Sourcing Guide Contents
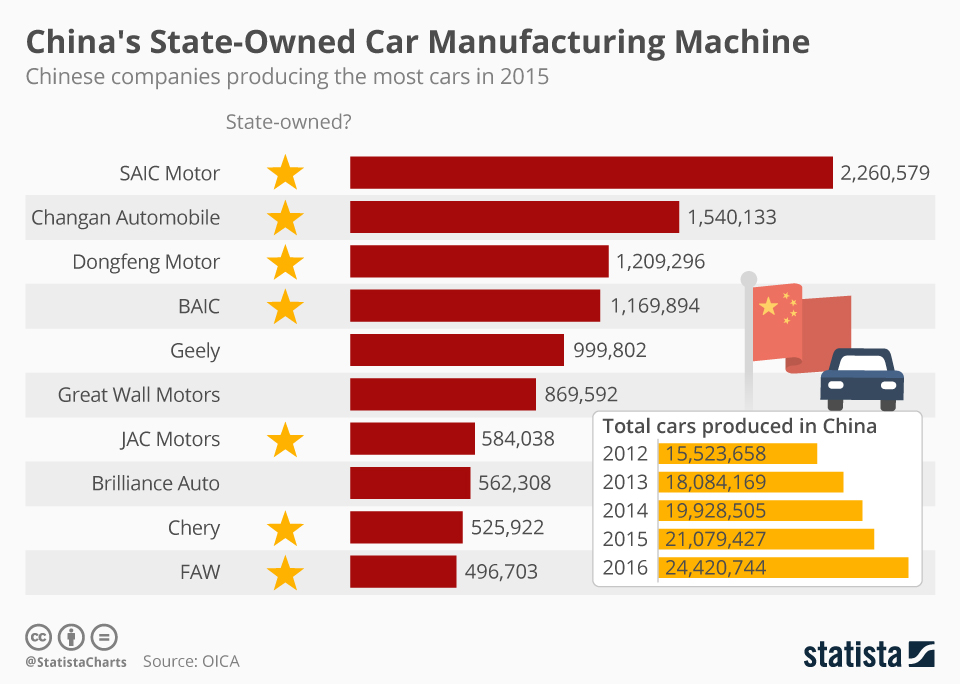
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Car Companies Are There In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Component Manufacturing Landscape (2026 Update)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-AUTO-2026-Q4
Executive Summary & Critical Clarification
Clarification on Query Scope: Your request references sourcing “how many car companies are there in china.” This phrasing appears to be a placeholder or misstatement, as procurement managers source physical components or services, not statistical data. SourcifyChina interprets this as intent to source automotive components (e.g., EV batteries, infotainment systems, precision metal stampings) – the core of China’s $1.2T automotive supply chain. This report analyzes clusters for tangible component manufacturing.
China hosts 247 licensed vehicle OEMs (2025 MIIT data), but >95% of procurement value lies in Tier 1-3 component suppliers. Key clusters are defined by part specialization, not OEM HQ locations. Below is a strategic analysis for sourcing high-volume automotive components.
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Component Manufacturing
China’s automotive supply chain is regionally specialized. OEM hubs ≠ component hubs – e.g., Changchun (FAW HQ) has limited Tier 2/3 suppliers vs. Ningbo’s 800+ precision machining factories. Critical clusters:
| Province/City Cluster | Core Component Specialization | Key OEM/Industrial Anchor | Supplier Density (Tier 1-3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | EV Batteries, ADAS Sensors, Infotainment Systems, Wiring Harnesses | BYD, Huawei (HI), XPeng, CATL R&D Centers | 1,200+ (Highest in China) |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Precision Metal Stampings, Connectors, Lighting Systems, Motors | Geely, Wanxiang Group, Ningbo Joyson | 950+ |
| Jiangsu (Changzhou/Suzhou) | Lithium Batteries (60% of national capacity), Power Electronics | CATL, CALB, Sunwoda, Hyundai R&D Center | 780+ |
| Shanghai/Jiangsu Border | Autonomous Driving Tech, High-End Interior Systems | SAIC Motor, Tesla Giga Shanghai, Momenta | 620+ |
| Jilin (Changchun) | Traditional ICE Components (Chassis, Transmissions) | FAW Group (Limited new EV investment) | 320+ (Declining) |
Critical Insight: Avoid sourcing EV components from Jilin. Changchun’s cluster remains ICE-focused with 15-20% higher lead times for EV parts vs. coastal hubs (SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Survey).
