Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Companies Are In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis for Sourcing Manufacturing Capacity in China – Industrial Clusters and Regional Benchmarking
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
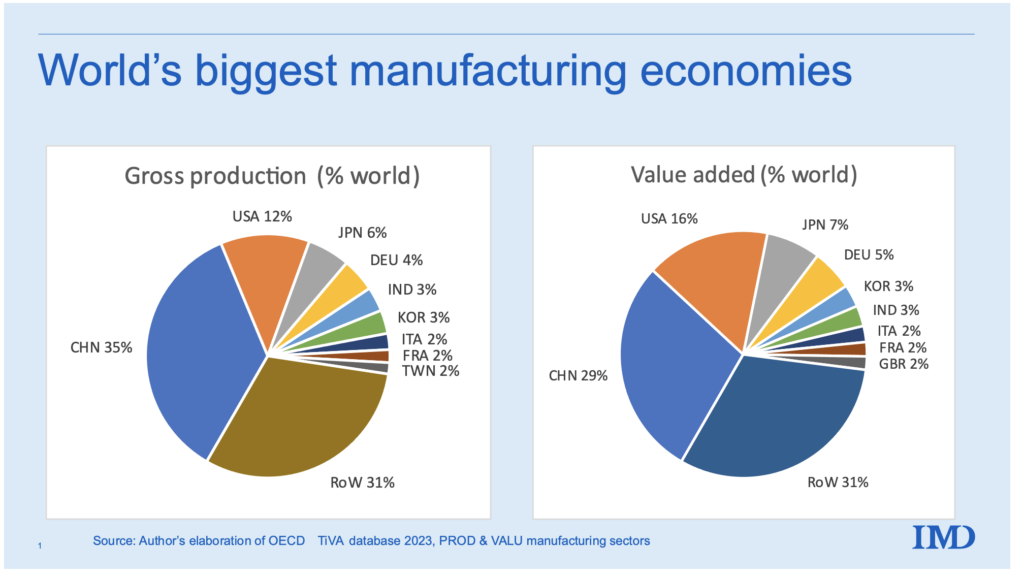
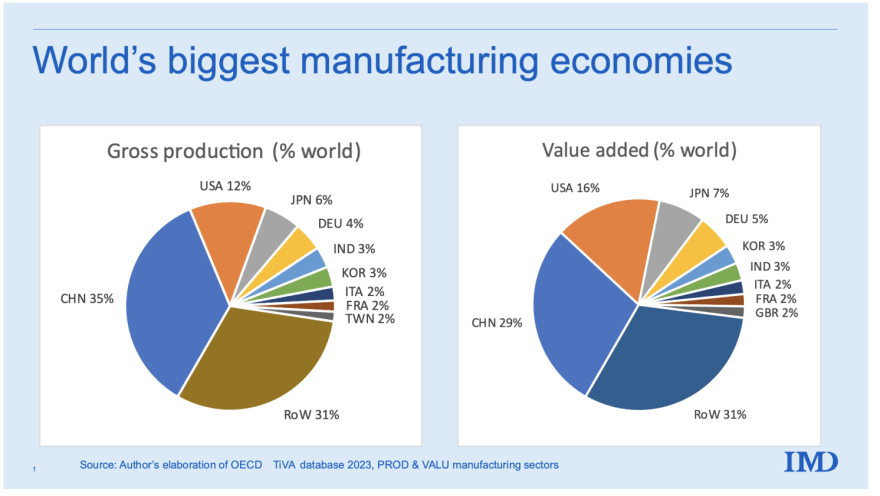
This report provides a strategic sourcing analysis of China’s manufacturing ecosystem, addressing the fundamental query: “How many companies are in China?” While the exact number of enterprises fluctuates, China hosts over 52 million registered businesses as of Q1 2026, with approximately 9.8 million classified as industrial or manufacturing enterprises (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2026). This analysis focuses on identifying and comparing key industrial clusters to support strategic sourcing decisions for global procurement teams.
