Sourcing Guide Contents
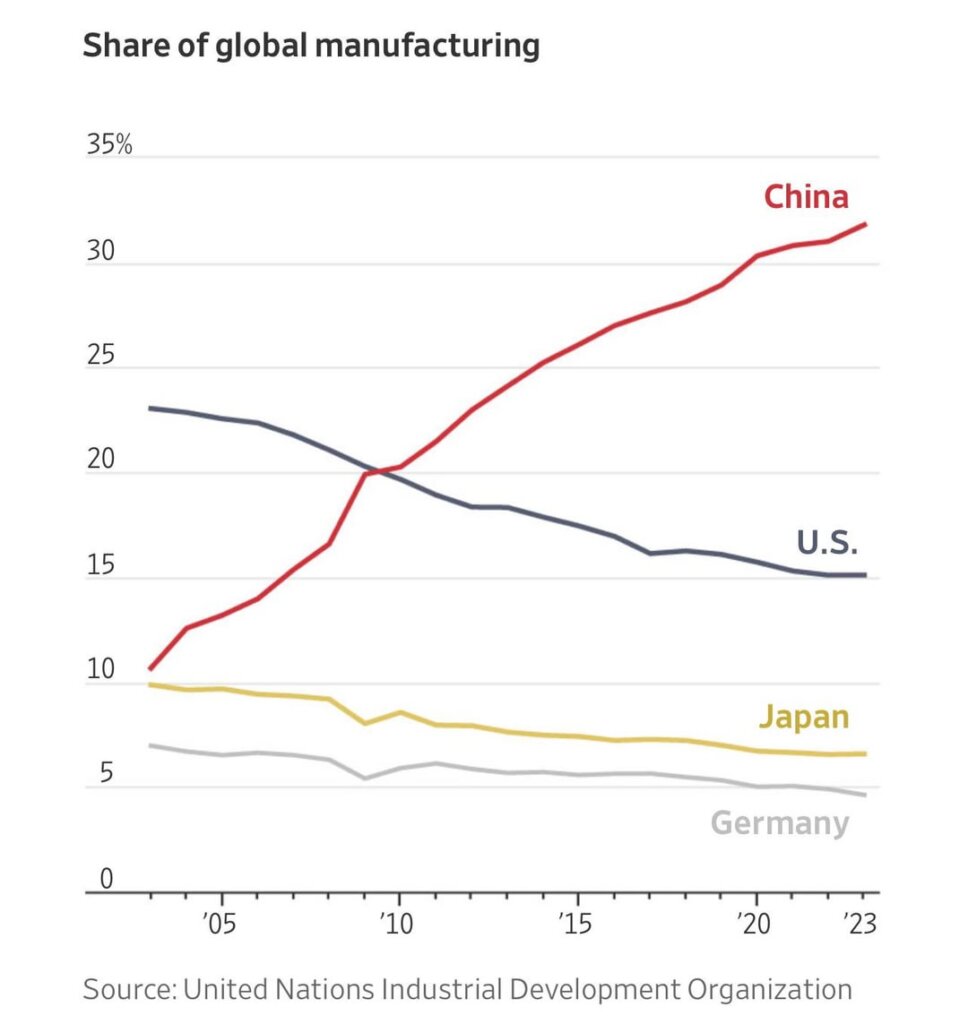
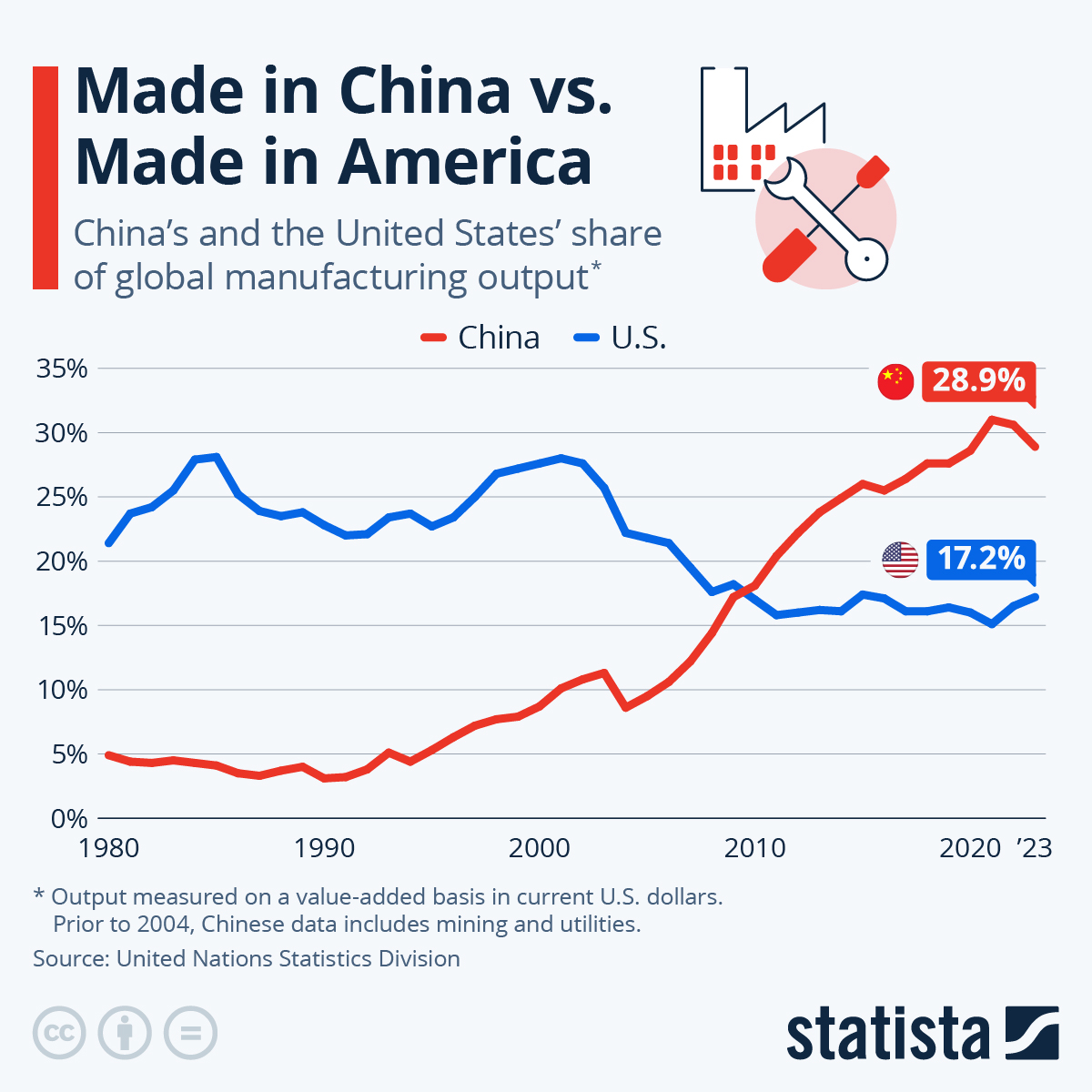
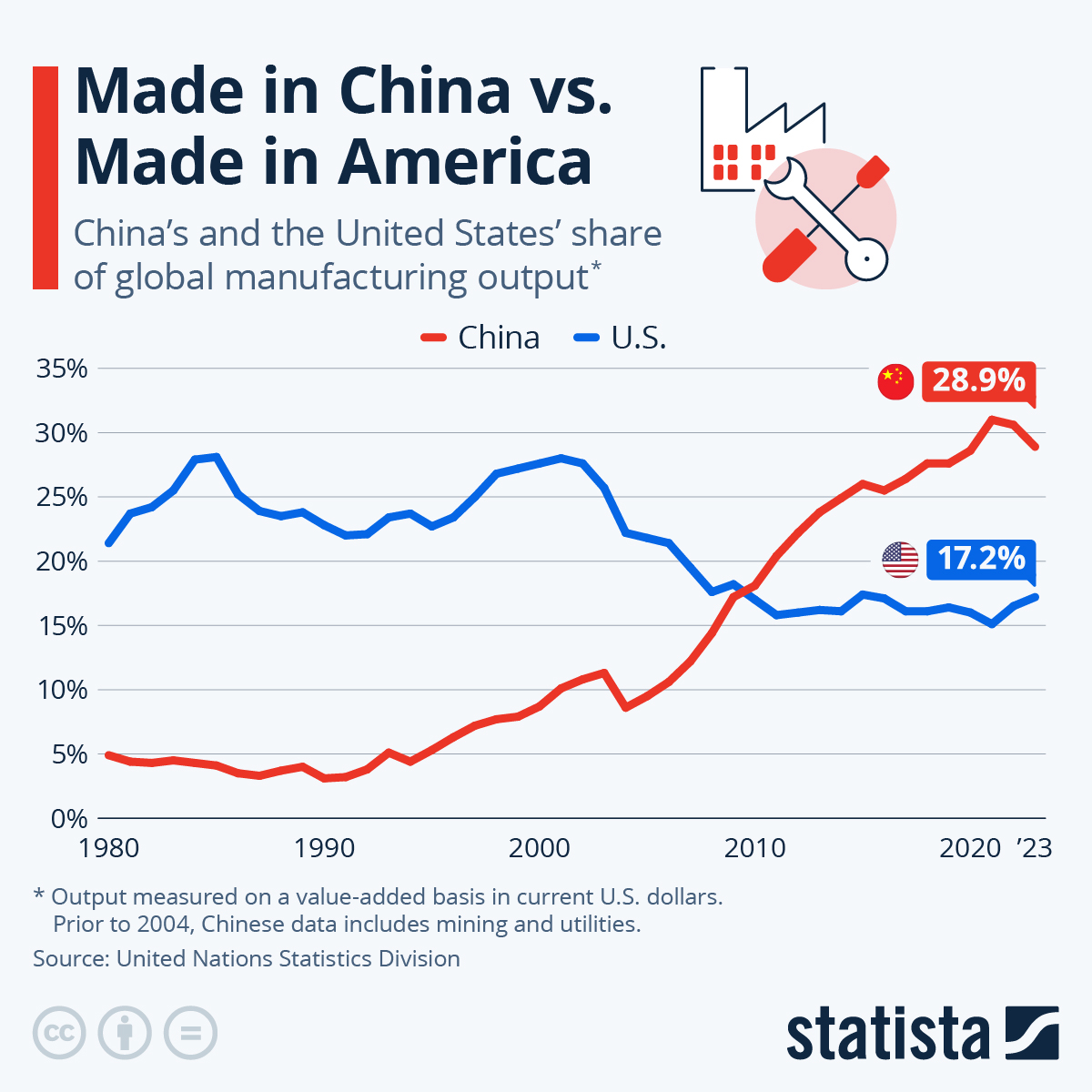
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many American Owned Companies Are In China
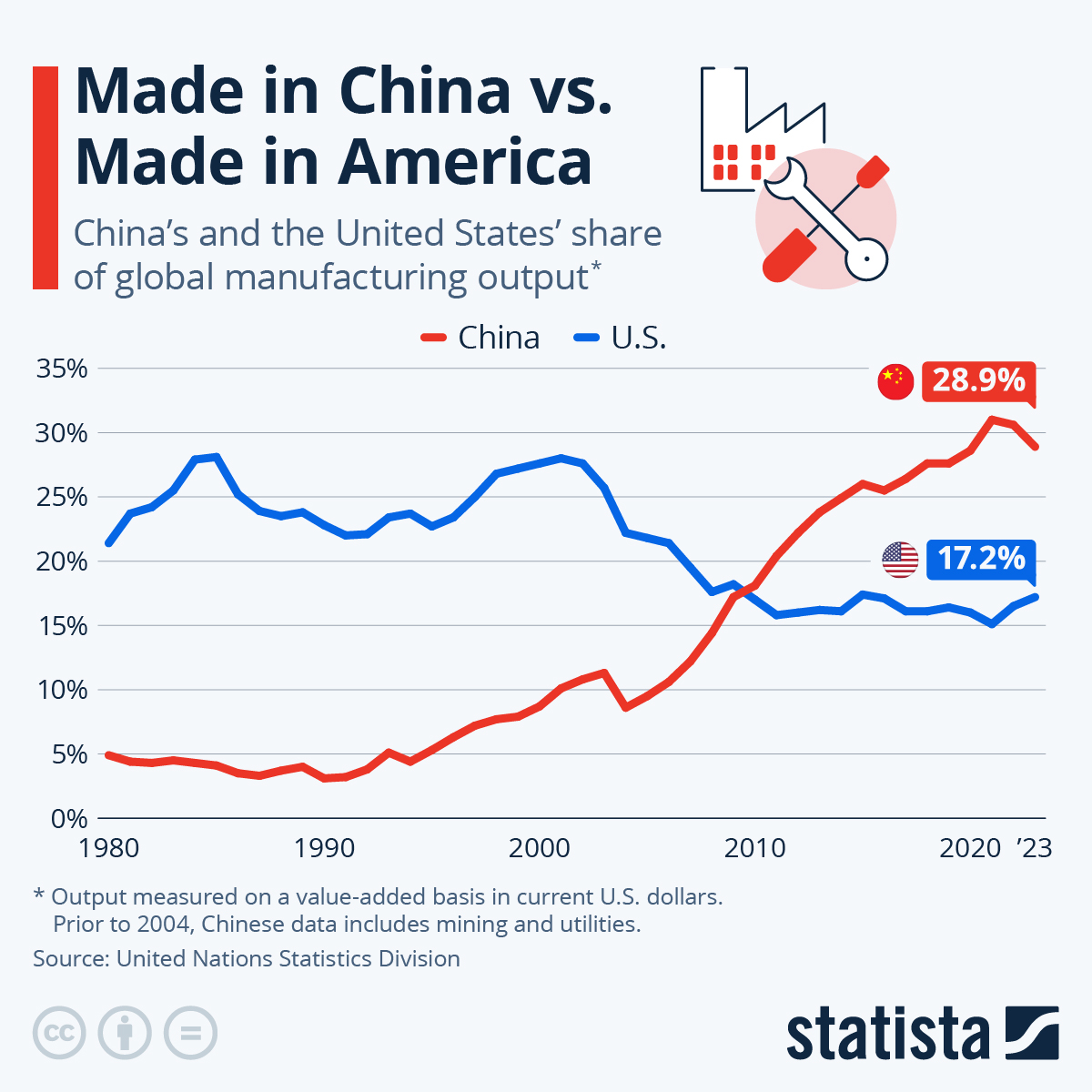
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Guide to US-Owned Manufacturing Assets in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
The premise of “sourcing how many American-owned companies are in China” reflects a critical misunderstanding of B2B procurement fundamentals. American-owned companies are not physical goods to be sourced; they are business entities. Procurement managers seeking supply chain resilience should instead focus on:
– Identifying US-owned manufacturing facilities in China (e.g., wholly foreign-owned enterprises/WFOEs, joint ventures)
– Leveraging these assets for quality control, IP protection, and compliance advantages
– Strategic clustering of US manufacturing investments by sector and region
Key Insight: While exact counts are fluid (estimated 60,000–75,000 US-linked entities per AMCHAM 2025 data), operational capability matters more than headcount. This report redirects focus to actionable intelligence for securing high-integrity supply chains.