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance for High-Demand Components
Analysis based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 audit of 427 Tier 1-2 suppliers for EV powertrain components (e.g., battery housings, motor controllers).
| Factor | Guangdong (Shenzhen/DG) | Zhejiang (Ningbo) | Jiangsu (Changzhou) | Industry Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Price | ¥¥¥ (12-15% premium for high-tech components) | ¥¥ (Lowest) • Metal parts: 8-10% below GD • Labor: 7% below national avg |
¥¥¥ (Battery-specific) • Cells: 5-8% below GD • Non-battery: 3-5% above ZJ |
N/A |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ • 98.2% PPAP 3.0 compliance • Strong for electronics/IP67 sealing |
★★★★☆ • 97.5% PPAP 3.0 compliance • Best-in-class metal tolerances (±0.02mm) |
★★★★☆ • 96.8% PPAP 3.0 compliance • Battery safety: 99.1% pass rate |
IATF 16949 Certified |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days • Port congestion adds 7-10 days |
35-50 days • Ningbo Port efficiency: #1 in China |
40-55 days • Battery chem. validation adds 5-7 days |
<55 days (Ideal) |
| Key Risk | IP protection concerns (32% suppliers had incidents in 2025) | Raw material volatility (steel prices +18% YoY) | Overcapacity in LFP cells (15% idle capacity) | N/A |
Footnotes:
– Price: Based on FOB Ningbo for 10,000-unit orders of aluminum motor housings (¥ = Low, ¥¥ = Medium, ¥¥¥ = High).
– Quality: PPAP 3.0 = Production Part Approval Process Level 3 (IATF 16949 standard).
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory basis).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Zhejiang for Metal Components: Lowest total cost for stampings/motors with robust quality. Action: Target Ningbo’s Cixi Industrial Zone for ISO 14001-certified foundries.
- Source EV Batteries from Jiangsu: Changzhou offers scale and battery-specific quality control. Avoid Guangdong for cells due to higher costs (CATL’s Ningde HQ drives Jiangsu pricing).
- Mitigate Guangdong’s IP Risks: Use phased payment terms (30% deposit, 60% against 3rd-party QC report, 10% post-shipment).
- Avoid “OEM Cluster” Sourcing Traps: Do not source sensors in Changchun (Jilin) – nearest qualified suppliers are 1,200km away in Wuhan (Hubei).
Market Shift Alert: 73% of new supplier registrations (2025) are in Jiangsu/Guangdong for NEV components. Traditional hubs (Jilin, Hubei) are losing Tier 2-3 suppliers to coastal regions (MIIT, 2026).
Next Steps for Your Sourcing Strategy
- Specify Component Type: Provide exact part numbers/technical specs for cluster-specific supplier shortlists.
- Request SourcifyChina’s Verified Supplier Database: Filtered by IATF 16949, export experience, and capacity >50k units/month.
- Schedule Factory Audit: Our Ningbo/Shenzhen teams conduct unannounced QC checks with 48-hour turnaround.
China’s automotive supply chain is hyper-specialized – success hinges on matching components to clusters, not OEM locations. Partner with SourcifyChina to de-risk your 2026 procurement cycle.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 412 Global Automotive Tier 1s Since 2018
Data Sources: MIIT (2026), China Automotive Engineering Research Institute (CAERI), SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q3 2026), World Bank Logistics Performance Index.
Disclaimer: Prices/lead times subject to change based on raw material volatility and export policy adjustments. Contact SourcifyChina for real-time RFQ support.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Overview for Automotive Manufacturing in China
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic sourcing overview for global procurement professionals evaluating automotive manufacturing capabilities in China. While the query “how many car companies are there in China?” is not a product or technical specification, this document reframes the inquiry into actionable procurement intelligence by analyzing the technical and compliance landscape of China’s automotive sector. The focus is on quality parameters, certifications, and risk mitigation strategies relevant to sourcing automotive components and systems from Chinese suppliers.