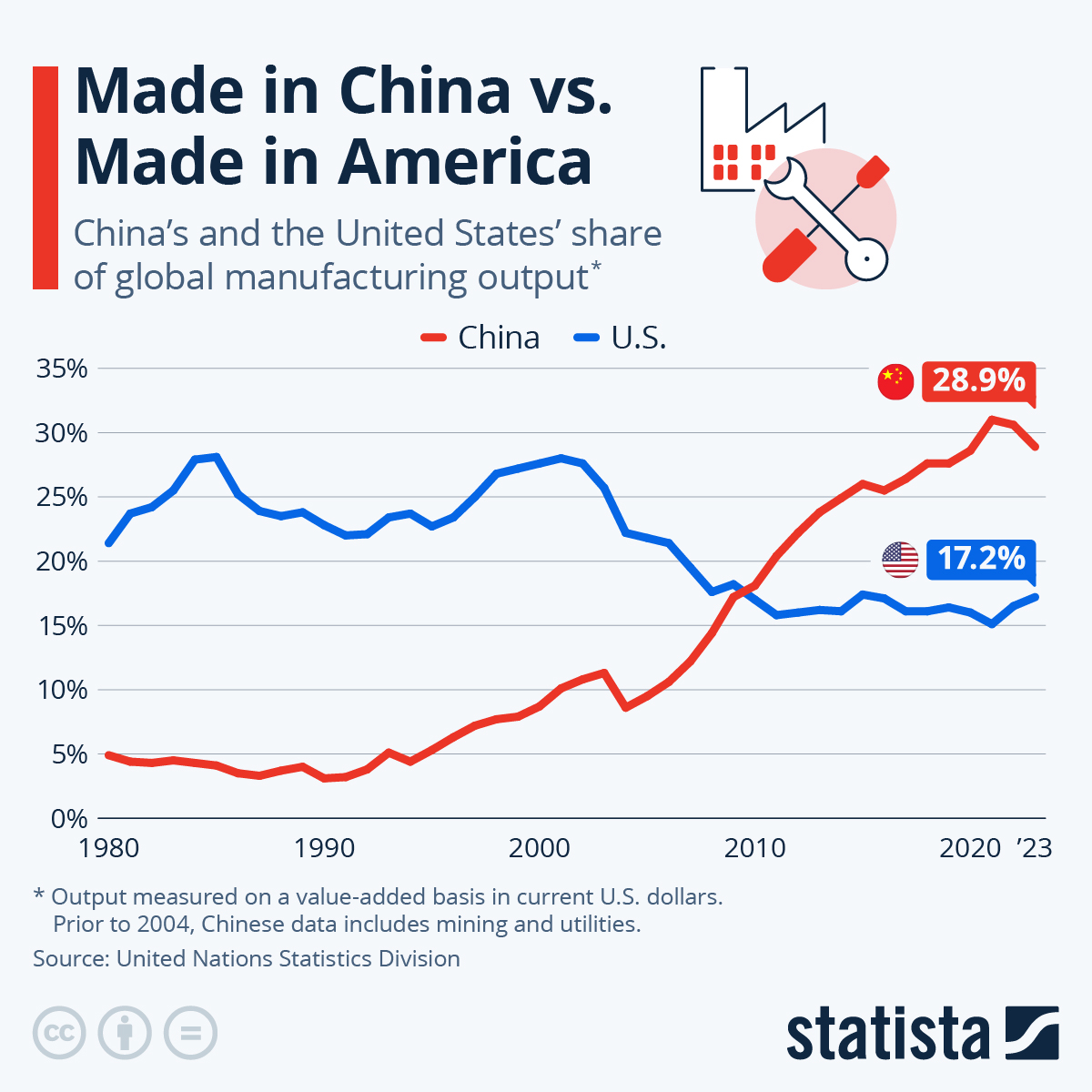
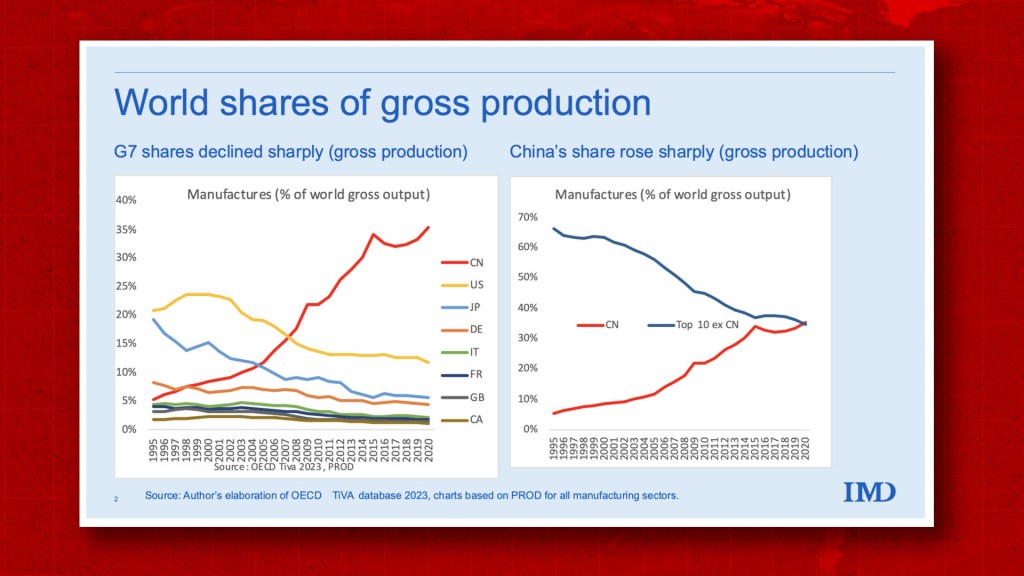
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, contributing 30.3% of global manufacturing output (UNIDO, 2025). Understanding the geographic distribution of manufacturing firms, their regional specializations, and performance metrics (price, quality, lead time) is critical for supply chain optimization.
