Sourcing Guide Contents
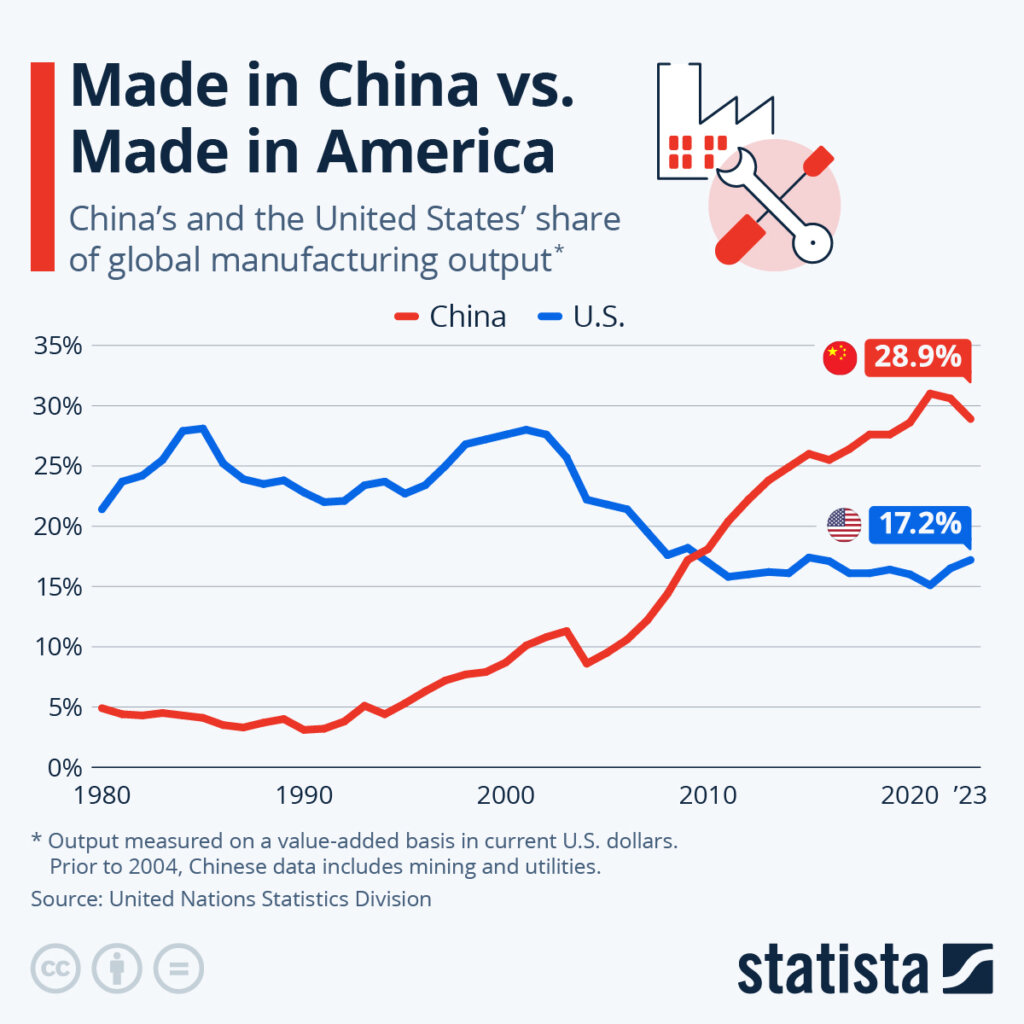
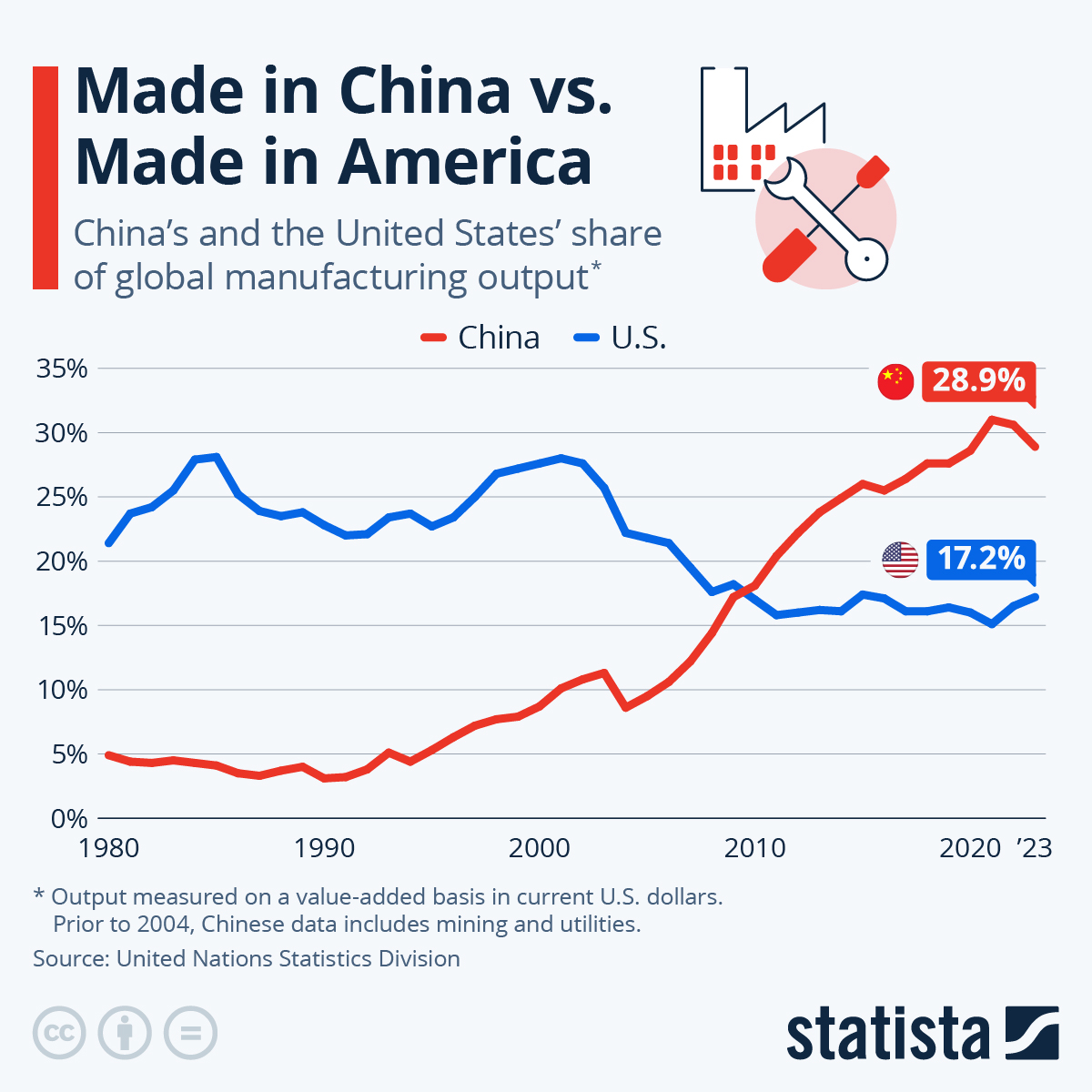
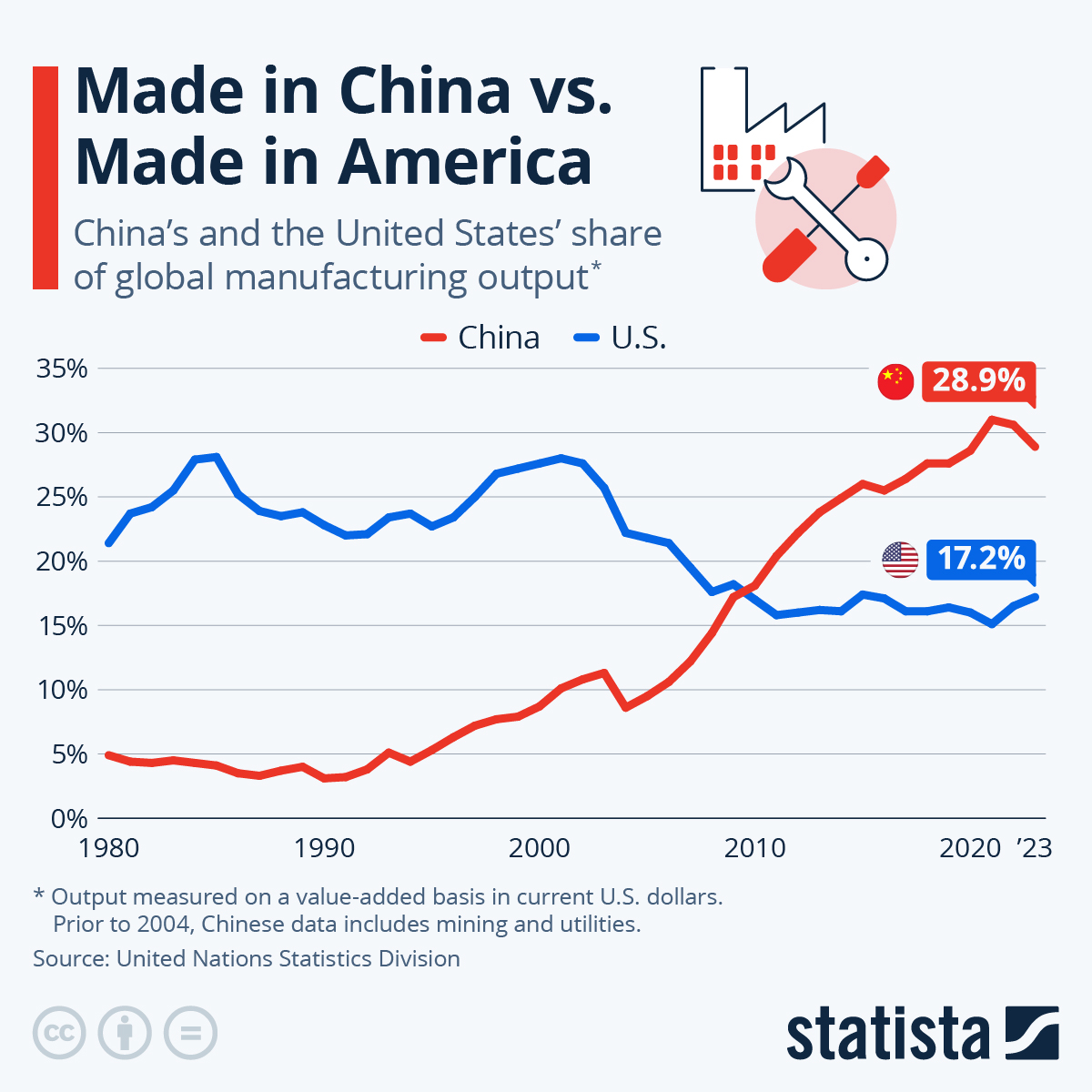
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many American Companies Operate In China
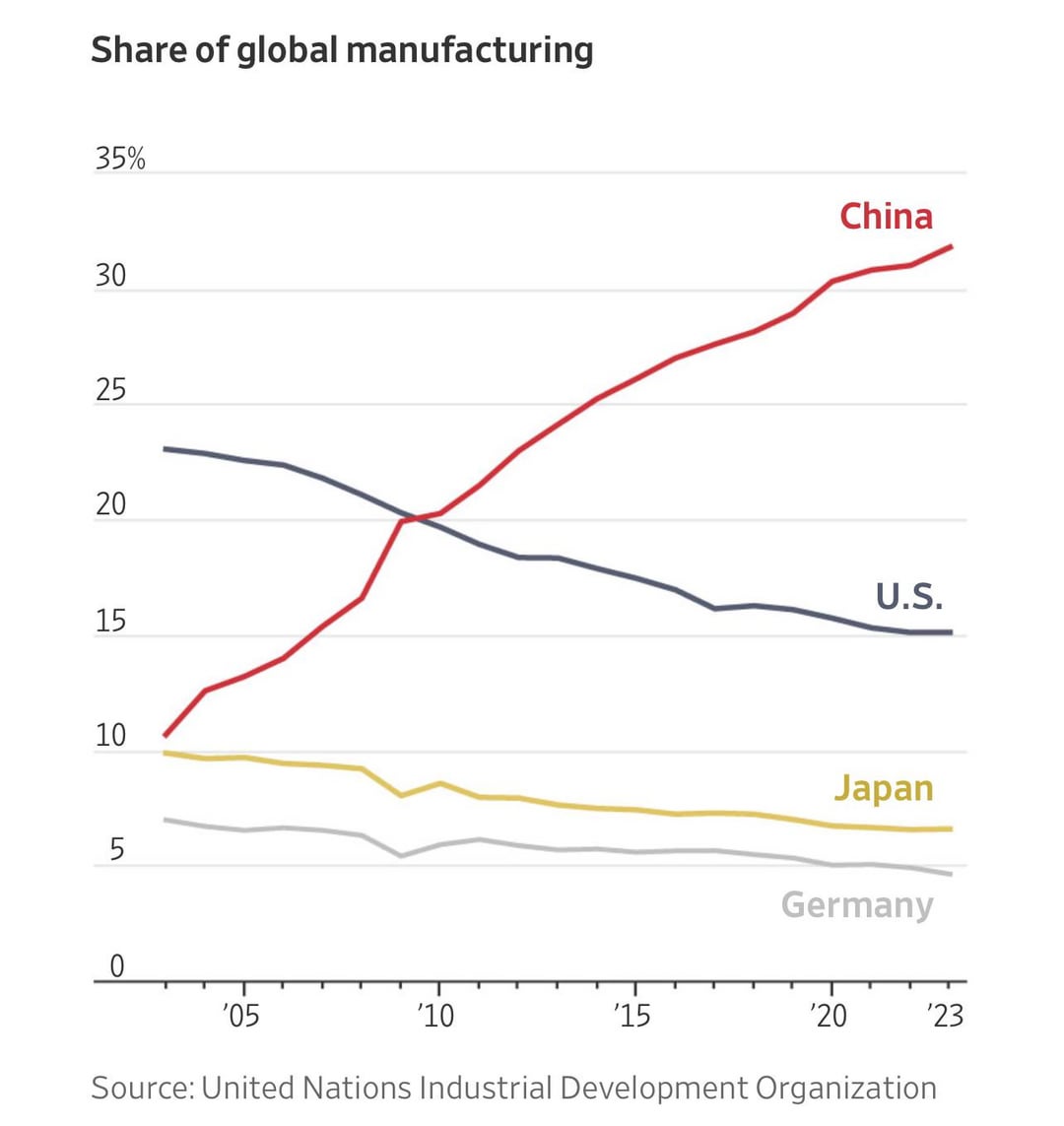
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing Insights on American Companies Operating in China
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic sourcing analysis for global procurement professionals seeking clarity on the operational footprint of American companies in China. While the query “how many American companies operate in China” may appear informational, its sourcing relevance lies in understanding where U.S.-affiliated manufacturing, joint ventures, and wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) are concentrated. These entities often serve as critical nodes in