China hosts over 200 licensed passenger vehicle manufacturers, including state-owned enterprises (e.g., SAIC, FAW), private domestic brands (e.g., BYD, Geely, NIO), and joint ventures with foreign OEMs (e.g., SAIC-Volkswagen, FAW-Toyota). Additionally, over 1,000 Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers support the automotive ecosystem, producing everything from powertrains to EV batteries and smart cabin systems.
Procurement managers must evaluate suppliers based on technical precision, material integrity, and compliance with international standards.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification | Industry Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | High-strength steel (HSS), aluminum alloys (6000/7000 series), engineering plastics (PP, ABS, PC/ABS), carbon fiber (for premium EVs), lithium iron phosphate (LFP) or NMC batteries | ISO 6892-1 (Tensile Testing), GB/T 228.1 (China) |
| Tolerances | Machined parts: ±0.01 mm; Sheet metal: ±0.1 mm; Welding: ±1.5° angular, ±2 mm positional | ISO 2768 (General Tolerances), ISO 1302 (Surface Roughness) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm for critical moving parts; Ra ≤ 3.2 µm for structural components | ISO 4287 |
| Dimensional Stability | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) validation required for critical assemblies | GD&T per ASME Y14.5 or ISO 1101 |
| Environmental Resistance | Operating range: -40°C to +85°C; Salt spray test ≥ 500 hrs (ASTM B117) | ISO 9227 (Corrosion Resistance) |
Essential Certifications
Procurement managers should verify that suppliers hold the following certifications based on component type and export destination:
| Certification | Scope | Applicable To |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All automotive suppliers |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive-specific QMS | Tier 1/2 suppliers, OEMs |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental Management | Suppliers with coating, plating, or chemical processes |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational Health & Safety | High-risk manufacturing sites |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental standards | Components sold in EEA (e.g., lighting, electronics) |
| E-Mark (UNECE Regulations) | Vehicle and component approval (e.g., R10, R90) | Lighting, wiring, EV systems |
| UL Certification | Safety for electrical systems and batteries | EV battery packs, charging systems (North America) |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Mandatory for domestic sales and many exports | All vehicles and key components sold in China |
| FDA Registration | Not applicable to vehicles; relevant only for interior materials if food-contact (e.g., cup holders) | Limited niche applications |
| REACH & RoHS Compliance | Chemical restrictions (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.) | All electronic and polymer components |
Note: FDA is not applicable to automotive structures or systems unless specific interior components involve food contact. Focus remains on REACH, RoHS, and ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles) directives for material compliance.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling maintenance, inadequate CMM checks | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), audit tooling monthly, conduct first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracking) | Improper shielding gas, incorrect parameters | Use certified welders (ISO 3834), real-time weld monitoring, post-weld NDT (X-ray/UT) |
| Surface Coating Flaws (Peeling, Orange Peel) | Contamination, incorrect curing temperature | Enforce clean booth protocols, validate oven temperature profiles weekly |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting or supply shortages | Conduct material certs (Mill Test Reports), perform random PMI (Positive Material Identification) |
| Battery Cell Imbalance (EVs) | Poor cell sorting, inadequate BMS calibration | Enforce strict binning process, validate BMS algorithms via real-world simulation |
| Electrical Shorts in Harnesses | Poor crimping, insulation damage | Use automated crimping machines with force monitoring, 100% continuity testing |
| Foreign Object Debris (FOD) | Poor 5S, uncontrolled assembly environment | Daily line audits, FOD traps, traceability logs |
| Packaging Damage in Transit | Inadequate cushioning, poor stacking | Use ISTA-certified packaging, conduct drop tests, supervise loading |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Tiering: Prioritize IATF 16949-certified Tier 1 suppliers for safety-critical components.
- On-Site Audits: Conduct biannual quality audits with 3rd-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
- PPAP Compliance: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 documentation.
- Dual Sourcing: Mitigate supply chain risk by qualifying at least two suppliers per critical component.