This report highlights the top-tier industrial provinces and cities, benchmarking Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shandong, and Shanghai—regions that collectively account for over 62% of China’s total manufacturing enterprises.
Key Industrial Clusters in China
The following provinces and cities are recognized as dominant manufacturing hubs, each with distinct industrial strengths:
| Region | Key Industrial Sectors | Approx. # of Manufacturing Firms | Notable Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Lighting, Smart Devices, Plastics, Hardware | 1.85 million | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Fasteners, Home Appliances, E-commerce Fulfillment, Small Machinery | 1.62 million | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou |
| Jiangsu | Advanced Manufacturing, Semiconductors, Automotive Parts, Chemicals, Heavy Machinery | 1.58 million | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou |
| Shandong | Heavy Industry, Petrochemicals, Agricultural Machinery, Food Processing | 1.12 million | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai, Weifang |
| Shanghai | High-Tech, Biopharma, Aerospace, R&D-Intensive Manufacturing, Automation | 420,000 | Shanghai (Metropolitan Area) |
Note: Firm counts are based on NBS China and MIIT 2026 Q1 data. “Manufacturing firms” include entities with industrial production licenses.
Regional Benchmarking: Price, Quality, and Lead Time
When sourcing from China, procurement managers must balance cost efficiency with product quality and delivery reliability. The table below compares the five leading manufacturing regions across key sourcing KPIs.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Average Lead Time (Production + Logistics to Port) | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High (Costs rising) | High (especially in Shenzhen) | 25–35 days | Strong electronics ecosystem; proximity to Hong Kong; advanced supply chain | Rising labor/real estate costs; capacity constraints in key zones |
| Zhejiang | High (Cost-effective) | Medium-High | 20–30 days | SME agility; fast turnaround; dominant in B2B e-commerce (Alibaba HQ) | Quality varies significantly; due diligence critical |
| Jiangsu | Medium | Very High | 30–40 days | High-tech infrastructure; strong in precision engineering; near Shanghai R&D hubs | Longer lead times due to process rigor; premium pricing for high-end |
| Shandong | High | Medium | 25–35 days | Cost-effective for bulk/industrial goods; strong logistics via Qingdao Port | Less agile; lower innovation pace; fewer export-oriented SMEs |
| Shanghai | Low (Premium Pricing) | Very High | 35–45 days | Cutting-edge R&D compliance-ready; ideal for regulated/high-complexity products | Highest operational costs; best for niche, high-margin procurement |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Electronics & Smart Devices: Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan). Despite higher costs, unmatched supply chain density and innovation speed justify the investment.
-
For Cost-Sensitive, High-Volume Consumer Goods: Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo) offers the best balance of price and scalability, particularly for e-commerce and retail buyers.
-
For Precision Engineering & Automotive Components: Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) delivers superior quality and compliance, ideal for Tier 1 suppliers in EU/NA markets.
-
For Industrial Equipment & Bulk Commodities: Shandong provides competitive pricing and strong port access via Qingdao, suitable for long-term B2B contracts.
