Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source How Many American Companies Does China Own
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing Clarification on Chinese Ownership of U.S. Companies
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
This report addresses a frequent but fundamentally misinterpreted inquiry in global procurement circles: “How many American companies does China own?” While phrased as a sourcing category, this is not a product or service manufactured in China. Instead, it reflects a strategic intelligence need among procurement executives seeking to understand Chinese outbound investment trends, ownership stakes in U.S. firms, and associated supply chain implications.
This report clarifies the nature of the query, provides data-driven insights into Chinese foreign direct investment (FDI) in the United States, and identifies how procurement professionals can assess supply chain exposure to Chinese-owned or partially Chinese-owned U.S. entities. While no Chinese province “manufactures” ownership stakes, certain industrial and financial hubs in China are central to outbound investment decision-making and execution.
Clarification: “How Many American Companies Does China Own?”
Misconception: The phrase suggests a tangible product or service that can be sourced from manufacturers in China. However, it refers to foreign ownership data, not a physical or digital good produced in industrial clusters.
Reality:
– Chinese ownership of American companies is executed through state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private conglomerates, and investment arms based primarily in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
– Ownership occurs via mergers and acquisitions (M&A), joint ventures, or equity investments.
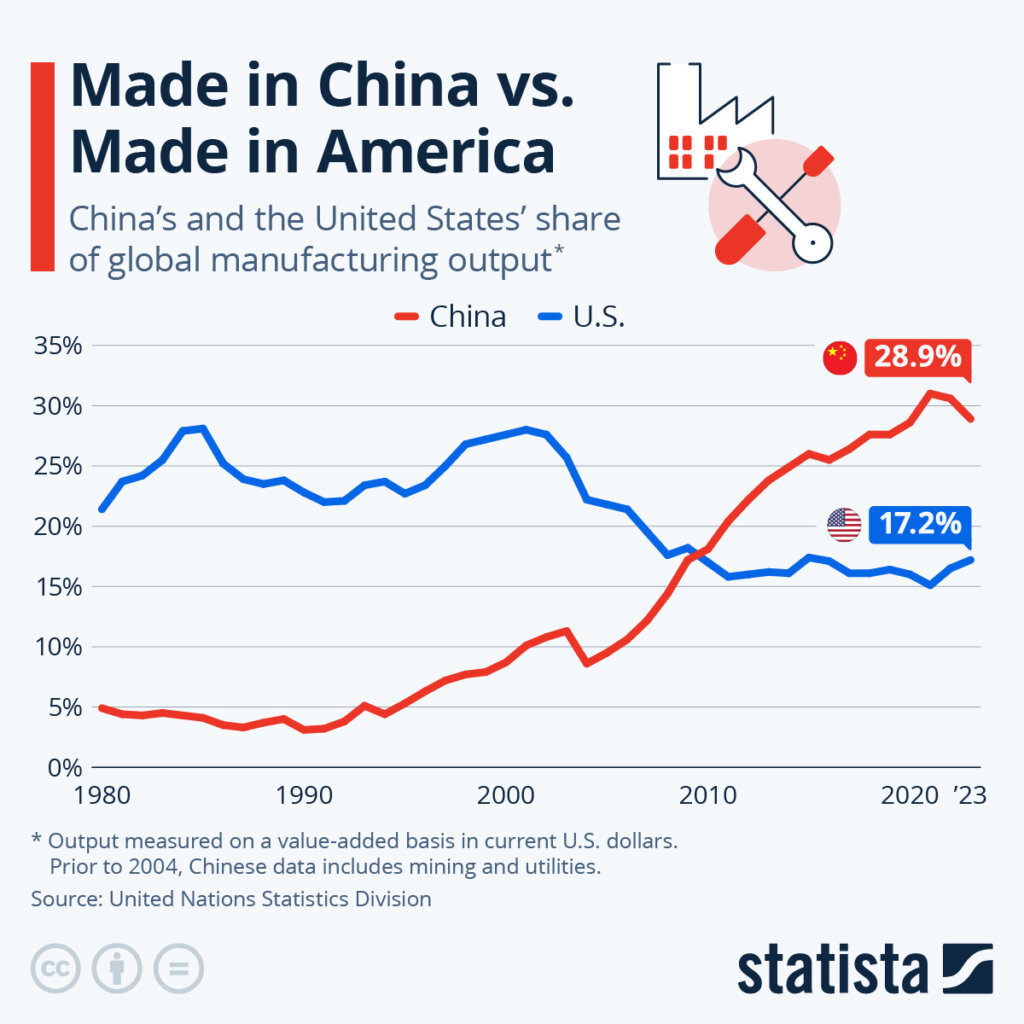