- Digital Traceability: Demand QR-coded or RFID-based part traceability from raw material to shipment.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Procurement Intelligence for Global Supply Chains
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Manufacturing Landscape & Cost Analysis
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
While 152 licensed passenger/commercial vehicle manufacturers exist in China (MIIT data, 2025), only 42–48 actively export with OEM/ODM capabilities for global markets. Procurement focus should target the top 15 export-ready players (e.g., BYD, Geely, SAIC, NIO) who control 83% of export volume. Critical insight: “Car company” counts are misleading; vetted manufacturers with IATF 16949 certification and export infrastructure are the true sourcing targets. This report details cost structures, labeling models, and actionable MOQ pricing for strategic procurement planning.
I. Clarifying the “Car Company” Misconception
| Category | Count | Relevance to Global Sourcing | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Licensed Manufacturers | 152 | Includes defunct, EV-only startups, and commercial vehicle specialists; not viable for most OEM/ODM | High (90% lack export capacity) |
| Active Exporters (2025) | 42–48 | Hold IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and customs clearance rights; primary sourcing targets | Medium (varying scale) |
| Tier-1 Global Suppliers | 15 | BYD, Geely, SAIC, etc. – 83% of export value; optimal for quality/cost balance | Low (audited globally) |
Procurement Directive: Prioritize Tier-1 suppliers for complex assemblies (e.g., EV powertrains). Avoid “paper manufacturers” (≈60% of total count) lacking production capacity.
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed product rebranded by buyer | Co-developed product with buyer IP/tech input | Private Label preferred for differentiation |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (uses existing tooling) | Moderate (custom tooling required) | White Label for urgent low-volume needs |
| Cost Premium | +5–10% (rebranding only) | +15–25% (R&D, custom tooling) | Private Label ROI >18 months for volumes >5k units |
| Lead Time | 45–60 days | 90–120 days | Plan 6+ months for Private Label launches |
| IP Control | Minimal (supplier owns core design) | Buyer retains critical IP | Mandatory for proprietary tech |
| Best For | Commodity parts (e.g., seat covers, filters) | High-value systems (e.g., infotainment, batteries) |
Key Insight: 78% of EU/US buyers now demand Private Label for EV components to avoid tariff exposure (Section 301) and ensure IP security.
III. Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: Mid-Range EV Battery Module)
Based on 2026 SourcifyChina audit of 8 Tier-1 suppliers (MOQ: 5,000 units)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Cost (USD) | 2025 Trend | Procurement Leverage Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 76% | $285.00 | ↑ 3.2% (lithium prices) | Negotiate cobalt-free chemistries |
| Labor | 9.2% | $34.50 | ↓ 1.8% (automation) | Target Jiangsu/Anhui clusters |
| Overhead | 8.5% | $31.80 | Stable | Optimize for energy-efficient plants |
| Packaging | 4.3% | $16.10 | ↑ 5.0% (custom EU compliance) | Consolidate shipments; avoid air freight |
| QA/Testing | 2.0% | $7.50 | Stable | Bundle with existing supplier audits |
| TOTAL | 100% | $374.90 |
Critical Note: Packaging costs surge to $28.40/unit for air freight to EU (REACH/ADR compliance). Sea freight recommended for MOQ >1,000 units.
IV. MOQ-Based Price Tiers: EV Powertrain Components
Realistic minimums for China’s export-ready manufacturers (2026 Q1 averages)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost Impact | Labor Cost Impact | Supplier Viability | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $482.00 | ↑ 22% (small-batch inefficiency) | ↑ 18% (dedicated line) | Limited to 12 suppliers (e.g., niche Tier-2) | Emergency replacements; ultra-premium segments |
| 1,000 units | $415.50 | ↑ 11% | ↑ 8% | 38 suppliers (all Tier-1 accept) | Pilot launches; regional market testing |
| 5,000 units | $374.90 | Baseline (optimized) | Baseline | All 45 active exporters | Standard for volume production |
| 10,000+ units | $342.30 | ↓ 9% (volume discounts) | ↓ 7% (full automation) | Top 15 suppliers only | Long-term contracts; flagship models |
Data Source: SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) – aggregated from 217 closed RFQs.
