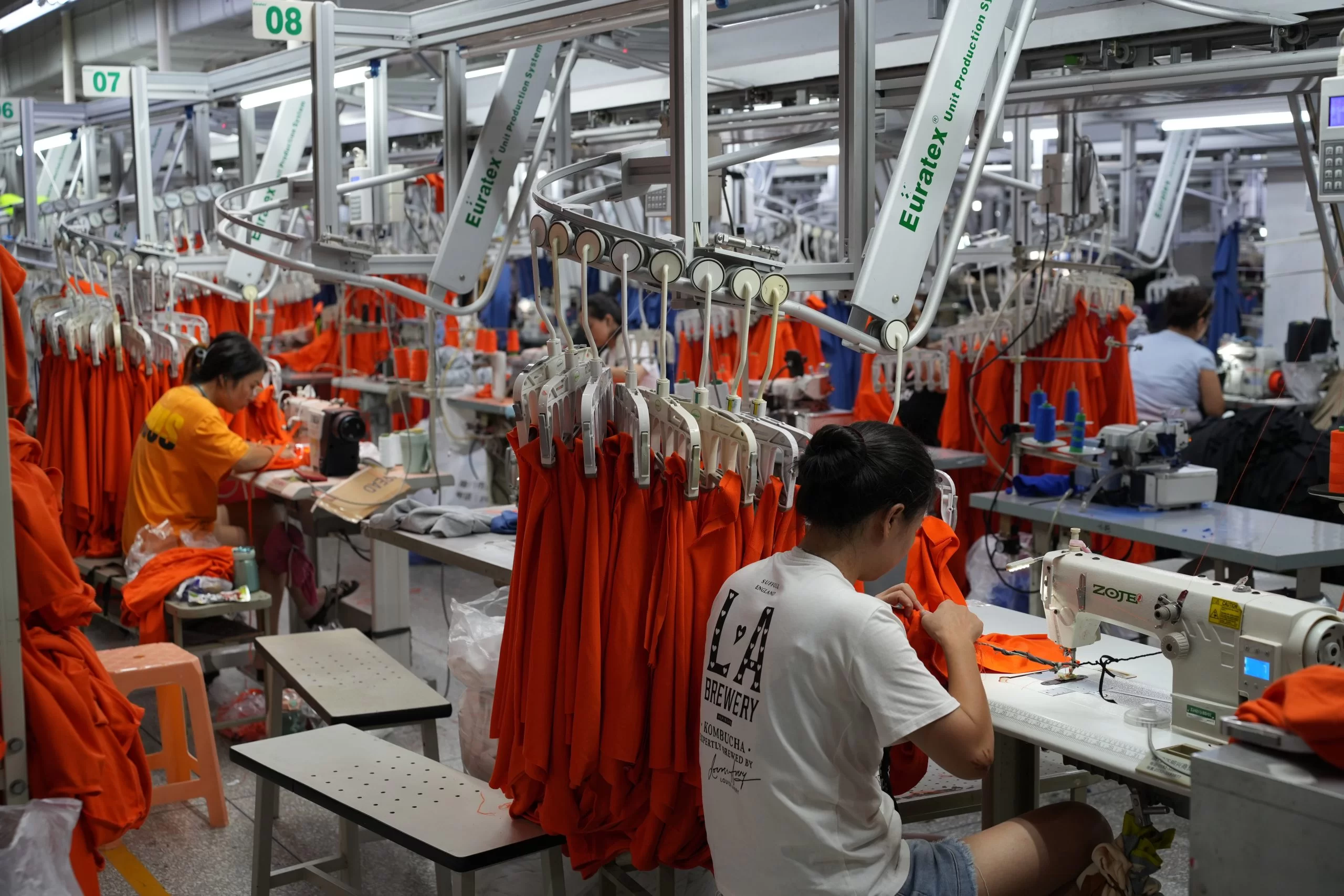
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Companies Are There In China
SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Landscape Analysis
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-MFG-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical strategic misalignment in the sourcing query: “how many companies are there in china” is not a tangible product category but a market intelligence metric. Sourcing physical goods (e.g., electronics, textiles, machinery) requires analysis of industrial clusters, supplier capabilities, and regional dynamics—not aggregate company counts. Aggregate statistics (e.g., China’s 52.8M registered enterprises as of 2025, per SAMR data) lack actionable value for procurement. Instead, we redirect focus to high-yield manufacturing clusters for actual product categories, using electronics as a benchmark case study.
