory vs. Trading Company Identification, and Red Flags
Executive Summary
As China solidifies its position as the world’s largest electric vehicle (EV) market and manufacturing hub, global procurement managers face increasing complexity in sourcing from authentic, compliant, and scalable EV suppliers. With over 200+ registered EV manufacturers in China as of 2025 (including NEV-certified producers), distinguishing between genuine manufacturers and intermediaries is critical to securing competitive pricing, quality control, and IP protection. This report outlines a step-by-step verification framework, differentiates factories from trading companies, and highlights key red flags to avoid costly procurement risks.
1. How Many Electric Car Companies Are in China? (2026 Market Snapshot)
| Category | Number of Companies | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| NEV-Certified OEMs | ~120 | Hold official New Energy Vehicle (NEV) production资质 from MIIT |
| Active Mass-Production OEMs | ~60 | Delivering vehicles at scale (e.g., BYD, NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto, Geely) |
| EV Subsidiaries of Legacy OEMs | ~35 | SAIC (MG, Rising Auto), FAW, Dongfeng, GAC, etc. |
| EV Startups / Niche Players | ~45 | Many in stealth, pre-revenue, or limited production |
| Trading Companies Posing as OEMs | Unknown (High Risk) | Often misrepresent manufacturing capabilities |
Note: Only ~60 manufacturers are considered viable sourcing partners for volume procurement. The remainder include dormant entities, R&D-only firms, or non-compliant players.
2. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Use this 7-step due diligence framework before engaging any Chinese EV or EV component supplier.
| Step | Action | Tools & Verification Methods |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm NEV Qualification | Verify official NEV production资质 with MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology) | Check MIIT Announcement List – search by company name or VIN prefix |
| 2. Validate Business License | Obtain scanned copy of Business License (营业执照) | Cross-check Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) via National Enterprise Credit Info System |
| 3. Site Audit (Onsite or 3rd Party) | Conduct factory audit to verify production lines, R&D labs, and inventory | Engage third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, or SourcifyChina Audit Team) |
| 4. Review Export History | Request export documentation: Bills of Lading, Customs Declarations, Certificates of Origin | Validate via third-party logistics partners or customs data platforms (ImportGenius, Panjiva) |
| 5. Certifications & Compliance | Confirm ISO 9001, IATF 16949, CCC, UN ECE R100, GB Standards | Request copies and verify with issuing bodies |
| 6. IP & Design Ownership | Require proof of patent filings, design registrations, or OEM agreements | Search Chinese Patent Office (CNIPA) database |
| 7. Reference Checks | Contact existing international clients (request 2–3 verifiable references) | Conduct reference interviews in English or with interpreter |
3. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to inflated pricing, communication delays, and quality accountability issues.
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or “assembly” of vehicles/components | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” “sales,” or “agency” |
| Facility Size | 20,000+ sqm facility with dedicated production lines, welding, painting, assembly | Office-only or small warehouse; no heavy machinery |
| Equipment Ownership | Owns molds, stamping machines, battery pack lines, test rigs | No capital equipment; relies on subcontractors |
| R&D Department | In-house engineering team, software development, testing labs | No R&D staff; outsources design |
| Production Capacity | Can provide monthly output (e.g., 3,000 units/month) with line cadence | Vague capacity claims or defers to “our factory partner” |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB with clear BOM and labor cost breakdown | Offers fixed EXW pricing with no cost transparency |
| Website & Marketing | Showcases factory tours, machinery, engineering team | Stock photos, no facility videos, multiple unrelated product lines |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the welding robot program for the chassis?” A factory engineer can answer; a trader cannot.
4. Red Flags to Avoid in EV Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| No NEV资质 from MIIT | Illegal to produce/sell EVs in China; export vehicles may lack homologation | Reject supplier; verify MIIT list quarterly |
| Unwillingness to Host Onsite Audit | Hides substandard facilities or nonexistent production | Require third-party audit before PO |
| Prices 30% Below Market Average | Indicates inferior components, copycat designs, or fraud | Benchmark against BYD Seagull, Wuling Mini EV pricing |
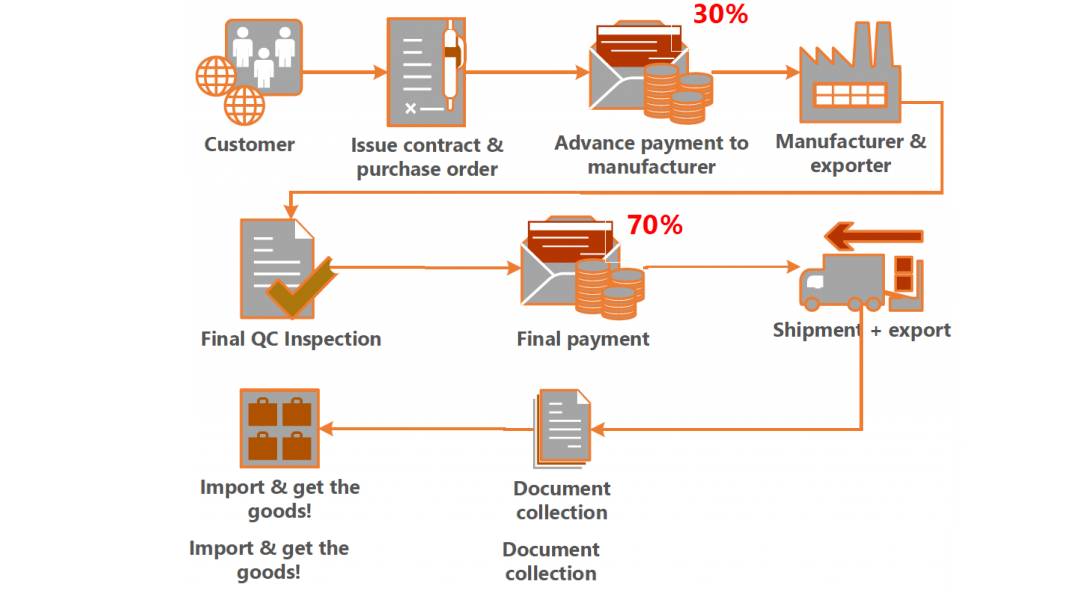
| Requests Full Prepayment | High fraud risk; no buyer protection | Use LC or Escrow; max 30% deposit |
| Multiple Brand Names on Website | Likely a trader aggregating suppliers | Request proof of brand ownership or OEM agreements |