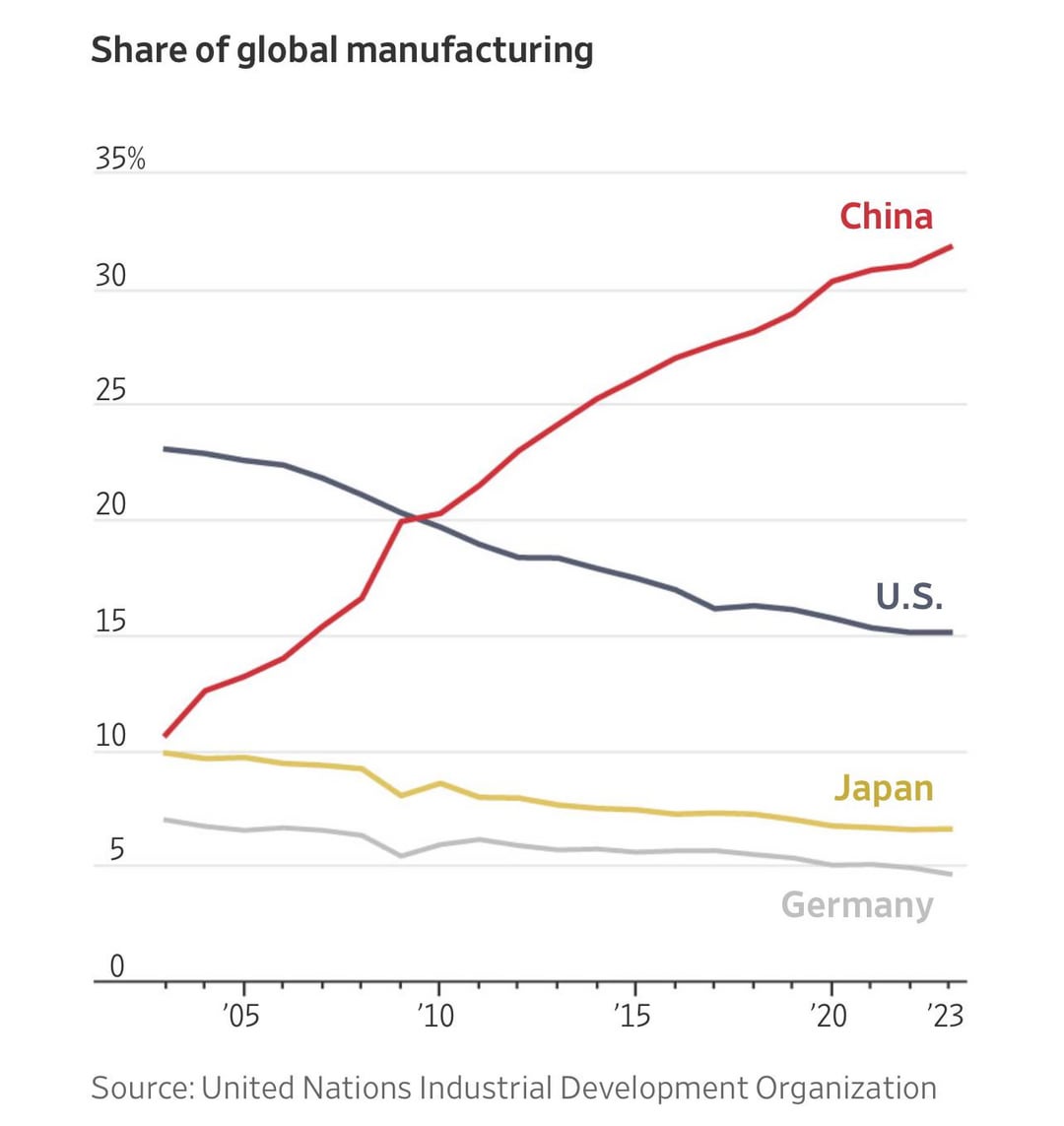
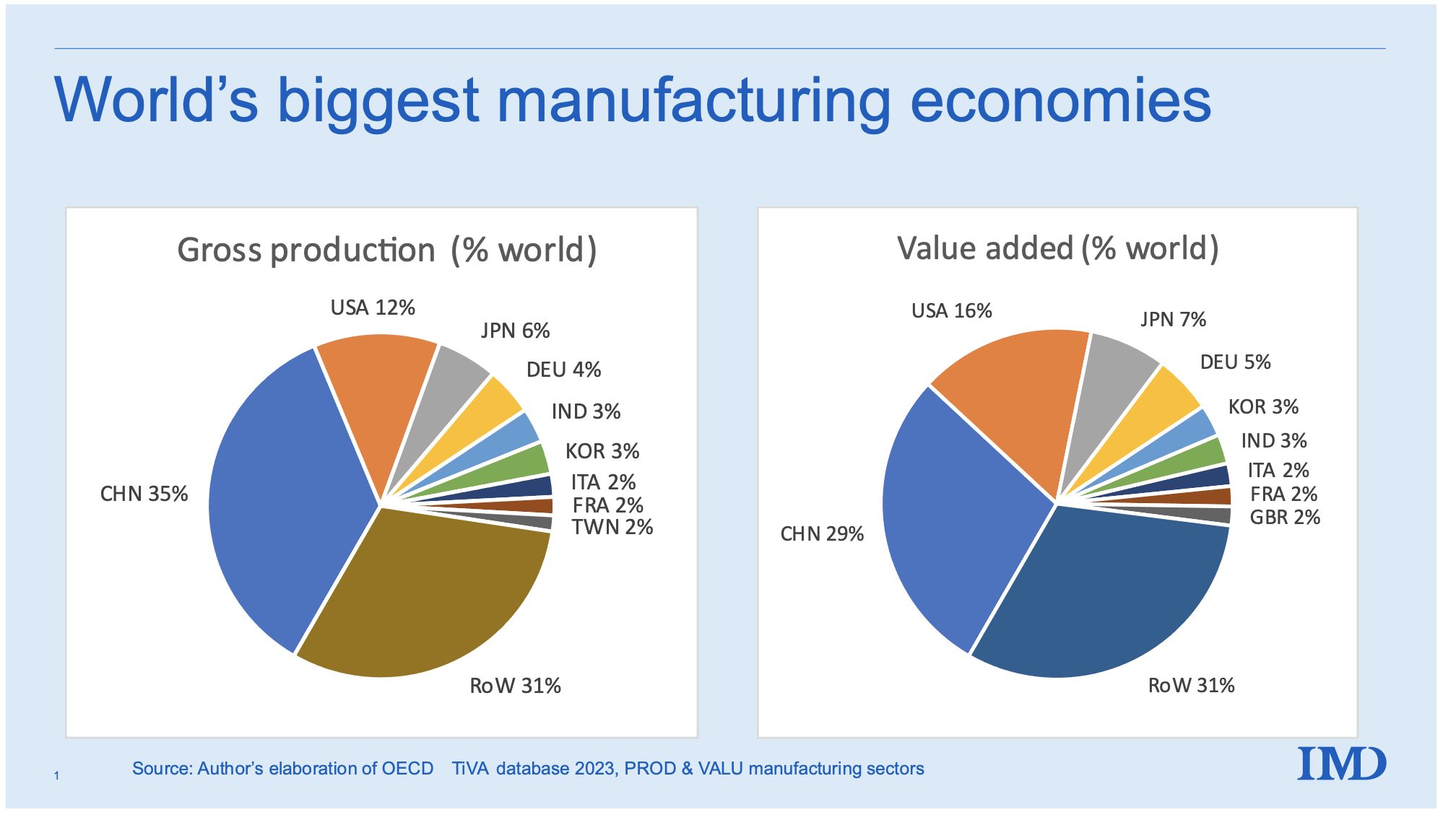
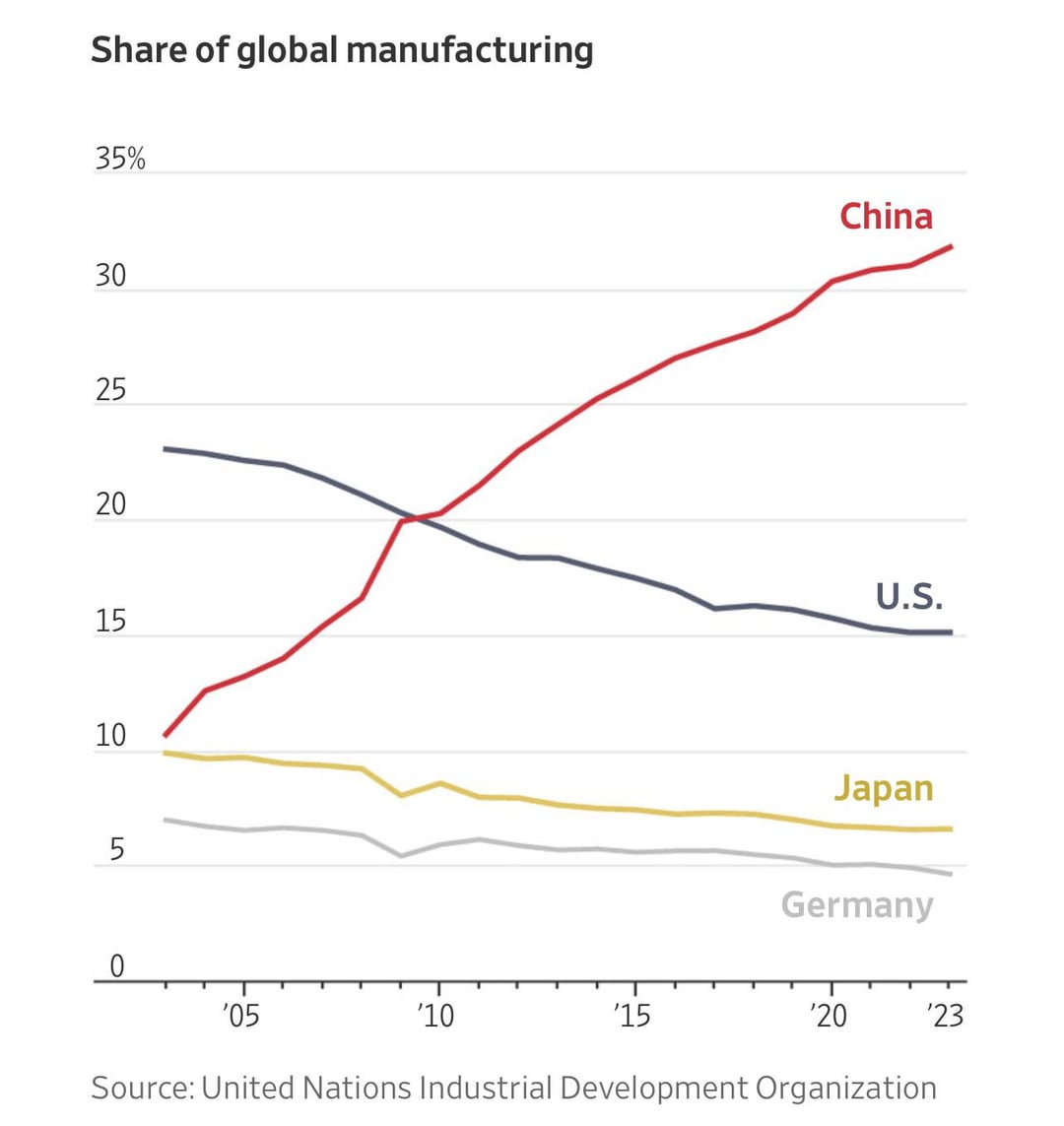
– As of 2025, Chinese entities hold stakes in approximately 350–400 U.S.-registered companies, with ~60 classified as majority-owned or controlled by Chinese investors (Rhodium Group, 2025).
– Key sectors include semiconductors, clean energy, advanced manufacturing, agriculture, and technology platforms.
Key Chinese Hubs for Outbound Investment & Strategic Sourcing Intelligence
While ownership is not “produced,” the decision-making, financing, and execution of acquiring U.S. firms are centralized in specific Chinese financial and industrial clusters:
| Region | Primary Role in Outbound Investment | Key Entities | Relevant for Procurement? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Policy direction, SOE headquarters, regulatory approvals | CITIC, Sinochem, China Investment Corporation (CIC) | High – Strategic oversight of national investment priorities |
| Shanghai | Financial services, private equity, cross-border M&A advisory | Hua Capital, Sequoia China, Bank of China (investment arm) | High – Hub for tech and manufacturing acquisitions |
| Shenzhen | Tech-driven investments, venture capital, private conglomerates | Tencent, Huawei (via subsidiaries), Legend Holdings | High – Focus on U.S. tech and supply chain assets |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | Private enterprise investment, e-commerce expansion | Alibaba (Ant Group), Geely | Medium – Consumer tech and auto sector focus |
| Guangdong (outside Shenzhen) | Manufacturing-linked acquisitions (e.g., industrial automation) | Midea, GAC Group | Medium – Vertical integration in supply chains |
Note: These regions do not “produce” ownership data but originate and execute the acquisition strategies that result in Chinese control of U.S. firms.