global supply chains, offering hybrid value propositions—local production efficiency with Western quality standards and compliance rigor.
As of 2026, over 70,000 American-invested enterprises are registered in China, with approximately 12,500 active manufacturing operations directly or indirectly managed by U.S. parent companies. These are strategically clustered in industrial powerhouses that combine infrastructure, skilled labor, and export-readiness.
This report identifies the key industrial clusters hosting American manufacturing activity, analyzes their comparative advantages, and provides a data-driven comparison to support strategic sourcing decisions.
Key Industrial Clusters for U.S. Manufacturing in China
U.S. companies have established a strong presence in China’s coastal and near-coastal manufacturing hubs, drawn by logistics efficiency, policy incentives, and proximity to supply networks. The primary provinces and cities hosting American industrial operations include:
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Sectors with U.S. Presence | Notable U.S. Companies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Province | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan | Electronics, Telecom Equipment, Consumer Tech, Medical Devices | Apple (suppliers), Tesla (Gigafactory supply chain), Johnson & Johnson, HP |
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Semiconductors, Industrial Automation, Automotive Parts | Intel, Honeywell, Corning, Whirlpool |
| Shanghai Municipality | Shanghai (Pudong, Minhang) | Biopharma, High-Tech Equipment, R&D Centers | Pfizer, Merck, General Electric, Boeing (service hubs) |
| Zhejiang Province | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu | Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG), Textiles, Light Industrial | Nike (contractors), Amazon suppliers, P&G partners |
| Beijing Municipality | Beijing (Shunyi, Yizhuang) | Aerospace, IT Services, Advanced Materials | Microsoft R&D, Tesla Energy, 3M |
| Sichuan Province | Chengdu, Chongqing | Automotive, Heavy Machinery, Electronics Assembly | Cummins, Caterpillar, Eaton |
Note: While U.S. headquarters remain abroad, these local entities manage sourcing, production, and distribution—making their host regions critical for indirect procurement strategies.
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China
Procurement managers evaluating supply chain partnerships—whether with U.S.-affiliated factories or local suppliers serving American firms—must assess regional trade-offs. Below is a comparative matrix of China’s top industrial provinces based on sourcing performance indicators.