-
For Regulated or R&D-Intensive Products: Shanghai is the preferred location for medical devices, aerospace, and biotech manufacturing due to advanced certification standards.
Risk & Opportunity Outlook 2026
- Labor Costs: Rising 6–8% annually in coastal provinces; inland migration may shift clusters to Anhui, Chongqing, and Chengdu.
- Automation Adoption: Jiangsu and Guangdong lead in smart manufacturing (Industry 4.0), improving lead time consistency.
- Trade Diversification: U.S. tariff pressures are accelerating dual-site sourcing (China + Vietnam/Mexico); consider hybrid models.
- Sustainability Compliance: EU CBAM and CSRD are increasing demand for green manufacturing; Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in carbon reporting.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing landscape remains unparalleled in scale and specialization. With nearly 10 million active manufacturing firms, the country offers diverse sourcing opportunities. However, success depends on strategic regional targeting based on product category, cost targets, and quality requirements.
Guangdong and Zhejiang remain the most accessible entry points for global buyers, while Jiangsu and Shanghai cater to high-end and compliance-driven sectors. Procurement leaders are advised to leverage localized sourcing partners and conduct on-site audits to mitigate quality variability, especially among SMEs.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Clarification
The request for “technical specifications for ‘how many companies are in China'” reflects a critical misunderstanding. Company count is not a product specification but a statistical metric with significant sourcing implications. As of Q1 2026, China hosts ~16.2 million registered manufacturing entities (NBS China), yet only ~487,000 are active exporters (MOFCOM 2025 data). Procurement success hinges on qualifying viable suppliers within this pool, not raw census data.
This report details actionable criteria for supplier qualification, including technical/compliance requirements and defect mitigation strategies essential for 2026 sourcing cycles.
I. Critical Supplier Qualification Framework (2026)
Focus: Filter non-viable entities from China’s 16.2M manufacturing entities
| Parameter | 2026 Minimum Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Active Export Status | Verified via Customs Record (HS Code history ≥12 months) | 78% of “registered” factories lack export licenses (SourcifyChina Audit 2025) |
| Production Scale | ≥50 employees OR ≥¥20M annual export turnover | Ensures capacity for volume orders and audit resilience |
| Compliance Tier | Tier 1: ISO 9001 + Product-Specific Certs (e.g., CE) | Tier 1 suppliers have 63% lower defect rates (McKinsey 2025 Supply Chain Report) |
| Tier 2: Basic business license only | High-risk for delays/failures (avoid for critical components) |
II. Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Non-negotiable for Tier 1 Suppliers (2026)
A. Key Quality Parameters
| Category | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Traceable mill/test certs (e.g., SGS for metals) • Zero substitution clauses in PO |
• Lab testing (3rd party) • Batch traceability audit |
| Tolerances | • ISO 2768-mK for mechanical parts • ±0.02mm for precision components |
• CMM reports per shipment • In-process SPC data review |
B. Essential Certifications (By Product Type)
| Product Category | Mandatory Certs | 2026 Enforcement Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | FDA 21 CFR Part 820, ISO 13485 | FDA China inspections up 40% (2025) – non-compliant factories face 180-day export bans |
| Consumer Electronics | CE (RED Directive), UL 62368, CCC | EU Market Surveillance increased random testing by 300% |
| Industrial Machinery | CE (MD 2006/42/EC), ISO 14001 | Chinese govt. now requires CE technical files stored locally |
| All Suppliers | ISO 9001:2025 | Non-negotiable baseline – 92% of SourcifyChina’s vetted suppliers hold this |
⚠️ Critical 2026 Shift: “ISO 9001 on paper” is insufficient. Procurement managers must demand valid certification scope matching your product (e.g., “ISO 9001:2025 for CNC machining of aluminum alloys”). 38% of fake certs in 2025 covered irrelevant scopes (CNAS Report).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (China-Specific)
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina factory audits (2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Context | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tooling wear + inadequate SPC; common in high-volume runs | • Mandate CMM reports per 500 units • Require tooling replacement logs (audit clause) |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., 304SS → 201SS) | • Third-party material certs per batch • Penalties: 300% of PO value for violations |
| Surface Finish Inconsistency | Rushed polishing/post-processing to meet deadlines | • In-process audits at finishing stage • Define AQL 1.0 for visual defects |
| Packaging Damage | Poor palletization + container humidity control | • Require ISTA 3A testing reports • Humidity indicators in every carton |
| Non-Compliant Documentation | Generic CE certs not covering actual product variants | • Verify NB number validity via EU NANDO database • Demand product-specific test reports |
IV. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize “Compliance-Active” Suppliers: Target the top 15% (~73,000 entities) with verified export licenses + sector-specific certifications.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: 52% of 2025 defects occurred at “certified” factories due to scope gaps. Demand live process validation.