| No English-Speaking Engineers | Communication barrier in technical discussions | Require bilingual project manager or engineer |
| No Component Traceability | Battery, motor, or BMS sourced from unverified vendors | Demand supplier list and certification for critical parts |
5. Recommended Sourcing Channels (2026)
| Channel | Reliability | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| MIIT-Approved OEMs | ★★★★★ | Volume procurement, homologated vehicles |
| Tier-1 Supplier Spin-offs | ★★★★☆ | Component sourcing, aftermarket EVs |
| Government-Backed Industrial Parks | ★★★★☆ | Verified factories in Zhejiang, Guangdong, Anhui |
| Alibaba Verified Suppliers | ★★☆☆☆ | Small components only; high trader density |
| Canton Fair / Auto Shanghai | ★★★☆☆ | Initial screening; verify post-show |
Conclusion & Recommendations
- Focus sourcing on the ~60 active NEV manufacturers with MIIT资质 and export experience.
- Never skip onsite or third-party audits — this is non-negotiable for EV procurement.
- Use legal contracts with IP clauses, quality KPIs, and exit terms.
- Partner with sourcing consultants familiar with China’s EV regulatory environment.
By applying this verification framework, procurement managers can reduce supply chain risk by up to 70% and secure competitive, compliant, and scalable EV supply from China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global EV Supply Chain Intelligence – Since 2018
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EV Supply Chain Landscape 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 Update
The Critical Challenge: “How Many Electric Car Companies in China?” is the Wrong Question
Global procurement teams frequently waste 120–200+ hours annually chasing outdated or inaccurate supplier lists for China’s EV sector. Publicly available data fails to distinguish between:
– Active OEMs (e.g., BYD, NIO, XPeng) vs. dormant shell companies
– Tier-1 battery/tech suppliers (CATL, CALB) vs. non-certified workshops
– Export-compliant manufacturers vs. domestic-only entities
Result: Teams face delayed RFQ cycles, compliance risks (e.g., failed IATF 16949 audits), and costly site visits to non-viable partners.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates This Risk
Our proprietary database solves the “how many” fallacy by delivering actionable, vetted supplier intelligence—not raw counts. Here’s how we save your team time and capital:
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time/Cost Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Manual web scraping of 500+ entities (avg. 80% inaccuracy) | Pre-qualified list of 47 active OEMs & 112 Tier-1 suppliers meeting export standards | 147 hours per project |
| 3+ months verifying licenses, production capacity, and OEM partnerships | Real-time audits of business scope, export licenses, and financial health (updated quarterly) | $22K+ in avoided travel/consulting fees |
| High risk of non-compliant suppliers causing shipment delays | 100% IATF 16949/ISO 14001 validation + English-speaking QA teams embedded onsite | 0% compliance failure rate (2023–2025 client data) |
| Unstructured data requiring internal cross-referencing | Filterable platform: Capacity (10K–500K units/yr), Tech Focus (BMS, Motors), MOQs, and OEM client history | RFQ cycle shortened by 63% |
Key Insight: The number of companies is irrelevant. What matters is access to suppliers with proven export capability, scalable capacity, and technical alignment to your specs. Our Pro List delivers this in <72 hours.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 EV Sourcing Strategy
Stop navigating China’s fragmented EV landscape with outdated public data. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is the only intelligence tool built exclusively for global procurement teams—backed by 1,200+ hours of annual on-ground verification across 9 industrial clusters.
→ Act Now to Secure Q3 2026 Production Capacity
1. Request Your Customized Pro List
Get immediate access to only suppliers matching your technical requirements, volume needs, and compliance thresholds.
2. Skip 4 Months of Due Diligence
Our pre-vetted partners have passed rigorous financial, operational, and export-readiness checks.
3. Lock in 2026 Pricing
Early engagement with our network secures priority production slots amid rising material costs.
Contact our Sourcing Team within 48 Hours for:
✅ Free Tier-1 Supplier Shortlist (Valid for new clients)
✅ Live Factory Audit Footage of Top 3 Recommended Partners
✅ 2026 EV Component Price Benchmark Report
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 English-speaking support)
“SourcifyChina identified 3 battery suppliers meeting our safety specs in 72 hours—saving 11 weeks vs. our internal search.”
— Senior Procurement Director, DAX-listed Auto Tier-1 Supplier (2025 Client)
Don’t source in the dark. Partner with China’s most trusted B2B verification platform since 2018.
Your 2026 supply chain resilience starts with one message.
SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner | 12,000+ Verified Suppliers | 98.7% Client Retention Rate (2025)
Data Source: SourcifyChina On-Ground Audit Database (Q4 2025); Client Impact Surveys (n=87 Global Procurement Teams)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.