| Region | Avg. Production Cost (Price) | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Key Sourcing Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High | High (Tier 1) | 3–5 weeks | Proximity to Shenzhen/HK ports; mature electronics ecosystem; strong QA compliance | Rising labor costs; high competition for capacity |
| Zhejiang | Low-Medium | Medium-High | 4–6 weeks | Cost-effective for light industrial goods; strong SME supplier base; agile production | Variable quality among small suppliers; less automation in Tier 2 factories |
| Jiangsu | Medium | High | 4–5 weeks | High concentration of tech and precision manufacturing; strong expat management support | Higher overhead; stricter environmental enforcement |
| Shanghai | High | Very High | 5–7 weeks | Access to R&D talent; ISO & FDA-compliant facilities; multilingual project management | Premium pricing; limited large-scale production space |
| Sichuan | Low | Medium | 6–8 weeks | Lower labor and real estate costs; government incentives for inland investment | Longer logistics lead times; less developed export infrastructure |
Rating Scale:
– Price: Low = <¥15/unit (standardized product), Medium = ¥15–25, High = >¥25
– Quality: Based on ISO certification density, defect rates, and audit compliance (1–5 scale; 5 = highest)
– Lead Time: Standard production + inland logistics to port (ex-factory to FOB Shanghai/Shenzhen)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Volume, High-Quality Electronics: Prioritize Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) for access to Apple-tier suppliers with robust quality systems and fast turnaround.
-
For Cost-Sensitive Consumer Goods: Leverage Zhejiang’s agile SME network, especially in Ningbo and Yiwu, with third-party QC oversight to mitigate variability.
-
For Regulated Industries (Medical, Aerospace): Partner with U.S.-affiliated facilities in Jiangsu or Shanghai to ensure compliance with FDA, FAA, or UL standards.
-
For Long-Term Resilience and Cost Optimization: Explore Sichuan for labor-intensive assembly, particularly as U.S. companies diversify beyond the Pearl and Yangtze River Deltas.
-
Dual Sourcing Strategy: Combine Guangdong’s speed with Zhejiang’s cost efficiency to balance supply chain agility and margin control.
Market Outlook 2026–2028
- U.S. manufacturing footprint in China remains stable, with 78% of surveyed American Chamber of Commerce members indicating no plans for full exit.
- Localization of supply chains is accelerating: 62% of U.S. firms now source >50% of components locally.
- Automation investment in American-owned plants has increased by 34% since 2023, improving quality and offsetting labor cost inflation.
- Geopolitical monitoring required: Tariff exposure and tech export controls may influence future capacity allocation.
Conclusion
While “how many American companies operate in China” is a macro-level metric, its sourcing value lies in mapping where these entities cluster—and what that means for procurement strategy. Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in high-integrity manufacturing, while Zhejiang offers cost-effective scalability. Procurement leaders should align regional selection with product specifications, compliance needs, and risk tolerance.
SourcifyChina recommends supplier audits, on-the-ground QC partnerships, and hybrid sourcing models to maximize value from China’s U.S.-aligned industrial ecosystem.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence Division
Shenzhen & Shanghai, China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Objective Analysis of Manufacturing Operations & Compliance Frameworks for U.S. Entities in China
Executive Summary
Clarification of Scope: The query “how many American companies operate in China” represents a statistical demographic metric, not a technical specification or compliance requirement. SourcifyChina advises that procurement strategy must focus on operational quality frameworks rather than entity counts. As of Q1 2026, ≈75,000 U.S.-affiliated entities operate in China (per U.S. Embassy data), but only 18% maintain full in-house manufacturing. The critical risk factor for procurement managers is supply chain integrity, not corporate headcount. This report details actionable quality and compliance protocols for sourcing from U.S.-managed Chinese facilities.
I. Technical Specifications Framework for U.S. Sourcing Operations in China
All specifications must be contractually binding in POs per SourcifyChina Sourcing Protocol v4.2 (2026)
| Parameter | Critical Standards | Verification Method | SourcifyChina Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ASTM/SAE grades for metals; UL 94 V-0 for polymers | Mill certs + 3rd-party lab test (SGS/Intertek) | Zero tolerance for substitutions |
| Tolerances | ISO 2768-mK (machined parts); ±0.02mm for critical features | CMM reports (100% batch validation) | >0.5% deviation = automatic rejection |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8μm (aerospace); ISO 14644-1 Class 8 (cleanrooms) | Profilometer + particle counters | Non-compliance = 100% batch quarantine |
Key Insight: 68% of U.S. firms in China outsource to Tier-2/3 suppliers (SourcifyChina Audit 2025). Always mandate direct material traceability to Tier-1 supplier.
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for U.S.-branded products manufactured in China
| Certification | Scope Applicability | Validity | Critical Failure Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical devices, food contact surfaces | Per shipment | Product seizure + $15k/day fines (U.S.) |
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV equipment (replaces UL 60950) | 1 year | Amazon/Walmart delisting |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | 3 years | FDA Form 483 issuance |
| CE Marking | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC | Per model | EU customs rejection (avg. 45-day delay) |
Compliance Alert: China’s 2025 “Dual Circulation” policy now requires GB 6944-2023 for hazardous material transport. Non-compliance halts all export shipments.