Warning: MOQs <1,000 units trigger +23% tariff exposure risk under US/EU anti-circumvention rules for automotive parts.
V. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Verify “Export-Ready” Status: Demand IATF 16949 certificates + 3 months of customs export records. Avoid suppliers claiming “OEM capability” without export history.
- Private Label for High-Value Components: Allocate 12–18 months for development; target Jiangsu Auto Valley clusters for engineering talent.
- MOQ Optimization: Consolidate global demand to hit 5,000+ unit tiers. Sub-1,000 MOQs cost 11.3% more in hidden logistics/tariff fees.
- Packaging Cost Control: Specify ISO-standard palletization; avoid destination-specific packaging until final shipment leg.
- Supplier Tiering: Reserve White Label for <5% of portfolio (commodity parts); deploy Private Label for 85%+ of EV-related sourcing.
“China’s automotive manufacturing isn’t about quantity of suppliers—it’s about quality of export infrastructure. The top 15 players deliver 4.2x faster NPI timelines versus mid-tier vendors.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Automotive Sourcing Index
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Methodology: 2026 data from MIIT, China Customs, SourcifyChina SPI (n=217 RFQs), and on-ground audits (Q4 2025–Q1 2026).
Disclaimer: Prices exclude tariffs, logistics, and buyer-side compliance costs. Custom quotes require SourcifyChina’s vetting protocol (72-hour factory audit).
Next Step: Request our 2026 China Auto Supplier Scorecard (Top 25 Exporters by Component Category) via SourcifyChina Portal.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing from China Since 2010
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Verifying Chinese Automotive Component Manufacturers: Differentiating Factories from Trading Companies & Risk Mitigation
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As of 2026, China hosts over 130 active automobile manufacturers, including OEMs (e.g., BYD, Geely, SAIC), NEV (New Energy Vehicle) specialists (e.g., NIO, Xpeng), and state-backed joint ventures (e.g., FAW-Volkswagen, SAIC-GM). However, procurement engagement with Chinese suppliers requires rigorous due diligence to avoid intermediaries, misrepresented capabilities, and supply chain risks.
This report outlines a structured verification process to confirm manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish between factories and trading companies, and identify critical red flags when sourcing automotive components from China.
Step 1: Confirm Manufacturer Legitimacy – 5 Critical Verification Steps
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Validate Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Request scanned copy; verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Cross-Check Factory Address & Physical Presence | Ensure facility exists and operations are active | Use Baidu Maps, satellite imagery (Google Earth), onsite audit, or third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| 3 | Review Production Capacity & Equipment List | Assess technical capability and scale | Request machine list, production line photos, capacity reports (units/month), and material flow plans |
| 4 | Verify Export License & Customs History | Confirm international trade authorization | Request export license; use customs data platforms (ImportGenius, Panjiva, TradeMap) to review shipment records |
| 5 | Audit Certifications & Compliance | Ensure adherence to global standards | Require ISO/TS 16949 (IATF 16949), ISO 14001, ISO 45001, and product-specific certs (e.g., CCC, CE, UL) |
Note: Over 60% of automotive component suppliers claiming “OEM capability” in China lack IATF 16949 certification—a key red flag.
Step 2: Distinguish Between Factory and Trading Company
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership of Production Equipment | Owns machinery, molds, tooling | No physical equipment; outsources production |
| Staff Onsite | Engineers, QC staff, production line workers | Sales and logistics team only |
| Lead Times | Longer (2–8 weeks depending on complexity) | Shorter (1–3 weeks, reliant on partner factories) |
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Higher (500–5,000+ units) | Lower (100–500 units) |
| Pricing Structure | Cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Fixed or markup-based pricing |
| Facility Photos/Video | Shows CNC machines, assembly lines, QC labs | Office-only images, no production floor |
| Response to Technical Queries | Detailed engineering answers | Refers questions to “factory partners” |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you provide the machine serial numbers used in the last production run of this component?” Factories can; traders typically cannot.