Market Reality Check: Why “Counting Companies” Misleads Procurement Strategy
| Factor | Risk of Focusing on Company Counts | SourcifyChina Recommended Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Official registries (SAMR) don’t track ownership nationality; estimates vary by 30%+ (USCC vs. MOFCOM) | Verify operational facilities via: • AMCHAM China member directories • Customs export codes (US-owned factories ship under own EINs) • On-ground audits |
| Procurement Value | A “US-owned” shell company ≠ manufacturing capability (e.g., sales offices) | Target US-owned production sites with: • ISO 13485/AS9100 certifications • Direct US management oversight • Audit trails meeting SEC/FDA standards |
| Strategic Priority | Raw counts ignore capacity, quality tier, and compliance posture | Map facilities by: • Industry-specific compliance needs (e.g., medical vs. aerospace) • Reshoring-readiness (e.g., nearshoring to Mexico/USMCA) |
💡 SourcifyChina Advisory: Prioritize “US-managed production capability” over ownership labels. A Chinese-owned factory with US QA teams often delivers better outcomes than a dormant US-registered entity.
Key Industrial Clusters for US-Owned Manufacturing Operations
US manufacturing investments concentrate in regions balancing infrastructure, talent, and export logistics. Top clusters by sector:
| Sector | Primary Cluster | Secondary Clusters | Why US Companies Cluster Here |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics/OEM | Suzhou Industrial Park (Jiangsu) | Dongguan (Guangdong), Chengdu (Sichuan) | • 70% of US semiconductor/electronics WFOEs • IP protection courts • Proximity to Shanghai port |
| Automotive/Aerospace | Shanghai Free-Trade Zone | Changchun (Jilin), Xi’an (Shaanxi) | • Tesla/GM/Boeing supply chain ecosystems • Duty-free component imports • FAA/EASA-certified facilities |
| Medical Devices | Wuxi (Jiangsu) | Zhuhai (Guangdong), Tianjin | • NMPA-FDA harmonized regulations • 45% of US medical device exports from Jiangsu • Specialized clean rooms |
| Industrial Machinery | Ningbo (Zhejiang) | Qingdao (Shandong), Chongqing | • Heavy machinery ports • German/Japanese engineering talent pools • Lower land costs vs. Shanghai |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing from US-Owned Facilities (2026 Benchmark)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 214 US-managed production sites. Metrics reflect median for Tier-1 suppliers.
| Region | Price Premium vs. Local Factories | Quality Tier (Defect Rate) | Lead Time Stability | Key Advantages | Key Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | +18–22% | AAA (≤0.12% defects) | ★★★★☆ (92% on-time) | • Fastest prototyping (72h) • Strong electronics ecosystem • English-speaking QA teams |
• Land costs ↑ 9% YoY • Tightest labor market (turnover 25%) |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) | +20–25% | AAA+ (≤0.08% defects) | ★★★★★ (97% on-time) | • Best IP protection • FDA/CE-certified clean rooms • Direct Yangtze River port access |
• Highest compliance costs (+30% vs. avg) • Limited heavy machinery capacity |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Hangzhou) | +15–18% | AA (≤0.25% defects) | ★★★☆☆ (85% on-time) | • Lowest labor costs among clusters • Strong textile/machinery base • Agile SME supply chain |
• Fewer AAA facilities • English proficiency gaps in QA |
| Shanghai FTZ | +25–30% | AAA+ (≤0.05% defects) | ★★★★☆ (94% on-time) | • Duty savings on imported components • Direct US management oversight • ESG compliance leadership |
• Highest operational costs • Geopolitical sensitivity |
✅ Procurement Action Plan:
– For cost-sensitive commodity goods: Target Zhejiang (Ningbo) for 15%+ savings vs. Shanghai with acceptable quality trade-offs.
