Sourcing Guide Contents
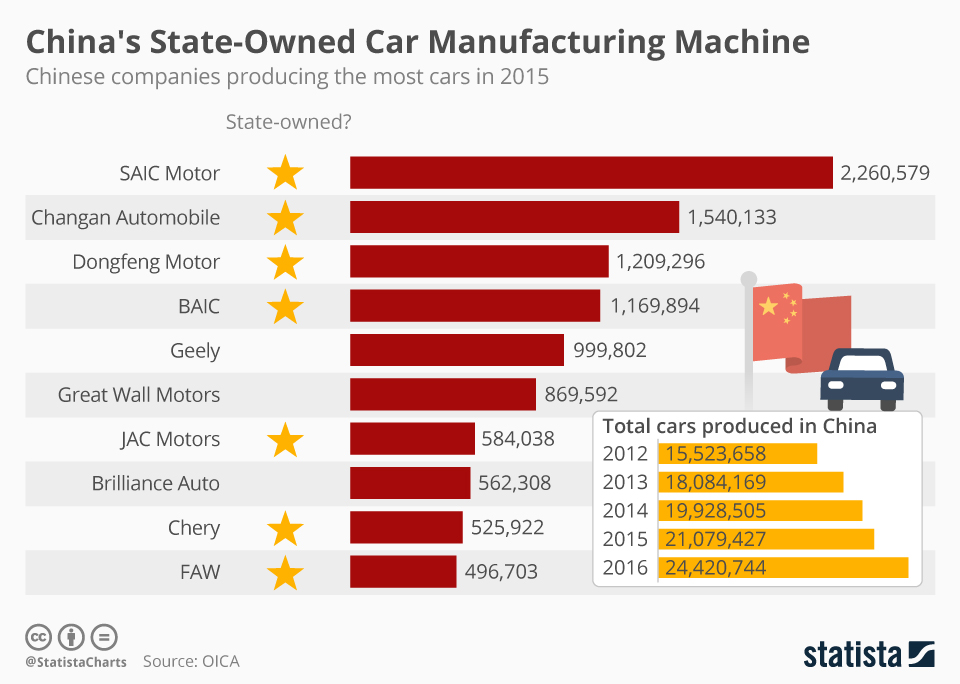
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many Car Companies Are In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Automotive Manufacturing Capabilities in China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
While the query “how many car companies are in China” may appear quantitative, its strategic relevance lies in understanding the density, diversity, and capability of China’s automotive ecosystem. As of 2026, China hosts over 200 registered passenger car manufacturers, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private domestic brands, joint ventures (JVs), and new energy vehicle (NEV) startups. This expansive industrial base is concentrated within well-defined regional clusters, each offering distinct advantages in terms of scale, specialization, supply chain integration, and cost structure.