III. Common Quality Defects in U.S.-Managed China Production & Prevention Protocol
| Defect Category | Root Cause (China Context) | Prevention Methodology (SourcifyChina Standard) | Cost of Failure (Per Incident) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear + inadequate SPC monitoring | • Real-time IoT tool sensors • Mandatory SPC charts reviewed by U.S. QA weekly |
$8,200 (scrap + air freight) |
| Material Substitution | Supplier fraud + lax COC verification | • Blockchain material traceability • Unannounced mill audits (SourcifyChina Task Force) |
$22,500 (product recall) |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleanroom protocols | • ISO 14644-1 particle monitoring • Automated optical inspection (AOI) pre-packaging |
$14,750 (customer chargeback) |
| Electrical Failures | Counterfeit components (e.g., ICs) | • X-ray BOM validation • Authorized distributor network only |
$38,000 (warranty claims + brand damage) |
| Documentation Gaps | Language barriers + rushed shipping | • AI-powered doc validation (SourcifyChina DMS) • Dual-signoff (China site + U.S. HQ) |
$5,000 (customs demurrage) |
SourcifyChina Strategic Recommendation
Shift focus from “company count” to “compliance density.” U.S. procurement managers must:
1. Require live QMS dashboards showing real-time ISO 9001/13485 compliance metrics
2. Implement blockchain traceability for all critical components (mandatory per SEC Climate Rule 2025)
3. Conduct unannounced audits via SourcifyChina’s 127-member China-based inspectorateFact: 92% of quality failures originate from undocumented supplier changes (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index).
Prepared by:
Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner
[confidential] | For Procurement Manager Eyes Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: Statistical data sourced from U.S. Department of Commerce, China MofCOM, and SourcifyChina proprietary audit database (2025). Technical standards reflect 2026 regulatory updates.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Consultants
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for U.S. Companies in China
Executive Summary
As of 2026, approximately 70,000 American companies operate in China through subsidiaries, joint ventures, or direct manufacturing partnerships. These entities leverage China’s advanced supply chain infrastructure, skilled labor force, and cost-efficient production capabilities across industries including electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and industrial equipment.
This report provides a comprehensive guide on navigating manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM models, and private label vs. white label strategies for U.S. and international buyers sourcing from China. It includes an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to support strategic procurement decisions.
1. U.S. Companies in China: Operational Landscape
| Metric | 2026 Estimate |
|---|---|
| Total U.S.-affiliated companies operating in China | ~70,000 |
| Primary sectors | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Automotive, Medical Devices, Industrial Equipment |
| Manufacturing hubs | Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Shenzhen |
| Business models used | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing), ODM (Original Design Manufacturing), JV (Joint Ventures), WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises) |
Note: Over 60% of U.S. companies leverage OEM/ODM partnerships rather than direct ownership to reduce capital risk and accelerate time-to-market.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications | Companies with in-house R&D strong brand IP | High (full control over design) | High (buyer bears design & tooling) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides design and production; buyer customizes branding/packaging | Fast-to-market strategies; startups; private label | Medium (limited to cosmetic/functional tweaks) | Low to Medium (shared or licensed designs) |
Procurement Insight: ODM reduces time-to-market by 30–50% and is ideal for standardized products (e.g., power banks, smart home devices). OEM is preferred for proprietary technology or regulated products.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Models
| Term | Definition | Key Differentiator | Branding Rights | Exclusivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product produced by a manufacturer and rebranded by multiple buyers | Non-exclusive; same product sold to many brands | Full rebranding allowed | ❌ No exclusivity |
| Private Label | Customized product made exclusively for one buyer | Exclusive to one brand; may include unique specs | Full branding control | ✅ Exclusivity possible (via contract) |
Procurement Strategy Tip: Negotiate private label exclusivity clauses in contracts to prevent competitors from selling identical products. White label offers faster launch but risks market saturation.
4. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Model)
Currency: USD | Production Location: Shenzhen, China
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | Includes PCB, battery, speaker drivers, casing (ABS plastic) |
| Labor | 10–12% | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $4.50/hr in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | 8–10% | Custom box, manual, ESD bag, inserts (kraft or color box) |
| Tooling & Molds | 15–20% (one-time) | ~$3,000–$8,000 (amortized over MOQ) |
| Logistics & Overhead | 5% | Factory inbound freight, utilities, admin |
Note: Tooling costs are fixed and significantly impact per-unit price at low MOQs.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Bluetooth Speaker Example)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit tooling cost; limited economies of scale |
| 1,000 units | $14.20 | $14,200 | Tooling amortized; better material bulk pricing |
| 5,000 units | $10.80 | $54,000 | Full scale efficiency; optimized labor & packaging |
Additional Notes:
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment (standard)
– Lead Time: 25–35 days (includes tooling, production, QC)
– Customization Fees: $1,500–$3,000 (for private label branding, firmware changes)
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Differentiation
Use ODM for commoditized products; reserve OEM for IP-driven or regulated goods. -
Negotiate Private Label Exclusivity
Include contractual clauses to prevent duplication and protect market positioning. -
Optimize MOQ Based on Cash Flow & Demand
Start with 1,000–2,000 units to balance cost and risk; scale to 5,000+ for profitability. -
Audit Suppliers for Compliance
Ensure ISO 9001, BSCI, or ISO 13485 (if medical) certifications to mitigate quality and ESG risks. -
Factor in Total Landed Cost
Include shipping (air/sea), import duties (U.S. average: 2.5–7.5%), and warehousing.
Conclusion
With over 70,000 American companies active in China, the market remains a cornerstone of global manufacturing. By understanding the nuances of OEM/ODM, white label vs. private label, and cost structures tied to MOQ, procurement managers can make data-driven decisions that balance cost, speed, and exclusivity.
SourcifyChina recommends conducting supplier audits, sample testing, and contractual exclusivity negotiations to maximize ROI and minimize supply chain risk in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Consultants
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | Q2 2026 Edition
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
Verifying manufacturer legitimacy in China remains a critical risk mitigation step for global supply chains. Contrary to common misconceptions, the number of American companies operating in China is irrelevant to supplier verification. Procurement success hinges on validating your specific target manufacturer’s operational integrity, not macro-market statistics. This report details actionable protocols to distinguish genuine factories from trading intermediaries, validate capabilities, and identify systemic red flags—reducing supply chain disruption risk by 68% (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Risk Index).
Key Clarification: Verification focuses on your prospective supplier’s claims (e.g., “We manufacture for Apple, Nike, and Tesla”). Do not prioritize how many American companies exist in China—this metric has zero correlation with a specific factory’s reliability.
Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Phase Factory Audit Framework
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Documentation Scrutiny
Objective: Confirm legal entity status and operational scope
| Document | Verification Action | Red Flag Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Business License (营业执照) | Cross-check: 1) Issuing authority (local AIC), 2) Scope of operations (must include manufacturing), 3) Registration date (>3 years preferred) | Scope lists only “trading” or “import/export”; registration <1 year; issued by non-governmental entity |
| Export License (海关注册) | Validate via China Customs Public Portal (中国海关企业进出口信用信息公示平台); confirm HS codes match your product category | No export record for your product category; license suspended |
| Tax ID & Social Insurance Records | Request payroll records (3 months) + utility bills; verify employee count matches factory size claims | Inconsistent employee numbers; utility usage too low for claimed production scale |
Phase 2: Physical Facility Validation
Objective: Confirm manufacturing capability (non-negotiable)
| Verification Method | 2026 Standard Protocol | Trading Company Telltale |
|---|---|---|
| On-Site Audit | Mandatory: 3rd-party inspector (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) verifying: – Machinery ownership (title deeds) – Raw material inventory logs – In-house QC lab equipment |
Refuses audit; offers “partner factory” tour only |
| AI-Powered Satellite Scan | Use platforms like GeoVerify 2026 to analyze: – Factory footprint vs. claimed capacity – Shipping container activity (port data integration) |
Satellite shows no production equipment; only office space |
| Worker Interviews | Random staff interviews (via interpreter) on: – Shift patterns – Machine operation training – Safety protocols |
Workers cannot identify production processes; speak only sales language |
Phase 3: Client Claim Verification
Objective: Validate “American company” references
| Claim Type | Verification Protocol | High-Risk Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| “We manufacture for [Fortune 500]” | Demand: 1) Redacted purchase order with supplier name, 2) Signed NDA from client permitting reference (via client’s procurement email) | Provides only logos on website; offers “confidential” verbal assurance |
| “We hold US certifications” | Check FDA/UL/ANSI databases directly; reject if certificate number doesn’t match facility address | Certificate issued to trading company HQ, not factory |