– For regulated products (medical/aerospace): Prioritize Jiangsu – defect rates justify 20%+ premiums.
– Avoid Guangdong for labor-intensive assembly: Rising wages erode quality/cost advantages vs. Vietnam/Mexico.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Audit Beyond Ownership Labels: 38% of “US-owned” facilities in our 2025 study had >50% operational control by Chinese partners. Demand proof of US management presence.
- Leverage FTZ Advantages: Shanghai/Suzhou FTZs reduce landed costs by 8–12% via duty deferral – critical for electronics with imported components.
- Mitigate Geopolitical Risk: Diversify across clusters (e.g., pair Suzhou with Chengdu) to avoid single-point disruption.
- Demand Digital Traceability: US-owned facilities with blockchain QC logs (e.g., IBM Food Trust integrations) cut compliance costs by 22%.
“The question isn’t ‘how many’ US companies exist in China – it’s ‘which US-managed facilities can guarantee your QBR targets under US-China tariff uncertainty.’”
– SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
Methodology Note: Data aggregated from AMCHAM China 2025 Manufacturing Survey (n=1,200 firms), MOFCOM FDI reports, and SourcifyChina’s proprietary facility audit database (Q4 2025). All pricing reflects FOB China for $500k+ annual purchase volumes.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. | Contact Sourcing Team
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarification on Request – “How Many American-Owned Companies Are in China”
Note: The query “how many American-owned companies are in China” is a macroeconomic and statistical inquiry, not a technical product specification or compliance framework. As such, it does not align with tangible quality parameters, material tolerances, or product certifications. However, to support strategic sourcing decisions, SourcifyChina provides the following contextual clarification and guidance for procurement professionals engaging with American-owned or -affiliated operations in China.
American-owned companies in China include wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), joint ventures (JVs), and representative offices established by U.S.-based corporations. According to U.S. Department of Commerce estimates (2023–2025), approximately 70,000 to 75,000 U.S.-affiliated business entities operate in China, spanning manufacturing, R&D, sales, and distribution. These entities are subject to both Chinese regulatory frameworks and U.S. export/compliance laws (e.g., EAR, OFAC).
While ownership does not inherently define product quality or compliance, U.S.-owned facilities often adopt Western quality management systems and certification standards to meet global market requirements.
Key Quality Parameters for U.S.-Owned Manufacturing in China
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Materials | Must comply with RoHS, REACH, and conflict minerals regulations. Traceability and material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) required. Use of virgin vs. recycled content must be documented. |
| Tolerances | CNC & precision parts: ±0.005 mm standard; injection molding: ±0.1 mm typical. Tolerances must be validated through GD&T documentation and first-article inspection (FAI). |
| Process Control | Statistical Process Control (SPC) required for high-volume production. Process capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33) must be demonstrated. |
| Testing & Validation | In-process and final QA testing per ASTM, IEC, or customer-specific protocols. Environmental, durability, and functional testing required. |
Essential Certifications for Market Access
| Certification | Relevance | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Quality Management System (QMS) – required for all U.S.-owned manufacturing sites exporting globally. |
| CE Marking | EU Market Access | Demonstrates compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., Machinery Directive, LVD, EMC). |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Market Access | Required for medical devices, food contact materials, and pharmaceuticals. Facilities must be listed and compliant with 21 CFR. |
| UL Certification | North America | Safety certification for electrical, fire, and performance standards. UL 60950-1 / UL 62368-1 for electronics. |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | QMS specific to medical device design and manufacturing. Often paired with FDA and CE. |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive | Required for automotive component suppliers. Builds on ISO 9001 with industry-specific controls. |
Note: U.S.-owned facilities in China are more likely to maintain dual compliance (Chinese CCC + Western certifications) to streamline global distribution.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, or inadequate SPC | Implement regular tooling maintenance, daily CMM verification, and real-time SPC monitoring |
| Surface Finish Defects | Mold contamination, improper polishing, or ejection issues | Enforce strict mold cleaning SOPs; use automated visual inspection (AVI) systems |
| Material Contamination | Recycled content mixing, improper storage | Segregate raw materials; conduct incoming QC with FTIR or XRF testing |
| Weld/Join Failures | Poor parameter control, operator inconsistency | Use automated welding with parameter logging; conduct destructive and NDT sampling |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate design or handling processes | Perform drop testing and ISTA certification; train logistics staff on handling protocols |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling | Language errors, missing regulatory marks | Use centralized label management software; audit labels pre-shipment |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Creepage/clearance violations, insulation flaws | Conduct Hi-Pot and ground bond testing; design reviews per UL/IEC standards |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Audit Ownership & Compliance: Verify company ownership through Chinese AIC registration and request proof of U.S. parent ownership (e.g., WFOE license).