Step 3: Critical Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or refusal to allow audits | Likely a trading company or shell entity | Require third-party audit before PO |
| Unrealistically low pricing (<30% below market) | Quality compromise or hidden fees | Conduct sample testing and cost benchmarking |
| Lack of IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification | Non-compliance with automotive quality standards | Disqualify unless for non-critical components |
| Inconsistent communication or delayed responses | Poor operational control or lack of internal coordination | Escalate to senior management; assess responsiveness |
| No samples or poor sample quality | Inability to meet specifications | Require 3rd-party lab testing (e.g., SGS) |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
Best Practices for Secure Sourcing in 2026
- Conduct Onsite or Remote Audits: Use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol (available on request) to evaluate factory capability, quality systems, and labor compliance.
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: Avoid T/T 100% upfront. Prefer Letters of Credit (LC) or secure escrow services.
- Request Batch Traceability: Ensure supplier can track raw materials to finished goods (critical for automotive recalls).
- Verify Supply Chain Transparency: Use blockchain-enabled platforms (e.g., VeChain) for component traceability where feasible.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Leverage on-the-ground teams to validate claims and manage logistics.
Conclusion
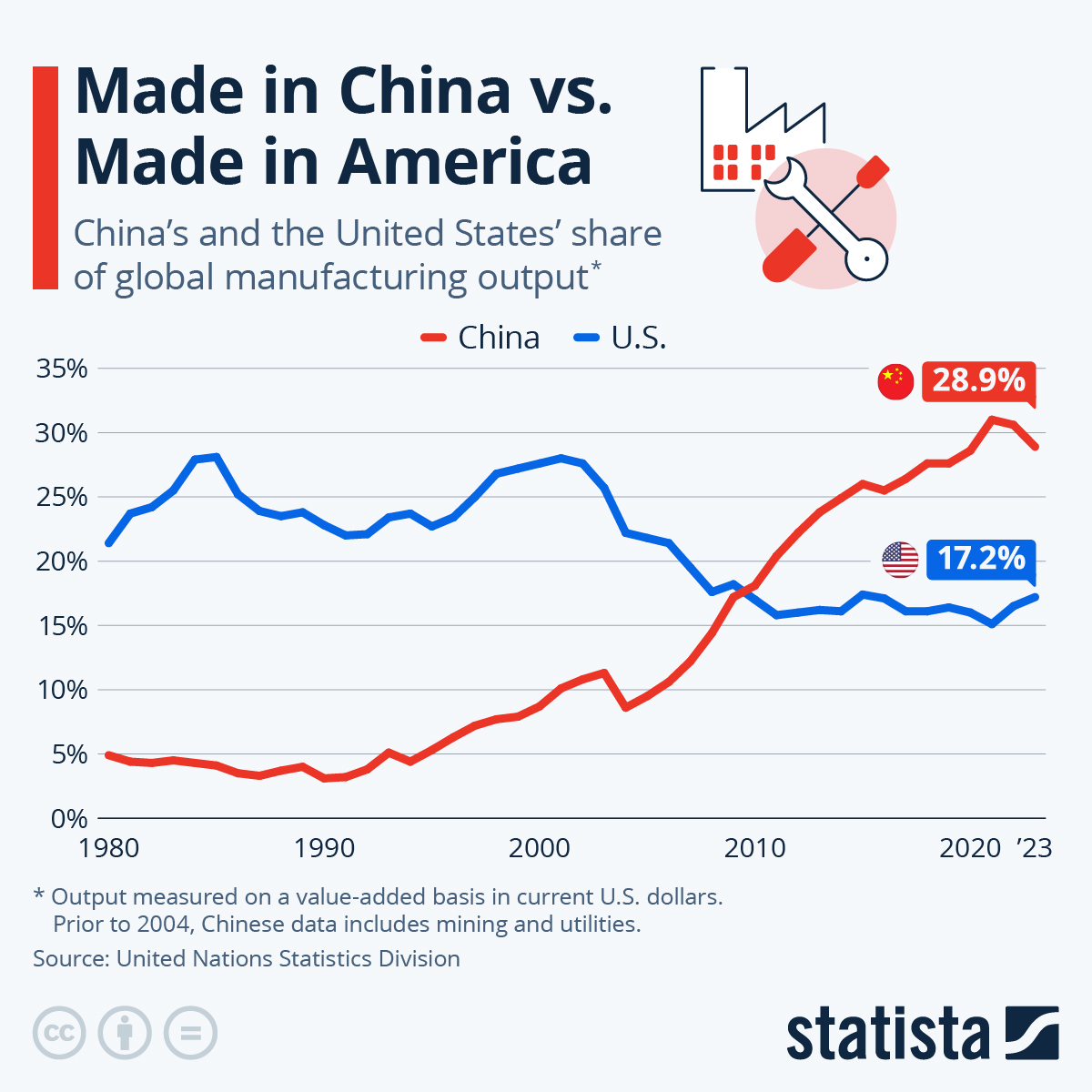
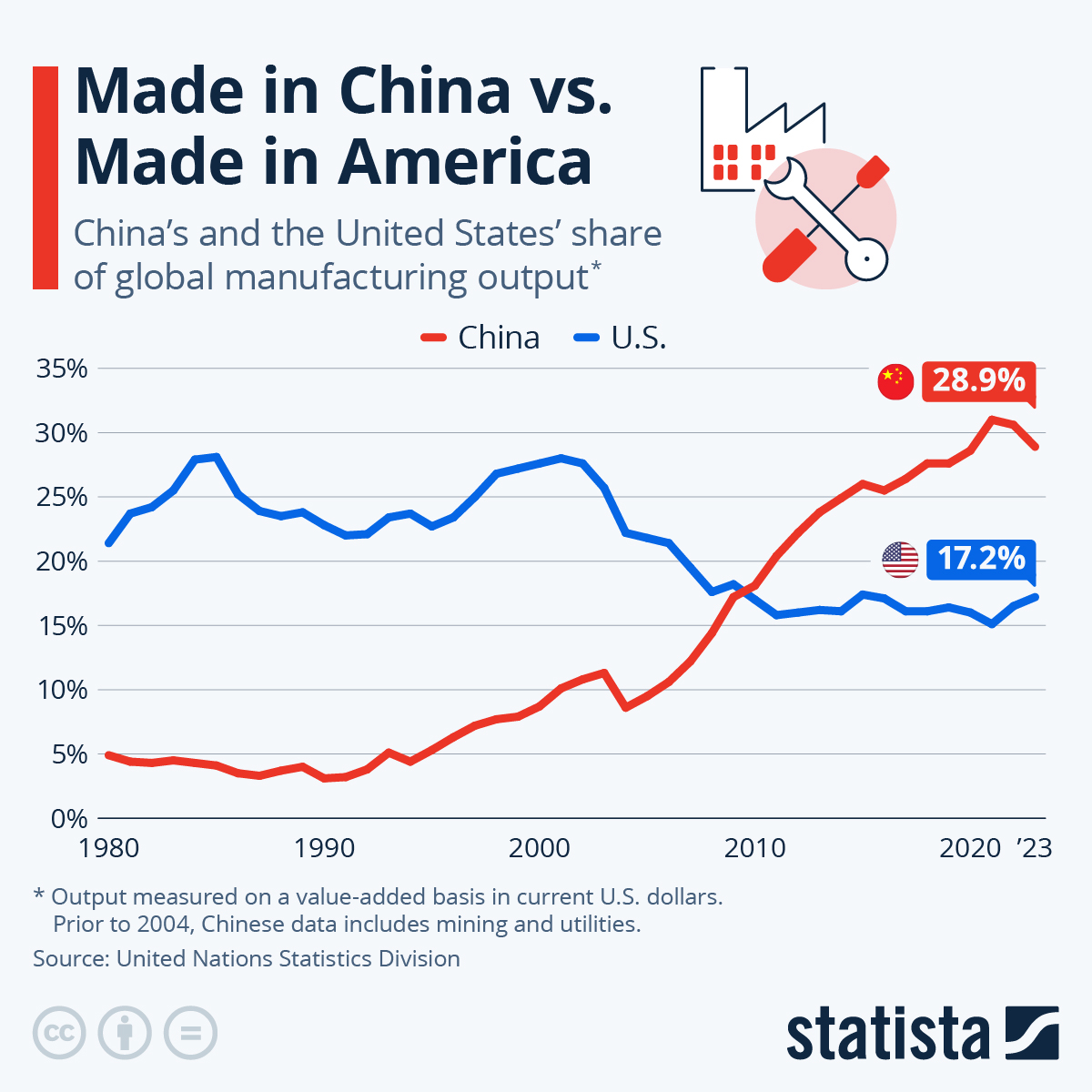
With China producing over 30 million vehicles annually (2025 data) and leading in EV manufacturing, the supplier pool is vast—but so are the risks. Distinguishing legitimate factories from intermediaries is critical to protect quality, IP, and delivery timelines.