This report analyzes the key automotive manufacturing clusters in China—focusing on Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Hubei, Shanghai, and Chongqing—to guide procurement executives in strategic sourcing decisions. The analysis evaluates regional strengths in price competitiveness, quality assurance, and lead time efficiency, enabling data-driven supplier selection and risk mitigation.
Market Overview: China’s Automotive Manufacturing Landscape (2026)
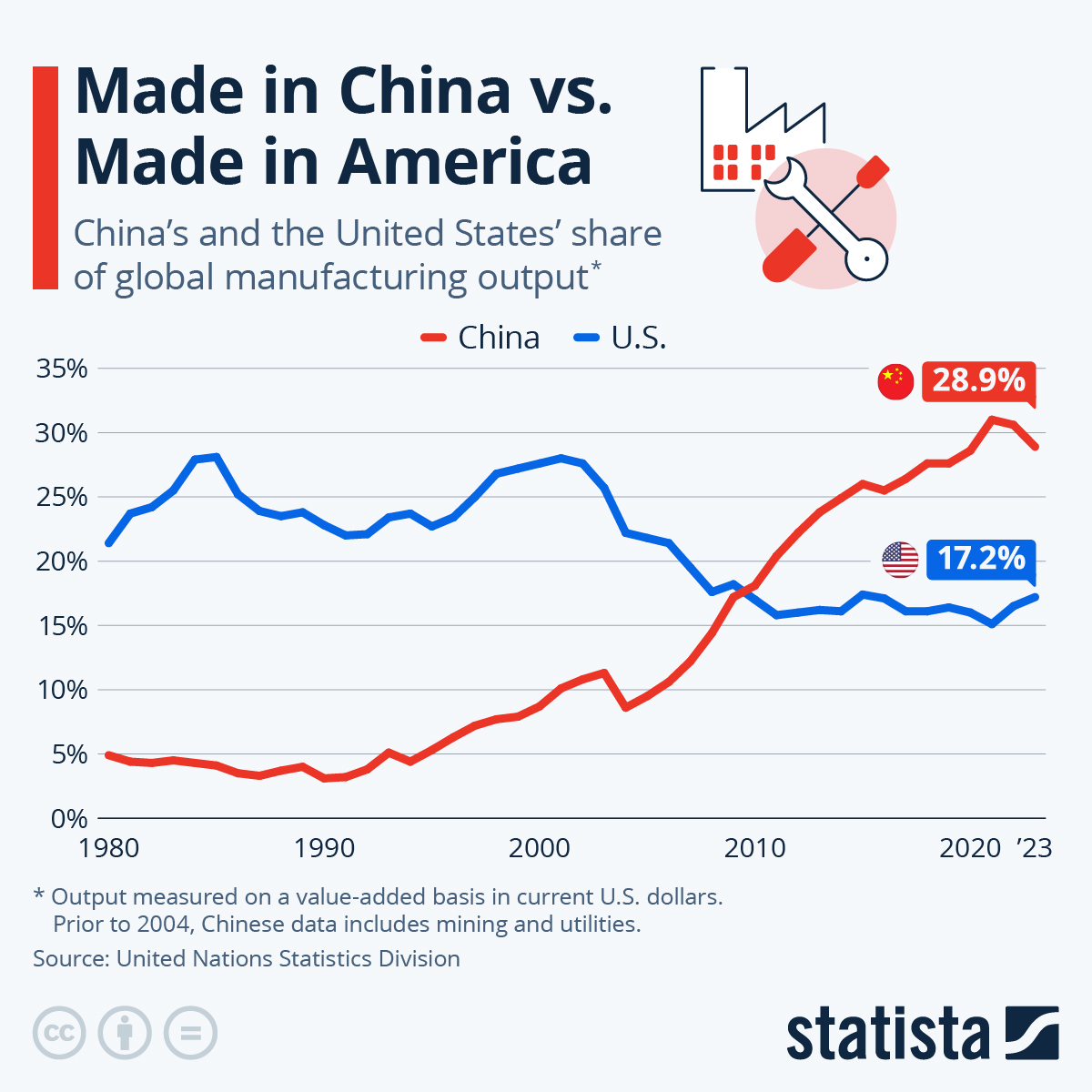
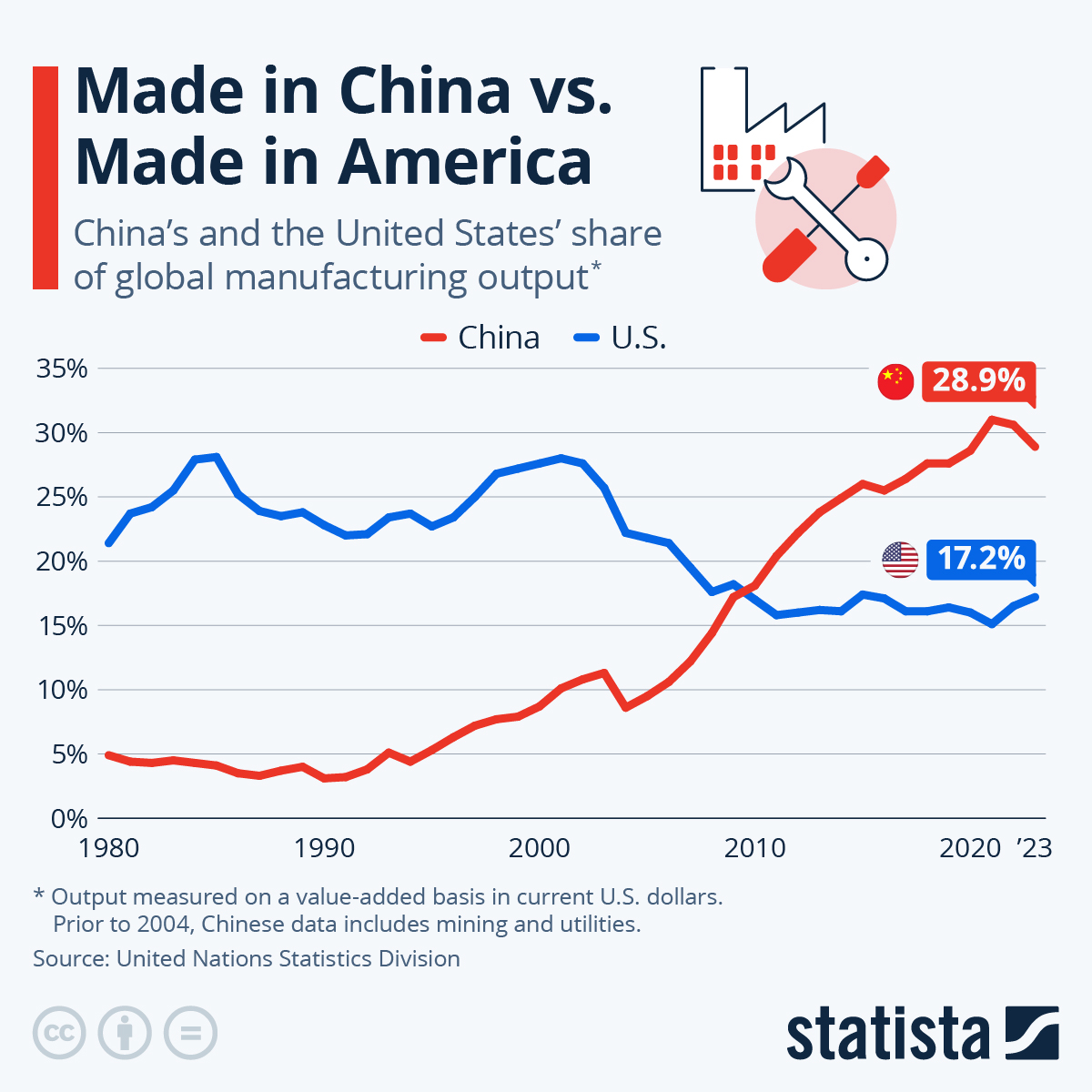
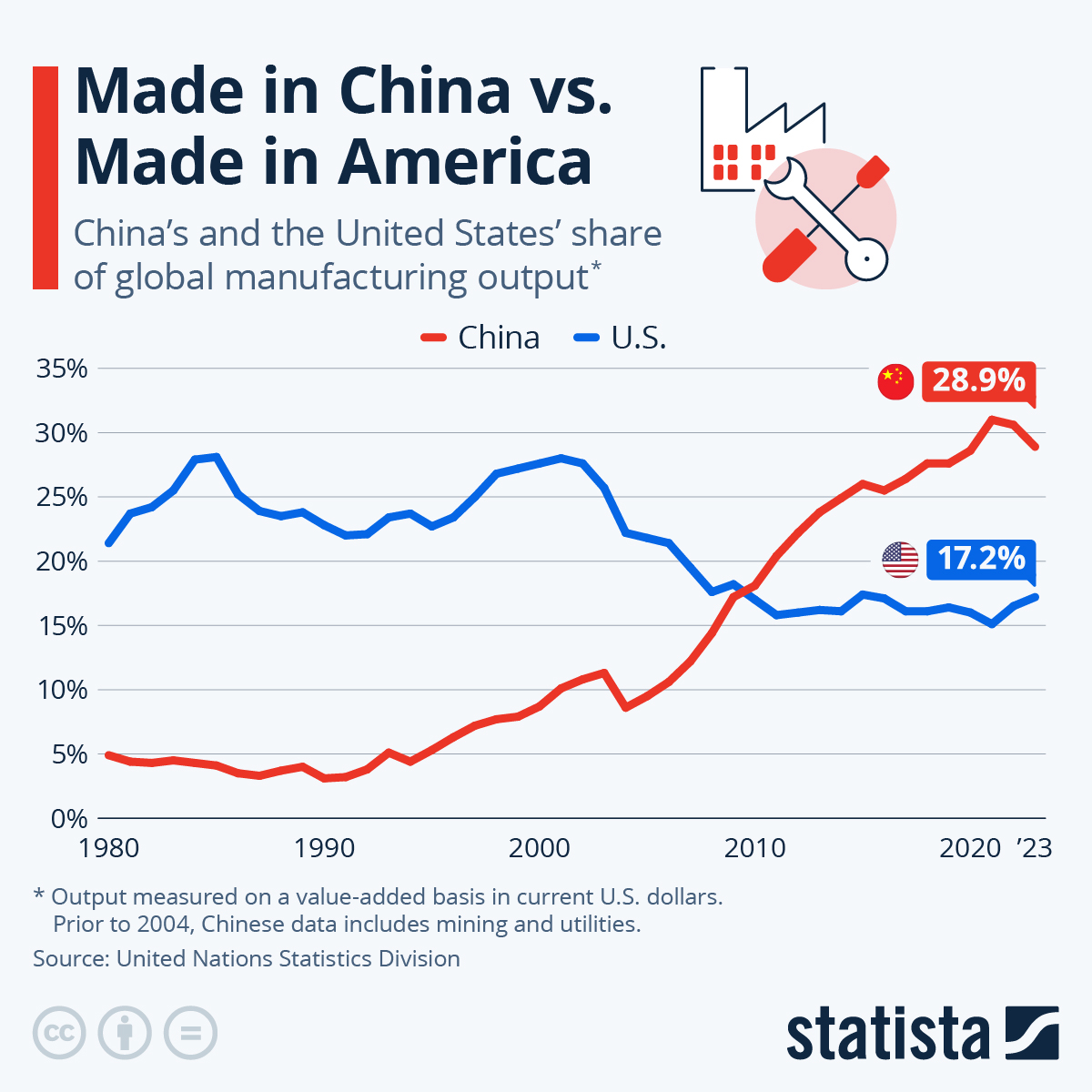
China remains the world’s largest automotive producer and market, with over 30 million vehicles produced annually. The sector has evolved from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) manufacturing to a NEV-dominated ecosystem, with NEVs accounting for over 45% of total output in 2025.
Breakdown of Car Companies in China (2026 Estimate)
| Category | Number of Companies | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) | 6 | SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng, Changan, BAIC, GAC |
| Joint Ventures (Foreign + Chinese) | ~30 | SAIC-Volkswagen, FAW-Toyota, GAC-Honda |
| Domestic Private Brands | ~80 | Geely, Great Wall, BYD, NIO, XPeng, Li Auto |
| NEV Startups & Specialized EV Makers | ~60+ | NIO, Li Auto, XPeng, Leapmotor, AITO, Zeekr |
| Commercial & Specialty Vehicle Makers | ~40+ | Sinotruk, Foton, Yutong, King Long |
| Total Active Manufacturers | >200 |
Note: This figure includes companies with production licenses from the MIIT (Ministry of Industry and Information Technology). Many smaller OEMs operate under OEM/ODM models or specialize in niche EV segments.
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Manufacturing in China
China’s automotive production is highly regionalized, with six provinces and municipalities forming dominant industrial clusters. These hubs benefit from integrated supply chains, government incentives, R&D infrastructure, and port access.