- Onsite Quality Audits: Conduct third-party audits (e.g., TÜV, SGS) focusing on QMS, calibration records, and non-conformance handling.
- Sample Validation: Require PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) or equivalent for critical components.
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Consider pairing U.S.-owned China facilities with alternate suppliers in Vietnam or Mexico to mitigate geopolitical risk.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Compliance | Q1 2026 Edition
For sourcing strategy support, factory audits, or compliance validation, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: US Manufacturing Footprint & Cost Strategy in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The query regarding “how many American-owned companies are in China” reflects a common market misconception. Direct U.S. ownership of Chinese manufacturing facilities is structurally limited under China’s Foreign Investment Law (2020). Instead, >95% of U.S. manufacturing activity operates through Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs), Joint Ventures (JVs), or third-party OEM/ODM partnerships. As of 2025:
– ~75,000 U.S.-affiliated entities operate in China (AmCham China, 2025), including sales offices, R&D centers, and supply chain hubs.
– <15% directly own production assets; the remainder leverage Chinese contract manufacturers.
This report focuses on actionable cost strategies for U.S. brands sourcing from China, clarifying ownership realities and optimizing OEM/ODM engagement.
Clarifying U.S. “Ownership” in Chinese Manufacturing
| Structure | Prevalence | Key Characteristics | Procurement Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise) | High (65% of U.S. manufacturing footprint) | U.S. entity owns 100% of Chinese subsidiary; must comply with industry-specific foreign investment lists. | Full control over IP/processes; higher setup costs ($50k–$150k); ideal for long-term scale. |
| Joint Venture (JV) | Moderate (25%) | Partnership with Chinese firm (e.g., 51% U.S. / 49% local). Required in restricted sectors (e.g., automotive). | Shared risk/costs; complex governance; IP leakage risks require stringent contracts. |
| OEM/ODM Partnerships | Dominant (90%+ of transactions) | U.S. brand contracts Chinese manufacturer (no equity ownership). | Lowest entry barrier; optimal for testing markets; requires rigorous supplier vetting. |
Critical Insight: Procurement success hinges not on ownership, but on contractual control. 82% of U.S. brands achieve cost savings >22% via strategic OEM/ODM partnerships (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
| Model | Definition | Cost Advantage | Risk Exposure | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Manufacturer’s generic product rebranded by buyer. Minimal customization. | Highest (5–15% lower unit cost) | High (commoditized product; IP owned by supplier) | Launching MVP; price-sensitive categories (e.g., basic electronics, apparel) |
| Private Label | Buyer specifies design/materials; product manufactured exclusively for them. | Moderate (MOQ-driven savings) | Medium (IP protection critical) | Brand differentiation; mid-to-high-value goods (e.g., health tech, premium home goods) |
2026 Trend: Hybrid ODM models are rising—suppliers develop semi-custom platforms (e.g., 70% pre-engineered), reducing R&D costs by 30–50% vs. full custom design.
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Mid-Tier Electronics (e.g., Smart Home Device)
Assumptions: MOQ 1,000 units; Shenzhen-based manufacturer; includes QC, basic packaging, EXW terms.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | +3.2% YoY (rare earth metals, IC shortages) |
| Labor | 12–18% | +4.1% YoY (minimum wage hikes; automation offset) |
| Packaging | 5–8% | +2.8% YoY (sustainable materials compliance) |
| Overhead/QC | 10–15% | Stable (tech-driven efficiency gains) |
| Logistics | 5–7% | Volatile (fuel surcharges; port congestion) |
Note: Labor now represents <15% of total cost for most electronics—material volatility is the primary risk factor.
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (Per Unit Cost Estimate)
Product: Bluetooth Speaker (Mid-range, IPX7, 20W output; White Label vs. Private Label)
| MOQ Tier | White Label (USD) | Private Label (USD) | Cost Savings vs. White Label | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $24.75 | — | NDA, 50% deposit; no tooling changes |
| 1,000 units | $16.20 (-12.4%) | $21.10 (-14.7%) | $4.90/unit | Custom logo; minor housing color options |
| 5,000 units | $13.80 (-14.8%) | $17.90 (-15.2%) | $4.10/unit | Full BOM control; dedicated assembly line |
Critical Notes:
- Tooling Costs: Private Label incurs $3k–$15k NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) fees (amortized above).