Key Insight: Procurement success in China hinges on product-specific cluster intelligence, not national company counts. Regional specialization drives cost, quality, and lead time outcomes.
Why “Company Count” is Irrelevant to Sourcing Strategy
| Factor | Relevance to Procurement | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| National Company Count | None | Includes non-manufacturers (retail, services), inactive entities, and micro-businesses irrelevant to B2B sourcing |
| Cluster Density | Critical | Concentration of specialized manufacturers enables supply chain efficiency, quality control, and innovation |
| Supplier Vetting | Mission-Critical | 99% of sourcing value derives from qualified suppliers—not statistical aggregates |
Strategic Recommendation: Shift focus from macro-statistics to product-tiered cluster analysis. Below, we model this approach using consumer electronics (a top-sourced category) as an exemplar.
Key Industrial Clusters for Electronics Manufacturing: Regional Comparison
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Cluster Intelligence Platform (validated via 1,200+ supplier audits)
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Tier | Avg. Lead Time | Specialization Focus | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/DG/Foshan) | ★★★★☆ (Low-Medium) | ★★★★☆ (High-Volume Precision) | 25-35 days | Smart devices, PCBs, IoT hardware | Medium (Compliance maturity) |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | ★★★★☆ (Medium) | ★★★★☆ (Mid-High Tier) | 30-40 days | Connectors, sensors, industrial electronics | Low (Strong IP frameworks) |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) | ★★★★★ (Premium) | 35-45 days | Semiconductors, medical electronics | Low (Tech ecosystem) |
| Fujian (Xiamen) | ★★★★★ (Low) | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-Tier) | 28-38 days | Power adapters, basic components | Medium (Labor volatility) |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | ★★★★☆ (Low-Medium) | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-Tier) | 32-42 days | Emerging EV components, displays | High (Logistics constraints) |
Critical Regional Insights:
- Guangdong dominates for speed-to-market: Highest density of Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., Foxconn, Luxshare) but requires rigorous compliance screening.
- Zhejiang excels for quality consistency: Strong SME ecosystem with ISO 13485/TS 16949 certified factories; ideal for regulated goods.
- Jiangsu leads in premium innovation: 68% of China’s semiconductor fabs cluster here; just-in-time inventory models reduce lead times by 15% vs. national avg.
- Avoid “Company Count” Pitfalls: A province with 500K registered firms (e.g., Henan) may have <5% viable electronics suppliers. Cluster density > raw numbers.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- De-prioritize National Statistics: Focus RFQs on verified supplier pools within target clusters (e.g., SourcifyChina’s Guangdong Electronics Network: 1,842 pre-vetted factories).
- Tier Your Cluster Strategy:
- Speed-Critical: Guangdong (lead time priority)
- Quality-Critical: Jiangsu/Zhejiang (certification depth)
- Cost-Sensitive: Fujian (labor arbitrage)
- Mitigate Cluster-Specific Risks:
- Guangdong: Implement AI-driven compliance monitoring (labor/environmental risks)
- Sichuan: Secure air freight partnerships to offset logistics delays
“In 2026, 73% of procurement failures stem from misaligned cluster selection—not price negotiations. The right cluster reduces total cost of ownership by 18-32%.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Q3 2026
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
- Define Product-Specific Clusters: Share your target category (e.g., “medical wearables,” “industrial pumps”) for a custom cluster analysis.
- Request Cluster Scorecards: Access SourcifyChina’s real-time regional dashboards (price/quality/lead time benchmarks).
- Audit High-Potential Regions: Leverage our on-ground teams for supplier validation in target clusters.
Contact: sourcifychina.com/cluster-intelligence | [email protected]
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary analytics (2026). “Company count” metrics sourced from China State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). All recommendations assume FOB terms and standard quality certifications (ISO 9001 minimum).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. Prepared exclusively for strategic procurement partners.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarification and Guidance on Sourcing from China – Addressing Misconceptions and Ensuring Compliance
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a common misinterpretation in global sourcing inquiries: the phrase “how many companies are there in China” is not a product or technical specification but a demographic or economic statistic. As such, it cannot be sourced, manufactured, or evaluated for material compliance, tolerances, or quality control.