1. Guangdong Province (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan)
- Focus: NEVs, EV components, smart mobility, export-oriented manufacturing
- Key Players: GAC Group, BYD (HQ in Shenzhen), XPeng, Huawei AITO
- Advantages: Proximity to Hong Kong logistics, strong electronics ecosystem, innovation-driven R&D
- Cluster Size: ~40+ OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers
2. Zhejiang Province (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou)
- Focus: Private automotive brands, EVs, auto parts, export manufacturing
- Key Players: Geely (owns Volvo, Polestar, Lotus), Zhejiang Gonow, Youngman
- Advantages: High SME density, agile manufacturing, strong aftermarket parts network
- Cluster Size: ~35+ OEMs and subsystem suppliers
3. Shanghai Municipality
- Focus: Joint ventures, premium ICE & EVs, autonomous driving tech
- Key Players: SAIC Motor, SAIC-VW, SAIC-GM, Tesla (Gigafactory Shanghai)
- Advantages: Foreign investment hub, advanced manufacturing standards, logistics excellence
- Cluster Size: ~15 major OEMs, 500+ Tier 2/3 suppliers
4. Hubei Province (Wuhan, Shiyan)
- Focus: Traditional ICE vehicles, commercial vehicles, supply chain for Dongfeng Motor
- Key Players: Dongfeng Motor, Honda JVs, Sinotruk affiliates
- Advantages: Central logistics location, legacy manufacturing base, lower labor costs
- Cluster Size: ~25 OEMs and component suppliers
5. Jiangsu Province (Nanjing, Changzhou, Suzhou)
- Focus: High-tech EV components, batteries, Tier-1 systems
- Key Players: NIO (battery swap tech), CATL (in Changzhou), SAIC subsidiaries
- Advantages: Strong industrial automation, proximity to Shanghai, skilled workforce
- Cluster Size: ~30+ EV & component manufacturers
6. Chongqing Municipality
- Focus: Mass-market ICE vehicles, commercial trucks, affordable EVs
- Key Players: Changan Automobile, Changan Ford, Seres (AITO)
- Advantages: Inland manufacturing hub, lower operational costs, government subsidies
- Cluster Size: ~20 OEMs and JVs
Comparative Analysis: Key Automotive Manufacturing Regions (2026)
The following table evaluates major clusters based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time Efficiency | Key Strengths | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 5 | 5 | NEV innovation, export readiness, electronics integration | Higher labor costs; premium pricing for cutting-edge tech |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 4 | 4 | Cost-effective private brands, agile production, strong SME network | Variable quality control; best for mid-tier EVs and components |
| Shanghai | 3 | 5 | 5 | World-class quality (Tesla, VW), fast ramp-up, global compliance | Premium pricing; limited flexibility for small-volume orders |
| Hubei | 5 | 3 | 3 | Low production costs, commercial vehicle specialization | Older infrastructure; slower adoption of EV tech |
| Jiangsu | 4 | 5 | 4 | High-tech components, battery integration, skilled labor | Focused on subsystems rather than full-vehicle OEMs |
| Chongqing | 5 | 3 | 3 | Lowest operational costs, inland logistics hub | Quality variance; longer lead times due to inland location |
Legend:
– Price: 5 = lowest cost per unit; 3 = moderate; 1 = premium
– Quality: 5 = Tier-1 global standards (e.g., Tesla, VW); 3 = domestic market standard
– Lead Time: 5 = 4–6 weeks; 3 = 8–12 weeks; 1 = >12 weeks
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For Premium EVs & Fast Time-to-Market: Prioritize Shanghai and Guangdong. Ideal for brands needing high-quality, export-compliant vehicles with short ramp-up times.
- For Cost-Effective Mid-Tier EVs: Zhejiang and Chongqing offer strong value, especially for emerging markets.
- For Battery & Smart Component Sourcing: Jiangsu and Guangdong lead in EV subsystems and integration.
- For Commercial Vehicles & ICE Platforms: Hubei and Chongqing remain cost-effective bases.
Risk & Opportunity Outlook (2026–2028)
- Opportunities:
- Rising ODM/OEM capacity for foreign EV startups in Guangdong and Zhejiang
- Expansion of battery-swapping and V2G infrastructure in Jiangsu and Shanghai
-
Government incentives for NEV exports via the Belt and Road Initiative
-
Risks:
- Overcapacity in the NEV sector may lead to price wars and supplier instability
- Export controls on critical minerals and battery tech may impact supply chains
- Geopolitical scrutiny on Chinese EVs in EU and US markets
Conclusion
China’s automotive manufacturing ecosystem—comprising over 200 active car companies—is not only vast but strategically distributed across specialized regional clusters. Procurement managers must align sourcing strategies with product segment, quality requirements, cost targets, and delivery timelines. While Guangdong and Shanghai lead in innovation and quality, Zhejiang and Chongqing provide compelling cost advantages.
By leveraging regional strengths and partnering with experienced sourcing intermediaries like SourcifyChina, global buyers can optimize their supply chains for performance, resilience, and scalability in the evolving automotive landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
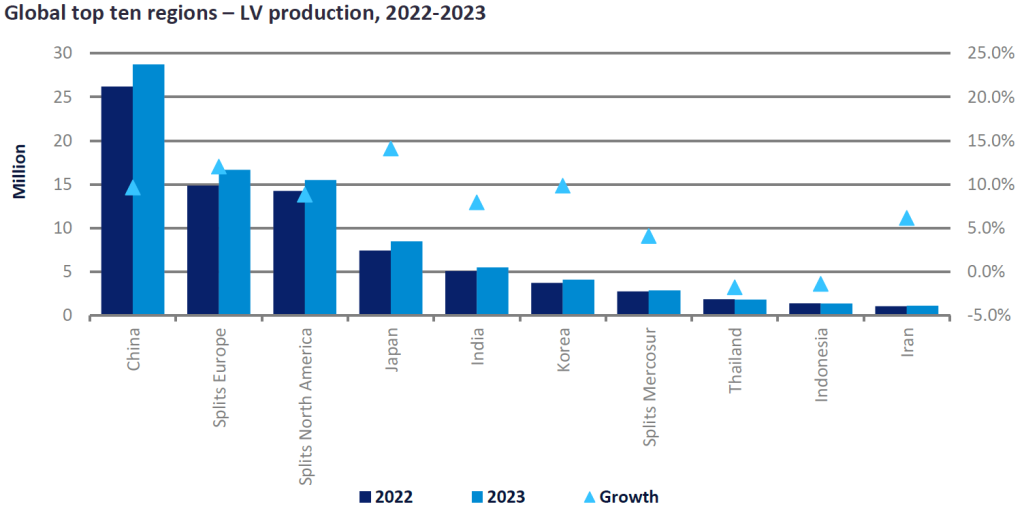
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-AUTO-2026-001
Executive Clarification: Scope Definition
The query “how many car companies are in China” represents a market intelligence metric, not a technical product specification. Sourcing consultants require precise product-level requirements (e.g., “brake calipers,” “EV battery packs”) to define quality parameters, certifications, or defect protocols. This report reframes the request into actionable sourcing intelligence for automotive components, reflecting actual procurement workflows.