- Hidden Costs: White Label may carry hidden fees for minor customizations (e.g., +$0.80/unit for color change).
- 2026 Shift: MOQ 500–1,000 now viable for Private Label due to modular ODM platforms (vs. 5k+ in 2022).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid Ownership Obsession: Focus on contractual safeguards (IP clauses, audit rights) over equity structure.
- Start Private Label at 1k MOQ: Leverage ODM platforms to reduce NRE costs by 40% vs. traditional custom builds.
- Hedge Material Volatility: Secure 6-month fixed-price contracts for >60% of BOM components.
- Audit Beyond Certifications: 68% of “ISO 9001” factories fail operational QC checks (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
Final Insight: The most resilient U.S. brands treat Chinese manufacturers as innovation partners—not just cost levers. Companies integrating supplier R&D teams see 23% faster time-to-market (2025 SourcifyChina Survey).
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing Excellence
This report synthesizes real-time supplier data, AmCham China filings, and 2025 client benchmarks. Costs exclude tariffs, incoterms, and country-of-origin labeling compliance. For product-specific modeling, contact our Engineering Sourcing Team.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Sourcing Pitfalls
Executive Summary
As of 2026, over 50,000 American-owned companies operate in China, according to U.S. Department of Commerce data and China-based investment surveys. While this represents a robust cross-border business ecosystem, it also introduces complexity in supply chain transparency. Many entities claiming “American ownership” are, in fact, trading companies or joint ventures with limited manufacturing control. For procurement managers, accurate manufacturer verification is essential to ensure quality, compliance, scalability, and IP protection.
This report outlines a structured due diligence framework to verify manufacturer legitimacy, distinguish true factories from trading intermediaries, and identify red flags in sourcing from China.
Step-by-Step Verification Process for Chinese Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools / Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Verify legal existence and scope | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) or third-party platforms like Tianyancha or Qichacha to check business license, registration date, legal representative, and registered capital. |
| 2 | Validate Ownership Structure | Determine if U.S.-owned or locally controlled | Request Articles of Incorporation, shareholder registry, or cross-reference with U.S. parent company filings (e.g., SEC, state Secretary of State records). Use due diligence reports from firms like Dun & Bradstreet or local legal counsel. |
| 3 | Onsite Factory Audit (or Third-Party Inspection) | Confirm physical production capability | Conduct an in-person audit or hire a certified inspection firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) to verify equipment, workforce, production lines, and quality control processes. |
| 4 | Request Production Documentation | Validate manufacturing capacity | Ask for machine lists, production schedules, employee count, utility bills (e.g., electricity usage), and export records (customs data via Panjiva or ImportGenius). |
| 5 | Review Export & Trade History | Assess track record and scale | Use import/export databases to confirm shipment volume, consistency, and destination countries. A true factory typically shows direct export history under its own name. |
| 6 | Verify Certifications and Compliance | Ensure regulatory alignment | Check for valid ISO, CE, RoHS, FDA, or industry-specific certifications. Confirm authenticity via certifying body websites. |
| 7 | Contact Existing Clients (Reference Checks) | Gauge reliability and performance | Request 3–5 client references, especially Western buyers. Follow up independently to confirm delivery timelines, quality, and communication. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | True Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., plastic injection molding) |
| Factory Address & Photos | Office-only locations; stock images; no machinery | Specific industrial zone address; floor plans, production line photos, worker uniforms |
| Pricing Structure | Higher MOQ flexibility; less detailed on production costs | Lower per-unit cost at scale; detailed cost breakdowns (material, labor, overhead) |
| Lead Times | Longer or variable (dependent on third-party production) | Shorter and consistent; direct control over scheduling |
| Communication Depth | Limited technical knowledge; defers to “our factory” | Engineers or production managers available; technical documentation provided |
| Export Documentation | Ships under client’s name or uses third-party exporters | Exports under own company name (check via customs data) |
| Website & Marketing | Showcases multiple unrelated product lines | Focuses on core product category; highlights machinery, R&D, and production capacity |
💡 Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you provide a list of machines used in production?” Factories can; traders typically cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or refusal to allow audits | High risk of front operation or scam | Disqualify supplier unless third-party audit is provided |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Indicates substandard materials, hidden fees, or middlemen markup | Compare with industry benchmarks; request detailed BOQ |
| Inconsistent or evasive communication | Potential language barriers or lack of transparency | Require direct contact with technical/management staff |
| No independent certifications or fake certificates | Non-compliance risk; possible counterfeiting | Validate certifications via issuing body websites |
| Requests for full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) or LC |
| Multiple unrelated product lines | Likely a trading company misrepresenting itself | Request proof of in-house production for each category |
| No export history under their name | May lack direct control over supply chain | Verify via customs data platforms (e.g., ImportGenius) |
Best Practices for 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Leverage Technology: Use AI-powered supplier verification platforms (e.g., Sourcify, InsightX, or SupplyPike) for real-time risk scoring.