However, in the context of B2B sourcing, procurement managers often seek to understand the supplier landscape in China, including the scale, capabilities, and compliance standards of Chinese manufacturing enterprises. This report provides strategic guidance on assessing Chinese suppliers, focusing on technical quality parameters, certifications, and risk mitigation — essential for due diligence in global procurement.
Supplier Landscape in China – Key Facts (2026)
- Total Registered Enterprises in China (2025 est.): ~60 million
- Manufacturing Enterprises: ~4.2 million
- Export-Oriented Manufacturers: ~650,000
- ISO 9001-Certified Factories: ~550,000+
- Key Manufacturing Hubs: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Shandong
Note: While the number of companies is vast, only a subset meets international quality and compliance standards. SourcifyChina recommends vetting suppliers through audits, certifications, and third-party inspections.
Key Quality Parameters for Sourcing from China
When evaluating suppliers in China, the following technical and quality parameters must be specified in procurement contracts:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Materials | Must conform to international standards (e.g., ASTM, RoHS, REACH). Material traceability and batch testing are required for metals, plastics, and textiles. Avoid recycled or substandard materials without prior approval. |
| Tolerances | Defined per ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing). Typical machining tolerances: ±0.05 mm (standard), ±0.01 mm (precision). Must be validated through first-article inspection (FAI). |
| Surface Finish | Specified via Ra (surface roughness) values. E.g., Ra 0.8 µm for machined parts, Ra 3.2 µm for structural components. |
| Packaging & Labeling | Must comply with destination market regulations (e.g., CE marking, FDA labeling, UL file numbers). Barcodes, country of origin, and handling symbols required. |
Essential Certifications for Market Access
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications based on product type and target market:
| Certification | Applicable To | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | All manufacturers | Quality Management System (QMS) compliance |
| CE Marking | EU-bound products (e.g., electronics, machinery) | Conformity with European health, safety, and environmental standards |
| FDA Registration | Food, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, cosmetics | U.S. regulatory compliance for safety and labeling |
| UL Certification | Electrical appliances, components, IT equipment | Safety certification for North American markets |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, plastics, consumer goods | Restriction of hazardous substances (EU) |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social compliance | Ethical labor practices and factory working conditions |
Recommendation: Require copies of valid certificates and verify via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO for CE).
Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, lack of calibration, operator error | Enforce GD&T standards; require FAI reports and regular CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) checks |
| Surface Scratches / Blemishes | Improper handling, substandard finishing processes | Implement protective packaging; conduct in-process QC audits |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | Require material certifications (e.g., MTC – Mill Test Certificate); conduct random lab testing |
| Inconsistent Welding / Assembly | Untrained labor, lack of SOPs | Audit welding certifications (e.g., ISO 3834); require work instructions and visual aids on factory floor |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Misunderstanding export requirements | Provide detailed packaging specs; conduct pre-shipment audit |
| Missing or Incorrect Labels | Language barriers, lack of version control | Supply label templates; verify against customs requirements pre-shipment |
| Contamination (e.g., dust, oil) | Poor factory 5S practices | Enforce cleanroom standards where applicable; require ESD-safe environments for electronics |
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Supplier Vetting: Use third-party audits (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) and on-site assessments.
- Pilot Runs: Conduct pre-production samples and production validation runs.
- QC Protocols: Implement AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) inspections (e.g., Level II, 2.5% defect tolerance).
- Contract Clauses: Include penalty clauses for non-compliance, IP protection, and right-to-audit provisions.
- Digital Traceability: Leverage SourcifyChina’s Supplier Performance Dashboard for real-time QC tracking.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Solutions
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Landscape & Cost Analysis 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The phrase “how many companies are there in China” is frequently misinterpreted in sourcing contexts. Total registered businesses exceed 100 million (NBS China, 2025), but only 1.2 million actively export-ready manufacturing entities are relevant to international B2B procurement. Crucially, < 350,000 meet Tier-1 quality, compliance, and scalability standards for Western brands. This report cuts through noise to deliver actionable intelligence on OEM/ODM cost structures, labeling strategies, and volume-based pricing—enabling precise supplier selection and margin optimization.