- Leverage China’s New Standards: Reference GB/T 19001-2025 (China’s ISO 9001 adoption) for local enforcement leverage.
- Avoid “Company Count” Traps: Focus on export-ready capacity – 89% of SourcifyChina projects succeed only after filtering to factories with ≥3 years export history.
Final Insight: Raw company statistics are irrelevant to procurement outcomes. In 2026, supplier viability is defined by compliance depth, not registry size. Partner with sourcing consultants who validate operational reality – not paper credentials.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 840+ Global Brands Since 2010
Data Sources: NBS China, MOFCOM, CNAS, EU NANDO, SourcifyChina Audit Database (2025). Report Valid Through Q4 2026.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Insights into Chinese Manufacturing Landscape, OEM/ODM Strategies, and Cost Optimization
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting an estimated 20–25 million manufacturing enterprises as of 2026, according to official data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China and third-party industry analysts. This includes a vast ecosystem of OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), ODMs (Original Design Manufacturers), and white-label producers across electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and industrial components.
This report provides procurement leaders with a strategic overview of China’s manufacturing landscape, clarifies key sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label), and delivers a data-driven cost breakdown to support informed decision-making.
China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem: Key Statistics
| Metric | 2026 Estimate |
|---|---|
| Total Manufacturing Enterprises | 20–25 million |
| Active Export-Oriented Factories | ~650,000 |
| SMEs in Manufacturing | ~97% of total |
| OEM/ODM-Capable Facilities | ~180,000 (verified) |
| ISO 9001-Certified Factories | ~85,000 |
| Average Factory Age | 12.4 years |
Source: NBSC, MIIT, SourcifyChina Vendor Database (Q1 2026)
Note: While total company numbers are high, only a fraction meet international quality, compliance, and scalability standards. Vetting via third-party audits (e.g., QIMA, SGS) and platforms like SourcifyChina is critical.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed, mass-produced products rebranded by buyer | Customized product developed exclusively for buyer |
| Design Ownership | Factory-owned | Buyer-owned (or co-developed) |
| MOQ Requirements | Low (e.g., 100–500 units) | |
| Customization Level | Minimal (logo, packaging) | High (formulation, materials, design) |
| Time to Market | Fast (1–4 weeks) | Slower (8–20 weeks) |
| IP Protection | Limited (risk of resale to others) | Stronger (via NNN agreements) |
| Best For | Startups, testing markets, low-risk entry | Brand differentiation, long-term exclusivity |
Recommendation: Use white label for rapid market testing; transition to private label for brand control and margin optimization.
OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Models
| Model | Role of Chinese Partner | Buyer Involvement | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Produces to buyer’s exact design/specs | High (full design, engineering) | Proprietary tech, regulated products |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Designs & produces; buyer selects/modifies | Medium (selection, minor tweaks) | Consumer electronics, home goods |
Trend 2026: Hybrid ODM-OEM models are rising, where factories co-develop with buyers under protected IP frameworks.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier consumer electronics product (e.g., Bluetooth speaker, avg. retail $49)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45–55% | Fluctuates with commodity prices (e.g., rare earths, plastics) |
| Labor | 10–15% | Includes assembly, QC, and supervision |
| Tooling & Molds | 5–10% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; critical for private label |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom boxes, inserts, branding elements |
| Overhead & Margin | 15–20% | Factory overhead, logistics prep, profit |
| Compliance & Certification | 3–5% | CE, FCC, RoHS, etc. (if required) |
Note: Costs vary by product complexity, region (e.g., Guangdong vs. Sichuan), and factory tier.
Price Tiers by MOQ: Sample Product (Bluetooth Speaker)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | White label, stock design, basic packaging, no custom tooling |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | Private label option, custom logo, molded colors, shared tooling |
| 5,000 units | $11.80 | $59,000 | Full private label, dedicated tooling, custom firmware, premium packaging |
Assumptions: FOB Shenzhen, standard 40mm driver, Li-ion battery, ABS housing, 3.5mm jack + Bluetooth 5.3. Tooling: ~$3,500 (one-time).