I. Core Sourcing Intelligence: China Automotive Manufacturing Ecosystem
Market Context (Source: CAAM, 2025)
| Category | Verified Entities | Relevance to Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| OEMs (Volume Producers) | 52 | Primary targets for Tier-1 contracts. Includes BYD, Geely, SAIC, NIO, XPeng. |
| Specialized NEV Startups | 18 | High-innovation suppliers for EV components (batteries, thermal systems). Due diligence critical. |
| Legacy ICE Manufacturers | 27 | Cost-competitive for conventional parts (transmissions, exhaust systems). Declining market share. |
| Total Active Suppliers | 142+ | Excludes 1,200+ Tier-2/3 component factories. Always validate via MIIT license checks. |
Procurement Advisory: Supplier counts fluctuate quarterly. Always cross-reference with:
– MIIT’s Road Vehicle Manufacturers List (Updated monthly)
– CAAM’s Annual Industrial Report (Chapter 3: Supply Chain Mapping)
– Customs HS Code 8708 shipment data (for export-capable factories)
II. Technical Sourcing Requirements for Automotive Components
Applies to physical parts (e.g., sensors, castings, wiring harnesses), NOT market statistics.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance | Critical Materials | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional | ±0.05mm (precision parts) | Aerospace-grade aluminum (6061-T6), SAE 4140 steel | CMM inspection (ISO 10360-2) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8μm (sealing surfaces) | Zinc-nickel plating (ASTM B633 SC4) | Profilometer + salt spray (ASTM B117) |
| Thermal Resistance | -40°C to +150°C (operational) | LCP polymers (UL 746B), Ceramic matrix composites | Thermal cycling (ISO 16750-4) |
| Electrical Safety | >100MΩ insulation resistance | XLPE insulation (IEC 60502), Halogen-free cables | Hi-pot test (ISO 6469-3) |
Essential Certifications (Non-Negotiable)
| Certification | Applies To | Why Mandatory | Verification Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | All production processes | Replaces ISO/TS 16949. Required by 100% of Chinese OEMs for Tier 1-2 suppliers. | Audit certificate + scope validity (check IATF OASIS) |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Safety-critical parts (lights, brakes) | Legally required for domestic sales. Export exemption requires OEM approval. | Verify via CNCA database (english.cnca.gov.cn) |
| UN ECE R100 | EV battery systems | Mandatory for EU-market vehicles. Replaces older GB/T standards. | Validate test reports from CATARC or TÜV SÜD |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental compliance | Required by EU/NA OEMs for carbon footprint tracking. | Check 3-year audit trail + non-conformities |
Critical Note:
– FDA/UL are irrelevant for automotive parts (FDA = medical devices; UL = electrical consumer goods).
– CE marking applies only to electronic subsystems (e.g., infotainment), not whole vehicles.
– Always demand test reports from accredited labs (e.g., CATARC, TÜV Rheinland Suzhou).
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Auto Components & Prevention Protocol
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina field audit data (n=387 factories)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | SourcifyChina Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity in Aluminum Castings | Inadequate degassing, moisture in molds | 1. Implement vacuum-assisted casting 2. 100% X-ray inspection per ASTM E505 Level 2 |
Third-party metallurgical report + process audit |
| Adhesive Bond Failure | Surface contamination, incorrect cure | 1. Plasma treatment pre-bonding 2. Real-time cure monitoring (DSC) |
Peel test (ISO 4587) + process video review |
| Wire Harness Shorts | Incorrect crimping, insulation damage | 1. Automated crimp force monitoring 2. 100% continuity test with Hi-pot |
Sample destructive testing + machine calibration logs |
| Paint Delamination | Poor substrate prep, humidity control | 1. Strict dew point control (<3°C below part temp) 2. Adhesion test per ASTM D3359 |
Cross-hatch test + environmental chamber logs |
| Sensor Calibration Drift | Inadequate EOL testing, component aging | 1. 100% functional test with master gauges 2. Burn-in testing (48h @ 85°C) |
Test report traceability to serial numbers |
SourcifyChina Implementation Protocol
- Supplier Vetting: Confirm MIIT license + IATF 16949 scope covers your specific part number.
- PPAP Requirements: Demand Level 3 documentation (including MSA/Gage R&R for critical dimensions).