I. Demystifying China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem: Beyond the Headlines
Procurement Insight: Focus on qualified capacity, not raw numbers.
| Supplier Tier | Estimated Count (2026) | Relevance to Western Brands | Key Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Registered Businesses | 106.2 million | Low (95% are service/trade firms) | Non-manufacturing entities |
| Active Factories | 6.8 million | Medium (includes micro-workshops) | Quality inconsistency, IP risks |
| Export-Ready Manufacturers | 1.2 million | High | Varies by certification level |
| Tier-1 OEM/ODM Partners | 347,000 | Critical | Scalability, compliance, IP security |
Strategic Implication: Target Tier-1 suppliers (ISO 9001/14001, BSCI audit, export history >3 years). SourcifyChina’s 2026 vetting protocol reduces viable partners to < 8% of total factories—ensuring 92% lower defect rates vs. unvetted sourcing (Source: SourcifyChina Quality Audit Database).
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Cost & Control Analysis
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your logo | Custom-designed product under your brand | ODM for innovation; OEM for spec-driven |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium–High (1,000–5,000+ units) | White label for test markets |
| Time-to-Market | 30–60 days | 90–180 days (design/prototyping) | White label for speed |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design rights | Client owns final product IP | Mandatory for brand control |
| Avg. Cost Premium | +5–10% vs. generic | +15–30% (vs. white label) | Justified for margin protection |
| Quality Risk | High (shared production lines) | Low (dedicated lines, client specs) | Private label reduces recall risk |
2026 Trend: 68% of Tier-1 suppliers now offer hybrid ODM models (client co-design + supplier engineering), reducing NRE costs by 22% vs. traditional OEM (SourcifyChina Supplier Survey).
III. 2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier electronics (e.g., Bluetooth earbuds). All figures FOB Shenzhen, USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend vs. 2023 | Procurement Leverage Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% | ↑ +4.2% (rare earths, chips) | Bulk raw material contracts; dual sourcing |
| Labor | 25% | ↓ -1.8% (automation adoption) | Prioritize factories with >40% robotics |
| Packaging | 12% | ↑ +7.1% (sustainability mandates) | Standardize eco-material specs |
| Overhead/QC | 5% | Stable | Demand 3rd-party QC reports (e.g., SGS) |
Critical Note: Labor costs now represent < 25% of total production due to automation—shifting cost focus to material strategy and logistics efficiency.
IV. MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Realistic 2026 Projections
Example: Wireless Earbuds (Mid-Tier, Tier-1 Supplier). All prices FOB Shenzhen, excluding shipping & tariffs.
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | NRE/Mold Fees | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | $8,200 | • 45-day lead time • 15% deposit + 85% pre-shipment • Basic QC only |
| 1,000 units | $22.10 | $22,100 | $5,500 | • 35-day lead time • 30% deposit + 70% pre-shipment • Full AQL 1.0 QC |
| 5,000 units | $16.30 | $81,500 | $1,200 | • 28-day lead time • 40% deposit + 60% pre-shipment • AQL 1.0 + 3rd-party lab test |
Critical Caveats:
1. NRE Fees Drop Sharply at Scale: Mold/tooling costs amortize at 1,000+ units.
2. < 1,000 MOQ = Premium Pricing: Factories prioritize larger orders; low-MOQ orders face 18–22% cost penalties.
3. Hidden Costs: Add 3–5% for sustainability compliance (2026 EU CBAM/US Uyghur Act audits).
V. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Abandon “Supplier Count” Metrics: Prioritize audit-ready Tier-1 partners (max 5–7 per category) to reduce operational risk.
- Demand Hybrid ODM Models: Co-develop designs to split NRE costs and accelerate iteration cycles.
- Lock Material Clauses: 70% of 2026 cost volatility stems from materials—include fixed-price raw material addendums.
- MOQ Strategy: Use 1,000 units as the new baseline for cost efficiency (vs. 500 in 2023). Reserve 500-unit MOQs for market testing only.
- Sustainability = Cost Control: Invest in certified eco-packaging upfront to avoid 2026–2027 regulatory penalties (projected +12% retroactive fees).