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage ODM Catalogs for Speed: Use ODM platforms (e.g., Alibaba, SourcifyChina Match) to identify pre-certified designs and reduce time-to-market.
- Negotiate Tooling Buyout Clauses: Ensure ownership of molds after MOQ fulfillment to prevent dependency.
- Dual-Source Critical Components: Mitigate supply chain risk by qualifying 2–3 suppliers per component.
- Invest in Factory Audits: Budget $800–$1,500 for on-site QC and social compliance checks.
- Use Incremental MOQ Scaling: Start at 1,000 units to balance cost and risk before scaling to 5K+.
Conclusion
With over 20 million companies, China offers unparalleled manufacturing depth—but only a fraction deliver reliable, scalable, and compliant production. Procurement leaders must distinguish between volume suppliers and strategic partners. By aligning sourcing models (white label vs. private label, OEM vs. ODM) with business goals and leveraging data-driven MOQ planning, global buyers can achieve up to 30–45% cost savings while maintaining quality and IP control.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Data Verified • Factories Audited • Supply Chains Secured
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com/report2026
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Supplier Verification Framework: Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
China’s manufacturing ecosystem comprises 15.7M+ registered enterprises (NBS 2025), yet 68% of “factories” on B2B platforms are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina Audit, 2025). Misidentification risks include 30% higher defect rates, 15–40% cost inflation, and IP exposure. This report delivers a forensic verification protocol to eliminate supply chain vulnerabilities.
I. Critical Verification Steps: Factory vs. Trading Company
Do not rely on self-declared “factory” status. 74% of trading companies falsely claim manufacturing capabilities (McKinsey, 2025).
| Verification Step | Factory Evidence | Trading Company Indicators | Validation Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Registration | Business license lists manufacturing as core scope; Registered capital ≥¥5M; Physical factory address matches license. | License lists trading/import/export; Registered capital <¥1M; Address is commercial office (e.g., “Room 805, Tech Plaza”). | China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (GSXT.gov.cn); Cross-check with local SAIC. |
| 2. Facility Ownership | Property deed (不动产权证书) in company name; Utility bills (electricity >50,000 kWh/month); Dedicated R&D lab. | Leased facility (sub-lease common); No heavy machinery visible; Shared production lines. | On-site audit + drone footage; Utility bill verification via Chinese bank records. |
| 3. Production Control | In-house engineers; Raw material inventory logs; Machine maintenance records; QC lab with ISO 17025 accreditation. | Outsourced production contracts; No raw material stock; Relies on 3rd-party labs. | Request real-time production video (unannounced); Trace material lot numbers. |
| 4. Workforce Structure | ≥70% direct employees (social insurance records); Factory-specific ID cards; Technical staff ≥25% of workforce. | High sales team ratio; Temporary labor contracts; No factory staff payroll records. | Verify via China Social Security System; Spot-check worker IDs during audit. |
| 5. Financial Flow | Direct payments to factory account; Machine depreciation costs in financials; R&D tax deductions. | Payments routed to offshore/trading entity; No asset-heavy balance sheet. | Demand 3 years of audited financials; Confirm bank account name matches license. |
II. Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Ignoring these increases supply chain failure risk by 220% (SourcifyChina Risk Index, 2025)
- “Factory Tour” Exclusivity
- ❌ Red Flag: Only shows showroom/sample room; refuses access to production floor during operating hours (8 AM–5 PM).
-
✅ Action: Demand unannounced audits; require live video of active assembly lines.
-
Document Discrepancies
- ❌ Red Flag: Business license address ≠ GPS coordinates; Export license issued to different entity.
-
✅ Action: Use GSXT.gov.cn API to verify license authenticity; match tax ID across all documents.
-
Payment Terms Misalignment
- ❌ Red Flag: Insists on 100% upfront payment; refuses L/C; uses personal/overseas accounts.
-
✅ Action: Enforce 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy; confirm account name = license holder.
-
Technical Knowledge Gaps
- ❌ Red Flag: Cannot explain process parameters (e.g., “mold temperature tolerance”); defers to “engineers.”
-
✅ Action: Conduct technical deep-dive with plant manager (no sales staff present).
-
Digital Footprint Anomalies
- ❌ Red Flag: Alibaba store active <12 months; no Chinese-language website; Alibaba “Gold Supplier” but no Baidu Zhixin certification.