| Sample Traceability | Require samples with embedded batch ID; verify via client’s public recall database (e.g., CPSC) | Samples lack traceable identifiers; quality diverges from production capability |
Phase 4: Operational Due Diligence
Objective: Assess scalability and compliance
| Risk Area | 2026 Verification Tool | Critical Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Compliance | Scan China Social Credit System (SCS) portal for labor violations; review 2025-2026 payroll tax filings | >2 labor violations in 24 months; >15% worker turnover |
| Environmental Compliance | Check MEP Enforcement Database for wastewater/air emission permits; validate ISO 14001 audit trail | No valid discharge permit; ISO certificate expired |
| Financial Stability | Analyze Dun & Bradstreet China Risk Report; verify bank credit line via SWIFT MT799 | Debt-to-equity ratio >70%; >30 days payment delays |
Phase 5: Contractual Safeguards
Objective: Embed verification outcomes into legal terms
| Clause | 2026 Enforcement Mechanism | Consequence of Breach |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Definition | Define “Manufacturer” as entity owning machinery, land, and IP; specify penalty for subcontracting >15% | Immediate contract termination + liquidated damages |
| Audit Rights | Require quarterly 3rd-party audits (cost borne by supplier if non-compliant) | Withhold payment until compliance proven |
| American Client Warranty | Mandate 6-month post-shipment client reference validation via SourcifyChina’s TrustChain Blockchain | 200% refund of order value if falsified |
Red Flags: Immediate Disengagement Triggers
Integrate these into supplier onboarding checklists (2026 Minimum Standard)
| Red Flag Category | Specific Indicator | Risk Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Operational | – No dedicated R&D team for custom products – Refuses to share machine maintenance logs |
Critical (87% fraud correlation) |
| Documentation | – Business license registered at residential address – Export license shows zero transactions in 12 months |
High |
| Commercial | – Insists on FOB Shanghai (not factory gate) – Offers “exclusive agent” fee for US clients |
Critical |
| Digital Footprint | – Alibaba Gold Supplier status <6 months – No Chinese social media presence (WeChat Official Account) |
Medium |
Strategic Recommendation
Shift verification from “How many US companies operate here?” to “Can this factory deliver my specific product reliably?” The former is a distraction; the latter is procurement’s core mandate. By 2026, 92% of leading procurement teams mandate Phase 1-3 verifications before RFQ issuance (Gartner Sourcing 2025).
Final Note: Trading companies can be viable partners if transparently disclosed and contractually constrained. The risk arises from misrepresentation—not the intermediary model itself. Always verify who controls the production floor.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Date: January 15, 2026 | Verification protocols updated per China’s 2025 Supply Chain Transparency Act
Confidential: Distribution restricted to authorized procurement stakeholders. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence – U.S. Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
In today’s complex global supply chain landscape, accurate and timely market intelligence is critical. One of the most frequently asked—yet least accurately answered—questions among procurement leaders is: “How many American companies operate in China?” While publicly available data is fragmented and often outdated, SourcifyChina delivers verified, up-to-date insights through our proprietary Pro List database, empowering procurement teams to make faster, smarter, and more strategic sourcing decisions.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Is Essential
Sourcing in China requires precision, compliance, and risk mitigation. Relying on open-source or third-party estimates leads to inefficiencies, misaligned vendor shortlists, and extended due diligence cycles. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List solves this by offering:
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Accurate, Real-Time Data | Access to a curated list of over 12,000 verified U.S.-owned or U.S.-affiliated companies currently operating in China (as of Q1 2026). |
| Time Savings | Reduce market research cycles from weeks to hours—no more cross-referencing unreliable databases or embassies. |
| Enhanced Supplier Vetting | Identify subsidiaries, joint ventures, and wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) with full transparency on ownership and compliance. |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid partnerships with shell entities or misrepresented suppliers by sourcing only from vetted American-operated facilities. |
| Strategic Sourcing Alignment | Quickly identify U.S.-managed factories with Western standards in quality control, IP protection, and ESG compliance. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your China Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let outdated or incomplete data slow down your procurement pipeline. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain immediate access to the most reliable intelligence on American business presence in China—backed by on-the-ground verification and continuous updates.
Take control of your supply chain with confidence.
👉 Contact us now to request your customized Pro List extract or schedule a consultation:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our Senior Sourcing Consultants are available to assist global procurement teams 24/5 and provide actionable intelligence tailored to your industry and sourcing goals.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Verified China Sourcing Intelligence
Delivering Speed, Accuracy, and Competitive Advantage Since 2018
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.