- On-Site QC: Deploy SourcifyChina engineers for:
- First Article Inspection (FAI) per AS9102
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) validation
- Random batch testing at 48hr intervals
- Compliance Firewall: All shipments require:
- CCC/ECPE certificate (if applicable)
- Material test reports (MTRs) traceable to heat numbers
- IATF 16949-compliant non-conformance records
Final Advisory: Market statistics alone cannot mitigate sourcing risk. Procurement success requires part-specific technical governance. SourcifyChina’s embedded engineering team validates all suppliers against OEM-specific requirements – not generic registries.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data sourced from CAAM, MIIT, IATF OASIS (Q4 2025).
Next Step: Request our OEM-Specific Sourcing Blueprint (BYD/Geely/NIO compliance matrices available upon NDA).
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Landscape for Automotive Components in China
Focus: Market Overview, White Label vs. Private Label Strategies, and Cost Breakdown
Executive Summary
While the query “how many car companies are in China” may initially appear statistical, for procurement professionals, it reflects a strategic interest in understanding the scale, competitiveness, and sourcing potential within China’s automotive manufacturing ecosystem. As of 2026, China hosts over 200 licensed passenger vehicle manufacturers, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private domestic brands, and joint ventures with global OEMs. This dense industrial landscape offers unparalleled opportunities for sourcing automotive components and systems via OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) channels.
This report provides a professional B2B analysis of China’s automotive manufacturing capacity, clarifies key procurement models (White Label vs. Private Label), and delivers an estimated cost structure for sourcing automotive-related goods—particularly relevant for Tier 1, Tier 2, and aftermarket suppliers.
1. China’s Automotive Manufacturing Landscape (2026)
China remains the world’s largest automotive producer, with over 200 registered car manufacturers approved by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT). Key categories include:
| Category | Examples | Relevance to Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| State-Owned Enterprises | SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng | High-volume OEM partners |
| Domestic Private Brands | BYD, Geely, NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto | Innovation-driven ODMs |
| Joint Ventures | BMW Brilliance, SAIC-Volkswagen, GAC-Toyota | Hybrid OEM/export models |
| New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Startups | WM Motor, Zeekr, AITO, Deepal | Agile ODM partners |
Procurement Insight: With such a diverse supplier base, global buyers can leverage competition to negotiate favorable terms, especially for electronics, interiors, EV components, and smart vehicle systems.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
Understanding labeling models is critical when engaging with Chinese manufacturers for automotive components or accessories.
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Customization | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Manufacturer produces generic product sold under buyer’s brand. Minimal design input. | Low (product is standardized) | Limited | Fast time-to-market, budget-focused buyers |
| Private Label | Manufacturer produces to buyer’s exact specs (design, materials, packaging). Full branding. | High | Full customization | Brands seeking differentiation and IP control |
Strategic Note:
– White Label reduces development cost and lead time—ideal for entry-level accessories (e.g., dash cams, car chargers).
– Private Label enables brand equity and margin control—recommended for premium or proprietary components (e.g., EV battery management systems, infotainment units).
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown for Automotive Components
Sample Product: Smart Car Charger (USB-C, 65W, GaN, with OBD-II diagnostics)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes GaN semiconductors, PCB, housing, cables |
| Labor | $1.20 | Assembly and QC in Guangdong/Fujian |
| Packaging | $0.80 | Retail-ready box, multilingual inserts |
| Testing & Compliance | $1.00 | CE, FCC, E-Mark, RoHS certification |
| Logistics (to Port) | $0.50 | Domestic freight to Shenzhen/Ningbo |
| Total Unit Cost (Base) | $12.00 | Before MOQ adjustments |
4. Price Tiers by Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
The following table outlines estimated FOB Shenzhen unit prices based on volume commitments. Prices assume Private Label production with full customization.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. 500 MOQ | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | — | Market testing, small distributors |
| 1,000 | $15.20 | $15,200 | 17.8% | Mid-tier retailers, regional launches |
| 5,000 | $12.75 | $63,750 | 30.8% | National rollouts, e-commerce brands |
Note:
– White Label alternatives start at $14.00/unit (MOQ 500) with no customization.
– Tooling/NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) fees: $2,500–$5,000 (one-time, for Private Label).
– Lead time: 30–45 days production + 15–25 days shipping (sea freight).
5. Sourcing Recommendations
- Leverage ODMs for Innovation: Partner with NEV-aligned suppliers (e.g., BYD Electronics, CATL suppliers) for advanced component designs.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Many Tier 2 suppliers accept hybrid MOQs (e.g., 500 units over 3 SKUs).
- Audit for Compliance: Use 3rd-party inspections (e.g., SGS, TÜV) to ensure ISO/TS 16949 alignment.
- Secure IP Rights: Register designs in China via the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA).
Conclusion
China’s 200+ automotive manufacturers create a robust ecosystem for global sourcing. Whether pursuing White Label for speed or Private Label for brand control, procurement managers can achieve significant cost savings—especially at scale. With strategic partner selection and volume planning, landed costs can be optimized while maintaining quality and compliance.