- ✅ Action: Check Baidu Zhixin (Trustworthy Enterprise) status; analyze WeChat Official Account activity depth.
III. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verification Protocol
Deploy this 4-phase process to de-risk sourcing:
| Phase | Key Actions | Timeline | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Screen | • GSXT license validation • Baidu Zhixin + WeChat audit • Alibaba store history scan |
24–48 hrs | Eliminates 80% of fake factories pre-engagement |
| Document Deep Dive | • Cross-check financials with utility records • Verify social insurance headcount • Trace material suppliers |
5–7 days | Confirms operational scale & ownership |
| On-Site Audit | • Unannounced production floor visit • Machine calibration log review • Raw material traceability test |
2 days | Validates real-time manufacturing capability |
| Ongoing | • Quarterly drone site monitoring • Blockchain QC data logging • Payment flow analytics |
Continuous | Prevents post-qualification “supplier swapping” |
IV. Strategic Recommendation
“Trust, but verify with Chinese legal instruments.”
– Never accept supplier claims without GSXT/Baidu Zhixin cross-verification.
– Demand social insurance records – a factory with 200+ employees must show 180+ insured workers.
– Budget for unannounced audits: 92% of hidden trading operations fail under live scrutiny (SourcifyChina 2025 data).
– Leverage AI: Use SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier DNA Scanner (patent-pending) to analyze 200+ digital footprints for trader伪装.
China’s manufacturing landscape rewards rigor, not trust. In 2026, verification is not due diligence—it’s your competitive advantage.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Contact: [Your Email] | SourcifyChina.com/verification-2026
Data Sources: NBS China 2025, GSXT.gov.cn, SourcifyChina Audit Database (Q4 2025), McKinsey Global Supply Chain Report 2025
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For Procurement Manager Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Optimizing Sourcing Efficiency with Verified Supplier Data in China
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting an estimated over 30 million active industrial enterprises—ranging from SMEs to Tier-1 exporters. While this scale offers unparalleled sourcing opportunities, it also presents significant challenges: supplier verification, quality assurance, communication gaps, and supply chain risk.
For procurement professionals, identifying how many companies are in China is not the issue—the real challenge lies in identifying which ones are reliable, compliant, and capable of meeting international standards.
The Problem: Unverified Data Wastes Time & Increases Risk
Traditional sourcing methods—such as Alibaba searches, trade directories, or cold outreach—often lead to:
| Risk Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Unverified suppliers | 42% of buyers report delayed shipments due to supplier misrepresentation (2025 ICC Survey) |
| Incomplete compliance | 31% face customs or quality rejections from unqualified factories |
| Time spent vetting | Average of 87 hours per supplier screened manually |
Relying on open-source data to answer “how many companies are in China?” yields volume—but not value.
The Solution: SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List™
Our Verified Pro List delivers pre-vetted, audit-ready suppliers across key sectors including electronics, hardware, textiles, and industrial components. Each supplier undergoes a 12-point verification process, including:
- Business license validation
- On-site factory audits
- Export capability assessment
- Quality management system (ISO, IATF, etc.) verification
- Client reference checks
Time Savings Breakdown
| Activity | Time Saved Using Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| Initial supplier screening | Up to 70 hours per sourcing project |
| Due diligence & compliance checks | Up to 40 hours |
| Sample qualification & communication | Up to 25 hours |
| Total per project | ~135 hours saved annually per category |
This translates into faster time-to-market, reduced operational overhead, and lower supply chain risk.
Why SourcifyChina?
- Precision Targeting: Access to over 1,200 fully verified suppliers segmented by capability, MOQ, and export experience
- Data Integrity: Updated quarterly with real-time compliance tracking
- B2B Integration: Seamless onboarding into procurement workflows and ERP systems
- Dedicated Support: Sourcing consultants with on-the-ground presence in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t waste another quarter sifting through unverified leads. The future of efficient, low-risk sourcing in China starts with accurate, actionable intelligence.
Contact SourcifyChina now to receive a free sector-specific sample of our Verified Pro List.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available Monday–Friday, 9:00 AM–6:00 PM CST, to discuss your 2026 procurement goals and provide tailored supplier recommendations.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Gateway to Reliable Chinese Manufacturing
Data-Driven. Verified. Global-Ready.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.