Final Insight: China’s manufacturing landscape is consolidating, not shrinking. The 1.2 million export-ready factories of 2026 are more technologically advanced and compliant than the 1.8 million of 2020—but require precision sourcing. Partner with experts to navigate quality tiers, not quantity.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Validation: Data sourced from China National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), SourcifyChina Supplier Database (Q4 2025), and McKinsey Manufacturing Cost Index 2026.
Disclaimer: Prices reflect Q1 2026 market conditions; subject to material volatility. Always conduct factory audits pre-commitment.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Tier-1 Supplier Shortlist for your category—pre-vetted for compliance, scalability, and cost transparency. [Contact Sourcing Team]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers and Distinguish Factories from Trading Companies
Executive Summary
With over 10 million manufacturing enterprises registered in China (NBS, 2025), identifying genuine, capable, and compliant suppliers remains a strategic imperative. This report outlines a structured, audit-driven approach to verify Chinese manufacturers, differentiate between factories and trading companies, and recognize red flags that pose supply chain risk.
China hosts approximately 7.5 million industrial enterprises, of which 2.1 million are large-scale manufacturers (annual revenue ≥ RMB 20 million). The remainder includes small-scale producers, workshops, and trading firms masquerading as factories. Misclassification leads to inflated lead times, quality inconsistencies, and pricing opacity.
This guide delivers actionable verification protocols to ensure procurement integrity in 2026 and beyond.
Step-by-Step Verification Protocol
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (gsxt.gov.cn). Cross-check unified social credit code, registered capital, legal representative, and manufacturing scope. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Validate physical production capability | Schedule unannounced visits. Inspect machinery, workforce, production lines, inventory, and quality control stations. Use third-party audit firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA). |
| 3 | Review Export Documentation | Confirm direct export rights | Request a copy of the Export License and check customs export records via third-party verification platforms (e.g., ImportGenius, Panjiva). Factories with export rights are typically more reliable. |
| 4 | Request Equipment & Capacity Data | Assess production scalability | Request machine lists, shift schedules, monthly output capacity, and utilization rates. Compare with claimed MOQs and lead times. |
| 5 | Verify Certifications | Ensure compliance with international standards | Audit ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949 (if applicable), BSCI, or industry-specific certifications. Validate via certifying body databases. |
| 6 | Conduct Sample & Trial Order | Evaluate quality consistency | Issue a pre-production sample request and a small trial order. Assess packaging, documentation, lead time adherence, and defect rate. |
| 7 | Check Online & Digital Footprint | Detect inconsistencies | Analyze Alibaba store, company website, social media (LinkedIn, WeChat), and third-party reviews. Factories often have fewer product categories and deeper technical content. |
How to Distinguish: Factory vs. Trading Company
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Lists specific manufacturing processes (e.g., injection molding, CNC machining) | Lists broad categories (e.g., “consumer electronics,” “home goods”) |
| Facility Footprint | Owns factory address; machinery visible on-site | Office-only location; no production equipment |
| Product Range | Limited to core competencies (e.g., only metal stamping parts) | Wide range across unrelated categories |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Offers fixed FOB prices with limited transparency |
| Lead Times | Can explain production scheduling and bottlenecks | Often vague; dependent on supplier availability |
| Customization Ability | Offers tooling, mold-making, engineering support | Limited to catalog items or minor modifications |
| Staff Expertise | Engineers and production managers available for technical discussion | Sales-focused team; limited technical depth |
Tip: Use Alibaba’s “Assessed Supplier” or “Gold Supplier + Onsite Check” badges as preliminary filters—but never as sole verification.
Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refuses on-site audit | Likely not a real factory or hides subpar conditions | Disqualify unless remote video audit with live Q&A is accepted |
| No business license provided | Illegal operation or identity fraud | Immediate disqualification |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Use of substandard materials, hidden fees, or scam | Benchmark against industry averages; request detailed quote breakdown |
| Generic product photos | Sourcing from multiple suppliers; quality inconsistency | Request custom sample with your branding or specifications |
| Pressure for large upfront payments | High risk of non-delivery or fraud | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No direct production staff access | Trading company inflating margins; limited control | Request to speak with production manager or QC lead |
| Inconsistent communication | Poor internal coordination; potential mismanagement | Assess responsiveness, language proficiency, and technical clarity |
Best Practices for 2026 Procurement
-
Leverage Digital Verification Tools
Use AI-powered platforms (e.g., Sourcify’s Supplier Intelligence Dashboard) to analyze supplier behavior, shipment history, and risk scores. -
Implement Tiered Supplier Onboarding
Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factory), Tier 2 (trading with factory access), or Tier 3 (dropship). Apply differentiated audit and monitoring protocols. -
Require Factory Transparency Reports
Mandate quarterly updates on capacity, workforce, and compliance status—especially for high-volume or mission-critical components. -
Diversify Sourcing Regions
Consider manufacturers in emerging industrial hubs (e.g., Chengdu, Hefei, Nanning) to mitigate concentration risks in Guangdong and Zhejiang.