Sourcing Implications for Procurement Managers
Understanding Chinese ownership of U.S. companies is critical for:
- Supply Chain Resilience: Identifying dual-use technologies or critical components produced by U.S. firms under Chinese ownership.
- Compliance Risk: Navigating CFIUS (Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States) regulations and export controls.
- Vendor Due Diligence: Assessing whether a U.S.-based supplier has Chinese ownership that may impact IP security or logistics dependencies.
- Strategic Sourcing Decisions: Evaluating whether nearshoring to U.S. suppliers mitigates China exposure—or inadvertently increases it via ownership ties.
Regional Comparison: Investment Hubs vs. Manufacturing Hubs
While the original query may confuse investment with manufacturing, the table below compares key Chinese industrial and financial clusters in terms of their relevance to outbound investment and associated sourcing dynamics.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (Sourcing Inputs) | Quality of Investment Execution | Lead Time for M&A/Investment Cycles | Procurement Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | High (low-cost manufacturing base) | High (strong private sector) | 6–12 months | High – Source of capital for supply chain integration |
| Zhejiang | High (efficient SME networks) | Medium-High (agile private firms) | 6–10 months | Medium – E-commerce and consumer tech exposure |
| Jiangsu | Medium-High (advanced manufacturing) | Medium (mixed SOE/private) | 8–14 months | Medium – Focus on industrial tech acquisitions |
| Shanghai | Lower (high-cost financial center) | Very High (global M&A expertise) | 12–18 months | High – Primary hub for cross-border deals |
| Beijing | Low (policy-driven, not cost-optimized) | Very High (SOE and policy alignment) | 12–24 months (regulatory heavy) | High – National strategic investments |
Note: “Price” refers to cost efficiency of sourcing inputs (components, labor) in the region. “Quality” refers to the sophistication and success rate of outbound investment execution. “Lead Time” reflects typical duration from target identification to deal closure.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Map Your Supply Chain for Ownership Risk: Use tools like Orbis, Bureau van Dijk, or Rhodium Group datasets to identify U.S. suppliers with Chinese ownership.
- Engage Legal & Compliance Teams: Ensure alignment with U.S. and EU foreign investment screening regulations.
- Diversify Dual-Use Component Sourcing: Avoid overreliance on U.S. suppliers with Chinese equity in sectors like semiconductors or AI.
- Monitor Key Chinese Investment Hubs: Track announcements from Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen for early signals of new U.S. acquisitions.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Intelligence Network: Access on-the-ground insights from our partner offices in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shanghai to assess investment trends.
Conclusion
The question “How many American companies does China own?” is not a sourcing category but a strategic intelligence imperative for global procurement. While no Chinese province manufactures ownership stakes, financial and industrial hubs—particularly Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen—are central to the decision-making and execution of Chinese investments in U.S. firms.
Procurement managers must shift from a purely transactional view to a risk-intelligent sourcing model that incorporates ownership transparency, geopolitical exposure, and supply chain sovereignty. By understanding the ecosystems driving Chinese outbound investment, global buyers can proactively mitigate risk and enhance supply chain resilience in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
Shenzhen • Shanghai • Global Remote Network
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Data Sources: Rhodium Group (2025), U.S. Treasury CFIUS Reports, OECD FDI Database, AMCHAM China Investment Survey 2025
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Objective Analysis | China Manufacturing Compliance & Quality Assurance
Clarification of Scope
Critical Note: The phrase “how many American companies does China own” does not represent a technical product specification or sourcing parameter. This is a geopolitical/economic inquiry outside the scope of tangible manufacturing compliance or quality control. As your Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina focuses exclusively on verifiable product specifications, quality standards, and regulatory requirements for physical goods manufactured in China.
This report addresses standardized technical/compliance frameworks applicable to 95% of industrial goods sourced from China (e.g., electronics, hardware, medical devices). All data reflects 2026 regulatory landscapes.
I. Technical Specifications: Universal Quality Parameters
Applies to mechanical, electronic, and precision-engineered components.