- Engage Local Expertise: Hire on-the-ground sourcing agents or legal advisors familiar with MOFCOM regulations and regional manufacturing clusters.
- Build Long-Term Partnerships: Prioritize suppliers open to joint audits, IP agreements, and continuous improvement programs.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on single sources, even if U.S.-owned, to mitigate geopolitical and operational risks.
Conclusion
While American-owned companies in China offer potential advantages in communication, quality standards, and IP alignment, ownership alone does not guarantee manufacturing capability. Rigorous verification is required to separate true factories from intermediaries and avoid costly supply chain disruptions.
By applying the due diligence framework outlined in this report, procurement managers can build resilient, transparent, and high-performance supply chains in China—positioning their organizations for sustainable growth in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 | Confidential — For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supplier Identification in China | Q3 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
The Critical Misconception: “How Many American-Owned Companies Are in China?”
Many procurement teams begin China sourcing with the flawed question: “How many American-owned companies operate in China?” This metric is inherently unverifiable and operationally irrelevant. China’s business registries (e.g., SAMR) do not track foreign ownership nationality, and estimates range wildly (5,000–50,000+) due to:
– Complex equity structures (e.g., US parent → HK subsidiary → WFOE in Shenzhen)
– “American-managed” vs. “American-owned” ambiguities
– Unverified online databases listing defunct or non-compliant entities
The Real Pain Point: Your team wastes 120+ hours/month sifting through unvetted Alibaba listings, expired registries, and unreliable third-party reports—only to face quality failures, compliance gaps, or IP risks.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves the Actual Problem
We bypass unanswerable census questions to deliver actionable, ownership-verified suppliers. Our Pro List targets your operational need: “Which American-owned/operated manufacturers meet my quality, compliance, and scalability requirements?”
Time & Risk Savings Comparison: DIY Research vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | DIY Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Month |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial supplier identification | 80+ hours (scraping, cross-checking) | <2 hours (curated list) | 78 hours |
| Ownership verification | 40+ hours (legal docs, site visits) | Pre-verified (WFOE docs, US parent proof) | 40 hours |
| Compliance screening (ISO, BSCI) | 30+ hours (manual audits) | Pre-screened (real-time compliance dashboard) | 30 hours |
| Quality assurance baseline | 25+ hours (PPAP, sample trials) | Factory-certified (3rd-party QC reports embedded) | 25 hours |
| Total | 175+ hours | <2 hours | 173+ hours |
Source: 2026 SourcifyChina Client Data (n=217 procurement teams)
Your Strategic Advantage: Precision, Not Guesswork
- Ownership Transparency: Every Pro List supplier provides:
- Notarized WFOE registration + US parent entity documentation
- Executive bios with US/China operational authority
- Direct contact with US-based management (no language barriers)
- Zero Verification Overhead: Skip B2B platforms flooded with trading companies. Our list includes only manufacturers with ≥51% US operational control.
- Compliance Built-In: All suppliers pass SourcifyChina’s 12-point audit (labor, environmental, IP protection)—reducing supply chain disruption risk by 92%.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 14 weeks to 11 days. We stopped chasing ghosts and started scaling.”
— Global Sourcing Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Firm
🚀 Your Call to Action: Optimize Q4 2026 Sourcing Cycles
Stop searching for unverifiable statistics. Start securing verified partners.
The 2026 Pro List includes 5,200+ American-owned/operated manufacturers across electronics, medical devices, and automotive—each pre-qualified for:
✅ Scalable production (MOQs ≤500 units)
✅ Export compliance (FDA, CE, UL pre-certified)
✅ Transparent pricing (FOB/Shenzhen with no hidden fees)
Act Now to Lock In Q4 Capacity:
1. Email: [email protected]
Subject Line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
→ Receive your tailored supplier shortlist within 4 business hours.
2. WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Message Template: “Request 2026 Pro List for [Industry] – [Company Name]”
→ Get instant access to our supplier database + free sourcing consultation.
Deadline: Pro List slots for Q4 2026 allocations close October 31, 2026. Suppliers with verified US ownership fill 3× faster.
Your time is capital. Stop investing it in unverified data.
SourcifyChina delivers certified ownership, compliance certainty, and operational speed—so your team sources smarter, not harder.
Contact us today. Your next reliable supplier is 2 hours—not 175—away.
SourcifyChina
Verified Manufacturing. Zero Guesswork.
[email protected] | +86 159 5127 6160 | www.sourcifychina.com/pro-list-2026
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.