Conclusion
With China’s manufacturing ecosystem evolving rapidly—driven by automation, green manufacturing, and supply chain resilience—due diligence is non-negotiable. Global procurement managers must adopt a forensic, data-backed approach to supplier verification. Distinguishing between genuine factories and intermediaries reduces cost leakage, improves quality control, and strengthens end-to-end supply chain visibility.
By implementing the steps and red flag alerts outlined in this report, procurement teams can build a compliant, agile, and high-performance supplier network in China for 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant
February 2026
Data Sources: National Bureau of Statistics (China), Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM), Panjiva, UN Comtrade, Internal SourcifyChina Audit Database
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Supplier Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Executive Insight: The Critical Challenge of Supplier Discovery in China
Global procurement managers consistently identify supplier verification as the #1 bottleneck in China sourcing (2026 SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Survey, n=327). When searching “how many companies are there in China,” generic search results yield 15–20 million unverified entities – including defunct, shell, or non-manufacturing entities. This creates dangerous inefficiencies:
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| 14–21 days wasted filtering fake listings, trading companies posing as factories, or non-relevant suppliers | <48 hours to identify pre-vetted manufacturers matching exact specifications |
| 68% risk of encountering misrepresented capabilities (e.g., “OEM” claims without tooling capacity) | Zero tolerance policy: All suppliers undergo 11-point onsite audits (ISO, production lines, export docs) |
| Average cost: $8,200+ per failed audit trip (travel, wasted engineering time) | $0 incremental cost: Audit reports, facility videos, and export history included in Pro List access |
Why “How Many Companies Are There in China?” Is the Wrong Question
The volume of registered entities (21.6 million per China State Administration for Market Regulation, 2025) is irrelevant to procurement outcomes. What matters:
✅ Active manufacturers with export licenses (only 12% of total entities)
✅ Capacity-aligned suppliers for your specific product category
✅ Compliance-certified partners (avoiding ESG/safety risks)
SourcifyChina’s Pro List cuts through noise by delivering only suppliers meeting 3 criteria:
1. Operational Verification: Onsite audit within 90 days
2. Export-Ready Status: Valid customs code + 6+ months export history
3. Category Specialization: e.g., “Medical-grade silicone injection molding” (not just “plastic products”)
Your Time-to-Value Advantage
Procurement teams using the Pro List achieve 83% faster supplier onboarding and 37% lower TCO by eliminating these critical delays:
| Time/Cost Factor | Traditional Process | With SourcifyChina Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Initial supplier shortlisting | 11.2 days | 0.8 days |
| Factory capability validation | 18.5 days (incl. travel) | 2.3 days (digital audit review) |
| First-article approval rate | 52% (due to capability gaps) | 89% |
| Risk of supply disruption (Year 1) | 31% | 7% |
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 2026
“Procurement leaders don’t count companies—they deploy verified capacity. Stop searching through noise; start sourcing with precision.”
The 2026 manufacturing landscape demands zero tolerance for unverified supplier data. With geopolitical volatility and ESG compliance pressures intensifying, your team cannot afford wasted weeks on unreliable leads.
👉 Take Action Before Q3 Sourcing Deadlines:
1. Email Support: Contact [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
→ Receive a customized supplier shortlist within 4 business hours
2. WhatsApp Priority Line: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support
→ Get real-time factory availability checks during Chinese business hours (GMT+8)
Special Q3 2026 Offer: First-time clients receive 3 complimentary supplier audits ($1,200 value) when confirming Pro List access by August 30, 2026.
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Verified Supplier Index (12,840 active manufacturers across 216 product categories). All suppliers undergo bi-annual re-audits per ISO 9001:2025 standards.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only. Not for redistribution.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.