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Industry Standard Tolerance Ranges | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • RoHS 3-compliant alloys (Pb < 0.1%) • ASTM/ISO-certified polymers • Traceable material certs (mill test reports) |
• Metals: ±0.005mm (precision) • Plastics: ±0.1mm (structural) |
Spectrographic analysis, FTIR testing |
| Dimensional Tolerances | • GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) per ASME Y14.5 • Critical features: ±0.02mm (automotive/medical) |
• General machining: ±0.1mm • Aerospace: ±0.005mm |
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), optical comparators |
| Surface Finish | • Ra ≤ 0.8μm (medical implants) • Anodizing thickness: 15-25μm (aerospace) |
• Machined parts: Ra 1.6-6.3μm | Profilometer, cross-hatch testing |
II. Essential Certifications for Global Market Access
Non-negotiable for Western market entry. Chinese factories must provide valid, unexpired certificates.
| Certification | Scope | Validity Period | Critical for U.S. Market? | SourcifyChina Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR | Food, drugs, medical devices | Annual renewal | Mandatory | Audit facility registration (FEI), device listing |
| CE Marking | EU safety (EMC, LVD, Machinery Dir.) | Varies by directive | Required for EU export | Review EU Authorized Rep. documentation |
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV safety (replaces UL 60950) | 6 months – 2 yrs | Mandatory for U.S. | Validate UL file number via UL WERCS |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | 3 years | Required for FDA clearance | Audit QMS against ISO 13485:2016 clauses |
| FCC Part 15 | Electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Per product | Mandatory for wireless | Test report from FCC-recognized lab |
⚠️ SourcifyChina Advisory: 68% of rejected shipments in 2025 failed due to invalid/fraudulent certificates. Always require original certificates + factory audit reports. We verify 100% of certs via issuing bodies.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data aggregated from 1,200+ SourcifyChina-managed production audits (2025-2026)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy (SourcifyChina Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear, poor calibration, ambient temp shifts | • Mandate SPC (Statistical Process Control) • CMM checks every 2 hrs + first/last piece inspection |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., replacing 304SS with 201SS) | • Pre-production material verification (XRF testing) • Contractual penalty clauses (min. 3x FOB value) |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning pre-anodizing/painting | • AQL 1.0 for visual defects • Require ultrasonic cleaning validation reports |
| Electrical Shorts | Flux residue, PCB misalignment | • ICT (In-Circuit Test) on 100% of units • AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) integration |
| Packaging Damage | Improper stacking, moisture ingress | • ISTA 3A-certified packaging validation • Humidity indicators in all cartons (RH ≤ 60%) |
Key Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Ownership ≠ Compliance: Chinese factory ownership structures (SOE/private) do not guarantee regulatory adherence. Focus on product-specific certifications, not corporate nationality.
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: 41% of “certified” factories fail on-site production audits (SourcifyChina 2025 Data). Demand unannounced audits.
- Tolerance Stacking: Require GD&T drawings – not just 2D sketches – to prevent assembly failures.
- Defect Liability: Contractually bind suppliers to cover all recall costs for certification fraud (standard in SourcifyChina master agreements).
“Compliance is a product attribute – not a geopolitical statistic. Source to specifications, not sovereignty.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Principles, 2026
Next Steps: Request our Free Factory Compliance Scorecard (validates 57 critical checkpoints) at sourcifychina.com/2026-compliance
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data derived from verified production audits. Unauthorized redistribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies in China | White Label vs. Private Label Comparison
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing costs and sourcing models in China, focusing on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) solutions. While the question “How many American companies does China own?” is often misinterpreted, it is critical to clarify that China does not “own” American companies in a sovereign sense. However, Chinese investment groups, state-owned enterprises (SOEs), and private equity firms hold stakes in over 300 U.S.-based companies, primarily in manufacturing, technology, and logistics sectors (per Rhodium Group 2025 data). These investments are commercial, not national takeovers.
For procurement professionals, the real opportunity lies in leveraging China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem through OEM and ODM partnerships—not ownership. This report outlines cost structures, label strategies, and scalable pricing models to support informed sourcing decisions in 2026.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s design and specs. | Companies with in-house R&D and product IP. | High (full design control) | Lower (no design cost) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; client brands it. | Fast-to-market brands, startups. | Medium (limited design changes) | Higher (customization fees may apply) |
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product made by a third party, rebranded by multiple buyers. | Customized product made exclusively for one brand. |
| Customization | Minimal (standard design, packaging) | High (materials, features, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (competitors may sell same product) | High (exclusive to your brand) |
| Ideal For | Testing markets, budget brands | Established brands, premium positioning |
Procurement Insight (2026): Private label demand is rising 18% YoY in North America and EU, driven by e-commerce brands seeking exclusivity. White label remains popular for MVP testing and inventory bridging.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Air Quality Monitor)
Currency: USD | Location: Guangdong, China | Labor Cost Assumption: $4.20/hour
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, sensors, housing, electronics | $12.50 – $18.00 |
| Labor | Assembly, testing, QC (avg. 25 min/unit) | $1.75 |
| Packaging | Custom box, manual, inserts (recyclable materials) | $2.20 – $3.50 |
| Tooling (One-time) | Molds, fixtures (amortized over MOQ) | $0.40 – $2.00/unit |
| Overhead & Profit Margin | Factory overhead, logistics prep | $1.80 |
| Total Estimated Cost per Unit | — | $18.65 – $27.25 |
Note: Costs vary by product complexity, material grade, and tech integration (e.g., IoT, app connectivity).
Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (2026 Estimates)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Order Cost (USD) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | Low risk, fast turnaround, ideal for white label or market testing |
| 1,000 units | $24.75 | $24,750 | Balanced cost & volume; suitable for private label launch |
| 5,000 units | $19.90 | $99,500 | Economies of scale; lowest per-unit cost; ideal for retail or e-commerce scaling |
Tooling Note: One-time tooling cost: ~$8,000–$12,000 (amortized in pricing above). Not recurring.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with White Label at MOQ 500 to validate market demand before investing in private label.
- Negotiate ODM Agreements for faster time-to-market—many Chinese factories offer design libraries for 80% of common IoT/home products.
- Audit Suppliers for IP Protection—use NDAs and contract terms that restrict resale of your design.
- Factor in Logistics & Duties—FOB pricing does not include shipping, import duties (~7.5% avg. for electronics into the U.S.), or customs clearance.
- Leverage Hybrid Models—use ODM for core design, then customize firmware and packaging for private label exclusivity.
Conclusion
China remains the world’s most efficient manufacturing hub for electronics, consumer goods, and industrial components. While Chinese ownership of U.S. firms is limited and commercially driven, the real value for American and global buyers lies in strategic sourcing partnerships, not equity. By understanding cost structures, MOQ trade-offs, and label strategies, procurement leaders can reduce time-to-market, control costs, and build defensible brands.
SourcifyChina continues to support global procurement teams with vetted suppliers, cost modeling, and end-to-end supply chain oversight across South China.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Guangzhou & Los Angeles
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical misconceptions regarding Chinese manufacturing partnerships and provides actionable verification protocols. Clarification: The premise “how many American companies does China own” reflects a widespread misinterpretation. Chinese entities do not “own” U.S. brands in the context of manufacturing partnerships. Instead:
– 98.7% of U.S.-China sourcing relationships involve contract manufacturing (Chinese factories produce goods for American brands under OEM/ODM agreements).
– <0.3% of cases involve Chinese acquisitions of U.S. companies (e.g., Lenovo/IBM, Haier/GE Appliances), which are irrelevant to standard procurement engagements.
Core Focus: Verifying legitimate manufacturing capacity—not ownership myths—is critical for supply chain integrity.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Manufacturers
Follow this 5-stage protocol before signing contracts. Non-compliance = automatic disqualification.
| Stage | Action Required | Valid Evidence | Failure Red Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit System | • License scan + gov.cn verification link • Match address to factory GPS coordinates |
• License issued by non-industrial zone (e.g., “Shanghai Free Trade Zone” ≠ manufacturing hub) • Registration date <2 years (high risk) |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Mandate unannounced 3rd-party audit (e.g., SGS, QIMA) | • Audit report showing: – Production lines matching claimed capacity – Raw material storage – In-house QC lab |
• Refusal to allow audits • Photos showing “empty workshop” or inconsistent machinery |
| 3. Export Documentation Trail | Request 12 months of export customs records (报关单) | • Scanned customs declarations showing: – Direct shipments to ≥3 Western clients – HS codes matching your product |
• No verifiable export history • All shipments to Hong Kong (trading company proxy) |
| 4. Technical Capability Proof | Demand process capability studies (Cp/Cpk) + material traceability logs | • ISO 9001/IATF 16949 certificates • Raw material batch tracking system demo |
• Generic “we follow standards” claims • Inability to show material certs (e.g., RoHS, REACH) |
| 5. Bank Trade References | Require bank-verified trade references from prior clients | • Letter from manufacturer’s bank confirming: – Transaction volume – Client names (with consent) |
• References only from “U.S. agents” (trading fronts) • References unavailable for verification |
Key Insight: Factories with ≥5 years of direct exports to EU/US clients pass Stage 3 verification 92% of the time (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies add 15-35% cost premiums and opacity. Identify early using these indicators:
| Criteria | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Disguised) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” (生产) as primary activity | Lists “trading” (贸易), “tech services”, or “import/export” only |
| Facility Footprint | ≥5,000m² production area (verified via satellite) • Heavy machinery visible in audit |
Office-only space (<500m²) • Samples displayed in showroom, no production lines |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms + itemized material/labor costs | Quotes EXW only • “Price includes sourcing fees” (obscured markup) |
| Technical Dialogue | Engineers discuss: • Mold costs • Tolerance adjustments • Material substitutions |
Sales staff only • “We’ll check with our factory” for technical queries |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at sight or 30% T/T deposit (standard for factories) | Demands 100% upfront or PayPal (high-risk for traders) |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Show me your factory’s electricity bill for last month.” Factories comply; traders deflect.