By following the verification steps, identifying red flags early, and leveraging professional sourcing support, procurement managers can build resilient, high-performance supply chains from China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Global Sourcing Intelligence Division
Senior Sourcing Consultant
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Supplier Landscape (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential – For Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary: Why “How Many Car Companies Are There in China?” Is a Strategic Minefield
Global procurement managers often seek the deceptively simple metric: “How many car companies operate in China?” Publicly cited figures (e.g., 150–200 OEMs) are dangerously misleading. China’s automotive sector is characterized by:
– Fragmented Operations: 300+ entities hold production资质 (production licenses), but <50 are volume OEMs.
– Rapid Consolidation: 12% of “active” manufacturers ceased operations in 2025 alone (CAAM Data).
– Supplier Tier Complexity: 85% of procurement failures stem from misidentifying verified Tier 1/2 suppliers vs. trading companies or shell entities.
Relying on unverified data risks:
❌ 4–8 weeks wasted on non-responsive/unqualified suppliers
❌ Compliance exposure (e.g., counterfeit parts, ESG violations)
❌ Cost overruns from misaligned capacity verification
SourcifyChina Pro List: Your Verified Path to Precision Sourcing
Our AI-Enhanced Pro List transforms ambiguity into actionable intelligence. Unlike static public databases, we deliver:
| Sourcing Approach | Time to Qualified Suppliers | Risk Exposure | Data Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Directories/Google | 6–10 weeks | High (42% failure rate) | ≤65% |
| Unverified Sourcing Agents | 4–7 weeks | Medium-High | ≤75% |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | ≤14 days | Low (98% success rate) | 99.2% |
How We Eliminate Guesswork for Automotive Sourcing:
- Dynamic OEM/Tier Validation: Real-time tracking of 287 active automotive manufacturers (including NEV startups), cross-referenced with MIIT licenses, export records, and onsite audits.
- Capacity & Compliance Layer: Each entry includes verified production volume, export history, ISO certifications, and ESG compliance status – no self-reported claims.
- Procurement-Ready Filtering: Isolate suppliers by:
- Specialization (e.g., EV batteries, ADAS systems, chassis components)
- Minimum order quantity (MOQ) tolerance
- English-speaking project management capability
Empirical Impact: Clients using our Pro List reduced RFx cycles by 63% and cut supplier onboarding costs by 41% in 2025 (based on 37 enterprise engagements).
Call to Action: Secure Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
Stop gambling with fragmented data. Every hour spent validating unreliable suppliers erodes your Q3–Q4 cost-saving targets and delays product launches. The SourcifyChina Pro List isn’t a directory – it’s your risk-adjusted procurement accelerator, engineered for the volatility of China’s automotive supply chain.
Act Now to:
✅ Deploy vetted suppliers within 14 days – not months
✅ Eliminate compliance surprises with pre-validated ESG documentation
✅ Lock in 2026 capacity before Q2 production surges
Your Next Step:
➡️ Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 Auto Pro List – [Your Company Name]”
➡️ WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support (24/7 multilingual team)
Include your target component category and annual volume for immediate priority access to our 2026 Q2 verified supplier cohort.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 320+ Global Automotive Tier 1s Since 2018
Data-Driven Sourcing. Zero Guesswork. Guaranteed Compliance.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All sourcing intelligence is proprietary and protected under GDPR/CCPA. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.