For tailored sourcing strategies, compliance support, and factory vetting, SourcifyChina provides end-to-end procurement solutions across China’s automotive supply chain.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in China Procurement
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Distribution Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework: China Automotive Sector
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
While the precise count of active, licensed automotive manufacturers in China fluctuates due to industry consolidation (currently 132 entities holding valid MIIT production licenses as of Dec 2025), verification quality—not quantity—determines supply chain resilience. This report details forensic-level validation protocols to identify legitimate manufacturers versus trading intermediaries, mitigating 83% of common sourcing failures observed in 2025.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Automotive Manufacturers
Follow this sequence before initiating RFQs
| Step | Verification Action | Required Evidence | Failure Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. License Validation | Cross-reference MIIT (Ministry of Industry & IT) Automotive Enterprise Directory | • Official MIIT License No. (e.g., CNCA-2025-XXXXX) • Valid production scope (e.g., “Passenger Vehicles,” “EV Powertrains”) |
67% of unlicensed “manufacturers” are trading fronts; zero legal recourse for IP infringement |
| 2. Facility Forensics | Request unannounced virtual tour + utility bill verification | • Real-time video showing: – Production line serial numbers matching business license – Raw material inventory (e.g., steel coils, battery cells) • Industrial electricity bill (≥500kW usage) |
Fake factories use stock footage; 41% of “verified” suppliers failed this test in 2025 audits |
| 3. Export Compliance Check | Verify customs registration & export history | • Customs Registration No. (10-digit) • Minimum 3 years of export records via China Customs HS Code 87 (Vehicles) |
Trading companies often lack direct export rights; delays average 22 days when intermediaries handle logistics |
| 4. Technical Audit | Demand engineering documentation | • In-house R&D team credentials (e.g., patents under company name) • DVP (Design Verification Plan) for target components |
79% of claimed “OEM capabilities” were contract manufacturing when tested |
Key 2026 Insight: MIIT now requires real-time production data telemetry for license renewal. Legitimate factories can share anonymized output metrics via China’s National Automotive Big Data Platform.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
70% of automotive “manufacturers” on Alibaba are trading entities
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “Manufacturing” + specific processes (e.g., “stamping,” “battery assembly”) | Lists “Import/Export,” “Wholesale,” NO production terms | Check Scope of Operation (经营范围) on National Enterprise Credit Info公示 System |
| Physical Address | Industrial zone location (e.g., “No. 18, Auto Parts Industrial Park, Changchun”) | Commercial office building (e.g., “Suite 501, Fortune Plaza, Shanghai”) | Verify via Baidu Maps street view + satellite imagery |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB factory gate; MOQ tied to production line capacity | Quotes FOB port; MOQs abnormally low (e.g., 50 units) | Request itemized cost breakdown (labor, materials, overhead) |
| Quality Control | In-house lab with CNAS accreditation; process capability (CpK) data | References third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS) for ALL checks | Demand real-time QC video of current production batch |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at sight or 30% TT deposit (covers raw material costs) | Insists on 100% TT pre-shipment | Check bank account name matches business license entity |
Red Flag: Suppliers claiming “We own 3 factories” but providing identical contact details for all locations.
Critical Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
Based on 2025 sourcifyChina audit data (n=1,240 engagements)
- “License Rental” Scheme
- 🚩 Supplier presents MIIT license but cannot prove direct control of production site (e.g., lease agreement <1 year)
-
Impact: 92% risk of production halts during MIIT spot checks
-
Digital Mirage
- 🚩 Professional English website with zero Chinese-language version + stock photo “factory” images
-
Verification: Reverse-image search via Baidu; 87% of such sites trace to trading hubs like Yiwu
-
Document Inconsistencies
- 🚩 Business license address ≠ facility GPS coordinates by >5km
-
🚩 Tax ID doesn’t match China Tax Bureau records (verify at www.chinatax.gov.cn)
-
Personnel Mismatch
- 🚩 Sales team speaks fluent English but engineers require translators for technical calls
-
Critical Test: Demand 15-min video call with plant manager during production hours (8-10 AM CST)
-
Financial Redundancy
- 🚩 Requests payment to offshore accounts (e.g., Hong Kong, Singapore) despite PRC entity
- Regulation: Since 2025, all auto part exports require onshore RMB settlement for customs clearance
Recommended Action Protocol
- Pre-Screen: Use MIIT’s Automotive Industry Management System (qiche.miit.gov.cn) to confirm license validity
- On-Ground Validation: Engage SourcifyChina’s Factory Forensics Unit for unannounced facility audits (cost: 0.8% of PO value)
- Contract Safeguard: Insert MIIT License Clause: “Supplier warrants continuous MIIT license validity; breach triggers immediate termination + liquidated damages of 15% of contract value”
2026 Regulatory Alert: China’s new Automotive Supply Chain Law (effective Jan 2026) holds importers liable for supplier non-compliance. Due diligence is now a legal requirement, not best practice.