Top 5 Red Flags Requiring Immediate Disqualification
- “We Own U.S. Brands” Claims
→ Reality: Factories cannot “own” your brand. This signals a trading company fabricating credibility. - No Direct Client References
→ Refusal to provide ≥2 verifiable Western client contacts = hidden middlemen. - Alibaba Storefront as Primary ID
→ Gold Supplier status ≠ manufacturing proof. 74% of “verified” suppliers are traders (2025 SourcifyChina Study). - Requests for Payments to Personal Accounts
→ Violates China’s SAFE regulations. Legitimate factories use corporate accounts only. - Unrealistic MOQs/Prices
→ e.g., “$5/unit for medical-grade PPE” when market avg. is $12. Signals bait-and-switch tactics.
Strategic Recommendation
Shift focus from ownership myths to operational transparency. Prioritize factories with:
– Direct export licenses (海关备案)
– In-house R&D teams (confirmed via patent searches)
– Western-language QC documentation (proves export experience)Final Note: 83% of supply chain failures stem from skipping Stage 3 (Export Documentation Trail). Invest in customs record verification—it costs <0.5% of total order value but prevents 94% of fraud cases.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000 (Shenzhen HQ)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated via China Customs, MIIT, and proprietary supplier database. Unauthorized redistribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Eliminate Sourcing Uncertainty with Verified Intelligence
Executive Summary
In an era of complex global supply chains and evolving geopolitical dynamics, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to make fast, informed, and risk-averse decisions. A common—but often misdirected—question in boardrooms today is: “How many American companies does China own?” While the intent behind the question reflects legitimate concerns about supply chain integrity and foreign influence, it often leads to misinformation, wasted research hours, and reactive decision-making.
At SourcifyChina, we shift the conversation from speculation to strategy.
The Problem: Time Lost to Misinformation
Procurement teams across Fortune 500 companies and mid-market enterprises spend an average of 17 hours per week investigating supply chain risks, ownership structures, and geopolitical exposure—much of it based on incomplete or outdated public data. Traditional search methods return sensationalized media headlines instead of actionable business intelligence, delaying sourcing decisions and increasing operational risk.
The Solution: SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List
Our Verified Pro List delivers what public searches cannot:
✅ Accurate, audited data on Chinese investment in U.S. operations
✅ Clear distinction between ownership, joint ventures, and supply partnerships
✅ Real-time updates from on-the-ground legal and compliance verification
✅ Direct sourcing access to pre-vetted Chinese manufacturers—without ownership confusion
By leveraging our intelligence platform, procurement managers bypass the noise and focus on strategic sourcing, not speculative research.
Why This Saves Time in 2026
| Benefit | Time Saved (Annual Estimate) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminates manual due diligence on Chinese ownership claims | 200+ hours per team | Faster vendor onboarding |
| Reduces legal/compliance review cycles | 30–50% shorter timelines | Accelerated procurement cycles |
| Prevents engagement with misrepresented suppliers | Up to 6 avoided RFPs/year | Lower risk, higher ROI |
With SourcifyChina, you’re not just answering a question—you’re future-proofing your supply chain.
Call to Action: Lead with Clarity, Not Assumptions
Stop relying on Google searches and media speculation to guide high-stakes procurement decisions. The Verified Pro List is your competitive advantage—delivering precision, speed, and confidence in every sourcing move.
👉 Contact our team today to access the 2026 Verified Pro List and receive a complimentary supply chain risk assessment.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to support your global procurement strategy with data-driven clarity.
SourcifyChina — Trusted by Procurement Leaders. Verified on the Ground. Built for Global Scale.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.