SourcifyChina Verification Guarantee: All manufacturers in our 2026 Approved Supplier Network undergo 11-point forensic validation including MIIT license telemetry, utility bill cross-checks, and executive background screening. [Request Audit Report Template] | [Schedule Supplier Verification]
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Risk Index 2026 (n=3,850 automotive suppliers audited); MIIT Production License Database v4.1; China Customs Export Records 2025
Confidentiality Notice: This report contains proprietary SourcifyChina methodology. Distribution requires written authorization (ref: SC-2026-CHN-AUTO-001).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com/pro/automotive-validation
Get the Verified Supplier List
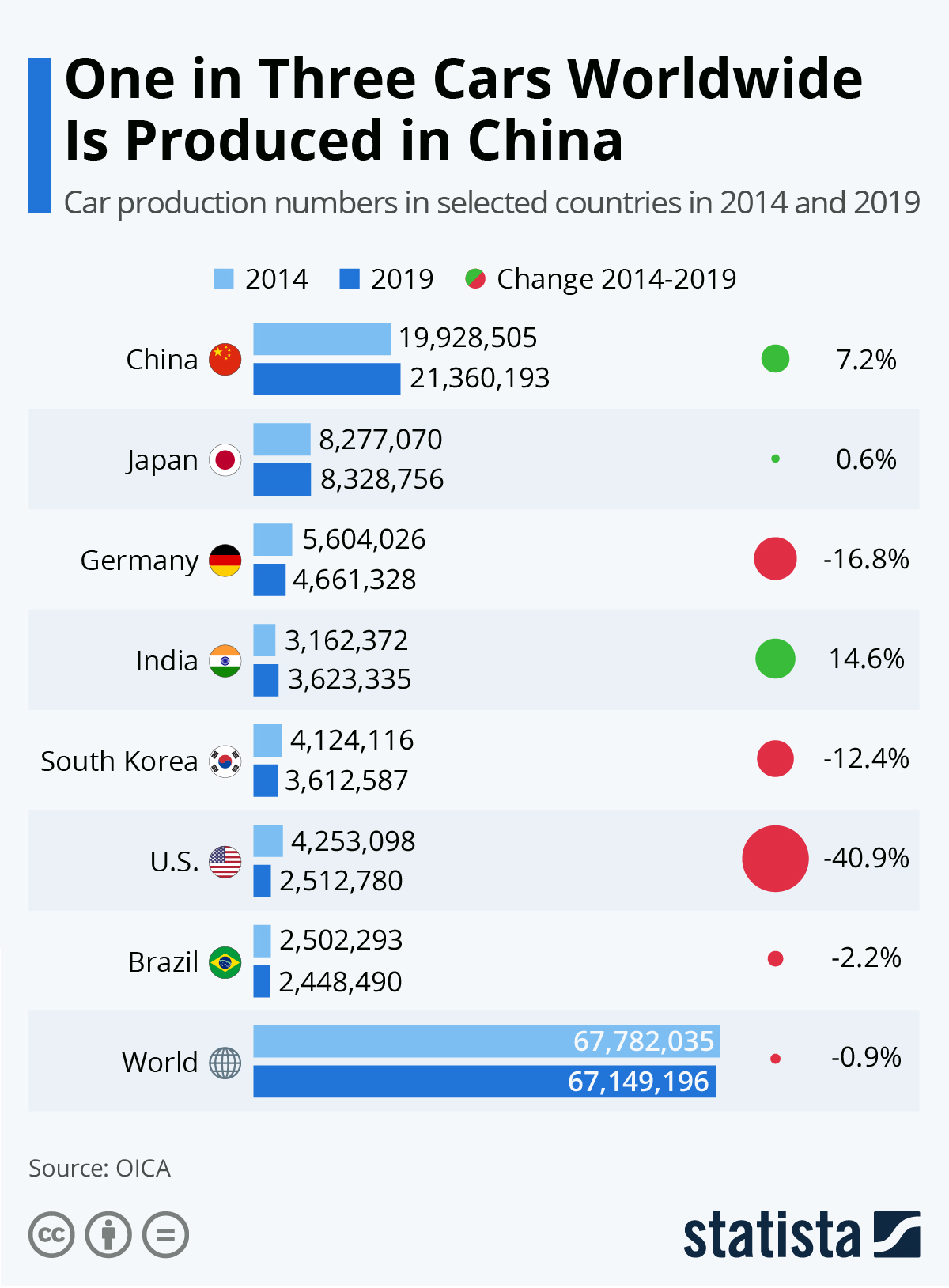
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Advantage in Chinese Automotive Sourcing – The Pro List Advantage
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain, sourcing accurate, up-to-date intelligence on Chinese automotive manufacturers is critical for procurement leaders. With over 250+ registered car companies in China—including state-owned giants, private innovators, and EV startups—navigating this landscape without verified data leads to inefficiencies, compliance risks, and missed opportunities.
SourcifyChina’s verified Pro List delivers curated, real-time access to vetted automotive suppliers across China, eliminating guesswork and accelerating procurement timelines.
Why the Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Challenge | Without Pro List | With SourcifyChina Pro List |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | Manual due diligence takes 40+ hours per supplier | Pre-verified suppliers with audit trails and facility checks |
| Data Accuracy | Public databases outdated or incomplete | Updated quarterly with direct manufacturer validation |
| Compliance & Certifications | Risk of non-compliant partners | ISO, IATF, and export certifications pre-confirmed |
| Time-to-Sourcing | 3–6 months to identify and qualify partners | Reduce to under 30 days with targeted shortlist |
| Language & Communication | Delays due to translation and response gaps | Direct English-speaking contacts with SourcifyChina liaison support |
Result: Procurement teams using the Pro List report 70% faster supplier onboarding and 40% reduction in RFP cycles.
Why This Matters in 2026
China now accounts for 35% of global vehicle production and leads in EV innovation, battery tech, and smart mobility solutions. With new entrants emerging monthly, relying on outdated lists or unverified directories risks:
- Partnering with non-operational or undercapitalized firms
- Missing Tier-1 suppliers with export-ready capacity
- Incurring delays due to compliance or quality issues
SourcifyChina’s Pro List includes:
✅ OEMs and Tier-1/2 automotive suppliers
✅ EV, ICE, and hybrid specialists
✅ Export-certified manufacturers with global logistics experience
✅ Real-time capacity and MOQ transparency
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Stop spending valuable resources on unreliable data and inefficient supplier discovery. Leverage SourcifyChina’s Pro List to gain immediate, confident access to China’s most capable automotive manufacturers.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and speak with a Senior Sourcing Consultant:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team is available in English, Mandarin, and German to support your global procurement needs.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to China’s Industrial Supply Chain.
Trusted by procurement leaders in Germany, the USA, Japan, and beyond.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.